Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Global City Innovative College
Transféré par
madypad0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
6 vues3 pages- The patient presented with an enlarged abdomen likely caused by excessive alcohol consumption over time which compromised his body's regulatory mechanisms.
- A nursing care plan was created to monitor the patient's fluid intake/output, vital signs, and abdominal size over an 8 hour shift and 2-3 week period to understand the cause and help decrease fluid volume and pressure in the abdomen.
- The plan involved bed rest, medications, and health education to help the patient live healthy and avoid alcohol in the long run.
Description originale:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce document- The patient presented with an enlarged abdomen likely caused by excessive alcohol consumption over time which compromised his body's regulatory mechanisms.
- A nursing care plan was created to monitor the patient's fluid intake/output, vital signs, and abdominal size over an 8 hour shift and 2-3 week period to understand the cause and help decrease fluid volume and pressure in the abdomen.
- The plan involved bed rest, medications, and health education to help the patient live healthy and avoid alcohol in the long run.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
6 vues3 pagesGlobal City Innovative College
Transféré par
madypad- The patient presented with an enlarged abdomen likely caused by excessive alcohol consumption over time which compromised his body's regulatory mechanisms.
- A nursing care plan was created to monitor the patient's fluid intake/output, vital signs, and abdominal size over an 8 hour shift and 2-3 week period to understand the cause and help decrease fluid volume and pressure in the abdomen.
- The plan involved bed rest, medications, and health education to help the patient live healthy and avoid alcohol in the long run.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 3
Global City Innovative College
College of Nursing and International Health Studies
NURSING CARE PLAN
Padilla, Madon Angelica S. Bautista,
Raymund, RN.
Mandaluyong City Medical Center
January 23, 2010
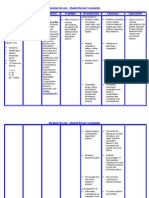
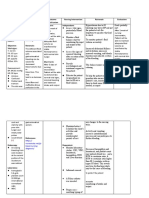
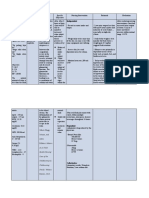
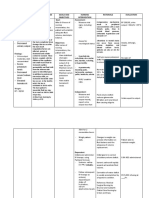
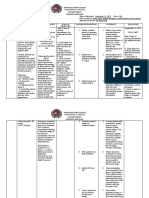
Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Rationale
Subjective: Fluid excess Drinking Short term: Independent:
N/A volume Alcohol In the course -Measure -reflects At the end of
Patient cannot related to of the intake and circulating the 8-hour
really compromised Absorbs intervention output. Weigh volume status. shift the client
verbalize regulatory alcohol in your the client will daily and note Weight gain is has gained
feelings due to mechanism as blood. Blood is understand weight gain. a sign of knowledge
weakness. manifested by processed in the cause of continuous about his
enlarged the liver . the fluid retention. condition.
Objective: stomach. enlargement -assess vital -respiratory is
-Abdominal The liver turns of his signs very important At the end of
area is bigger alcohol to stomach. regularly. because there the 8-hour
than the usual water and might be shift the client
body size carbon In 2 hours the pulmonary will decrease
requirement. dioxide. patient will congestion. his pressure in
-Eyes are feel less the abdomen
yellow (Liver can only pressure in the -fluid excess and decrease
metabolize area with -monitor blood maybe fluid volume.
certain increased fluid pressure associated
amounts of volume and with high
alcohol) decreased blood
drinking more edema. pressure.
alcohol -measure size
Long term: of abdominal -this will help
Increases In 2-3 weeks area. Note if you monitor
alcohol level in the patient will its getting the patient
blood stream. learn how to larger or decreased
live healthy decreasing in abdominal
Loss of and stay away size. area may be a
albumin from alcoholic good sign.
beverages.
-Bedrest -may promote
Portal recumbency-
hypertension induced
increase dieresis.
hepatic Independent:
pressure or -Monitor
liver blood electrolytes -to correct
flow further
-Administer imbalances
Accumulation medications
of fluids in the
peritoneum Vitamin K
Causing -prevention of
symptoms Ceftriaxone hemorrhage
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Nursing Care PlanDocument11 pagesNursing Care PlanKirstin del CarmenPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Liver CirDocument2 pagesNCP Liver CirBhabykhrishPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesData Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals Intervention Rationale EvaluationmarielfmerlanPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Excess Fluid VolumeDocument4 pagesNCP Excess Fluid VolumeIngrid Nicolas100% (1)
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Liver CirrhosisDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Liver Cirrhosisderic100% (27)
- Acute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesAcute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanKrisianne Mae Lorenzo Francisco80% (5)
- Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesChronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRuva Oscass JimmyPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationKRISTINE BULACANPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMelody B. MiguelPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Liver CirrhosisDocument2 pagesNCP Liver Cirrhosismarlx5100% (3)
- NCP GI EditedDocument4 pagesNCP GI EditednicolePas encore d'évaluation
- Overview of The DiseaseDocument12 pagesOverview of The DiseasePresciousPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument2 pagesNursing DiagnosisNoemi Javier ZamoraPas encore d'évaluation
- Chronic Renal DiseaseDocument12 pagesChronic Renal DiseaseNohaira SADANGPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan For Liver CirrhosisDocument14 pagesNursing Care Plan For Liver Cirrhosisken93% (75)
- Fluid Volume Deficit Related To Active Fluid Volume LossDocument3 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Related To Active Fluid Volume LossMelDred Cajes BolandoPas encore d'évaluation
- Nurses Pocket Guide by Doenges, Moorhouse, Murr 11 Edition Pg. 327-330 Pediatric Nursing by Potts and Mandleco ThomsonDocument3 pagesNurses Pocket Guide by Doenges, Moorhouse, Murr 11 Edition Pg. 327-330 Pediatric Nursing by Potts and Mandleco ThomsonMikaela Angeles NazarPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP ProperDocument9 pagesNCP Properstephanie eduartePas encore d'évaluation
- Agn - NCPDocument3 pagesAgn - NCPRap De la CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Signs & Symptoms: Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalancesDocument3 pagesSigns & Symptoms: Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalancesMerielLouiseAnneVillamilPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Dengue FeverDocument3 pagesNCP Dengue Feveralfonselay63% (8)
- Nursing Diagnosis Fvd2Document2 pagesNursing Diagnosis Fvd2ghellersPas encore d'évaluation
- In Premature Ventricular Complex, An Impulse That Starts in A Ventricle and Is Conducted Through The Ventricles Before The Next Normal SinusDocument7 pagesIn Premature Ventricular Complex, An Impulse That Starts in A Ventricle and Is Conducted Through The Ventricles Before The Next Normal SinushelloaPas encore d'évaluation
- Excess Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesExcess Fluid VolumeyuddPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care PL WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesNursing Care PL WPS OfficeDhan IvanPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment SubjectiveDocument4 pagesAssessment Subjectivejeziel_16Pas encore d'évaluation
- AppendectomyDocument2 pagesAppendectomyDARLENE ROSE BONGCAWILPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study Ward 3a 3BDocument15 pagesCase Study Ward 3a 3BInfection QcghPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Excess Fluid VolumeDocument3 pagesNCP Excess Fluid VolumeJ.G RPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan: Uterine MyomaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Uterine Myomashiramu86% (50)
- Emilio Aguinaldo College: School of NursingDocument2 pagesEmilio Aguinaldo College: School of NursingdaliaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP 3rd ROTATIONDocument17 pagesNCP 3rd ROTATIONMarie Ashley CasiaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP and Drug Study (Isph-Gs Nursery)Document4 pagesNCP and Drug Study (Isph-Gs Nursery)Cristyl Shine BariaoPas encore d'évaluation
- NAME: Kristine Diane Q. Aviles Year: Bsn3 NURSING CARE PLAN FOR Liver CirrhosisDocument2 pagesNAME: Kristine Diane Q. Aviles Year: Bsn3 NURSING CARE PLAN FOR Liver Cirrhosiskristinedianne.avilesPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument5 pagesNCP Deficient Fluid VolumeCHRISTINE GRACE ELLOPas encore d'évaluation
- Ricafort, Maxine S. GRP 2H Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesRicafort, Maxine S. GRP 2H Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMaxine RicafortPas encore d'évaluation
- DM ncp2Document1 pageDM ncp2Mark PabalanPas encore d'évaluation
- AssessmentDocument3 pagesAssessmentharlequingirl_116Pas encore d'évaluation
- NCP With DsDocument11 pagesNCP With DsMissDyYournursePas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Volume Deficit (GI Bleeding) NCPDocument2 pagesFluid Volume Deficit (GI Bleeding) NCPReina Samson100% (1)
- Assessment Inference Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Inference Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationSteffi Blair OngPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation EvaluationIvy Villalobos100% (1)
- Excess Fluid Volume Related To Sodium IntakeDocument5 pagesExcess Fluid Volume Related To Sodium IntakeNil GyiPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP For Dehydration 1Document3 pagesNCP For Dehydration 1Khalid KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP in HA SLDocument2 pagesNCP in HA SLCharisse AdallaPas encore d'évaluation
- Esrd NCPDocument7 pagesEsrd NCPSharmaine Camille de LeonPas encore d'évaluation
- Cirrhosis of The LiverDocument2 pagesCirrhosis of The LiverBheru LalPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan With Fdar: Lorma Colleges Con Template Related Learning ExperienceDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan With Fdar: Lorma Colleges Con Template Related Learning ExperienceMelinda Cariño BallonPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Kidney Injury W/ Hyperkalemia NCPDocument5 pagesAcute Kidney Injury W/ Hyperkalemia NCPMyrvic Ortiz La OrdenPas encore d'évaluation
- Pedia NCPDocument9 pagesPedia NCPTyn TynPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument3 pagesNCP Deficient Fluid VolumeDoneva Lyn MedinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2 1Document3 pagesModule 2 1Lacangan, Thea YvonnePas encore d'évaluation
- Actual Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesActual Nursing Care PlanMaria Francheska OsiPas encore d'évaluation
- Excess Fluid Volume Related To Compromised Renal Regulatory Mechanisms As Evidenced by Glomerular Filtration RateDocument4 pagesExcess Fluid Volume Related To Compromised Renal Regulatory Mechanisms As Evidenced by Glomerular Filtration RateSHINIPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP GRAND CASE PRE C Nursing ProblemsDocument9 pagesNCP GRAND CASE PRE C Nursing ProblemsAngie Mandeoya100% (1)
- Ascites, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandAscites, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Conn Syndrome, (Hyper-Aldosteronism) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandConn Syndrome, (Hyper-Aldosteronism) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment of Knowledge, Attitude and Awareness Regarding Cone Beam Computed Tomography Among Dental Graduates in Pune City, IndiaDocument5 pagesAssessment of Knowledge, Attitude and Awareness Regarding Cone Beam Computed Tomography Among Dental Graduates in Pune City, IndiaSakina JigarPas encore d'évaluation
- Dams Video Based TestDocument30 pagesDams Video Based TestPandey AyushPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Negligence in Ghana Another Look at Asantekramo 1Document3 pagesMedical Negligence in Ghana Another Look at Asantekramo 1SAMMY100% (1)
- Talk & Thrive Therapeutic Services: Sadaf Rizwan Mariya Ubaid Khan Saima AliDocument1 pageTalk & Thrive Therapeutic Services: Sadaf Rizwan Mariya Ubaid Khan Saima Alimariya khanPas encore d'évaluation
- HydrotherapyDocument40 pagesHydrotherapyThopu UmamaheswariPas encore d'évaluation
- Corns and Calluses - Diagnosis and Treatment - Mayo ClinicDocument5 pagesCorns and Calluses - Diagnosis and Treatment - Mayo Clinicahmad saadPas encore d'évaluation
- JBI Critical Appraisal-Checklist For Case Reports2017Document5 pagesJBI Critical Appraisal-Checklist For Case Reports2017AriaDanurdoroPas encore d'évaluation
- Kami Export - Kevin Farina - CirculatorySystemSEDocument4 pagesKami Export - Kevin Farina - CirculatorySystemSEKevin FarinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Relapsing Polychondritis Case Presentaion Feb 2009 DR - BugnahDocument21 pagesRelapsing Polychondritis Case Presentaion Feb 2009 DR - BugnahDr.Sherif Bugnah100% (4)
- GTD Case StudyDocument9 pagesGTD Case StudyZnarf Izlah Sadanreb100% (1)
- TestDocument4 pagesTestmelodyfathiPas encore d'évaluation
- Critical Care Nephrology Core Curriculum 2020 PDFDocument18 pagesCritical Care Nephrology Core Curriculum 2020 PDFMartín FleiPas encore d'évaluation
- SB 3 Flu VaccineDocument2 pagesSB 3 Flu VaccineBIANNE KATRINA GASAGASPas encore d'évaluation
- Disease and Disease TransmissionDocument48 pagesDisease and Disease TransmissionAYO NELSONPas encore d'évaluation
- Epidemiology of Sarcopenia Prevalence, Risk FactoDocument9 pagesEpidemiology of Sarcopenia Prevalence, Risk FactoW Antonio Rivera MartínezPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study 101: Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm With Acute Kidney InjuryDocument8 pagesCase Study 101: Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm With Acute Kidney InjuryPatricia Ann Nicole ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Livro Robbins PathologyDocument18 pagesLivro Robbins Pathologyernestooliveira50% (2)
- NUR 115 - LAB ACTIVITY # 1aDocument2 pagesNUR 115 - LAB ACTIVITY # 1aMoira Julianne Serognas Brigoli100% (2)
- Janet RowleyDocument1 pageJanet RowleyANA GABRIELA PEREZ VIDALPas encore d'évaluation
- Gut Rebuilding Protocol : Standard Process Supplements Lunch DinnerDocument1 pageGut Rebuilding Protocol : Standard Process Supplements Lunch DinnerSteve KellerPas encore d'évaluation
- Marc A. Levitt: AuthorDocument16 pagesMarc A. Levitt: AuthorAlonso Rodriguez EscobedoPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute and Chronic HepatitisDocument72 pagesAcute and Chronic HepatitisArun George100% (3)
- XN-1500 10p ENDocument5 pagesXN-1500 10p ENHarika PutraPas encore d'évaluation
- Prognostic Factors Affecting The Mortality of Burn Injuries Patients in Dr. Sardjito General Hospital, Yogyakarta, IndonesiaDocument8 pagesPrognostic Factors Affecting The Mortality of Burn Injuries Patients in Dr. Sardjito General Hospital, Yogyakarta, IndonesiaYeni PuspitasariPas encore d'évaluation
- The Worry Wars:: Equipping Our Child Clients To Effectively Fight Their FearsDocument16 pagesThe Worry Wars:: Equipping Our Child Clients To Effectively Fight Their FearsAngeliki HoPas encore d'évaluation
- Menstrupedia Comic: The Friendly Guide To Periods For Girls (2014), by Aditi Gupta, Tuhin Paul, and Rajat MittalDocument4 pagesMenstrupedia Comic: The Friendly Guide To Periods For Girls (2014), by Aditi Gupta, Tuhin Paul, and Rajat MittalMy Home KaviPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Antenatal Care Handbook ISBNDocument59 pagesBasic Antenatal Care Handbook ISBNAuliamusy100% (1)
- Social Change Campaign in IndiaDocument7 pagesSocial Change Campaign in IndiaGauri GargPas encore d'évaluation
- Excel PenelitianDocument8 pagesExcel PenelitianNisak HumairokPas encore d'évaluation
- Ptosis Definition of Eyelid Ptosis: Abnormally Low Position of The Upper Eyelid Margin Caused by PoorDocument6 pagesPtosis Definition of Eyelid Ptosis: Abnormally Low Position of The Upper Eyelid Margin Caused by PoortiamaharaniPas encore d'évaluation