Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Liquid Liquid Extraction
Transféré par
Ah_boy0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
917 vues1 pageLab Report
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentLab Report
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
917 vues1 pageLiquid Liquid Extraction
Transféré par
Ah_boyLab Report
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 1
Abstract
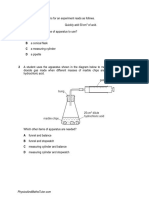
Liquid-liquid extraction is a method used for the separation of a mixture using
two immiscible solvents. Objectives of the first experiment was to determine the
distribution coefficient for the system organic solvent-propionic acid-water and to
show its independence on concentration and objectives for the second experiment is
to demonstrate how a mass balance is performed on the extraction column and to
measure the mass transfer coefficient with the aqueous phase as the continuous
medium. First experiment, 3 different volume of propionic acid of 5, 3 and 1 mL was
mixed up with 50mL organic solvent and 50mL of de-ionised water in conical flask.
The sample of upper and bottom layer this mixture then titrated with 0.1M sodium
hydroxide (NaOH) solution using phenolphthalein as indicator. The volume of NaOH
used to turn the mixture color into light pink was then recorded to determine the
distribution coefficient. The value of distribution coefficient, K by titration with 0.1 M
NaOH is 0.519 in 5mL of propionic acid, 0.462 for 3mL propionic acid and 0.604 for
1mL propionic acid. For the second objectives, the experiment was done using
liquid-liquid extraction unit to obtain feed, raffinate and extract sample. The sample
was titrated against 0.1M and 0.025M NaOH until the sample color turn into light
pink. The value of mass transfer coefficient from liquid-liquid extraction unit was
1.2914 x 10-4 for 0.1M NaOH and 2.6426 x 10 -5 for 0.025M NaOH. During titration,
continuous stirring is important to make sure the titrated sample is mixed well with
the NaOH. If possible used magnetic stirrer to ensure the sample mixed well. Slowly
added the NaOH to obtain the desired light pink color during the titration process.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Formal Report 1 Expt 27 Chem 26.1Document6 pagesFormal Report 1 Expt 27 Chem 26.1Franz ValenciaPas encore d'évaluation
- LLE Experiment 2Document10 pagesLLE Experiment 2Syafiq IzzuddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Determination of Total Acidity in VinegarDocument11 pagesDetermination of Total Acidity in VinegarJAN JERICHO MENTOYPas encore d'évaluation
- Formal Report 1 Expt 7 Chem 26.1Document6 pagesFormal Report 1 Expt 7 Chem 26.1Franz Valencia100% (1)
- Lab Report 1 TitrimetryDocument3 pagesLab Report 1 TitrimetryJoevelyn ValdezPas encore d'évaluation
- Leucine ProjectDocument17 pagesLeucine ProjectpvatssssPas encore d'évaluation
- An Accurate and Simple Titration Method Was Used For Determining of The Concentration of Carboxylic Acid in The Both Liquid Phases at EquilibriumDocument2 pagesAn Accurate and Simple Titration Method Was Used For Determining of The Concentration of Carboxylic Acid in The Both Liquid Phases at Equilibriumsolehah misniPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Report Experiment 2 Flores V1Document10 pagesLab Report Experiment 2 Flores V1Hazel BalasbasPas encore d'évaluation
- Determination of Acidity and Alkalinity: Experiment No: DateDocument5 pagesDetermination of Acidity and Alkalinity: Experiment No: DateNanditha APas encore d'évaluation
- Determining Molarity Through AcidDocument10 pagesDetermining Molarity Through Acidapi-284534960Pas encore d'évaluation
- Exp 3 Lab ReportDocument3 pagesExp 3 Lab ReportAlyssa OrtegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Report 1Document10 pagesLab Report 1Alex XanderPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 1: Determination of Total Acidity of Vinegar: Final Laboratory ReportDocument13 pagesExperiment 1: Determination of Total Acidity of Vinegar: Final Laboratory ReportEunice OpinioPas encore d'évaluation
- Phytochemical Analysis Laboratory Manual: Hebron University Prepared by Dr. Abdel Qader A. QawasmehDocument20 pagesPhytochemical Analysis Laboratory Manual: Hebron University Prepared by Dr. Abdel Qader A. QawasmehQOSSAY ALHROUSHPas encore d'évaluation
- FR3 Potentiometric TitrationDocument3 pagesFR3 Potentiometric TitrationRio ImbaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Report ChemDocument15 pagesLab Report Chemapi-328401829Pas encore d'évaluation
- Titration Purity of Maleic Acid UpdatedDocument11 pagesTitration Purity of Maleic Acid UpdatedMinichPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 3: Preparing SolutionDocument4 pagesExperiment 3: Preparing SolutionÇiğdem DÜLGERBAKİPas encore d'évaluation
- Laboratory Two - GlucoseDocument11 pagesLaboratory Two - GlucoseSarahPas encore d'évaluation
- Fakulty of Sustainable Agriculture RT10303 Chemistry For Agriculture Dr. Lum Mok Sam Practical 2Document5 pagesFakulty of Sustainable Agriculture RT10303 Chemistry For Agriculture Dr. Lum Mok Sam Practical 2Noor AmyrahPas encore d'évaluation
- Ka & Molar Mass of a Weak AcidDocument7 pagesKa & Molar Mass of a Weak AcidLeslie Sarah100% (1)
- Experiment 2Document5 pagesExperiment 2aeydrusPas encore d'évaluation
- Exp 1Document17 pagesExp 1Nor SyuhailaPas encore d'évaluation
- Determination of The Concentration of Acetic Acid in VinegarDocument16 pagesDetermination of The Concentration of Acetic Acid in VinegarFirdaus HaziqPas encore d'évaluation
- Isolation and Characterization of ProteinsDocument4 pagesIsolation and Characterization of ProteinsTROY CULDER SZEPas encore d'évaluation
- Bioanalytycal Chemistry Practical ReportDocument6 pagesBioanalytycal Chemistry Practical ReportDee-Pree CuprinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Acid Rain IIDocument3 pagesAcid Rain IIMaxWittPas encore d'évaluation
- Acid-Base TitrationDocument7 pagesAcid-Base TitrationPok Wan SoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Determination of Mixed Alkali Using Double Indicator TitrationDocument5 pagesDetermination of Mixed Alkali Using Double Indicator TitrationNathaniel JosephPas encore d'évaluation
- Interpreting Data from Standardization LabDocument2 pagesInterpreting Data from Standardization LabApril JoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem TitrationDocument14 pagesChem Titrationapi-441551987Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 1Document18 pagesLab 1Syah MiePas encore d'évaluation
- Biochem Formal ReportDocument6 pagesBiochem Formal ReportTacttoPas encore d'évaluation
- Name-Siddhant Kumar REG. NO - 2018UGCE002 Subject - Environmental Engineering LabDocument28 pagesName-Siddhant Kumar REG. NO - 2018UGCE002 Subject - Environmental Engineering LabGolu kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochem Formal ReportDocument5 pagesBiochem Formal ReportRouville SosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Exp Chemy 3Document5 pagesExp Chemy 3Nur AthirahPas encore d'évaluation
- Acids, Bases and Salts ExperimentDocument5 pagesAcids, Bases and Salts ExperimentCharca Manilay100% (1)
- Quantitative Determination of Soda Ash Composition by Double Indicator TitrationDocument6 pagesQuantitative Determination of Soda Ash Composition by Double Indicator Titrationyzzacamillea100% (1)
- Lab LleDocument20 pagesLab LleMuhamad Baihakhi Shamsudin100% (1)
- Tritation Lab ReportDocument8 pagesTritation Lab Reportapi-343706830Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Sba ProjectDocument10 pagesChemistry Sba Project4L Anisha SieudassPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochem Lab Formal Report - FinalsDocument5 pagesBiochem Lab Formal Report - FinalsAlyssa Nicole PadillaPas encore d'évaluation
- THanna StudentversionDocument10 pagesTHanna StudentversionMahesh KhamitkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Report 2Document8 pagesLab Report 2api-296431001Pas encore d'évaluation
- Exp 6 CHM420Document4 pagesExp 6 CHM4202023491958Pas encore d'évaluation
- Exp 1 Vinegar Sample ReportDocument4 pagesExp 1 Vinegar Sample Reportmuhammad aliPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 1 - Formal Report - Aguilar Alih BassarDocument15 pagesExperiment 1 - Formal Report - Aguilar Alih Bassarmedz dharPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab ReporttttDocument12 pagesLab ReporttttJustine LubianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Report - Titration of VinegarDocument7 pagesChemistry Report - Titration of VinegarSabestPas encore d'évaluation
- AP Chemistry Lab Brockport High School NY USA Titration of Acids and Bases MR KeeferDocument2 pagesAP Chemistry Lab Brockport High School NY USA Titration of Acids and Bases MR KeeferMuhammad Arif LangaahPas encore d'évaluation
- Isolation of Rna and Uv MeasurementDocument5 pagesIsolation of Rna and Uv MeasurementDanAdamL33% (3)
- Determination Citric Acid in Fruit JuiceDocument7 pagesDetermination Citric Acid in Fruit JuiceJacob Agdon33% (6)
- SKL Lab Report 2Document10 pagesSKL Lab Report 2Nisha Lauren VishvanathPas encore d'évaluation
- Exp 3Document5 pagesExp 3MarkPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisD'EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- Fourth International Conference on Non-Aqueous Solutions: Vienna 1974D'EverandFourth International Conference on Non-Aqueous Solutions: Vienna 1974V. GutmannPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical Manual of Analytical ChemistryD'EverandPractical Manual of Analytical ChemistryÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (3)
- CHE 620 Project Management Group ReportDocument2 pagesCHE 620 Project Management Group ReportAh_boyPas encore d'évaluation
- Flow Rate Input Type Time (Min) Inlet Conductivity (MS/CM) Outlet Conductivity (MS/CM)Document2 pagesFlow Rate Input Type Time (Min) Inlet Conductivity (MS/CM) Outlet Conductivity (MS/CM)Ah_boyPas encore d'évaluation
- Apparatus LleDocument2 pagesApparatus LleAh_boyPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Absorption Pressure DropDocument15 pagesGas Absorption Pressure DropAh_boyPas encore d'évaluation
- Discussion SoapDocument4 pagesDiscussion SoapAh_boy100% (12)
- ProcedureDocument1 pageProcedureAh_boyPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.3 AimsDocument1 page1.3 AimsAh_boyPas encore d'évaluation
- ProcedureDocument1 pageProcedureAh_boyPas encore d'évaluation
- CVBG Tip Of The Month: Robb Gunter's Super Quench FormulaDocument1 pageCVBG Tip Of The Month: Robb Gunter's Super Quench Formulaguytr2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Q3 M2 Consumer ChemistryDocument16 pagesQ3 M2 Consumer Chemistrymoni kim100% (1)
- Textile IndustryDocument24 pagesTextile IndustryAjay KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Inf Ufc 85Document13 pagesInf Ufc 85Luciano Montellano Abasto100% (2)
- Organizational Study Report at Travancore Cochin ChemicalsDocument59 pagesOrganizational Study Report at Travancore Cochin ChemicalsSarath P Babu100% (4)
- Company Profile PT Sasfindo Multi Yasa OKDocument6 pagesCompany Profile PT Sasfindo Multi Yasa OKAbdul Sani YatimPas encore d'évaluation
- ChemicalDocument44 pagesChemicalLal BaloushiPas encore d'évaluation
- ProteinDocument16 pagesProteinGwen Cua50% (2)
- Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDocument11 pagesChemistry Investigatory Project11AN Kanishk Kumar S100% (3)
- Effect of Different Pretreatments On Functional PropertiesDocument10 pagesEffect of Different Pretreatments On Functional PropertiesRND GelatinPas encore d'évaluation
- Extraction TheoryDocument32 pagesExtraction TheoryFida RoinikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry in Everyday Life ProjectDocument27 pagesChemistry in Everyday Life ProjectTarun TanwarPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 1A Alkali Metals Elements Compounds Pharmaceutical UsesDocument2 pagesGroup 1A Alkali Metals Elements Compounds Pharmaceutical UsesCharlyn Keith100% (1)
- Pulp Paper Sector ReportDocument38 pagesPulp Paper Sector ReportBambangsPas encore d'évaluation
- Process Discription PDFDocument41 pagesProcess Discription PDFAshish TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Learners Copy Phys Scie Mod 4Document16 pagesLearners Copy Phys Scie Mod 4Lynlyn ClorPas encore d'évaluation
- Cape Chemistry Unit 2 Practicals GuideDocument30 pagesCape Chemistry Unit 2 Practicals GuideDaniel Roopchand67% (3)
- Iit-Aiims-Screening-Test-Sample-Qns (1) - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2Document32 pagesIit-Aiims-Screening-Test-Sample-Qns (1) - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2gogulishanthPas encore d'évaluation
- Wehib Chemicals TradingDocument9 pagesWehib Chemicals TradingYIMER MESHESHAPas encore d'évaluation
- Acids Bases and Salts For Grade 7Document36 pagesAcids Bases and Salts For Grade 7raynjeremay100% (1)
- C3 Chemical ReactionsDocument58 pagesC3 Chemical ReactionsInaayah WahrPas encore d'évaluation
- Pretreatment of TextileDocument169 pagesPretreatment of TextileAbel TayePas encore d'évaluation
- AATCC 100-2004 Assesment of Antibacterial Dinishes On Textile MaterialsDocument3 pagesAATCC 100-2004 Assesment of Antibacterial Dinishes On Textile MaterialsAdrian CPas encore d'évaluation
- Pihkal: Chapter Nine Other Methods of Making PhenylacetoneDocument10 pagesPihkal: Chapter Nine Other Methods of Making Phenylacetones rPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise 6c ChemistryDocument7 pagesExercise 6c Chemistryapi-533545229Pas encore d'évaluation
- 8 - Inorganic Salt AnalysisDocument95 pages8 - Inorganic Salt AnalysisArkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Measurement (Multiple Choice) QPDocument8 pagesMeasurement (Multiple Choice) QPHridyansh KothariPas encore d'évaluation
- Sparkwiz Academy: Part TestDocument17 pagesSparkwiz Academy: Part TestSayak SenGuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- S Block Ncert SolutionsDocument32 pagesS Block Ncert SolutionsManish ShuklaPas encore d'évaluation
- Media Preparation GuideDocument72 pagesMedia Preparation GuideAgrim KhatryPas encore d'évaluation