Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Speech Production CSD 211
Transféré par
api-311020466Description originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Speech Production CSD 211
Transféré par
api-311020466Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Monday, March 21, y
CSD 211
Speech Production
- 4 processes of speech
respiration
phonation
resonation
articulation
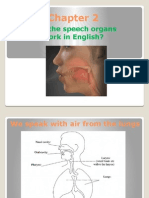
- Respiration
Primary biological function = exchange of
sustaining oxygen for carbon dioxide
Speech function = extend and control exhalation to allow for speech production
- Phonation
Primary biological function = prevent foreign materials from entering the trench and
lungs
Speech function = generate sound production
- Resonation
Chambers for sound travel
Pharynx (naso(nose), oro(oral), laryngo(throat))
Oral
Nasal
- Articulation
As the venerating and resonated air column passes through the mouth. the tongue, the
teeth, and other structures in the mouth break up the airstream into the sounds of
speech.
Organs of Articulation
- Articulators
Monday, March 21, y
Hard Palate
Lips
Velum
Tongue
Uvula
Mandible
Teeth
Monday, March 21, y
- Active Articulators
Anatomical structure that moves during the production of speech sounds
Monday, March 21, y
Lateral tongue
Lower Lip
Tongue surface
Tongue tip
Central, anterior, posterior
Monday, March 21, y
- Passive Articulators
Immovable portion of the vocal tract, paid with an active articulator
Upper lip
Upper teeth
Alveolar ridge
Hard palate
Soft palate
Glottis
- Consonant Articulation
Place of articulation: location of interaction between the active and passive
articulators
Generally named according to the passive articulator, the one which moves less in forming
the sound
labial, dental, alveolar, palatal, velar, glottal
Manner of articulation: way the airstream is modified as a result of articulator
interaction
Stop-plosive, nasal, fricative, affricative, affricate, approximates
Voicing: presence or absence of val fold vibration
Voiced, Voiceless
- Places of Articulation:
Bilabial
Labial b, p, m
Two lips
Labiodental
f, v
Interdental
,
Tongue tip and (upper) teeth
Alveolar
d, t, s, z, n
Tongue tip or lade and alveolar ridge
PostAlveolar
,
Tongue tip behind alveolar ridge but not hard palate
5
Monday, March 21, y
Palatal
j
Tongue and hard palate
Velar
g, k,
Back of tongue and soft plate
Glottal
h
Vocal Folds
- Resonating cavities oro-nasal process
Oral: soft palate is raised so there is a velar closure
Nasal: soft palate is lowered so air escapes from nose
- Manner of articulation
Stop plosive
- Oral cavitiy completely closed, velum up, pressure builds up then is released in an
explosive sound
Nasal
- Oral cavity vompletely closed, velum down, airstream directed into nasal cavity
Fricative
- Active/passive articulators approximate so air travels trough a point of constriction
Affricative
- stop-plosive releasing into
Approximates
Cognates
- Similar articulation, one voiceless, one voiced
Voiceless, no cognates:
Voiced, no cognate: m, n, ng, w, r, l, j
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Phonetics IDocument40 pagesPhonetics Iサイ-ドさんPas encore d'évaluation
- Articulation and AcousticDocument13 pagesArticulation and AcousticNhã Trâm TrầnPas encore d'évaluation
- ConsonantsDocument13 pagesConsonantsMOHAMMAD AGUS SALIM EL BAHRIPas encore d'évaluation
- Phonetics and PhonoDocument24 pagesPhonetics and PhonoMOHAMMAD AGUS SALIM EL BAHRIPas encore d'évaluation
- Phonet and Phono 1Document25 pagesPhonet and Phono 1Mohammad Agussalim El BahriPas encore d'évaluation
- Symbol Systems: Nonverbal Symbols: Lesson 4Document24 pagesSymbol Systems: Nonverbal Symbols: Lesson 4Idate PatrickPas encore d'évaluation
- Description of Consonants - PlaceDocument12 pagesDescription of Consonants - PlaceArunachalam GPas encore d'évaluation
- Vocal Elements: Voiced - The Vocal Folds Are Set in Voiceless - The Vocal Folds Do Not VibrateDocument3 pagesVocal Elements: Voiced - The Vocal Folds Are Set in Voiceless - The Vocal Folds Do Not VibrateIdate PatrickPas encore d'évaluation
- Speech Organs and ArticulationsDocument19 pagesSpeech Organs and ArticulationsNur Wahidah IsmailPas encore d'évaluation
- Mustaqim, M Shafiq Speech OrganDocument23 pagesMustaqim, M Shafiq Speech OrgankilopilasPas encore d'évaluation
- Cleft Palate and Speech: Define The Term "Speech"Document5 pagesCleft Palate and Speech: Define The Term "Speech"juw46Pas encore d'évaluation
- Linb09 Final NotesDocument102 pagesLinb09 Final NotesAnwen ZhangPas encore d'évaluation
- ENGLISH Presentation Speech MechanismDocument22 pagesENGLISH Presentation Speech MechanismGaurav Kumar MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- EnglishDocument3 pagesEnglishSaba AnatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Speech MechanismDocument34 pagesSpeech MechanismErl Dy0% (1)
- Places and Manners of ArticulationDocument14 pagesPlaces and Manners of Articulationcamila100% (1)
- Oral CavityDocument65 pagesOral Cavityugwuokeprince4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Phonetics and PhonologyDocument2 pagesPhonetics and PhonologyHồ Như QuỳnhPas encore d'évaluation
- Speech MechanismDocument2 pagesSpeech MechanismangelicaPas encore d'évaluation
- Oral CavityDocument20 pagesOral CavityadileidalaaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Sounds of English LanguageDocument26 pagesThe Sounds of English LanguageEstudio Contable CAO Asesores Y ConsultoresPas encore d'évaluation
- The Function of TongueDocument11 pagesThe Function of TongueAndrea LawPas encore d'évaluation
- Phonetics 1Document13 pagesPhonetics 1Farras FawwazPas encore d'évaluation
- The Speech MechanismDocument5 pagesThe Speech MechanismSittie HijaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Speech Organs: Fatin Amira Nor Albaniah Noor Badariah Nur AtiqahDocument12 pagesSpeech Organs: Fatin Amira Nor Albaniah Noor Badariah Nur AtiqahFatin AmiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Speech Consideration IN COMPLETE Dentures: by Ekramul Haque Under The Guidance of DR Shaista AfrozDocument55 pagesSpeech Consideration IN COMPLETE Dentures: by Ekramul Haque Under The Guidance of DR Shaista AfrozPremshith CpPas encore d'évaluation
- English Sound Systems: By: Noorasmad Mat Ripin 1 Pismp KsDocument18 pagesEnglish Sound Systems: By: Noorasmad Mat Ripin 1 Pismp KsNoorasmad Mat RipinPas encore d'évaluation
- Speech OrganDocument35 pagesSpeech OrganAnonymous AisyzyPas encore d'évaluation
- The Speaking Process and The Organs of SpeechDocument1 pageThe Speaking Process and The Organs of SpeechVictoria DegorioPas encore d'évaluation
- Articulatory PhoneticsDocument47 pagesArticulatory PhoneticsDardarsky FegiPas encore d'évaluation
- Phonetics and Phonology - PPTX - Google Slides PDFDocument13 pagesPhonetics and Phonology - PPTX - Google Slides PDFSalwa abPas encore d'évaluation
- The Articulatory SystemDocument5 pagesThe Articulatory SystemSukma Dwiaugita RahardjoPas encore d'évaluation
- PhoneticsDocument9 pagesPhoneticsNguyễn Đình ĐạtPas encore d'évaluation
- Speech Mechanism 1aDocument30 pagesSpeech Mechanism 1aNathania AnindyaPas encore d'évaluation
- How Speech Organs Work in Producing The Speech Sounds?Document33 pagesHow Speech Organs Work in Producing The Speech Sounds?shangar omerPas encore d'évaluation
- PhoneticsDocument134 pagesPhoneticsArabella Mae DuquePas encore d'évaluation
- The Organs of Speech and Their WorkDocument5 pagesThe Organs of Speech and Their WorkMaryPas encore d'évaluation
- 1) PhonologyDocument14 pages1) PhonologyAnna-Marie DroščínováPas encore d'évaluation
- How The Speech Organs Work in English?Document18 pagesHow The Speech Organs Work in English?haithamPas encore d'évaluation
- THE SOUNDS OF LANGUAGE PerubahanDocument15 pagesTHE SOUNDS OF LANGUAGE PerubahanArtika WulandariPas encore d'évaluation
- Clase 2 - Aparato FonadorDocument13 pagesClase 2 - Aparato FonadorLeticia de la PazPas encore d'évaluation
- ConsonantsDocument26 pagesConsonantsNguyệt MaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Consonants Summary Prepared By: Mustafa RamadanDocument26 pagesConsonants Summary Prepared By: Mustafa RamadanKhalil Abu AwwadPas encore d'évaluation
- Speech and MalocclusionDocument36 pagesSpeech and MalocclusionDrNidhi KrishnaPas encore d'évaluation
- PheoneticsDocument27 pagesPheoneticsShivam SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Speech OrgansDocument5 pagesHuman Speech OrgansLouise anasthasya altheaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Speaking Process: Enged 317Document34 pagesThe Speaking Process: Enged 317Grezzly BearPas encore d'évaluation
- Engphon Chapter 2Document10 pagesEngphon Chapter 2Muhamad IbrohimPas encore d'évaluation
- Session 4Document43 pagesSession 4SaturnPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of Speech MechanismDocument5 pagesParts of Speech MechanismEren100% (3)
- Oral Cavity Hard & Soft Palate: Dr. Bashir Ahmed ShaikhDocument19 pagesOral Cavity Hard & Soft Palate: Dr. Bashir Ahmed ShaikhHamza IqbalPas encore d'évaluation
- Phonetics and Phonology: Ling. 501 April 15, 2009Document81 pagesPhonetics and Phonology: Ling. 501 April 15, 2009Rosalie BaybayonPas encore d'évaluation
- Speech Assessment and Nasopharyngoscopy HO 11 07 11Document164 pagesSpeech Assessment and Nasopharyngoscopy HO 11 07 11catatutuPas encore d'évaluation
- The Speaking ProcessDocument2 pagesThe Speaking ProcessJames William100% (1)
- Phonetics Intro Ling PDFDocument31 pagesPhonetics Intro Ling PDFChuchito Rosiles GuadarramaPas encore d'évaluation
- Voiceless Voiced: Bilabial BilabialDocument4 pagesVoiceless Voiced: Bilabial BilabialAhmed El-SaadanyPas encore d'évaluation
- Universal Method For The Saxophone - Based Upon The Celebrated Works Of A. Mayeur, H. Klose And Others, And Containing The Complete Fingerings For The Latest Improved SaxophonesD'EverandUniversal Method For The Saxophone - Based Upon The Celebrated Works Of A. Mayeur, H. Klose And Others, And Containing The Complete Fingerings For The Latest Improved SaxophonesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (4)
- Slide Show 7 - PolDocument23 pagesSlide Show 7 - Polapi-311020466Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mid-Term Study GuideDocument2 pagesMid-Term Study Guideapi-311020466Pas encore d'évaluation
- Definitions For Final - HisDocument5 pagesDefinitions For Final - Hisapi-311020466Pas encore d'évaluation
- History Final Practice ExamDocument10 pagesHistory Final Practice Examapi-311020466Pas encore d'évaluation
- Slide Show 5 - PolDocument15 pagesSlide Show 5 - Polapi-311020466Pas encore d'évaluation
- Key Terms of MidtermDocument3 pagesKey Terms of Midtermapi-311020466Pas encore d'évaluation
- Vowels csd211Document4 pagesVowels csd211api-311020466Pas encore d'évaluation
- Slide Show 4 - PolDocument13 pagesSlide Show 4 - Polapi-311020466Pas encore d'évaluation
- Slide Show 6 - PolDocument32 pagesSlide Show 6 - Polapi-311020466Pas encore d'évaluation
- Slide Show 2 - PolDocument12 pagesSlide Show 2 - Polapi-311020466Pas encore d'évaluation
- Slide Show 1-PolDocument8 pagesSlide Show 1-Polapi-311020466Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fricatives CSD 211Document2 pagesFricatives CSD 211api-311020466Pas encore d'évaluation
- Slide Show 3 - PolDocument23 pagesSlide Show 3 - Polapi-311020466Pas encore d'évaluation
- Study Guide csd211Document2 pagesStudy Guide csd211api-311020466Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction CSD 211Document2 pagesIntroduction CSD 211api-311020466Pas encore d'évaluation
- Speech in Context Diacritics CSD 211Document2 pagesSpeech in Context Diacritics CSD 211api-311020466Pas encore d'évaluation
- Stop Plosive csd211Document1 pageStop Plosive csd211api-311020466Pas encore d'évaluation
- Monophthongs csd211Document2 pagesMonophthongs csd211api-311020466Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nasals csd211Document1 pageNasals csd211api-311020466Pas encore d'évaluation
- Review Midterm csd211Document2 pagesReview Midterm csd211api-311020466Pas encore d'évaluation
- Final Exam Review CSD 211Document1 pageFinal Exam Review CSD 211api-311020466Pas encore d'évaluation
- Graphemes CSD 211Document1 pageGraphemes CSD 211api-311020466Pas encore d'évaluation
- Dialect Note BankDocument2 pagesDialect Note Bankapi-311020466Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ipa csd211Document4 pagesIpa csd211api-311020466Pas encore d'évaluation
- CSD 211 AffricatesDocument2 pagesCSD 211 Affricatesapi-311020466Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction Into Linguistics:: A Teaching GuideDocument48 pagesIntroduction Into Linguistics:: A Teaching GuideElsa Safitri100% (2)
- l6 LIN228H5 F21Document66 pagesl6 LIN228H5 F21Xinjie ZhouPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3Document4 pagesChapter 312a734Trần Nguyễn Thanh ThúyPas encore d'évaluation
- English Phonetics and PhonologyDocument10 pagesEnglish Phonetics and PhonologyNguyen Thi PhuPas encore d'évaluation
- Edwin Arlington Robinson'S "Richard'S Cory": A Literary-Linguistic InvestigationDocument52 pagesEdwin Arlington Robinson'S "Richard'S Cory": A Literary-Linguistic InvestigationRoy Lustre AgbonPas encore d'évaluation
- Phonology Part 2Document27 pagesPhonology Part 2Maulana Rasyid RidhoPas encore d'évaluation
- Answers To Written Exercises: (I) (Ha:f)Document20 pagesAnswers To Written Exercises: (I) (Ha:f)GonnyNhãPas encore d'évaluation
- Sofl Library Answers To PhoneticsDocument32 pagesSofl Library Answers To PhoneticsYermek RamazanovPas encore d'évaluation
- ConsonantsDocument65 pagesConsonantskeihoina keihoinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Consonant Characteristics: Prepared by TserendolgorDocument17 pagesConsonant Characteristics: Prepared by TserendolgorZula ArvisPas encore d'évaluation
- MRC-107 RADIO PALLET TM Veis.s SV2IPWDocument158 pagesMRC-107 RADIO PALLET TM Veis.s SV2IPWΒΕΗΣ ΣΤΕΛΙΟΣ Veis SteliosPas encore d'évaluation
- The English AlphabetDocument6 pagesThe English AlphabetbelbachirPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary PhonologyDocument2 pagesSummary PhonologyRe BaladastraPas encore d'évaluation
- Manner of ArticulationDocument6 pagesManner of ArticulationDian Hadi NurrohimPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 12Document11 pagesAssignment 12Mai NguyễnPas encore d'évaluation
- Speech Production: ArticulatorsDocument3 pagesSpeech Production: ArticulatorsJoannaPilakPas encore d'évaluation
- Manner of ArticulationDocument17 pagesManner of ArticulationparaloversomeonePas encore d'évaluation
- Session 1Document20 pagesSession 1sergio lizzanoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Consonant Sounds of EnglishDocument2 pagesThe Consonant Sounds of EnglishnnnnnnPas encore d'évaluation
- PHONOLOGY, Definition ofDocument37 pagesPHONOLOGY, Definition ofKrystelle Joy ZipaganPas encore d'évaluation
- International Phonetic AlphabetDocument15 pagesInternational Phonetic AlphabetAndrewgene TeologoPas encore d'évaluation
- Noorul Hadith 009 - September & October 2019Document64 pagesNoorul Hadith 009 - September & October 2019Mohammad Omar FaruqPas encore d'évaluation
- Phonological Variation and Change in RomanianDocument27 pagesPhonological Variation and Change in RomanianLaurentiu Marian MihailaPas encore d'évaluation
- Vowels Short and Long SoundsDocument8 pagesVowels Short and Long SoundsNazia SiddiquePas encore d'évaluation
- Manner of ArticulationDocument2 pagesManner of ArticulationzelindaaPas encore d'évaluation
- English ManualDocument66 pagesEnglish ManualSibasish Singh SamantaPas encore d'évaluation
- An Introduction To Speech ProductionDocument11 pagesAn Introduction To Speech ProductionPetruta IordachePas encore d'évaluation
- The Loser - 'S Guide To PhoneticsDocument54 pagesThe Loser - 'S Guide To PhoneticsTobiáš ZíkaPas encore d'évaluation
- (123doc) Trac Nghiem Ngu Am Am Vi Hoc Tieng AnhDocument18 pages(123doc) Trac Nghiem Ngu Am Am Vi Hoc Tieng AnhMai Thi NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Mal Phonetic Reader - RemovedDocument66 pagesMal Phonetic Reader - RemovedReshmi R NairPas encore d'évaluation