Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
5 3 2 8
Transféré par
johnDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
5 3 2 8
Transféré par
johnDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
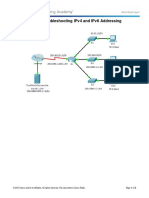
Packet Tracer - Examine the ARP Table
Topology
Addressing Table
Device
Interface
MAC Address
Switch Interface
Gg0/0
0001.6458.2501
G0/1
S0/0/0
N/A
N/A
G0/0
00E0.F7B1.8901
G0/1
S0/0/0
N/A
N/A
10.10.10.2
Wireless
0060.2F84.4AB6
F0/2
10.10.10.3
Wireless
0060.4706.572B
F0/2
172.16.31.2
F0
000C.85CC.1DA7
F0/1
172.16.31.3
F0
0060.7036.2849
F0/2
172.16.31.4
G0
0002.1640.8D75
F0/3
Router0
Router1
Objectives
Part 1: Examine an ARP Request
Part 2: Examine a Switch MAC Address Table
Part 3: Examine the ARP Process in Remote Communications
Background
This activity is optimized for viewing PDUs. The devices are already configured. You will gather PDU information
in simulation mode and answer a series of questions about the data you collect.
2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 1 of 4
Packet Tracer - Examine the ARP Table
Part 1: Examine an ARP Request
Step 1: Generate ARP requests by pinging 172.16.31.3 from 172.16.31.2.
a.
Click 172.16.31.2 and open the Command Prompt.
b.
Enter the arp -d command to clear the ARP table.
c.
Enter Simulation mode and enter the command ping 172.16.31.3. Two PDUs will be generated. The
ping command cannot complete the ICMP packet without knowing the MAC address of the destination.
So the computer sends an ARP broadcast frame to find the MAC address of the destination.
d.
Click Capture/Forward once. The ARP PDU moves Switch1 while the ICMP PDU disappears, waiting
for the ARP reply. Open the PDU and record the destination MAC address. Is this address listed in the
table above? No
e.
Click Capture/Forward to move the PDU to the next device. How many copies of the PDU did Switch1
make? 3
f.
What is the IP address of the device that accepted the PDU? 172.16.31.3
Open the PDU and examine Layer 2. What happened to the source and destination MAC addresses?
g.
The source became the destination, and the mac of 172.16.31.3 turned into ffff:ffff:ffff:
h.
Click Capture/Forward until the PDU returns to 172.16.31.2. How many copies of the PDU did the switch
make during the ARP reply? 1
Step 2: Examine the ARP table.
a.
Note that the ICMP packet reappears. Open the PDU and examine the MAC addresses. Do the MAC
addresses of the source and destination align with their IP addresses? yes
b.
Switch back to Realtime and the ping completes.
c.
Click 172.16.31.2 and enter the arp a command. To what IP address does the MAC address entry
correspond? 172.16.31.3
In general, when does an end device issue an ARP request?
d.
when it dosn't know the receivers mac address
Part 2: Examine a Switch MAC Address Table
Step 1: Generate additional traffic to populate the switch MAC address table.
a.
From 172.16.31.2, enter the ping 172.16.31.4 command.
b.
Click 10.10.10.2 and open the Command Prompt.
c.
Enter the ping 10.10.10.3 command. How many replies were sent and received? 4 sent, and 4 received
Step 2: Examine the MAC address table on the switches.
a.
Click Switch1and then the CLI tab. Enter the show mac-address-table command. Do the entries
correspond to those in the table above? yes
b.
Click Switch0, then the CLI tab. Enter the show mac-address-table command. Do the entries
correspond to those in the table above? yes
c.
Why are two MAC addresses associated with one port?
Because both device connect to one port through the access point.
2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 2 of 4
Packet Tracer - Examine the ARP Table
Part 3: Examine the ARP Process in Remote Communications
Step 1: Generate traffic to produce ARP traffic.
a.
Click 172.16.31.2 and open the Command Prompt.
b.
Enter the ping 10.10.10.1 command.
c.
d.
Type arp a. What is the IP address of the new ARP table entry? 172.16.31.1
Enter arp -d to clear the ARP table and switch to Simulation mode.
e.
Repeat the ping to 10.10.10.1. How many PDUs appear? 2
f.
Click Capture/Forward. Click the PDU that is now at Switch1. What is the target destination IP
destination address of the ARP request? 172.16.31.1
g.
The destination IP address is not 10.10.10.1. Why?
The gateway address of the router interface is stored in the IPv4 configuration of the hosts. If the
receiving host is not on the same network, the source uses the ARP process to determine a MAC
address for the router interface serving as the gateway
Step 2: Examine the ARP table on Router1.
a.
Switch to Realtime mode. Click Router1 and then the CLI tab.
b.
Enter privileged EXEC mode and then the show mac-address-table command. How many MAC
addresses are in the table? Why?
There are 0, this command is something different that the command show mac address-table
c.
Enter the show arp command. Is there an entry for 172.16.31.2? yes
What happens to the first ping in a situation where the router responds to the ARP request?
It times out.
2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 3 of 4
Packet Tracer - Examine the ARP Table
Suggested Scoring Rubric
Activity Section
Part 1: Examine an ARP
Request
Part 2: Examine a Switch
MAC Address Table
Part 3: Examine the ARP
Process in Remote
Communications
Question
Location
Possible
Points
Step 1
10
Step 2
15
Part 1 Total
25
Step 1
Step 2
20
Part 2 Total
25
Step 1
25
Step 2
25
Part 3 Total
50
Total Score
100
2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Earned
Points
Page 4 of 4
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 8 4 1 2Document2 pages8 4 1 2john100% (1)
- 8 3 1 4Document3 pages8 3 1 4john100% (3)
- 7 4 1 2Document2 pages7 4 1 2johnPas encore d'évaluation
- 7 2 4 9Document3 pages7 2 4 9johnPas encore d'évaluation
- 7 3 2 9Document5 pages7 3 2 9johnPas encore d'évaluation
- 8.1.3.8 Packet Tracer - Investigate Unicast, Broadcast, and Multicast Traffic InstructionsDocument4 pages8.1.3.8 Packet Tracer - Investigate Unicast, Broadcast, and Multicast Traffic InstructionsFaisal0% (1)
- 6 4 3 4Document4 pages6 4 3 4johnPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 4 3 3Document5 pages6 4 3 3johnPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.3.1.3 Packet Tracer - Identify MAC and IP AddressesDocument3 pages5.3.1.3 Packet Tracer - Identify MAC and IP AddressesAldrian HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- 6.3.1.8 Packet Tracer - Exploring Internetworking DevicesDocument6 pages6.3.1.8 Packet Tracer - Exploring Internetworking DevicesParthPatel100% (8)
- 6 4 1 3Document4 pages6 4 1 3johnPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 2 4 6Document5 pages3 2 4 6johnPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 2 4 4Document5 pages4 2 4 4john67% (3)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- PDFDocument72 pagesPDFGCMediaPas encore d'évaluation
- What are plot pointsDocument19 pagesWhat are plot pointsOpeeron OpeePas encore d'évaluation
- SSC CGL Tier 2 Quantitative Abilities 16-Nov-2020Document17 pagesSSC CGL Tier 2 Quantitative Abilities 16-Nov-2020aPas encore d'évaluation
- Miles and Snow's Organizational StrategiesDocument15 pagesMiles and Snow's Organizational StrategiesVirat SahPas encore d'évaluation
- Rashi - Effusion CytDocument56 pagesRashi - Effusion CytShruthi N.RPas encore d'évaluation
- AMSY-6 OpManDocument149 pagesAMSY-6 OpManFernando Piñal MoctezumaPas encore d'évaluation
- Is the Prime Minister Too Powerful in CanadaDocument9 pagesIs the Prime Minister Too Powerful in CanadaBen YuPas encore d'évaluation
- Facebook Use Case Diagram Activity Diagram Sequence DiagramDocument21 pagesFacebook Use Case Diagram Activity Diagram Sequence DiagramSaiPas encore d'évaluation
- UCO Reporter 2021, December Edition, November 26, 2021Document40 pagesUCO Reporter 2021, December Edition, November 26, 2021ucopresident100% (2)
- User Manual: Imagenet Lite™ SoftwareDocument93 pagesUser Manual: Imagenet Lite™ SoftwareDe Mohamed KaraPas encore d'évaluation
- EN4264 Final Essay - GeraldineDocument25 pagesEN4264 Final Essay - GeraldineGeraldine WongPas encore d'évaluation
- GO vs. CA Case DigestDocument1 pageGO vs. CA Case Digestunbeatable38100% (4)
- Tahap Kesediaan Pensyarah Terhadap Penggunaan M-Pembelajaran Dalam Sistem Pendidikan Dan Latihan Teknik Dan Vokasional (TVET)Document17 pagesTahap Kesediaan Pensyarah Terhadap Penggunaan M-Pembelajaran Dalam Sistem Pendidikan Dan Latihan Teknik Dan Vokasional (TVET)Khairul Yop AzreenPas encore d'évaluation
- Connotative and Denotative, Lexical and StylisticDocument3 pagesConnotative and Denotative, Lexical and StylisticEman Jay FesalbonPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Intelligent BuildingsDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Intelligent Buildingsmamta jainPas encore d'évaluation
- Aerospace Propulsion Course Outcomes and Syllabus OverviewDocument48 pagesAerospace Propulsion Course Outcomes and Syllabus OverviewRukmani Devi100% (2)
- (AC-S08) Week 08 - Pre-Task - Quiz - Weekly Quiz - INGLES III (14653)Document3 pages(AC-S08) Week 08 - Pre-Task - Quiz - Weekly Quiz - INGLES III (14653)Eduardo Arucutipa60% (5)
- 28 Nakshatras - The Real Secrets of Vedic Astrology (An E-Book)Document44 pages28 Nakshatras - The Real Secrets of Vedic Astrology (An E-Book)Karthik Balasundaram88% (8)
- Book Chapter Microtomy Frozen Sections CryostatDocument15 pagesBook Chapter Microtomy Frozen Sections Cryostatbszool006Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mil PRF 46010FDocument20 pagesMil PRF 46010FSantaj Technologies100% (1)
- A To Z of Architecture PDFDocument403 pagesA To Z of Architecture PDFfaizan100% (1)
- Economy 1 PDFDocument163 pagesEconomy 1 PDFAnil Kumar SudarsiPas encore d'évaluation
- Colorectal Disease - 2023 - Freund - Can Preoperative CT MR Enterography Preclude The Development of Crohn S Disease LikeDocument10 pagesColorectal Disease - 2023 - Freund - Can Preoperative CT MR Enterography Preclude The Development of Crohn S Disease Likedavidmarkovic032Pas encore d'évaluation
- Philippine Bank of Communications Vs Commissioner of Internal RevenueDocument2 pagesPhilippine Bank of Communications Vs Commissioner of Internal RevenueNFNL100% (1)
- Polyester Staple Fibre Product ListDocument2 pagesPolyester Staple Fibre Product Listnunu7478Pas encore d'évaluation
- Joey Cena 2Document1 pageJoey Cena 2api-635313033Pas encore d'évaluation
- St. Helen Church: 4106 Mountain St. Beamsville, ON L0R 1B7Document5 pagesSt. Helen Church: 4106 Mountain St. Beamsville, ON L0R 1B7sthelenscatholicPas encore d'évaluation
- Facebook Privacy FTC Complaint Docket No. C-4365Document19 pagesFacebook Privacy FTC Complaint Docket No. C-4365David SangerPas encore d'évaluation
- Diagnostic Test in Mapeh 8: Department of EducationDocument4 pagesDiagnostic Test in Mapeh 8: Department of Educationcarl jayPas encore d'évaluation
- FINAL Conflicts 2019 Official Guidelines PDFDocument48 pagesFINAL Conflicts 2019 Official Guidelines PDFxsar_xPas encore d'évaluation