Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
SAP Monitoring Tcodes
Transféré par
prasaramDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
SAP Monitoring Tcodes
Transféré par
prasaramDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
SAP Basis Monitoring Document
Introduction
System monitoring is a daily routine activity and this document provides a
systematic step by step procedure for Server Monitoring. It gives an overview of
technical aspects and concepts for system monitoring.
Monitoring Tcodes
Checking Application Servers (SM51)
This transaction is used to check all the active application server.
Monitoring Work Processes for Individual Instances (SM50).
Displays all running, waiting, stopped and PRIV processes related to a
particular instance. Under this step we check all the process, the process status
should always be waiting or running. If any process is having status other then
waiting or running we need to check that particular process and report
accordingly.
Monitoring System wide Work Processes (SM66)
We can quickly investigate the potential cause of a system performance problem
by checking the work process load and can use the global work process
overview to:
• Monitor the work process load on all active instances across the system
• Identify locks in the database (lock waits).
Using the Global Work Process Overview screen, we can see at a glance:
• The status of each application server
• The reason why it is not running
• Whether it has been restarted
• The CPU and request run time
• The user who has logged on and the client that they logged on to
• The report that is running
We record only those processes which are showing problems and not having
running status.
Monitoring Update Processes (SM13)
Execute Transaction SM13 and put * in the field USER.
This transaction is used to check the following activities:
1. Is the update active, if not , was it deactivated by system or by user.
2. Have any update been cancelled.
3. Is there a long queue of pending updates older than 10 minutes.
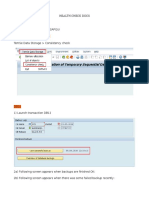
Monitoring Lock Entries (SM12)
Execute Transaction SM12 and put * in the field User Name
We can use lock statistics to monitor the locks that are set in the system. We
record only those lock entries which are having date time stamp of previous
day.
Monitoring System Log (SM21)
We can use the log to pinpoint and correct errors occurring in the system and its
environment. We check log for the previous day, and time is entered as shown in
the screen below. Then select Radio Button Problems and Warnings and press
Reread System Log.
We write total number of records, as shown in the screen below, in our log and
analyze the problems which are not displayed in ST22.
CPU Utilization (ST06)
In CPU Utilization we record User, System, Idle and Wait percentage utilization
from the above screen.
Available Space in Database (DB02)
Space statistics are taken from the below screen and we record Total Size in
GB and Total free space in percentage.
Checking Missing indexes (DB02)
At the same screen missing indexes statistics can also be checked
by pressing Missing Indexes button, below screen pops up. Record
primary and secondary missing indexes.
ABAP Dump Analysis (ST22)
Here we check for previous day’s dumps.
Open the details log of each and every dump by double clicking it and try to find
out any suitable notes, analyze them and propose suitable solution as per SAP
standards.
Spool Request Monitoring (SP01)
In spool request monitoring execute sp01 and put * in the field Created By and
press execute button.
Here we record only those requests which are terminated with problems.
Number of Print Requests (SPAD)
Execute SPAD and press Admin button.
Now select Print Request Overview button.
Record Total Print Requests from below screen.
Monitoring Batch Jobs (SM37)
Execute SM37 and put * in the field User Name record number of Scheduled,
Cancelled, Released and Finished requests.
Batch Input Session Lock (SM35)
Execute SM35 and press Locked Button. Record number of requests displayed.
Database Performance Monitor (ST04)
Record Quality %, if its is >=95 write 0 else write actual percentage displayed.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Basis Daily Monitoring TDocument15 pagesBasis Daily Monitoring TMarcelo Del Canto RodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- 60 SAP Basis Interview Questions & Answers (2022 Update)Document29 pages60 SAP Basis Interview Questions & Answers (2022 Update)surya sapbasis23Pas encore d'évaluation
- R3 ArchitectureDocument5 pagesR3 ArchitectureRanjeet SalunkhePas encore d'évaluation
- BASIS AssignmentDocument7 pagesBASIS AssignmentmbashaPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Live CacheDocument4 pagesWhat Is Live CacheKapil Satish PatilPas encore d'évaluation
- Detailed Analysis of Monitoring Process: Standard System ChecksDocument37 pagesDetailed Analysis of Monitoring Process: Standard System ChecksRam PrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- SAP Basis - Daily Check List: SAP Logon Connection TestDocument6 pagesSAP Basis - Daily Check List: SAP Logon Connection Testkhaled_dudePas encore d'évaluation
- St22 Sap DumpsDocument36 pagesSt22 Sap DumpssryallaPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Monitor SAP System and Do Performance ChecksDocument24 pagesHow To Monitor SAP System and Do Performance ChecksRupam DasPas encore d'évaluation
- SAP Basis GuideDocument14 pagesSAP Basis Guideranjan_4779Pas encore d'évaluation
- SAP Housekeeping - The Computer Center Management System (CCMS)Document40 pagesSAP Housekeeping - The Computer Center Management System (CCMS)KumarReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Checks When SAP R3 Is Very SlowDocument34 pagesChecks When SAP R3 Is Very Slowanandvisit1983Pas encore d'évaluation
- Update St-Pi y St-APIDocument9 pagesUpdate St-Pi y St-APIMiguel Angel Orellana SandovalPas encore d'évaluation
- Upgrade SAP Kernel: Step by Step Tutorial: What Is A Kernel?Document8 pagesUpgrade SAP Kernel: Step by Step Tutorial: What Is A Kernel?gauravpanwar8Pas encore d'évaluation
- Workload Monitor ST03NDocument3 pagesWorkload Monitor ST03NKishore KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Ehp UpgradeDocument9 pagesEhp UpgradeRohit AgarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- SAP Health CheckDocument24 pagesSAP Health Checkhembeck119Pas encore d'évaluation
- SAP Basis - Daily Check List SAP How To Step by Step Guide With Screen ShotDocument6 pagesSAP Basis - Daily Check List SAP How To Step by Step Guide With Screen ShotRafael Andrade FagundesPas encore d'évaluation
- What To Monitor in ST03Document5 pagesWhat To Monitor in ST03barun581Pas encore d'évaluation
- Performance TuningDocument3 pagesPerformance TuningHari Prasad ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Run SAP Transaction ST03Document46 pagesHow To Run SAP Transaction ST03xjacoPas encore d'évaluation
- Basis Realtime Questions and AnswersDocument18 pagesBasis Realtime Questions and AnswersMadhu SudhanPas encore d'évaluation
- ST03NDocument6 pagesST03NSurya NandaPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Guide Replication From Non-ABAPDocument23 pagesHow To Guide Replication From Non-ABAPSunil RaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sap Basis - Su01 User Id CreationDocument8 pagesSap Basis - Su01 User Id CreationsudhakarPas encore d'évaluation
- Daily MonitoringDocument54 pagesDaily MonitoringNagaPas encore d'évaluation
- Checklist For System Monitoring Sap BasisDocument3 pagesChecklist For System Monitoring Sap BasisUday LPas encore d'évaluation
- SAP Java Troubleshooting MonitoringDocument24 pagesSAP Java Troubleshooting MonitoringTeegala BalreddyPas encore d'évaluation
- SAP Memory ManagementDocument16 pagesSAP Memory ManagementDevender5194Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hana Daily Monitoring TemplateDocument7 pagesHana Daily Monitoring Templatehembeck119Pas encore d'évaluation
- Kernel - Upgrade Using SUM - Software Update ManagerDocument10 pagesKernel - Upgrade Using SUM - Software Update Managermhku1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Daily Activity Report - COATS-PRD Systems 15th Oct 2015Document47 pagesDaily Activity Report - COATS-PRD Systems 15th Oct 2015Aryan ChoudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- ST05Document2 pagesST05Gowtham Ravi100% (1)
- Common Abap Dumps and Their MeaningDocument4 pagesCommon Abap Dumps and Their MeaningGoutham Sri KrishnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Transport DocumentDocument7 pagesTransport DocumentSatish KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- SAP ECC6 EHP6 Upgrade Steps PDFDocument14 pagesSAP ECC6 EHP6 Upgrade Steps PDFprasadPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.SAP System Monitoring PDFDocument11 pages4.SAP System Monitoring PDFsreekanth0325Pas encore d'évaluation
- Performance Tuning of SAP SystemDocument19 pagesPerformance Tuning of SAP Systemcoolaryan83Pas encore d'évaluation
- Oracle St04Document9 pagesOracle St04khaled_dudePas encore d'évaluation
- SAP Memory Management Collection by St4rcH1LDDocument25 pagesSAP Memory Management Collection by St4rcH1LDKunal MajumdarPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Download SAP KernelDocument11 pagesHow To Download SAP KernelDeepak GokuPas encore d'évaluation
- Sap LicenseDocument6 pagesSap LicenseSatish KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Sap Implementation and Administration GuideDocument326 pagesSap Implementation and Administration GuideAshish SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Upgrade From ECC 4.6 To ECC 6Document13 pagesUpgrade From ECC 4.6 To ECC 6prem_09Pas encore d'évaluation
- MainDocument76 pagesMainAnonymous Yw2XhfXvPas encore d'évaluation
- Remote Function Call (RFC)Document11 pagesRemote Function Call (RFC)Kishore Kumar100% (1)
- Health Check Docs Status of Sap System:-: Done by Connecting To The SAPGUIDocument22 pagesHealth Check Docs Status of Sap System:-: Done by Connecting To The SAPGUIArulraj Kudanthai100% (1)
- Downloading SAP Kernel PatchesDocument21 pagesDownloading SAP Kernel PatchesAkshay GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- SAP System Directories On UNIXDocument10 pagesSAP System Directories On UNIXSudhakar ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Sap Ecc6 Ehp6 Upgrade StepsDocument23 pagesSap Ecc6 Ehp6 Upgrade StepsDevender5194Pas encore d'évaluation
- Upgrading SAP Host Agent Without Extracting The SAPHOSTAGENT ArchiveDocument3 pagesUpgrading SAP Host Agent Without Extracting The SAPHOSTAGENT ArchivePeter Naveen NaviPas encore d'évaluation
- C TADM51 731 Sample QuestionsDocument3 pagesC TADM51 731 Sample QuestionssudhagarrajuPas encore d'évaluation
- System Monitoring StepsDocument18 pagesSystem Monitoring StepsKishore KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Sap Monitor TransactionsDocument33 pagesSap Monitor Transactionsitjob65Pas encore d'évaluation
- What Is System MonitoringDocument22 pagesWhat Is System MonitoringNaveen YarramsettyPas encore d'évaluation
- System Monitoring: SAP BASIS Consultant's RoleDocument59 pagesSystem Monitoring: SAP BASIS Consultant's Roleprachi wadraliPas encore d'évaluation
- Basis Perform Health Check Daily On The SystemDocument4 pagesBasis Perform Health Check Daily On The Systemgodiee77Pas encore d'évaluation
- Basis T CodesDocument9 pagesBasis T Codesmn_dhillon1268Pas encore d'évaluation
- SAP Basis - Daily Check ListDocument6 pagesSAP Basis - Daily Check ListinfotcsPas encore d'évaluation