Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Transportation Engineering Week 1A
Transféré par
Marc MathieuDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Transportation Engineering Week 1A
Transféré par
Marc MathieuDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
6/14/2016
CE 414
(TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING)
POLICIES AND GUIDELINES IN THE CLASSROOM
Prayer. Each class begins and ends with a prayer.
Greeting. Students greet the teacher Good morning, Sir. Praised be Jesus and Mary!
before the beginning of the class.
Attendance. Only for valid reasons can students be excused from class.
Identification Card. A validated student identification card must always be worn by all
students.
Promptness. Students are expected to come to class on time. After the first checking of
attendance, the student(s) is considered late. If the student is not present after the end of
lecture/discussion during the second checking of attendance, it is considered absent.
Participation. As much as possible, students are to participate in class discussions and
activities.
Intellectual Integrity. Cheating is strictly prohibited. Any form of dishonesty shall be
dealt with accordingly. Honesty is the best policy.
Use of Cellular phones and other Electronic Gadgets. All cellular phones and other
electronic gadgets must be put in silent mode inside the classroom at all times
otherwise gadgets will be confiscated.
Energy Conservation. Lights and fans are put off by the one nearest the switch after
every class.
Submission of Requirements. Class requirements are to be submitted on time.
Courtesy. Respect for others is practiced at all times and in all places.
COURSE INFORMATION
Course Code
Course Title
Course
Description
: CE 414
: Transportation Engineering
: This course deals to the planning, design, operation, and management of
transportation facilities. This course is also multidisciplinary and requires
knowledge from specialized fields such as psychology, economics, ecology
and environment, sociology, management, optimization, graph theory,
probability theory, statistics, computer simulation, and other areas of civil
engineering (such as structural and geotechnical engineering).
Pre-requisite : CE322 (Highway Engineering)
Co-requisite : None
Credit
: 3.0 units Lecture
Class
Schedule
: 3 hours per week
Lecture Grade
Assessment Method
Quizzes
Periodical Examinations
Project
Assignments/Seatworks
Class Participation
Total
Weights
30%
30%
25%
10%
5%
100%
Base 40, 75 Passing Grade
What is transportation system?
A transportation system may be defined as
consisting of the:
Fixed facilities
Flow entities
Control system
that permit people and goods to overcome the
friction of geographical space efficiently in
order to participate in a timely manner in
some desired activity.
6/14/2016
The functional components of a transportation
system
A. Fixed Facilities
The physical components of the system
that are fixed in space and constitute the
network of links (e.g. roadway segments,
railway track, and pipes) and nodes (e.g.
intersections, interchanges, transit terminals,
harbors and airports) of the transportation
system.
The functional components of a transportation
system
C. Control System
It consists of vehicular control and flow
control. Vehicular control refers to the
technological way in which individual
vehicles are guided on the fixed facilities.
The flow control system consists of the
means that permit the efficient and smooth
operation of streams of vehicles and the
reduction of conflicts between vehicles.
The functional components of a transportation
system
B. Flow Entities and Technology
The units that traverse the fixed facilities.
They include vehicles, container units,
railroad cars, and so on.
TRANSPORTATION SYSTEM
CLASSIFICATION
CLASSIFICATION SCHEMES
CLASSIFICATION SCHEMES
Any transportation system consists of various modes
of travel ranging from walking to driving to use of crafts
that fly. One way of classifying a transportation system
would then be to form classes of different modes of travel.
Such classification is termed modal classification.
A little thought at this stage will show that all modes of
travel consist of the same set of elements such as a person
who drives, the vehicle which is driven, the path that is
used, the user who uses the mode, and the like. Therefore,
another way of looking at a transportation system could be
to look at its elements. Such a classification is termed
elemental classification.
Another very different way of looking at a
transportation system, is from the point of view of functions
that a transportation engineer needs to carry out. For
example, a transportation engineer may need to analyze
and design facilities to be used by vehicles, or may need to
determine routes of buses, or may even need to chalk out a
plan of transportation-related activities. We can therefore
classify the field of transportation engineering functionally.
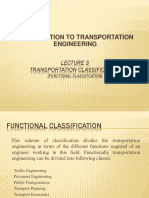
Such a classification is termed functional classification.
6/14/2016
The
figure
shows
a
diagrammatic representation
of the classification schemes.
Transportation
engineering
can
be
viewed
as
the
engineering
of
the
transportation
systems----a
conglomeration of different
modes of transport which in
turn consists of various basic
elements. Also, it can be seen
that
transportation
engineering as a field requires
various
functions
like
planning,
pavement
engineering, and so forth.
I. Roadways
From a transportation engineers standpoint, the important aspects
related to the roadways mode of transport include:
Safe and efficient operation and control of road traffic
Layout of roads
Structural design of the roadway (pavement design)
Roadway-based public transportation
II. Railways
From a transportation engineers standpoint, the important aspects
related to railway mode of transport include:
Safe and efficient operation and control of rail traffic
Layout of rail tracks
Structural design of the subgrade on which rail tracks run
Planning of stations or terminals for railway vehicles.
B. Elemental Classification
A transportation system can be classified in terms of the basic
elements which constitute any mode of transport. These basic
elements are identified in the following:
Driver: Every mode of transportation has a driver who controls the
vehicle used in that mode of transportation.
Vehicle: The vehicles which are used in transportation have certain
characteristics which influence the design and operation of the
transportation facility.
Way: Every mode of transportation uses a specified path which is either
constructed or charted.
Control: In order to ensure safety and efficiency of operation, there are
system level controls which are imposed on the movement of the
vehicles.
Terminal: This is a location where the vehicles of a mode stop for
various reasons.
User: Obviously any transportation system runs to provide service to its
users.
A. Modal Classification
A mode of transport may be simply defined as a means
of transportation. A mode, according to this definition,
includes walking, automobile, bus, train, ferry-boat, ship,
aircraft, helicopter, and so on. However, all these modes use
either the road, the rail tracks, the waterways (like rivers,
travel paths in oceans), or the airways. Hence, a slightly
different way of classifying the transportation systems
according to modes would be to define classes as groups of
modes which use a particular surface. In this definition
then, there are, in general, four classes---the roadways, the
railways, the waterways, and the airways.
III. Waterways
From a transportation engineers standpoint, the important aspects
related to this mode of transport include:
Safe and efficient operation and control of ship traffic especially at
and near ports
Planning and operations of ports
IV. Airways
From a transportation engineers standpoint, the important aspects
related to the airways mode of transport include:
Safe and efficient operation and control of air traffic especially at
and near airports
Planning and operation of airports
Orientation of runways and layout of taxiways
Planning the parking pattern of aircraft
Structural design of the runways, taxiways and aprons
Planning and operation of vehicle circulation and parking on the
land-side of airports.
C. Functional Classification
This scheme of classification of transportation engineering divides
this discipline in terms of the different functions required of an engineer
working in this field. Functionally, transportation engineering can be
divided into the following primary classes:
Traffic Engineering: This area of transportation engineering deals with the
analysis, design and operation of transportation facilities used by vehicles of
various transportation modes.
Pavement Engineering: This area of transportation engineering deals with
the structural analysis and design of the way used by different modes of
transportation.
Public Transportation: The area of public transportation is concerned with
the analysis, design, and operation of public transportation systems. A public
transportation system is a transportation system which operates to move the
general public from one point to another.
Transport Planning: It deals with planning transportation facilities which will
be able to meet the present and future needs in a sustainable manner.
Transport Economics: This area studies the various economic costs and
benefits of building and operating different transportation facilities
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Design of High-Speed Railway Turnouts: Theory and ApplicationsD'EverandDesign of High-Speed Railway Turnouts: Theory and ApplicationsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (4)
- Highway Engineering: Planning, Design, and OperationsD'EverandHighway Engineering: Planning, Design, and OperationsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (24)
- CC503 Traffic Engineering Course OverviewDocument33 pagesCC503 Traffic Engineering Course OverviewNik AliffPas encore d'évaluation
- Bus Terminal Design GuidedlineDocument18 pagesBus Terminal Design GuidedlinePudu Mounika100% (1)
- Lecture 3Document9 pagesLecture 3Rehman AwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Planning of Transportation SystemsDocument11 pagesPlanning of Transportation SystemsMike WheazzyPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Transportation EngineeringDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Transportation Engineeringzain IshaqPas encore d'évaluation
- TRANSPOENG Module 1Document56 pagesTRANSPOENG Module 1BryanHarold BrooPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Transportation Planning and EngineeringDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Transportation Planning and EngineeringPrabin Adhikari100% (1)
- TRANSPOENG Module 1.1 - Land Use-Transportation InteractionDocument22 pagesTRANSPOENG Module 1.1 - Land Use-Transportation InteractionBryanHarold BrooPas encore d'évaluation
- TRANSENG ReviewerDocument90 pagesTRANSENG ReviewerAce De GuzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- TransportPlanning&Engineering PDFDocument121 pagesTransportPlanning&Engineering PDFItishree RanaPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 CE 122 Intro To Traffic & Highway EngineeringDocument18 pages01 CE 122 Intro To Traffic & Highway EngineeringJan Kenneth BarazonPas encore d'évaluation
- ReviewerDocument11 pagesReviewerBryant Joseph Tugcay VelascoPas encore d'évaluation
- Transportation EngineeringDocument32 pagesTransportation EngineeringKAYE AIRA DE LEONPas encore d'évaluation
- Transportation Planning & EngineeringDocument34 pagesTransportation Planning & EngineeringSenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Essential guide to transportation infrastructure planningDocument15 pagesEssential guide to transportation infrastructure planningVivudh Krishna ShuklaPas encore d'évaluation
- Transportation PlanningDocument17 pagesTransportation PlanningyashaswiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Transportation Planning ProcessDocument29 pagesTransportation Planning ProcessGraciele Sera-Revocal100% (2)
- 3 Module No. 1 - Principles of Transportation Engg Introduction2Document5 pages3 Module No. 1 - Principles of Transportation Engg Introduction2Mikki AleluyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Traffic EngineeringDocument36 pagesIntroduction To Traffic EngineeringzakeriyaPas encore d'évaluation
- TPE Lecture 2 (12-2-15)Document33 pagesTPE Lecture 2 (12-2-15)Fortiter FysproPas encore d'évaluation
- Transportation Engineering Course OutlineDocument33 pagesTransportation Engineering Course OutlineKisstar MbuyaPas encore d'évaluation
- ES CE - Civil Engineering Orientation Lecture Notes - 6Document3 pagesES CE - Civil Engineering Orientation Lecture Notes - 6Mae TadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Functional Classification OverviewDocument5 pagesFunctional Classification OverviewLawrence SalazarPas encore d'évaluation
- Traffic Engineering and Management: Special PPT'S Included LastDocument276 pagesTraffic Engineering and Management: Special PPT'S Included LastRajkumar EkkelliPas encore d'évaluation
- Transpo ReportDocument5 pagesTranspo ReportRaymart CubidPas encore d'évaluation
- Transportation and Traffic Class SVDocument16 pagesTransportation and Traffic Class SVHussam JamalPas encore d'évaluation
- Mulungushi University Highway Engineering CourseDocument20 pagesMulungushi University Highway Engineering CoursePenelope MalilwePas encore d'évaluation
- Lctr_1-2_1706504988206888883565b7331c50207 (1)Document33 pagesLctr_1-2_1706504988206888883565b7331c50207 (1)vishal60928Pas encore d'évaluation
- Transportation EngineeringDocument3 pagesTransportation EngineeringNyel SaduestePas encore d'évaluation
- Traffic Engineering-Lecture 1Document10 pagesTraffic Engineering-Lecture 1Ahmad Salih100% (1)
- Transportation Planning Chapter SummaryDocument111 pagesTransportation Planning Chapter SummarydzikrydsPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1-Utp PDFDocument6 pagesModule 1-Utp PDFAryan ArynPas encore d'évaluation
- Role of Transportation in Society (39Document44 pagesRole of Transportation in Society (39KingPas encore d'évaluation
- CE451-Mid ModuleDocument29 pagesCE451-Mid ModuleecobuildconstructionltdPas encore d'évaluation
- TR 631 LT 2.1 - Traffic Forecasting and ModellingDocument38 pagesTR 631 LT 2.1 - Traffic Forecasting and ModellingGilbert MaroPas encore d'évaluation
- Design Criteria For Highways and RailwaysDocument7 pagesDesign Criteria For Highways and RailwaysDale MalazzabPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 - Introduction To Transport PlanningDocument6 pages1 - Introduction To Transport PlanningKwasi Agyeman-Boakye100% (1)
- Vtu Me Transport First YearDocument46 pagesVtu Me Transport First YearAbhishek AbPas encore d'évaluation
- Transportation EngineeringDocument47 pagesTransportation Engineeringnicole.galvezPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 1Document70 pagesLec 1Akhlaq AmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Managing Transportation OperationsDocument44 pagesManaging Transportation OperationsIdris SaheedPas encore d'évaluation
- Industrial Engineering Applications: Abhishek Kumar Rasika IyerDocument12 pagesIndustrial Engineering Applications: Abhishek Kumar Rasika IyerAbhishek KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Highway Module 1 3 - CLEARDocument48 pagesHighway Module 1 3 - CLEARJino MancaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Civil Engineering Faculty of Engineering & TechnologyDocument19 pagesDepartment of Civil Engineering Faculty of Engineering & TechnologyUmar SaiduPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1Document38 pagesChapter 1yuy ihiyiyjdhPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1: Introduction To Transportation Planning: by Rei Robin Roland Tumambing, CE, RMP Elective2EDocument54 pagesModule 1: Introduction To Transportation Planning: by Rei Robin Roland Tumambing, CE, RMP Elective2ENicole De LeonPas encore d'évaluation
- ENG11Document4 pagesENG11Jayri FelPas encore d'évaluation
- Transpo - Chapter 3Document21 pagesTranspo - Chapter 3nors lagsPas encore d'évaluation
- Transportation Planning ProcessDocument43 pagesTransportation Planning ProcessAncheta Suzanne ClarissePas encore d'évaluation
- Ceg552 - Chapter 6Document116 pagesCeg552 - Chapter 6Anis NabihahPas encore d'évaluation
- TRAFFIC ENGINEERNIG PrezentacijaDocument10 pagesTRAFFIC ENGINEERNIG PrezentacijaAna StojadinovićPas encore d'évaluation
- TRAFFIC ENGINEERING COURSE OUTLINEDocument21 pagesTRAFFIC ENGINEERING COURSE OUTLINEErvina AhyudanariPas encore d'évaluation
- Multimodal TransportDocument24 pagesMultimodal Transportashishdhaloch1995100% (1)
- Travel Time and Delay StudiesDocument16 pagesTravel Time and Delay StudiesArvin Jay AlvindaPas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER 4 - Introduction To Transportation PlanningDocument16 pagesCHAPTER 4 - Introduction To Transportation PlanningJamie ZaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Transportation EngineeringDocument9 pagesTransportation EngineeringRaquel PanillosPas encore d'évaluation
- Implementing Automated Road Transport Systems in Urban SettingsD'EverandImplementing Automated Road Transport Systems in Urban SettingsPas encore d'évaluation
- Data-Driven Traffic Engineering: Understanding of Traffic and Applications Based on Three-Phase Traffic TheoryD'EverandData-Driven Traffic Engineering: Understanding of Traffic and Applications Based on Three-Phase Traffic TheoryPas encore d'évaluation
- ES 3-Lecture 1Document26 pagesES 3-Lecture 1Marc MathieuPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Derivatives IntegralsDocument4 pagesCommon Derivatives Integralsapi-243574449Pas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Set No. 2Document2 pagesProblem Set No. 2Marc MathieuPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment (Due Dec 11) PDFDocument1 pageAssignment (Due Dec 11) PDFMarc MathieuPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction (Basic Concepts)Document18 pagesIntroduction (Basic Concepts)Marc MathieuPas encore d'évaluation
- D2435 OnedimconsolidDocument10 pagesD2435 OnedimconsolidHilana OliveiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz No. 1 (Answer Key) PDFDocument2 pagesQuiz No. 1 (Answer Key) PDFMarc MathieuPas encore d'évaluation
- Soil Mechanics Laboratory: A Guide For Preparing Laboratory ReportsDocument10 pagesSoil Mechanics Laboratory: A Guide For Preparing Laboratory ReportsohnthaikPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear First-Order Differential EquationsDocument6 pagesLinear First-Order Differential EquationsMarc MathieuPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Set No. 3Document3 pagesProblem Set No. 3Marc MathieuPas encore d'évaluation
- Factoring Cubic PolynomialsDocument2 pagesFactoring Cubic PolynomialsAshish YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Set No. 1Document4 pagesProblem Set No. 1Marc MathieuPas encore d'évaluation
- Separable First-Order Differential Equations PDFDocument8 pagesSeparable First-Order Differential Equations PDFMarc MathieuPas encore d'évaluation
- Seismic Code RequirementsDocument34 pagesSeismic Code Requirementsronison78Pas encore d'évaluation
- Principles and Practices of Seismic Microzonation - Case Studies IDocument17 pagesPrinciples and Practices of Seismic Microzonation - Case Studies IMarc MathieuPas encore d'évaluation
- CSA Lab Manual IV YEAR 2015 2016 1Document95 pagesCSA Lab Manual IV YEAR 2015 2016 1Marc MathieuPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Curricula Bachelor of Science in Civil Engineering PDFDocument36 pagesSample Curricula Bachelor of Science in Civil Engineering PDFBellPas encore d'évaluation
- 103 20160404025022Document15 pages103 20160404025022Marc MathieuPas encore d'évaluation
- Highway SpiralsDocument8 pagesHighway SpiralsChandrasiri de SilvaPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculating Minimum Curve Radii Using Superelevation RatesDocument28 pagesCalculating Minimum Curve Radii Using Superelevation RatesMarc MathieuPas encore d'évaluation
- DPWH-JICA Technical Standards and GuidelinesDocument163 pagesDPWH-JICA Technical Standards and GuidelinesmnvalentePas encore d'évaluation
- Technical Standards and Guidelines For Planning and Design PDFDocument144 pagesTechnical Standards and Guidelines For Planning and Design PDFPedro Marfito Jr.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pavement Design DPWHDocument8 pagesPavement Design DPWHSwerthson Wasawas83% (6)
- Soil Mechanics PlatesDocument16 pagesSoil Mechanics PlatesMarc MathieuPas encore d'évaluation
- 0 4365 P2Document704 pages0 4365 P2Marc MathieuPas encore d'évaluation
- Appendix D - Alignment and SuperelevationDocument22 pagesAppendix D - Alignment and SuperelevationMarc MathieuPas encore d'évaluation
- ASTEC Brochure PDFDocument23 pagesASTEC Brochure PDFMarc MathieuPas encore d'évaluation
- Pavement Design DPWHDocument8 pagesPavement Design DPWHSwerthson Wasawas83% (6)
- FGGBKLT EfdgfdDocument19 pagesFGGBKLT EfdgfdGelo PlamencoPas encore d'évaluation
- Automotive Functional Safety Best-Practices - ISO 26262 Standard - EmbitelDocument5 pagesAutomotive Functional Safety Best-Practices - ISO 26262 Standard - Embitelprasanna_npPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Design ThinkingDocument20 pagesWhat Is Design ThinkingPrathamesh PittulePas encore d'évaluation
- The Next Generation of Plastic Sheet PilingDocument2 pagesThe Next Generation of Plastic Sheet PilingNguyen Thanh LuanPas encore d'évaluation
- 010 Frank Pecafil Application Guide BRDocument22 pages010 Frank Pecafil Application Guide BREduardo Gamarra PerezPas encore d'évaluation
- Architecture technology: Zaha Hadid's twisting Leeza Soho skyscraperDocument21 pagesArchitecture technology: Zaha Hadid's twisting Leeza Soho skyscrapersarahPas encore d'évaluation
- Ahmed ArafiaDocument6 pagesAhmed ArafiaAbhilash PaulPas encore d'évaluation
- Resume - Mark Edison D Fellone - 2014Document2 pagesResume - Mark Edison D Fellone - 2014api-262936729Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gujarat Technological University: Aeronautical EngineeringDocument16 pagesGujarat Technological University: Aeronautical EngineeringNiik StarPas encore d'évaluation
- HandbookDocument146 pagesHandbookbluishimagePas encore d'évaluation
- An Introduction To CNC MachinesDocument20 pagesAn Introduction To CNC MachinesBHAVESHPas encore d'évaluation
- Silangan Fit OutDocument5 pagesSilangan Fit OutNova CastyPas encore d'évaluation
- Supertall Building Chilled Water Distribution SI May 30 2015Document10 pagesSupertall Building Chilled Water Distribution SI May 30 2015185412Pas encore d'évaluation
- Seismic Demand Evaluation For A The Northridge Earthquake 4-Story Steel Frame Structure Damaged inDocument27 pagesSeismic Demand Evaluation For A The Northridge Earthquake 4-Story Steel Frame Structure Damaged insanh137Pas encore d'évaluation
- Implementation of a discontinuous Galerkin model for sediment transport on unstructured meshesDocument19 pagesImplementation of a discontinuous Galerkin model for sediment transport on unstructured meshesEndless LovePas encore d'évaluation
- Site PlanDocument1 pageSite PlanARJUN PRASHANTHPas encore d'évaluation
- Part 541 - Drafting and DrawingsDocument8 pagesPart 541 - Drafting and DrawingsLuis David Molina CarvalhoPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer System MaintenanceDocument4 pagesComputer System MaintenanceJeruPas encore d'évaluation
- Machine Design R S KurmiDocument1 pageMachine Design R S KurmiDenish PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- En Wikipedia Org Wiki Civil EngineeringDocument22 pagesEn Wikipedia Org Wiki Civil EngineeringSushanta Kumar RoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Control Theory Lecture OverviewDocument34 pagesControl Theory Lecture OverviewsakshiPas encore d'évaluation
- TOPIC (All Caps, Font 22, Bold, No Underline and No Italics, Centered)Document4 pagesTOPIC (All Caps, Font 22, Bold, No Underline and No Italics, Centered)Pawan GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- IIT Madras Bolted Connections GuideDocument30 pagesIIT Madras Bolted Connections GuidepjuvvadiPas encore d'évaluation
- SGS IND Construction Material Inspection in India A4 EN 10 PDFDocument2 pagesSGS IND Construction Material Inspection in India A4 EN 10 PDFIndra MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Concrete Structure II Sessional: Dhaka University of Engineering & TechnologyDocument22 pagesDesign of Concrete Structure II Sessional: Dhaka University of Engineering & TechnologyumrumrumrPas encore d'évaluation
- What Are The Fundamental Properties of MaterialsDocument1 pageWhat Are The Fundamental Properties of MaterialsArden Antonio CabaisPas encore d'évaluation
- AcronymsDocument65 pagesAcronymsSaid TouhamiPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Mechanical EngineerDocument2 pagesElectrical Mechanical Engineerapi-78757571Pas encore d'évaluation
- CIVIL ENGINEERING prEN 1995-2 2004 (Final Draft) - Design of Timber Structures - Bridges PDFDocument29 pagesCIVIL ENGINEERING prEN 1995-2 2004 (Final Draft) - Design of Timber Structures - Bridges PDFcaballerolangPas encore d'évaluation
- Classified Advertising: TEL: 444 666 09 FAX: 444 188 11 PB NO. 533Document5 pagesClassified Advertising: TEL: 444 666 09 FAX: 444 188 11 PB NO. 533vsraj1999Pas encore d'évaluation
- RESUMEDocument3 pagesRESUMEWaqar Ali ShahPas encore d'évaluation