Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
GXM GSH
Transféré par
GerardLumTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
GXM GSH
Transféré par
GerardLumDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
jslum.
com | Medicine
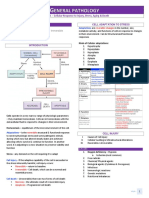
GXM & GSH Antiglobulin test (Coombs test)
AHG (Antihuman globulin) – produced via animals by injection of human globulin,
Compatibility testing compleme nt, immunoglob ulin
Prevent haemolysis AHG + Human RBC (coated with Ig antibody) or complement
Agglutination – indicate +ve test
Donor’s blood is not compatible/ safe for transfusion
Blood grouping
AHG enhance red cell agglutination (red cells coated by antibodies)
Reagents/ equipments
Anti A, B, AB (direct grouping)
Blood from recipient (cells, serum)
Tile, Test tubes
Centrifuge
Known cells – O, A, B (indirect grouping)
Principle
Antigen-antibody reaction causes RBC agglutination
Cross Matching (GXM) Group Screen Hold (GSH)
To transfuse compatible red cells to patients Group Screen Hold
Principle ABO, Rhesus grouping Red blood cell antibody Keep screened sample
Red cells from donor (same ABO, RhD) tested against recipient (patient) serum of patient’s blood screening until need arise
Agglutination – incompatible donor red cells Patient’s serum tested Will not be cross-
Methods against reagent red matched until needed
Detecting clinically significant IgM antibodies (cold) – saline in room temperature cells (known red cell
Detecting clinically significant IgM, IgG antibodies (warm) – saline 37°C antigens)
Detecting immune antibodies (mainly IgG) – indirect antiglobulin test (AHG test) Using known red cell
at 37°C antigens (red cell panel
Cross matching test I, II, III) – indirect
Coomb’s test
+ve result will show
agglutination
(indicate patient has
specific antibody(s ) to
antigen(s))
Results of antibody screening
Postive (+ve) Negative (-ve)
Identify antibody – type of red cell When blood is required, cross-
antibody matching will be performed
(saline, room temperature)
Compatible blood will be supplied Blood issued as soon as neede d
after full cross-matching & typed Full cross-matched proceed in lab
(negative for antigen to particular Blood is taken even when procedure
antibody) is not finished
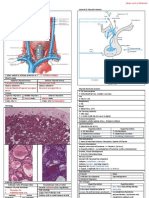
Red cell antibodies to
Advantages of GSH
Minor blood groups
↓ Blood stock (for blood cross -matching - n ot needed for blood transfu sion)
• Lewis, Duffy, Kell antigens (on red cell surface) ↓ Blood wastage & Expiry date
Major blood groups
Safe blood is supplied to patients (equal to doing GXM)
• ABO, Rhesus D antigen (very immunogenic) Blood is delivered ASAP when needed
Development of Red cell antibodies by
Indications for GSH
Naturally
Cases of elective surgery (chances of not using is ↑ than using blood)
Immune me chanisms
Blood request is not more than 2 units
Adult cases only
Negative for red cell antibody screening
No history of recent blood transfusion
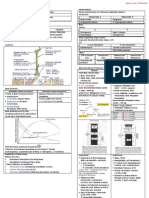
Gel card method
GXM & GSH
AHG is pre-added in gel card column
Agglutination show as layer of red cells on top of gel column
Red cell agglutination (incompatible donor) – Test tube, Blood film
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Essentials of ABO -Rh Grouping and Compatibility Testing: Theoretical Aspects and Practical ApplicationD'EverandEssentials of ABO -Rh Grouping and Compatibility Testing: Theoretical Aspects and Practical ApplicationÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Blood Bank (2 Week) : Antibody ScreensDocument5 pagesBlood Bank (2 Week) : Antibody ScreensAngela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Esophageal Varices AMJDocument35 pagesEsophageal Varices AMJAli Al.JuffairiPas encore d'évaluation
- Maximum Surgical Blood Ordering ScheduleDocument9 pagesMaximum Surgical Blood Ordering SchedulesshawashPas encore d'évaluation
- Bacteriology Table PDFDocument21 pagesBacteriology Table PDFZatanna Zatara100% (1)
- Acute Myeloid LekumiaDocument34 pagesAcute Myeloid LekumiaBhuwan ThapaPas encore d'évaluation
- Adequacy Criteria: ExceptionsDocument3 pagesAdequacy Criteria: ExceptionsPranayPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 7 Genetic and Pediatric Diseases (P. 243-272, Nature of Genetic Abnormalities Contributing To Human DiseaseDocument16 pagesCH 7 Genetic and Pediatric Diseases (P. 243-272, Nature of Genetic Abnormalities Contributing To Human DiseaseJustine HungPas encore d'évaluation
- Revision Notes Haematology 1 6 PDFDocument23 pagesRevision Notes Haematology 1 6 PDFCattrainuhPas encore d'évaluation
- Red Blood Cell Anomalies: Elliptocytes & Oval MacrocyteDocument12 pagesRed Blood Cell Anomalies: Elliptocytes & Oval MacrocyteSHUPATUSSAI100% (1)
- Cervical CytologyDocument9 pagesCervical CytologyAezel Cruz100% (1)
- MSBOSDocument6 pagesMSBOSAmir MuhrizPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) System: Dr.C.S.N.VittalDocument27 pagesHuman Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) System: Dr.C.S.N.VittalCsn VittalPas encore d'évaluation
- Soft Tissue TumoursDocument8 pagesSoft Tissue TumoursGerardLum100% (2)
- Hematoxylin+and+eosin+staining 4 PDFDocument11 pagesHematoxylin+and+eosin+staining 4 PDFChristine Año100% (3)
- GPHT1 Lab 3 Shift Reviewer Pap's Smear Prepared By: C Papanicolau'S MethodDocument5 pagesGPHT1 Lab 3 Shift Reviewer Pap's Smear Prepared By: C Papanicolau'S MethodCatherine MerillenoPas encore d'évaluation
- BOMBAY Blood GroupDocument14 pagesBOMBAY Blood Groupmail2jackal0% (1)
- Bone Marrow TransplantationDocument21 pagesBone Marrow TransplantationMorrison George100% (1)
- Blood Transfusion, Complications and ManagementDocument14 pagesBlood Transfusion, Complications and ManagementRubini Devi100% (1)
- 5 Myeloproliferative NeoplasmsDocument49 pages5 Myeloproliferative NeoplasmsEliza Stanescu100% (1)
- CytologyDocument12 pagesCytologyEsther HutagalungPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Group Systems ISBTDocument25 pagesBlood Group Systems ISBTkusumahpratiwi100% (1)
- Interpretation of Full Blood CountDocument25 pagesInterpretation of Full Blood CountClementPas encore d'évaluation
- Bone Marrow TransplantDocument8 pagesBone Marrow TransplantPSRI hospitalPas encore d'évaluation
- WBC Pathology: Lecturer: Associate Professor T. A. GrekovaDocument49 pagesWBC Pathology: Lecturer: Associate Professor T. A. GrekovaFaheem MusthafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Pathology: Pathology Is The Study (Logos) of Disease (Pathos)Document44 pagesIntroduction To Pathology: Pathology Is The Study (Logos) of Disease (Pathos)53-Deepankar SutradharPas encore d'évaluation
- WBC DisordersDocument32 pagesWBC Disordersbpt295% (19)
- 3 Bone Marrow ExaminationDocument105 pages3 Bone Marrow ExaminationShourav SarkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Adaptation & Response To Injury by NikitaDocument3 pagesCell Adaptation & Response To Injury by NikitaMedical Student NotesPas encore d'évaluation
- WBC Lymph Node SpleenDocument12 pagesWBC Lymph Node Spleendr brijesh TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Myelodysplastic Syndromes Hematology 1: 1. MDS With Multilineage Dysplasia (MDS-MLD)Document9 pagesMyelodysplastic Syndromes Hematology 1: 1. MDS With Multilineage Dysplasia (MDS-MLD)Joezer Gumangan VeranoPas encore d'évaluation
- Antibody DetectionDocument7 pagesAntibody DetectionhamaadaPas encore d'évaluation
- HAEMOPOIESISDocument6 pagesHAEMOPOIESISDiyana ZahariPas encore d'évaluation
- Cerebrospinal Fluid CSF Analysis and InterpretatioDocument6 pagesCerebrospinal Fluid CSF Analysis and InterpretatioIoana CucuPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Hematology Case StudyDocument6 pagesClinical Hematology Case StudyRomie SolacitoPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Blood SmearDocument59 pages1 Blood SmearGabi Tim100% (1)
- Classification of AnemiaDocument33 pagesClassification of Anemialieynna4996Pas encore d'évaluation
- Neoplasia 2011 ADocument45 pagesNeoplasia 2011 ACassey Koi FarmPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Smear ExaminationDocument65 pagesBlood Smear Examinationqlephon100% (2)
- 04 AntigenDocument30 pages04 AntigenVivin Syamsul ArifinPas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory Cytology: DR Mohammed Shahin, JR (Academic), Dept of Pathology & Lab Medicine, AIIMS BhubaneswarDocument62 pagesRespiratory Cytology: DR Mohammed Shahin, JR (Academic), Dept of Pathology & Lab Medicine, AIIMS BhubaneswarShruthi N.RPas encore d'évaluation
- Neutropenia by DR Gireesh Kumar K P, Department of Emergency Medicine, Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences, Kochi, KeralaDocument10 pagesNeutropenia by DR Gireesh Kumar K P, Department of Emergency Medicine, Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences, Kochi, KeralaSreekrishnan TrikkurPas encore d'évaluation
- PECOMADocument25 pagesPECOMAAnan JaiswalPas encore d'évaluation
- Aplastic AnaemiaDocument21 pagesAplastic AnaemiaAbhinav ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- AnemiaDocument11 pagesAnemiacentrino1780% (5)
- Tumor MarkersDocument14 pagesTumor MarkersPatrick LizarondoPas encore d'évaluation
- Von Willebrand DiseaseDocument7 pagesVon Willebrand DiseaseRanjith KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Bonemarrow 4 180106181202Document94 pagesBonemarrow 4 180106181202Caroline K.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ex3 Abo Forward Grouping Group7Document19 pagesEx3 Abo Forward Grouping Group7marielle rosePas encore d'évaluation
- Thalassemi ADocument23 pagesThalassemi Ainterna MANADO100% (1)
- Erythrocyte Sedimentation RateDocument21 pagesErythrocyte Sedimentation RateKarshey Alagad ObutPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 4 Blood CultureDocument14 pagesExperiment 4 Blood CulturesarahinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Histology of Sensory & Motor Nerve EndingsDocument2 pagesHistology of Sensory & Motor Nerve EndingsErnie G. Bautista II, RN, MD100% (1)
- POLYCYTHEMIADocument48 pagesPOLYCYTHEMIAPoova RagavanPas encore d'évaluation
- Describe The Molecular Basis Underlying Haematological MalignancyDocument3 pagesDescribe The Molecular Basis Underlying Haematological MalignancyAlison HinesPas encore d'évaluation
- Cellular PathologyDocument58 pagesCellular PathologyRKPas encore d'évaluation
- Compatibility Testing - BloodDocument5 pagesCompatibility Testing - BloodMunish DograPas encore d'évaluation
- Cross MatchingDocument5 pagesCross MatchingMustafa KhandgawiPas encore d'évaluation
- Antibody Screening and IdentificationDocument13 pagesAntibody Screening and IdentificationAnonymouscatPas encore d'évaluation
- Serology 1Document28 pagesSerology 1yousernamePas encore d'évaluation
- ThalassaemiaDocument4 pagesThalassaemiaGerardLum100% (4)
- Vesico Ureteral RefluxDocument1 pageVesico Ureteral RefluxGerardLumPas encore d'évaluation
- Thyroid PhysiologyDocument2 pagesThyroid PhysiologyGerardLum100% (2)
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument4 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionGerardLum100% (2)
- ThrombophiliaDocument3 pagesThrombophiliaGerardLum100% (1)
- Urinary Tract Infections in ChildrenDocument1 pageUrinary Tract Infections in ChildrenGerardLumPas encore d'évaluation
- Prostate GlandsDocument3 pagesProstate GlandsDragan PetrovicPas encore d'évaluation
- Skeletal Muscle RelaxantsDocument1 pageSkeletal Muscle RelaxantsGerardLum100% (2)
- Soft Tissue TumoursDocument8 pagesSoft Tissue TumoursGerardLum100% (2)
- Renal Function in Disease StateDocument2 pagesRenal Function in Disease Statedamai140390Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument6 pagesSexually Transmitted DiseasesGerardLum100% (3)
- Pathogenesis Bleeding DisordersDocument4 pagesPathogenesis Bleeding DisordersGerardLumPas encore d'évaluation
- Soft Tissue InfectionsDocument3 pagesSoft Tissue InfectionsGerardLum100% (1)
- Renal Excretion of DrugsDocument3 pagesRenal Excretion of DrugsGerardLum100% (3)
- Pathology of TestesDocument4 pagesPathology of TestesGerardLum100% (1)
- Posterior Pituitary SyndromeDocument1 pagePosterior Pituitary SyndromeGerardLumPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of Blood TransfusionDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Blood TransfusionGerardLum100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Calcium, Phosphate HomeostasisDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of Calcium, Phosphate HomeostasisGerardLum100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Nerve InjuryDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Nerve InjuryGerardLum100% (1)
- Pituitary DysfunctionDocument2 pagesPituitary DysfunctionGerardLum0% (1)
- Pathology of DiabetesDocument4 pagesPathology of DiabetesGerardLum100% (4)
- Pathology GlomerulonephritisDocument4 pagesPathology GlomerulonephritisGerardLum100% (2)
- Pathogenesis Chronic Complications DiabetesDocument5 pagesPathogenesis Chronic Complications DiabetesGerardLum100% (1)
- Pituitary Gland PathologyDocument4 pagesPituitary Gland PathologyGerardLumPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathology of Thyroid DiseasesDocument5 pagesPathology of Thyroid DiseasesGerardLum100% (2)
- Overview of AnaemiaDocument2 pagesOverview of AnaemiaGerardLumPas encore d'évaluation
- Paediatrics OrthopaedicsDocument5 pagesPaediatrics OrthopaedicsGerardLumPas encore d'évaluation
- Nocturnal EnuresisDocument1 pageNocturnal EnuresisGerardLumPas encore d'évaluation
- Obstructive UropathyDocument3 pagesObstructive UropathyGerardLum100% (1)
- Nsaids DrugsDocument2 pagesNsaids DrugsIrene Zae MwandotoPas encore d'évaluation
- NEJM Review Mar 2018 Autoimmune Polyendocrine SyndromesDocument10 pagesNEJM Review Mar 2018 Autoimmune Polyendocrine SyndromesBrian Almodovar BuenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lymphoma CancerDocument34 pagesLymphoma CancerwasihaiderkPas encore d'évaluation
- 05-8404 - CD4% Easy Count Kit - 10-03-24 - Rev009Document2 pages05-8404 - CD4% Easy Count Kit - 10-03-24 - Rev009Dinesh SreedharanPas encore d'évaluation
- Plants That Fight CancerDocument314 pagesPlants That Fight CancerMai Elnaggar100% (4)
- Feeling FatiguedDocument3 pagesFeeling FatiguedSimon and Schuster100% (2)
- Immune Network Theory: Geoffrey W. HoffmannDocument5 pagesImmune Network Theory: Geoffrey W. HoffmannarshiaPas encore d'évaluation
- T5X Leaflet ENDocument4 pagesT5X Leaflet ENWaseem A. AlkhateebPas encore d'évaluation
- Natural Remedies: Causes of Typhoid FeverDocument3 pagesNatural Remedies: Causes of Typhoid FeversakuarPas encore d'évaluation
- AF SeedingDocument6 pagesAF SeedingdonkeyendutPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 9 Antihuman Globulin TestingDocument9 pagesLec 9 Antihuman Globulin TestingMelaine Grace Gemoranion GeopanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Genetics SummariesDocument462 pagesMedical Genetics SummariesMohd RahimiPas encore d'évaluation
- (PPT) Kuliah 14. Aging Process Dan Aging Population - Dr. Suka AryanaDocument51 pages(PPT) Kuliah 14. Aging Process Dan Aging Population - Dr. Suka AryanaXxx PappaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ram Kumar CBC-ReportDocument1 pageRam Kumar CBC-ReportRahul palPas encore d'évaluation
- Basics of Monoclonal Antibodies For ToxicologistsDocument3 pagesBasics of Monoclonal Antibodies For ToxicologistsRN Pharma WorldPas encore d'évaluation
- Upgrade BrainDocument24 pagesUpgrade BrainBranko SlanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam Jan 2014Document3 pagesExam Jan 2014Insani Abdi BangsaPas encore d'évaluation
- JF Nov 04 Web VersionDocument8 pagesJF Nov 04 Web VersionAndrew GrazianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Concise Clinical Review: Role of Biologics in AsthmaDocument13 pagesConcise Clinical Review: Role of Biologics in AsthmaHossam HamzaPas encore d'évaluation
- EBME 306 QUIZ - 10 2010 Version 1 With AnswersDocument3 pagesEBME 306 QUIZ - 10 2010 Version 1 With AnswersHammad ZulqadarPas encore d'évaluation
- Warm and Cold Type of IHADocument2 pagesWarm and Cold Type of IHAHanisha EricaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Syllabus For Integrated M.SC Course - Niser Semester 1Document11 pagesBiology Syllabus For Integrated M.SC Course - Niser Semester 1Samyabrata SahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Avian Mycoplasmosis Update - 2005Document9 pagesAvian Mycoplasmosis Update - 2005hoodapunePas encore d'évaluation
- Malignant Otitis Externa in Patients With Diabetes Mellitus: Case ReportDocument0 pageMalignant Otitis Externa in Patients With Diabetes Mellitus: Case ReportSuci PramadianiPas encore d'évaluation
- UntitledDocument280 pagesUntitledSITANSHU KUMAR KHATUAPas encore d'évaluation
- Vaccinium Meridionale y AspirinaDocument58 pagesVaccinium Meridionale y AspirinaMaria Elena MaldonadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Keeping You: Four Hidden FactorsDocument18 pagesKeeping You: Four Hidden FactorsgenerjustnPas encore d'évaluation
- Immuno GlowDocument11 pagesImmuno GlowNoly ClaveringPas encore d'évaluation
- 0610 s22 QP 23 ANSDocument12 pages0610 s22 QP 23 ANSAbdullah ZubairPas encore d'évaluation
- Virus BioinformaticsDocument332 pagesVirus BioinformaticsVictor Delgado PPas encore d'évaluation
- MRI Scan Is Harmless. Justify?: ZoologyDocument11 pagesMRI Scan Is Harmless. Justify?: ZoologyMahesh YadavPas encore d'évaluation