Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
H (U, V) 1 If - U V : X y Hxy
Transféré par
Zülal İlayda Özcan0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
5 vues2 pagesMedical imaging
Titre original
A1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentMedical imaging
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
5 vues2 pagesH (U, V) 1 If - U V : X y Hxy
Transféré par
Zülal İlayda ÖzcanMedical imaging
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
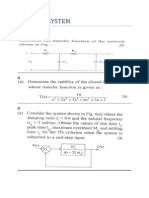
BME 560 Assignment 1
1 ( x2 y 2 )
1
exp
Illustrate with
2
2
2
a sketch how the FWHM and are found on the plot of a Gaussian.
1. Derive the FWHM of a general Gaussian PSF: h( x, y )
2. Consider an ideal low-pass filter:
H(u,v) = 1 if 0<u<0 and 0<v<0; = 0 otherwise.
Using properties of the 1D Fourier transform, show what the PSF of such a system would be.
How does it change with the cutoff 0? What effect would this system have on the appearance of
edges in an image?
3. A one-dimensional imaging system is composed of a cascade of two LSI subsystems. These
subsystems have the following PSFs:
2
2
h1 ( x) e x / 2 and h2 ( x) e x / 8 where x is in millimeters.
(a) Determine the FWHM of each subsystem;
(b) Determine the FWHM of the complete system;
(c) Which subsystem has the greatest effect on the performance of the complete system?
Comment on how improvements in each subsystem would change the overall system
performance.
4. (a) Describe a method by which you can evaluate the contrast of a Gaussian function or
something like it on a background.
(b) The data file A1data.txt contains the data from a profile of a noisy image. Using Matlab or
Excel (or other means), estimate the CNR of the Gaussian object in the center.
5. How does a linear filter affect the NEQ of an image? Show this mathematically.
6. Three imaging systems are found to have the Resolution/Noise relationships shown below.
(a) Compare the performance of systems 1 and 2. Which of these two would you choose in an
application requiring a physician to see small objects? Which would you choose in an
application requiring quantitative accuracy in large regions? Explain your reasoning.
(b) Compare the performance of systems 1 and 3. Which of these two would you choose in an
application requiring a physician to see small objects? Which would you choose in an
application requiring quantitative accuracy in large regions? Explain your reasoning.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Examination SIPE 2008Document4 pagesExamination SIPE 2008mrinal570Pas encore d'évaluation
- Exam 2020Document9 pagesExam 2020Aavesh DagarPas encore d'évaluation
- Self Assessment IDPDocument12 pagesSelf Assessment IDPaniketbhuniaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hybrid Systems - TutorialDocument66 pagesHybrid Systems - TutorialKarthik VazhuthiPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 3Document7 pagesExperiment 3Usama NadeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis of Oscillations With Eigenanalysis andDocument8 pagesAnalysis of Oscillations With Eigenanalysis andMadhusudhan SrinivasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Harnessing Bistable Structural Dynamics: For Vibration Control, Energy Harvesting and SensingD'EverandHarnessing Bistable Structural Dynamics: For Vibration Control, Energy Harvesting and SensingPas encore d'évaluation
- WSN20100100007 87680380Document5 pagesWSN20100100007 87680380Alan CheePas encore d'évaluation
- Abstraction and Counterexample-Guided Refinement in Model Checking of Hybrid SystemsDocument22 pagesAbstraction and Counterexample-Guided Refinement in Model Checking of Hybrid Systemszhi.han1091Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nonlinear Control Feedback Linearization Sliding Mode ControlD'EverandNonlinear Control Feedback Linearization Sliding Mode ControlPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity 03Document11 pagesActivity 03Joshua AbadPas encore d'évaluation
- Applying The Optimal Control in The Study of Real World PhenomenaDocument15 pagesApplying The Optimal Control in The Study of Real World PhenomenaVasile SentimentPas encore d'évaluation
- Adaptive Synchronization of Chaotic Systems and Its Application To Secure CommunicationsDocument10 pagesAdaptive Synchronization of Chaotic Systems and Its Application To Secure CommunicationsRafael Gonçalves de LimaPas encore d'évaluation
- Control System Questions Ias MainsDocument9 pagesControl System Questions Ias MainsPushkar SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- A Modeling Approach of System Reliability Based On StatechartsDocument7 pagesA Modeling Approach of System Reliability Based On StatechartsFDS_03Pas encore d'évaluation
- Selection of A ModelDocument5 pagesSelection of A ModelKartavya BhagatPas encore d'évaluation
- HW2 PDFDocument4 pagesHW2 PDFAshishPas encore d'évaluation
- Circom 30Document7 pagesCircom 30Mada Sanjaya WsPas encore d'évaluation
- Automatic ControlDocument14 pagesAutomatic Controlmagdi elmalekPas encore d'évaluation
- Questions & Answers On Discrete Time Systems ImplementationDocument38 pagesQuestions & Answers On Discrete Time Systems Implementationkibrom atsbha0% (1)
- Controlengg Compiled Sridar (Session 1 8)Document60 pagesControlengg Compiled Sridar (Session 1 8)Prem T RajuPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 1 Non Linear ControlDocument21 pagesLecture 1 Non Linear ControlShivan BiradarPas encore d'évaluation
- Hybrid Dynamic Systems Tutorial PDFDocument66 pagesHybrid Dynamic Systems Tutorial PDFkkkprot100% (1)
- Evolutionary Algorithms for Mobile Ad Hoc NetworksD'EverandEvolutionary Algorithms for Mobile Ad Hoc NetworksPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 s2.0 S0005109812003391 Main Sliding EstDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S0005109812003391 Main Sliding EstAymen OmariPas encore d'évaluation
- TSK Fuzzy Function ApproximatorsDocument11 pagesTSK Fuzzy Function ApproximatorsAdam KliberPas encore d'évaluation
- Control Systems - Experiment 3Document16 pagesControl Systems - Experiment 3EnesVSPas encore d'évaluation
- Control Engineering Test One PDFDocument3 pagesControl Engineering Test One PDFMayanja Mugizi MhamudPas encore d'évaluation
- Control Engg NotesDocument58 pagesControl Engg NotesTudor Octavian RusuPas encore d'évaluation
- Nonlinear Control System Design by Quantifier Elimination: J. Symbolic Computation (1997) 24, 137-152Document16 pagesNonlinear Control System Design by Quantifier Elimination: J. Symbolic Computation (1997) 24, 137-152Parti Ledger LPas encore d'évaluation
- Modeling Inverse Kinematics in A Robotic Arm (Matlab)Document11 pagesModeling Inverse Kinematics in A Robotic Arm (Matlab)Robinson Peralta100% (1)
- Simulink Basics TutorialDocument143 pagesSimulink Basics TutorialHiếu HuỳnhPas encore d'évaluation
- FeedConunit 2Document51 pagesFeedConunit 2Jerc ZajPas encore d'évaluation
- Controls Infosheet and Sample Problems 0Document11 pagesControls Infosheet and Sample Problems 0Md Nur-A-Adam DonyPas encore d'évaluation
- Object Detection and Shadow Removal From Video StreamDocument10 pagesObject Detection and Shadow Removal From Video StreamPaolo PinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Prediction: The Technique, Its Solution and Application To SpeechDocument20 pagesLinear Prediction: The Technique, Its Solution and Application To SpeechVardhan RoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Fuzzy Logic PaperDocument8 pagesFuzzy Logic PaperVirat KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Adaptive Neural-Networks-Based Fault Detection and Diagnosis Using Unmeasured StatesDocument11 pagesAdaptive Neural-Networks-Based Fault Detection and Diagnosis Using Unmeasured StatesWalid AbidPas encore d'évaluation
- Antenna Azimuth Position Control System VerificationDocument4 pagesAntenna Azimuth Position Control System VerificationmsbajoriPas encore d'évaluation
- Hybrid Physics-Based and Data-Driven PHM: H. Hanachi, W. Yu, I.Y. Kim and C.K. MechefskeDocument13 pagesHybrid Physics-Based and Data-Driven PHM: H. Hanachi, W. Yu, I.Y. Kim and C.K. MechefskeSudipto RayPas encore d'évaluation
- EEET2486 Laboratory2 Guide S2 2020-1Document13 pagesEEET2486 Laboratory2 Guide S2 2020-1Nam DinhPas encore d'évaluation
- Output Linear Feedback For A Class of Nonlinear Systems Based On The Invariant Ellipsoid MethodDocument6 pagesOutput Linear Feedback For A Class of Nonlinear Systems Based On The Invariant Ellipsoid MethodinfodotzPas encore d'évaluation
- Accelerating A Medical 3D Brain Mri Analysis Algorithm Using A High-Performance Reconfigurable ComputerDocument6 pagesAccelerating A Medical 3D Brain Mri Analysis Algorithm Using A High-Performance Reconfigurable Computerhub23Pas encore d'évaluation
- Control of Networked and Complex SystemsDocument7 pagesControl of Networked and Complex SystemsAvighan MajumderPas encore d'évaluation
- Face Recog Using Wavelet Transformations PDFDocument5 pagesFace Recog Using Wavelet Transformations PDFRahul JainPas encore d'évaluation
- CSI Tutorial v1.5Document4 pagesCSI Tutorial v1.5VincentPas encore d'évaluation
- Research Inventy: International Journal of Engineering and ScienceDocument7 pagesResearch Inventy: International Journal of Engineering and ScienceinventyPas encore d'évaluation
- University of Oslo: Faculty of Mathematics and Natural SciencesDocument4 pagesUniversity of Oslo: Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciencesasalifew belachewPas encore d'évaluation
- An Introduction To 3G Monte-Carlo Simulations Within: PromanDocument11 pagesAn Introduction To 3G Monte-Carlo Simulations Within: PromanSanjeev KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Model Predictive Control Based On Adaptive Hinging Hyperplanes ModelDocument11 pagesModel Predictive Control Based On Adaptive Hinging Hyperplanes ModelssuthaaPas encore d'évaluation
- 10.1016@s1474 66701751984 9Document6 pages10.1016@s1474 66701751984 9Fatiha HAMDIPas encore d'évaluation
- Adding Noise To Improve MeasurementDocument8 pagesAdding Noise To Improve MeasurementMegha AgarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Trabajo VibracionesDocument17 pagesTrabajo VibracionesCesar BautistaPas encore d'évaluation
- Combined Fuzzy-Logic Wavelet-Based Fault Classification Technique For Power System RelayingDocument8 pagesCombined Fuzzy-Logic Wavelet-Based Fault Classification Technique For Power System Relayingوليد موسىPas encore d'évaluation
- Soft Computing Aug2021MakeupDocument3 pagesSoft Computing Aug2021MakeupVaanya SaxenaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Description of T He Proposed SystemDocument10 pages2 Description of T He Proposed SystemGautham ShettyPas encore d'évaluation
- A Parallel Particle Swarm OptimizerDocument7 pagesA Parallel Particle Swarm OptimizerMichael ClarkPas encore d'évaluation
- A Novel Background Extraction and Updating Algorithm For Vehicle Detection and TrackingDocument5 pagesA Novel Background Extraction and Updating Algorithm For Vehicle Detection and TrackingSam KarthikPas encore d'évaluation
- Chaotic Based Secure Hash Algorithm: International Journal of Emerging Trends & Technology in Computer Science (IJETTCS)Document7 pagesChaotic Based Secure Hash Algorithm: International Journal of Emerging Trends & Technology in Computer Science (IJETTCS)International Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementPas encore d'évaluation
- SHM - Presentation (Nestor Castaneda)Document30 pagesSHM - Presentation (Nestor Castaneda)engineersrulePas encore d'évaluation
- hw1 Fall04Document1 pagehw1 Fall04Zülal İlayda ÖzcanPas encore d'évaluation
- CTFT DTFT DFTDocument6 pagesCTFT DTFT DFTZülal İlayda ÖzcanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter2 Spring2010Document106 pagesChapter2 Spring2010Zülal İlayda ÖzcanPas encore d'évaluation
- Big QuizDocument2 pagesBig QuizZülal İlayda ÖzcanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap5-6 Spring10Document125 pagesChap5-6 Spring10Zülal İlayda ÖzcanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter1 Spring11Document53 pagesChapter1 Spring11Zülal İlayda ÖzcanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap4 Fall10Document95 pagesChap4 Fall10Zülal İlayda ÖzcanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap3 Fall10Document105 pagesChap3 Fall10Zülal İlayda ÖzcanPas encore d'évaluation
- Bivariate NormalDocument11 pagesBivariate NormalaharisjoPas encore d'évaluation
- Transformation of Human: Between Good and EvilDocument7 pagesTransformation of Human: Between Good and EvilZülal İlayda ÖzcanPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Congestion SolutionDocument4 pagesPower Congestion SolutionAriev IkankPas encore d'évaluation
- Public Key CryptographyDocument34 pagesPublic Key CryptographyMajid KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Forecasting-Seasonal ModelsDocument34 pagesForecasting-Seasonal Modelssuriani hamsahPas encore d'évaluation
- Kundur DTS Chap5Document10 pagesKundur DTS Chap5antex nebyuPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Manual CryptologyDocument81 pagesLab Manual Cryptologyaudichyaharshali22Pas encore d'évaluation
- Position Control of DC Motor Using Genetic Algorithm Based PID ControllerDocument35 pagesPosition Control of DC Motor Using Genetic Algorithm Based PID ControllerSarat Chandra100% (1)
- Combinatorial Optimization by Graph Pointer Networks and Hierarchical Reinforcement LearningDocument8 pagesCombinatorial Optimization by Graph Pointer Networks and Hierarchical Reinforcement LearningSreekrishna DasPas encore d'évaluation
- The Four Color TheoremDocument4 pagesThe Four Color TheoremMara BalaitaPas encore d'évaluation
- LN05 KEAT020827 07 ME LN05 Demand Estimation and ForecastingDocument31 pagesLN05 KEAT020827 07 ME LN05 Demand Estimation and ForecastingCarlene UgayPas encore d'évaluation
- BusinessFinance12 Q1 Mod4 Basic Long Term Financial Concepts V5 FSDocument28 pagesBusinessFinance12 Q1 Mod4 Basic Long Term Financial Concepts V5 FSEllah OllicetnomPas encore d'évaluation
- SP14 CS188 Lecture 3 - Informed SearchDocument69 pagesSP14 CS188 Lecture 3 - Informed Searchimoptra143Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1697mining Web Graphs For RecommendationsDocument12 pages1697mining Web Graphs For RecommendationsPurushothama ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Target Classification: An Application of Artificial Neural Network in Intelligent Transport SystemDocument4 pagesTarget Classification: An Application of Artificial Neural Network in Intelligent Transport Systemeditor_ijarcssePas encore d'évaluation
- Youssef Hamadi, Eric Monfroy, Frédéric Saubion (Auth.), Youssef Hamadi, Eric Monfroy, Frédéric Saubion (Eds.) - Autonomous Search-Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg (2012)Document307 pagesYoussef Hamadi, Eric Monfroy, Frédéric Saubion (Auth.), Youssef Hamadi, Eric Monfroy, Frédéric Saubion (Eds.) - Autonomous Search-Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg (2012)Alvaro Gómez RubioPas encore d'évaluation
- 2009 Laporte - The VRPDocument10 pages2009 Laporte - The VRPViqri AndriansyahPas encore d'évaluation
- Signals and Systems Using Matlab Chapter 8 - Sampling TheoryDocument14 pagesSignals and Systems Using Matlab Chapter 8 - Sampling TheoryDiluPas encore d'évaluation
- Transportation Problem Investment Strategy: Submitted by Jatin Arora (191089) Nitish Goel (191100) Hemant Kumar (191101)Document31 pagesTransportation Problem Investment Strategy: Submitted by Jatin Arora (191089) Nitish Goel (191100) Hemant Kumar (191101)Nitish GoelPas encore d'évaluation
- Machine Learning Applications For Precision AgricuDocument38 pagesMachine Learning Applications For Precision AgricuShreya GaikwadPas encore d'évaluation
- Research of Artificial Intelligence in MedicineDocument6 pagesResearch of Artificial Intelligence in MedicineInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- MSC Part II IT 2015 Question Bank Mumbai UniversityDocument6 pagesMSC Part II IT 2015 Question Bank Mumbai UniversityJayesh ShindePas encore d'évaluation
- CPS 4801 Artificial Intelligence: Instructor: Tian (Tina) TianDocument36 pagesCPS 4801 Artificial Intelligence: Instructor: Tian (Tina) TianGuiaki GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec25 Place RouteDocument36 pagesLec25 Place RouteSindhu RajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment OverheadsDocument33 pagesAssignment OverheadsBishnu Ram GhimirePas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture24 - Testing Part 3Document20 pagesLecture24 - Testing Part 3Karim GhaddarPas encore d'évaluation
- Convolution 18.031, Haynes Miller and Jeremy OrloffDocument10 pagesConvolution 18.031, Haynes Miller and Jeremy OrloffPrineezyPas encore d'évaluation
- DBMS MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) - SanfoundryDocument16 pagesDBMS MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) - SanfoundryEzekiel JamesPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 14Document18 pagesChapter 14Dona Kris GumbanPas encore d'évaluation
- Predicting Short-Term Stock Prices Using Ensemble Methods and Online Data SourcesDocument39 pagesPredicting Short-Term Stock Prices Using Ensemble Methods and Online Data SourcesCNTT-1C-17 Vương Thị Diệu LinhPas encore d'évaluation
- Back Propagation AlgorithmDocument13 pagesBack Propagation AlgorithmHerald RufusPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Set 2Document4 pagesProblem Set 2dianazokhrabekova100% (1)