Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Biology 1984 Paper I
Transféré par
Lok Lok0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
3 vues12 pagesCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
PDF ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
3 vues12 pagesBiology 1984 Paper I
Transféré par
Lok LokDroits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 12
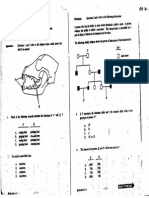
5. (©) The diagram below shows how a person’s blood. ireated when his
kidneys cannot function properly in removing urea. Solution X which
is fed into the machine contains glucose and mineral salts at the same
concentration as normal plasma.
dialysis tubing with
permeability similar
to the capillary wall blood from
{ the person
solution Xin a
blood returned
to the person
(@ State and explain the change in the urea concentration in the
blood after treatment.
Gi) Why is it necessary for solution X to have the same concentration
of glucose and mineral salts as normal plasma?
(ii) What is the advantage of passing solution X in a dizection opposite
to that of the blood?
(iv) What would be the effect of allowing the blood to flow through
a greater number of dialysis tubes? Give a reason for your
(0 marks)
END OF PAPER
B4.CE-BIO I-24 Be
HONG KONG EXAMINATIONS AUTHORITY
HONG KONG CERTIFICATE OF EDUCATION EXAMINATION 1984
ey RB
BIOLOGY PAPER |
8.30 am-10.00 am (13 hours)
This paper must be answered in English
Attempt THREE questions only.
Each question consists of three parts.
All questions carry equal marks.
Ofeste Ram
Hong Kong Examinations Authority
Al Rights Reserved: 1984
B4.CE-810 1-1
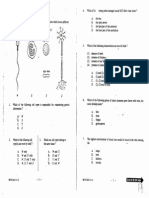
1, @)__ The diagram below shows part of the human body
(The parts are not drawn to the same scale.)
4.08810 1-2 ite
@
(i)
‘
ii)
(iv)
)
wi)
4.CE-B10 1-3
Yt is D2 Apart from digestion, what other function does it
have?
What are the two blood vesels that carry blood to C?
‘What is the blood vessel that drains blood away from C?
State and explain the difference in glucose level between the
blood leaving D and that leaving C shortly after a meal
Using the letters in the diagram, show the route by which blood
flows from D to E
State two ways by which blood glucose can be used in £.
(12 marks)
1, (@) Digestive juices were collected from two regi , A and B, of @
the alimentary canal of a rat. Each preparation was divided into four
test-tubes, to which a semple of boiled plant tissue was added. Food
tests were carried out on each tube, and the results are shown in the
tables below
Experiment 1 (using digestive juice from region A)
Food test Biuret test Benedict's/Fehling’s test * ai)
1
‘Tube no al n a3 M4 1
Time when
food test | at Ohour | after 1 hour | at O hour | after 1 hour
was applied =
violet | blue blue red
Observation | colour | colour | solution | precipitate
Experiment I! (using digestive juice from region B)
Food test Biuret test Benedict’s/Fehling’s test
Tube no. BI B2 83 Bt
Time when
food test | at Ohour | after 1 hour | at O hour | after 1 hour
was applied
violet | violet blue red
Observation | coour | colour | solution | precipitate
246-810 1-4 pe e4c6-810 1-5
(Yrring to the tube numbers, indicate which tubes) gave
4 positive result for
(1) the Biuret test
(2) the Benedict’s/Fehling’s test.
‘What conclusion can be drawn from the results of
(1) the Biuret test in experiment 17
(2) the Benedict’s/Fehling’s test in experiment 11?
Give one name each for the regions A and B and hence suggest
the names of the juices collected.
(8 marks)
a ==>
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- CE Biology 1989 Paper 2Document10 pagesCE Biology 1989 Paper 2Lesley LamPas encore d'évaluation
- CE Biology 1989 Paper 1Document10 pagesCE Biology 1989 Paper 1Lesley LamPas encore d'évaluation
- 1989 Biology Paper I Marking SchemeDocument15 pages1989 Biology Paper I Marking Schemeapi-3822784Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2012 DSE English exam paperDocument24 pages2012 DSE English exam paperLesley LamPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology 1985 Paper IIDocument11 pagesBiology 1985 Paper IILesley LamPas encore d'évaluation
- CE Biology 1988 Paper 2Document11 pagesCE Biology 1988 Paper 2Lesley LamPas encore d'évaluation
- CE Biology 1988 Paper 1Document8 pagesCE Biology 1988 Paper 1Lesley LamPas encore d'évaluation
- CE Biology 1987 Paper 1 + Marking Scheme PDFDocument19 pagesCE Biology 1987 Paper 1 + Marking Scheme PDFLesley LamPas encore d'évaluation
- CE Biology 1988 Paper 1 + Marking SchemeDocument15 pagesCE Biology 1988 Paper 1 + Marking SchemeLesley LamPas encore d'évaluation
- CE Biology 1987 Paper 1 + Marking Scheme PDFDocument19 pagesCE Biology 1987 Paper 1 + Marking Scheme PDFLesley LamPas encore d'évaluation
- CE Biology 1986 Paper 1Document12 pagesCE Biology 1986 Paper 1Lesley LamPas encore d'évaluation
- CE Biology 1986 Paper 2Document11 pagesCE Biology 1986 Paper 2Lesley LamPas encore d'évaluation
- CE Biology 1989 Paper 1Document10 pagesCE Biology 1989 Paper 1Lesley LamPas encore d'évaluation
- CE Biology 1989 Paper 2Document10 pagesCE Biology 1989 Paper 2Lesley LamPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology 1985 Paper IDocument12 pagesBiology 1985 Paper ILesley LamPas encore d'évaluation
- CE Biology 1986 Paper 1Document12 pagesCE Biology 1986 Paper 1Lesley LamPas encore d'évaluation
- HKCEE - Biology - 1984 - Paper II - Q PDFDocument12 pagesHKCEE - Biology - 1984 - Paper II - Q PDFKelvin MakPas encore d'évaluation
- CE Biology 1989 Paper 1Document10 pagesCE Biology 1989 Paper 1Lesley LamPas encore d'évaluation
- CE Biology 1987 Paper 1 + Marking Scheme PDFDocument19 pagesCE Biology 1987 Paper 1 + Marking Scheme PDFLesley LamPas encore d'évaluation
- CE Biology 1989 Paper 2Document10 pagesCE Biology 1989 Paper 2Lesley LamPas encore d'évaluation
- 1989 Biology Paper I Marking SchemeDocument15 pages1989 Biology Paper I Marking Schemeapi-3822784Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1989 Biology Paper I Marking SchemeDocument15 pages1989 Biology Paper I Marking Schemeapi-3822784Pas encore d'évaluation
- CE Biology 1988 Paper 2Document11 pagesCE Biology 1988 Paper 2Lesley LamPas encore d'évaluation
- CE Biology 1986 Paper 2Document11 pagesCE Biology 1986 Paper 2Lesley LamPas encore d'évaluation
- CE Biology 1988 Paper 1Document8 pagesCE Biology 1988 Paper 1Lesley LamPas encore d'évaluation
- CE Biology 1986 Paper 2Document11 pagesCE Biology 1986 Paper 2Lesley LamPas encore d'évaluation
- CE Biology 1988 Paper 1 + Marking SchemeDocument15 pagesCE Biology 1988 Paper 1 + Marking SchemeLesley LamPas encore d'évaluation
- CE Biology 1986 Paper 1Document12 pagesCE Biology 1986 Paper 1Lesley LamPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology 1985 Paper IIDocument11 pagesBiology 1985 Paper IILesley LamPas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)