Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
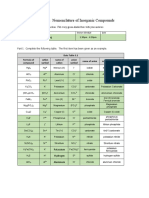
Element Group Cation Element Group Anions
Transféré par
Charlotte Tan0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
91 vues3 pagesAtoms will gain electrons or lose electrons so as to achieve a stable noble gas structure. Examples: Sodium atom will lose an electron during chemical reaction and form 1 single bond. Valency of sodium is +1 oxygen atom will gain / share 2 electrons and form 2 single bonds or a double bond.
Description originale:
Titre original
Chemistry
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentAtoms will gain electrons or lose electrons so as to achieve a stable noble gas structure. Examples: Sodium atom will lose an electron during chemical reaction and form 1 single bond. Valency of sodium is +1 oxygen atom will gain / share 2 electrons and form 2 single bonds or a double bond.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
91 vues3 pagesElement Group Cation Element Group Anions
Transféré par
Charlotte TanAtoms will gain electrons or lose electrons so as to achieve a stable noble gas structure. Examples: Sodium atom will lose an electron during chemical reaction and form 1 single bond. Valency of sodium is +1 oxygen atom will gain / share 2 electrons and form 2 single bonds or a double bond.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 3
Valency – the combining power of an atom or radical.
Atoms will gain electrons or lose
electrons so as to achieve a stable noble gas structure.
Examples:
Sodium atom will lose an electron during chemical reaction and form 1 single bond.
Valency of sodium is +1
Oxygen atom will gain/share 2 electrons during chemical reaction and form 2 single
bonds or a double bond.
Valency of oxygen is -2
Element Group Cation Element Group Anions
Group1 [+1] Group4 [-4]
Lithium Li Li+
Carbon C C4-
Sodium Na Na+ Group5 [-3]
Potassium K K+ Nitrogen N N3-
Group2 [+2] Group6 [-2]
Beryllium Be Be2+
Oxygen O O2-
Magnesium Mg Mg2+ Sulphur S S2-
Calcium Ca Ca2+ Group7 [-1]
Group3 [+3] Fluorine F F-
Aluminium Al Al3+ Chlorine Cl Cl-
Bromine Br Br-
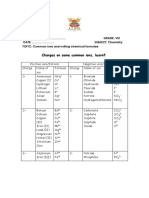
Some Atoms have multiple valencies. There are two common names for the following ions.
ION IUPAC SYSTEM ION IUPAC SYSTEM
2+ 3+
Fe iron II Fe iron III
Cu+ copper l Cu2+ copper II
Au+ gold I Au3+ gold III
Sn2+ tin II Sn4+ tin IV
Pb2+ lead II Pb4+ lead IV
Hg+ mercury I Hg2+ mercury II
Cr2+ chromium II Cr3+ chromium III
Mn2+ manganese II Mn3+ manganese III
RADICALS OR POLYATOMIC IONS
- Consist of group of atoms of more than one kind of element attached by covalent
bonds. They do not often come apart in ionic reactions. The charge on the radical is
for the whole group of atoms as a unit.
Names and charges of some common radicals:
(NH4)+ ammonium
(NO3)- nitrate
(NO2)- nitrite
(SO3)2- sulphite
(SO4)2- sulphate
(PO4)3- phosphate
(HCO3)- hydrogen carbonate
(CO3)2- carbonate
(OH)- hydroxide
(Cr2O7)2- dichromate
(MnO4)- permanganate
Cu+ Copper(I) Cu2+ Copper(II)
Copper(I) oxide Copper(II) chloride
Cu+ O2- Cu2+ Cl-
Cu2O CuCl2
Fe2+ Iron(II) Fe3+ Iron(III) Fe3+ Iron(III) Fe3+ Iron(III)
Iron(II) chloride Iron(III) chloride Iron(III) oxide Iron(III) sulphate
Fe2+ Cl- Fe3+ Cl- Fe3+ O2- Fe3+ (SO4)2
FeCl2 FeCl3 Fe2O3 Fe2(SO4)3
2- 2- 2-
(SO4) Sulphate (SO3) Sulphite S Sulphide
Sodium sulphate Sodium sulphite Sodium sulphide
Na+ (SO4)2- Na+ (SO3)2- Na+ S2-
Na2SO4 Na2SO3 Na2S
ammonium carbonate H2 O
(NH4)+ (CO3)2 C6H6
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Common IonsDocument3 pagesCommon IonsabdallaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fe CL Fe CL Fecl: Charge of The Ion Oxidation States of Transition MetalsDocument1 pageFe CL Fe CL Fecl: Charge of The Ion Oxidation States of Transition MetalsSuzaki KurushiPas encore d'évaluation
- Coordination Chemistry—XIV: Plenary Lectures Presented at the XIVth International Conference on Coordination Chemistry Held at Toronto, Canada, 22—28 June 1972D'EverandCoordination Chemistry—XIV: Plenary Lectures Presented at the XIVth International Conference on Coordination Chemistry Held at Toronto, Canada, 22—28 June 1972A. B. P. LeverPas encore d'évaluation
- Formulae of Common IonsDocument1 pageFormulae of Common IonsJoel OkohPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 - Ionic Bonding ActivityDocument4 pages10 - Ionic Bonding Activityapi-292000448Pas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersD'EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersPas encore d'évaluation
- Ionic Puzzle ActivityDocument4 pagesIonic Puzzle ActivityEngr Mumtaz0% (1)
- Extractive Metallurgy 2: Metallurgical Reaction ProcessesD'EverandExtractive Metallurgy 2: Metallurgical Reaction ProcessesÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- 2.10 Naming Binary Nonmetal CompoundsDocument6 pages2.10 Naming Binary Nonmetal Compoundsmqdzpmjp2rPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical BondingDocument11 pagesChemical BondingXenia Mae FloresPas encore d'évaluation
- CHEM Semis BubbaDocument5 pagesCHEM Semis BubbaNorlyn Mae MarcialPas encore d'évaluation
- Nomenclature of Inorganic Compounds: Report SheetDocument3 pagesNomenclature of Inorganic Compounds: Report SheetAEsmilingPas encore d'évaluation
- Formulas and Nomenclature of Ionic and Covalent CompoundsDocument6 pagesFormulas and Nomenclature of Ionic and Covalent CompoundsRaven FranciscoPas encore d'évaluation
- Formulas & Nomenclature PDFDocument6 pagesFormulas & Nomenclature PDFYatish PantPas encore d'évaluation
- Naming Ionic CompoundsDocument17 pagesNaming Ionic CompoundsReena NasriPas encore d'évaluation
- ACFrOgAKjYyPDA8imA1n06RTHYhmcZyQfXBSGYi5Ul3iZ4tznc3KA75jGjJ5z79-K8DlCA4lS6s4YPAGa9JU3hUpukNLW3ARrct1BFVU1FITpLNKtizdLNeJ4PgnikitvzfS2ImJ2ohAnBH4JZbIDocument2 pagesACFrOgAKjYyPDA8imA1n06RTHYhmcZyQfXBSGYi5Ul3iZ4tznc3KA75jGjJ5z79-K8DlCA4lS6s4YPAGa9JU3hUpukNLW3ARrct1BFVU1FITpLNKtizdLNeJ4PgnikitvzfS2ImJ2ohAnBH4JZbIbenjamin.morenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Bonding: Why Bond Anyway?Document45 pagesChemical Bonding: Why Bond Anyway?PutRi Charolin GintingPas encore d'évaluation
- Table For Urry Q3Document1 pageTable For Urry Q3andyPas encore d'évaluation
- Valency and Formulae-HandoutDocument3 pagesValency and Formulae-HandoutABHAVYA RAJPas encore d'évaluation
- General Chemistry 1 Learning CompetenciesDocument1 pageGeneral Chemistry 1 Learning CompetenciesMon ColinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Write The Formulas For The Following Ionic Compounds:: Bonding and Naming WS 4Document2 pagesWrite The Formulas For The Following Ionic Compounds:: Bonding and Naming WS 4Bea Lha Zandra BesingaPas encore d'évaluation
- Complete NomenclatureDocument10 pagesComplete NomenclaturezainalexanderaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5 Coordination CompoundDocument36 pagesChapter 5 Coordination Compoundammar zakariaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Formula Writing Worksheet PDFDocument4 pagesChemical Formula Writing Worksheet PDFkezia0% (1)
- Chemistry 110 Lab: 3 (Aq) (Aq) (S) 3 (Aq)Document10 pagesChemistry 110 Lab: 3 (Aq) (Aq) (S) 3 (Aq)ariana baigorriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cations: Al Aluminium Fe Iron (III) CR Chromium (III)Document2 pagesCations: Al Aluminium Fe Iron (III) CR Chromium (III)NPPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Ions and Their ChargesDocument2 pagesCommon Ions and Their ChargesSJ SuingPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Ions and Their Charges: From The Table: Ions To Memorize Cations Name Cations NameDocument2 pagesCommon Ions and Their Charges: From The Table: Ions To Memorize Cations Name Cations NameChantelle W. SHUMPas encore d'évaluation
- p18 - p19 Compounds Ionic-AnswersDocument8 pagesp18 - p19 Compounds Ionic-Answersapi-423980580Pas encore d'évaluation
- General Chemistry 2 Module 3Document6 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Module 3Jason Vinluan CarinanPas encore d'évaluation
- Formulas and Nomenclature of Ionic and Covalent Compounds: ContentsDocument13 pagesFormulas and Nomenclature of Ionic and Covalent Compounds: Contentsawesome avedPas encore d'évaluation
- CHEMISTRYDocument9 pagesCHEMISTRYXyiee ViorPas encore d'évaluation
- FILE NO 3 Exercise 2 Chemical Formula Writing and Naming of Compounds RevDocument2 pagesFILE NO 3 Exercise 2 Chemical Formula Writing and Naming of Compounds RevEJ TaylanPas encore d'évaluation
- Formulas and Nomenclature of Ionic and Covalent CompoundsDocument12 pagesFormulas and Nomenclature of Ionic and Covalent CompoundsJason Enduro BayuPas encore d'évaluation
- MODULE 2tables As ReferencesDocument10 pagesMODULE 2tables As ReferencesJuneyale Padilla100% (1)
- 08RedoxNotes 221010 132804Document24 pages08RedoxNotes 221010 132804Abdullah AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- PCQA supplement: Common cations and anionsDocument4 pagesPCQA supplement: Common cations and anionsrnlpzcyPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Ion ChargesDocument1 pageCommon Ion ChargesMoganan SubramaniamPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical NomenclatureDocument7 pagesChemical NomenclatureKeith Lavin100% (1)
- ChemistryDocument7 pagesChemistryPauline Oliva ZurbitoPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced-Chem Q1 LP7Document6 pagesAdvanced-Chem Q1 LP7Francesca BuenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Valencies of Ions (For 9th and 10th)Document6 pagesValencies of Ions (For 9th and 10th)Irene AbhilashPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Class 10 Lecture 1 (3 April)Document5 pagesChemistry Class 10 Lecture 1 (3 April)allroundersaksham304Pas encore d'évaluation
- Types of CompoundsDocument15 pagesTypes of CompoundsJonard PedrosaPas encore d'évaluation
- LIST OF CATIOS AND ANIONSDocument7 pagesLIST OF CATIOS AND ANIONSrituPas encore d'évaluation
- List of Common Cations Name Symbol ChargeDocument4 pagesList of Common Cations Name Symbol ChargernlpzcyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Ion Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesChemistry Ion Cheat SheetTiffany Gallina100% (4)
- Charge of ElementsDocument1 pageCharge of ElementsKagarine__LaroussePas encore d'évaluation
- NomenclatureDocument68 pagesNomenclatureel tetraPas encore d'évaluation
- g20 Tejada, Maria Genina C. - q4 LT 9 - Chemical Writing FormulaDocument1 pageg20 Tejada, Maria Genina C. - q4 LT 9 - Chemical Writing FormulaGenina TejadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Most Elements' Valency NESDocument2 pagesMost Elements' Valency NESHakim AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- Cations: Ions and Charges Cations With Multiple ChargesDocument1 pageCations: Ions and Charges Cations With Multiple ChargesJohn Rey BayoguingPas encore d'évaluation
- ApsummerDocument5 pagesApsummerLayleePas encore d'évaluation
- Naming Compounds Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesNaming Compounds Cheat SheetYSA BELLEPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Ions - Polyatomic IonsDocument2 pagesCommon Ions - Polyatomic IonsMak ItiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cations AnionsDocument1 pageCations AnionsTiviya Tarini ManiamPas encore d'évaluation
- ionicChargesChart PDFDocument1 pageionicChargesChart PDFronit675Pas encore d'évaluation
- Test Paper Class 10 Term 2 ChemistryDocument3 pagesTest Paper Class 10 Term 2 ChemistryrudraprasadgiriPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem 240 Lab Manual With Problems - 2013Document177 pagesChem 240 Lab Manual With Problems - 2013Mark Cliffton BadlonPas encore d'évaluation
- Examples of Chemical BondsDocument11 pagesExamples of Chemical BondsRondel ForjesPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution JEE (Advanced) - 2018 Paper-1 (PCM)Document36 pagesSolution JEE (Advanced) - 2018 Paper-1 (PCM)NKPas encore d'évaluation
- General Chemistry I - Q2 M7.1 Ionic & Covalent BondsDocument22 pagesGeneral Chemistry I - Q2 M7.1 Ionic & Covalent BondseliPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Molymod BondingDocument20 pagesUnderstanding Molymod BondingVina Zavira Nizar100% (1)
- 16a Periodic Table GeneralDocument13 pages16a Periodic Table GeneralfarahPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 20F: Chemistry Exam Review 1 of 6Document6 pagesScience 20F: Chemistry Exam Review 1 of 6Ram Russel Casao PangilinanPas encore d'évaluation
- Aluminum CarbonateDocument3 pagesAluminum Carbonateapi-243043108Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1) Introduction To Organic Chemistry Chem 32 (Up Manila)Document51 pages1) Introduction To Organic Chemistry Chem 32 (Up Manila)Paul AlcosPas encore d'évaluation
- Coordination CompoundsDocument19 pagesCoordination Compoundsaamir siddiquiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sejarah Unsur Kimia Bumi PDFDocument449 pagesSejarah Unsur Kimia Bumi PDFJon WheelerPas encore d'évaluation
- AP Chemistry Exam Review: Ionic Charges and Atomic StructureDocument32 pagesAP Chemistry Exam Review: Ionic Charges and Atomic Structurelycheejello100% (3)
- IGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences Metals RevisionDocument3 pagesIGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences Metals RevisionSky LimPas encore d'évaluation
- Transition Elements (B.sc-Ii) Inorganic Chemistry Paper-IDocument32 pagesTransition Elements (B.sc-Ii) Inorganic Chemistry Paper-IPinky SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Iesc 103Document12 pagesIesc 103Debasish DeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes Chemistry 1 301 400Document100 pagesNotes Chemistry 1 301 400c0ldh337Pas encore d'évaluation
- Stoichiometry Type 1Document29 pagesStoichiometry Type 1paramarthasom1974Pas encore d'évaluation
- Carbon and Its Compounds: AnswersDocument5 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds: AnswersAyush AgarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- The Summary of Biologi Text Book Campbell Reece (Benjamin Cummings)Document7 pagesThe Summary of Biologi Text Book Campbell Reece (Benjamin Cummings)LirofiatillahPas encore d'évaluation
- (Amaleaks - Blogspot.com) Chem-112 Week 11-20Document25 pages(Amaleaks - Blogspot.com) Chem-112 Week 11-20Shimea Salisid0% (1)
- Bond Valence Parameters Inorganic StructuresDocument4 pagesBond Valence Parameters Inorganic StructuresDavid MartinezPas encore d'évaluation
- Carbon Its CompoundsDocument54 pagesCarbon Its CompoundsthinkiitPas encore d'évaluation
- 9th - PS-Lesson Plan BookDocument39 pages9th - PS-Lesson Plan Bookmadhumita.kothawalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Answer Key HMWK - 1 CHPT 9 - 10Document11 pagesAnswer Key HMWK - 1 CHPT 9 - 10jts399Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chem Topic 4 Questions + AnswersDocument25 pagesChem Topic 4 Questions + AnswersOscarHigson-Spence50% (2)
- 03 - Atoms and MoleculesDocument20 pages03 - Atoms and MoleculesAtharv SoniPas encore d'évaluation
- Larkin Lab ReportDocument3 pagesLarkin Lab ReportChristopherAguilar33% (3)
- SHS Physical Science Q1 SLM - 3Document25 pagesSHS Physical Science Q1 SLM - 3Adalee ColleenPas encore d'évaluation