Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Soil Consolidation 3
Transféré par
Bryan EweDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Soil Consolidation 3
Transféré par
Bryan EweDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
KAEA 3233 - SOIL MECHANICS II
Soil Consolidation
Part 3
Department of Civil Engineering
Faculty of Engineering
University of Malaya
Time Rate of Consolidation
Time Rate of Consolidation
Time Rate of Consolidation
Time Rate of Consolidation
Time Rate of Consolidation
Time Rate of Consolidation
Time Rate of Consolidation
Time Rate of Consolidation
Time Rate of Consolidation
Time Rate of Consolidation
Average degree of consolidation
Coefficient of Consolidation, Cv
Coefficient of Consolidation, Cv
Coefficient of Consolidation, Cv
Coefficient of Consolidation, Cv
Example 6
Example 7
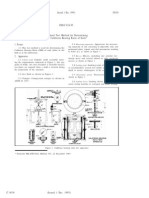
A soil profile is shown in figure. A surcharge load of 96 kN/m2 is applied on the
ground surface. Determine the following:
a) How high the water will rise in the piezometer immediately after the application
of load.
b) After 104 days of the load application, h = 4 m. Determine the coefficient of
consolidation (cv) of the clay soil.
Example 8
Example 9
Example 10
Precompression
Precompression
Vertical Drain
Method to speed up the flow of water from the soil mass so that maximum
settlement can be accelerated for highly compressible soil (increase the
rate of settlement).
The flow distance must be smaller than the thickness of the clay layer
If the clay layer is thin, the use of vertical drain is uneconomical
Vertical Drain
Vertical Drain
Vertical Drain
Vertical Drain
Vertical Drain
Vertical Drain
Vertical Drain
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- EPS WE Paper 2022 - AugustDocument13 pagesEPS WE Paper 2022 - AugustThamindu JayaweeraPas encore d'évaluation
- C2112 - Problem Sheet Consolidation 1Document2 pagesC2112 - Problem Sheet Consolidation 1Chen JianxiongPas encore d'évaluation
- Embankments On Organic Soils SurchargeDocument9 pagesEmbankments On Organic Soils SurchargethadikkaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Consolidation of Soil For Foundation by Using Sand DrainsDocument7 pagesConsolidation of Soil For Foundation by Using Sand DrainsBernd CastellarPas encore d'évaluation
- Consolidation of Soil For Foundation by Using Sand DrainsDocument7 pagesConsolidation of Soil For Foundation by Using Sand DrainsAulia Nurul AnnisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Consolidation Test1Document6 pagesConsolidation Test1Ramesh BabuPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture - 1 - CVNG 2009 - Soil Mechanics 2Document19 pagesLecture - 1 - CVNG 2009 - Soil Mechanics 2Ellesha JacksonPas encore d'évaluation
- Consolidation TestDocument6 pagesConsolidation TestManish AryaPas encore d'évaluation
- Soil Compaction CLASS NOTESDocument14 pagesSoil Compaction CLASS NOTESkkcollins395Pas encore d'évaluation
- Consolidation Settlement Examples 4 - Solutions-2Document18 pagesConsolidation Settlement Examples 4 - Solutions-2Sujani MaarasinghePas encore d'évaluation
- NPTEL Course: Ground ImprovementDocument67 pagesNPTEL Course: Ground ImprovementNurullah Akbulut100% (1)
- 463III B.Tech II Semester Examinations, APRIL 2011 GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING-IDocument8 pages463III B.Tech II Semester Examinations, APRIL 2011 GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING-Isujan_duttaPas encore d'évaluation
- Improvement of Silty Clay by Vacuum Preloading Incorporated With Electroosmotic MethodDocument8 pagesImprovement of Silty Clay by Vacuum Preloading Incorporated With Electroosmotic MethodNathan RodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Preloading and Prefabricated Vertical Drains Design For Foreshore Land Reclamation Projects: A Case StudyDocument10 pagesPreloading and Prefabricated Vertical Drains Design For Foreshore Land Reclamation Projects: A Case Studyrakhbir100% (1)
- GRP3 EXP11 Consolidation-Test-1Document18 pagesGRP3 EXP11 Consolidation-Test-1PEÑA, Malich APas encore d'évaluation
- Soil Restraint On Buckling Oil and Gas Pipelines Buried in Lumpy Clay FillDocument10 pagesSoil Restraint On Buckling Oil and Gas Pipelines Buried in Lumpy Clay FillUmar KidaPas encore d'évaluation
- ConsolidationDocument6 pagesConsolidationKanchana Randall100% (1)
- CV 631107081Document7 pagesCV 631107081lim kang haiPas encore d'évaluation
- 9A01602 Geotechnical Engineering - IDocument7 pages9A01602 Geotechnical Engineering - IsivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- 2011 Exam GeotechnicalDocument9 pages2011 Exam GeotechnicalAhmed AwadallaPas encore d'évaluation
- Soil Compaction: A. General PrinciplesDocument6 pagesSoil Compaction: A. General PrinciplesIcha EstradaPas encore d'évaluation
- Buttling, S and Zhong, R (2017) - Monitoring of An Embankment Project Using Rigid Inclusions and Vacuum Consolidation During and After ConstructionDocument10 pagesButtling, S and Zhong, R (2017) - Monitoring of An Embankment Project Using Rigid Inclusions and Vacuum Consolidation During and After ConstructionStephen ButtlingPas encore d'évaluation
- GeotechnicsDocument10 pagesGeotechnicsaPas encore d'évaluation
- GEO 2 Prob Set Take 2 Chap 9Document3 pagesGEO 2 Prob Set Take 2 Chap 9John Pierce GumapacPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes 1 - Soil CompactionDocument50 pagesNotes 1 - Soil CompactionTang Ching Pang100% (1)
- Experiment 3: Permeameter Fix ColumnDocument6 pagesExperiment 3: Permeameter Fix ColumnMohamad Haziq Bin MuradPas encore d'évaluation
- 1D Consolidation Test Lab ManualDocument15 pages1D Consolidation Test Lab Manualogul100% (2)
- Cep GeotechnicalDocument14 pagesCep GeotechnicalAzmat NaseemPas encore d'évaluation
- Coefficient of ConsolidationDocument4 pagesCoefficient of ConsolidationSiva JothiPas encore d'évaluation
- Consolidation Test: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesConsolidation Test: ObjectivejemuelPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 2 - ConsolidationDocument22 pagesLecture 2 - ConsolidationMonique AldanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 7Document4 pagesTutorial 7Seanam DMPas encore d'évaluation
- Soil Improvement For A Road Using The Vacuum Preloading MethodDocument8 pagesSoil Improvement For A Road Using The Vacuum Preloading MethodFarid MarufPas encore d'évaluation
- Vibroflotation ProcedureDocument4 pagesVibroflotation ProcedureManop MethaPas encore d'évaluation
- OTC 10991 Partially-Drained Loading of Shallow Foundations On SandDocument9 pagesOTC 10991 Partially-Drained Loading of Shallow Foundations On SandSamuel Laura HuancaPas encore d'évaluation
- Consolidation of ClayDocument17 pagesConsolidation of ClayMD Anan MorshedPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study of The Changi East Land Reclamation Project SingaporeDocument13 pagesCase Study of The Changi East Land Reclamation Project SingaporeVictoria JungPas encore d'évaluation
- Annex - Ground Improvement Works at Changi EastDocument4 pagesAnnex - Ground Improvement Works at Changi EastlittlestepjPas encore d'évaluation
- r7320101 Geotechnical EngineeringDocument4 pagesr7320101 Geotechnical Engineeringvamsi253Pas encore d'évaluation
- Oedometer Test: Soil Mechanics 2 CE PC 504Document26 pagesOedometer Test: Soil Mechanics 2 CE PC 504SumanHaldarPas encore d'évaluation
- Consolidation TestDocument4 pagesConsolidation TestrbhavishPas encore d'évaluation
- EXPeriment 6Document12 pagesEXPeriment 6Chakshu GautamPas encore d'évaluation
- Soil Consolidation Solved ProblemsDocument16 pagesSoil Consolidation Solved ProblemsBurhan MPas encore d'évaluation
- Consolidation Test - Lab ManualDocument5 pagesConsolidation Test - Lab ManualAmira SyazanaPas encore d'évaluation
- CH067Document6 pagesCH067PabloPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 Consolidation Theory PDFDocument24 pagesChapter 4 Consolidation Theory PDFSufian PianPas encore d'évaluation
- Consolidation Test by RatiyalaDocument6 pagesConsolidation Test by RatiyalaBhawanujan PerinparajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Soils Examination Practice QuestionsDocument3 pagesSoils Examination Practice QuestionsIsaiah BristolPas encore d'évaluation
- The Need For Consolidation Theory: Magnitude and The Rate ofDocument2 pagesThe Need For Consolidation Theory: Magnitude and The Rate ofChristine Joyce A. CortezPas encore d'évaluation
- ConsolidationDocument42 pagesConsolidationalishagarcia01Pas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment To Conduct Compaction TestDocument9 pagesExperiment To Conduct Compaction TestAyaz BhattiPas encore d'évaluation
- Compaction Oct2010Document23 pagesCompaction Oct2010Akshthagowda848_1952Pas encore d'évaluation
- OTC 12194 Experimental Investigations of The Cyclic Response of Suction Caissons in SandDocument9 pagesOTC 12194 Experimental Investigations of The Cyclic Response of Suction Caissons in SandLTE002Pas encore d'évaluation
- CBR TestDocument8 pagesCBR Testshree_iitPas encore d'évaluation
- Ground Improvement Case Histories: Compaction, Grouting and GeosyntheticsD'EverandGround Improvement Case Histories: Compaction, Grouting and GeosyntheticsÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (3)
- Ground Improvement Case Histories: Embankments with Special Reference to Consolidation and Other Physical MethodsD'EverandGround Improvement Case Histories: Embankments with Special Reference to Consolidation and Other Physical MethodsPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Piles Under Cyclic Loading: SOLCYP RecommendationsD'EverandDesign of Piles Under Cyclic Loading: SOLCYP RecommendationsAlain PuechPas encore d'évaluation
- Reservoir Engineering in Modern Oilfields: Vertical, Deviated, Horizontal and Multilateral Well SystemsD'EverandReservoir Engineering in Modern Oilfields: Vertical, Deviated, Horizontal and Multilateral Well SystemsPas encore d'évaluation
- Green Building - Diamond PDFDocument54 pagesGreen Building - Diamond PDFBryan EwePas encore d'évaluation
- L1-Introduction To Prestressed ConcreteDocument13 pagesL1-Introduction To Prestressed ConcreteBryan EwePas encore d'évaluation
- L3-Materials and SpecificationsDocument7 pagesL3-Materials and SpecificationsBryan EwePas encore d'évaluation
- Ms 1934 Part 3 2007-Methods of Test For Masonry - Part 3 Determination of Initial Shear Strength-850492Document19 pagesMs 1934 Part 3 2007-Methods of Test For Masonry - Part 3 Determination of Initial Shear Strength-850492Bryan EwePas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture1 - Intro and Concrete MaterialsDocument42 pagesLecture1 - Intro and Concrete MaterialsBryan EwePas encore d'évaluation
- WK 4 Trip Distribution AnalysisDocument9 pagesWK 4 Trip Distribution AnalysisBryan EwePas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 6 (B) - Yield Line ExamplesDocument25 pagesLecture 6 (B) - Yield Line ExamplesBryan Ewe100% (1)
- Lecture 7-Wastewater & Activated Sludge TreatmentDocument45 pagesLecture 7-Wastewater & Activated Sludge TreatmentBryan EwePas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 3 - Critical Path Method 1 PDFDocument25 pagesLecture 3 - Critical Path Method 1 PDFBryan EwePas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 3 - Critical Path Method 1 PDFDocument25 pagesLecture 3 - Critical Path Method 1 PDFBryan EwePas encore d'évaluation
- Three Pinned ArchesDocument3 pagesThree Pinned ArchesAztec MayanPas encore d'évaluation
- Thin WallDocument4 pagesThin WallBryan EwePas encore d'évaluation
- Law of ContractDocument66 pagesLaw of ContractBryan EwePas encore d'évaluation
- Stress Distribution 2Document15 pagesStress Distribution 2Bryan EwePas encore d'évaluation
- Stress Distribution 3Document16 pagesStress Distribution 3Bryan EwePas encore d'évaluation