Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Stupendously Booooring2
Transféré par
elizabethscribdDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Stupendously Booooring2
Transféré par
elizabethscribdDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Stupendously Fascinating Formula Sheet!
The following formulas are valid whether or not the exponents are integers or rationals. Assume
x, y, a, b, c, d are all Real numbers, and no denominator ever equals zero.
Exponents Rule:
x 2 = x ⋅ x = xx multiply x with itself 2-times, x 3 = x ⋅ x ⋅ x = xxx multiply x with itself 3-times
so x n = x ⋅ x ⋅ x ⋅ ⋅ ⋅ x multiply x with itself n-times
Add the exponents Rule:
x m ⋅ x n = x m +n because x m ⋅ x n = xxx ⋅ ⋅ ⋅ x ⋅ xxx ⋅ ⋅ ⋅ x multiply x with itself (m+n)-times
x x 2 xx x x x2 xx x x 1 1 1
=1 , so 2 = = ⋅ = 1 ⋅ 1 = 1 and so on, 3 = = ⋅ ⋅ = 1 ⋅ 1 ⋅ = and so on,
x x xx x x x xxx x x x x x
x 3 xxx x x x
and = = ⋅ ⋅ = 1⋅1⋅ x = x ,
x2 xx x x 1
Subtract the exponents Rule:
xm
so in general n
= x m −n multiply x with itself (m-n)-times
x
Negative exponents Rule:
1 1
x −n = −n
= xn
xn x
(x ) = (x
2 3 2
⋅ x 2 ⋅ x 2 ) = x 2⋅3 = x 6 , so in general
(x ) = (x
m n m
⋅ x m ⋅ x m ⋅ ⋅ ⋅ x m )[ multiply_ n − times] = x mn
Multiply the exponents Rule:
(x )
m n
= x mn multiply x with itself (m× n)-times
Negative exponents and Multiplying exponents Together:
(x )
−m n
= (xm )
−n
= x −mn (x )
−m −n
= x mn
Different bases, multiplication, division and exponents
( xy ) n = x n y n because ( xy) n = xy ⋅ xy ⋅ xy ⋅ ⋅ ⋅ xy[ multiply_ n − times] = x n y n
n n
x xn y −n x x x x x xn y −n
= n = −n because = ⋅ ⋅ ⋅ ⋅ ⋅ [ multiply _ n − times ] = n = −n
y y x y y y y y y x
Multiplying binomials
( a + b )( c + d ) = ac + ad + bc + bd
special _ cases :
( x + y )( x − y ) = xx − xy + yx − yy = x 2 − y 2
( x + y ) 2 = x 2 + 2 xy + y 2
( x − y ) 2 = x 2 − 2 xy + y 2
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 1970 Zwiebach Part1Document143 pages1970 Zwiebach Part1Ben Schmitz100% (1)
- Math 157 CN SolutionsDocument295 pagesMath 157 CN SolutionsTharin KhaledPas encore d'évaluation
- Ssce 1793 Test 1 201420152Document4 pagesSsce 1793 Test 1 201420152Gantan Etika MurtyPas encore d'évaluation
- Law of ExponentsDocument10 pagesLaw of ExponentsAlvin Ignacio SiladanPas encore d'évaluation
- List of FormulaDocument4 pagesList of Formulasofiea hazriPas encore d'évaluation
- Mate 1 - 2do ParcialDocument6 pagesMate 1 - 2do ParcialAustin PetrovaPas encore d'évaluation
- Section 6.9, The Hyperbolic Functions and Their InversesDocument3 pagesSection 6.9, The Hyperbolic Functions and Their InversesDiegoPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculus 03 Rules For Finding DerivativesDocument4 pagesCalculus 03 Rules For Finding DerivativesKenneth James Andales SabuboPas encore d'évaluation
- Homework No. 4 ME 5113Document32 pagesHomework No. 4 ME 5113Nixon LagrisolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fixed Point Iteration TheoremDocument19 pagesFixed Point Iteration TheoremBalu ChanderPas encore d'évaluation
- Roots and CoefficientsDocument5 pagesRoots and CoefficientsHatsady ThonginPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz 1 - Math 102 (Differential Calculus) - Psu UrdanetaDocument5 pagesQuiz 1 - Math 102 (Differential Calculus) - Psu UrdanetaJames Querimit De LunaPas encore d'évaluation
- T3 SolutionsDocument4 pagesT3 SolutionstoaobmbPas encore d'évaluation
- MAT102 TutSolutionsDocument12 pagesMAT102 TutSolutionsLetsile UtlwangPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution Techniques For Elementary Partial Differential Equations, Third Edition, Instructors Solutions Manual Y)Document192 pagesSolution Techniques For Elementary Partial Differential Equations, Third Edition, Instructors Solutions Manual Y)quasiestelarPas encore d'évaluation
- 2017 Mid SolDocument13 pages2017 Mid SolvickyPas encore d'évaluation
- Preparatory Questions: Solutions To Tutorial 5Document8 pagesPreparatory Questions: Solutions To Tutorial 5TOM DAVISPas encore d'évaluation
- Factoring and Solving Polynomial EquationsDocument13 pagesFactoring and Solving Polynomial EquationsMark Francis HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Math 106: Review For Exam II - SOLUTIONS: Udv Uv Vdu Uv DX Uv U VDXDocument6 pagesMath 106: Review For Exam II - SOLUTIONS: Udv Uv Vdu Uv DX Uv U VDXsakPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes-Derivatives of Trig PDFDocument7 pagesNotes-Derivatives of Trig PDFDondon TayabanPas encore d'évaluation
- 2008 ACJC MA H2 P1 Prelim SolnDocument10 pages2008 ACJC MA H2 P1 Prelim SolnAmbrieshKarthikPas encore d'évaluation
- List of Formula sscm1023 Chap1 To 4Document4 pagesList of Formula sscm1023 Chap1 To 4Aisyah NadhirahPas encore d'évaluation
- Y Sin 4 X +cos: I. Find The Derivative of Y. Show The Complete Solution. A. Solution: Using The Sum/difference RuleDocument3 pagesY Sin 4 X +cos: I. Find The Derivative of Y. Show The Complete Solution. A. Solution: Using The Sum/difference RuleFranchezca WestermannPas encore d'évaluation
- Algebra in Economics and Business: Foreign Trade UniversityDocument24 pagesAlgebra in Economics and Business: Foreign Trade UniversityNhi Lê ÂnPas encore d'évaluation
- KEY Math 115-009 Calculus 1 Circle One: Grade My Work / Answers Exam 2Document3 pagesKEY Math 115-009 Calculus 1 Circle One: Grade My Work / Answers Exam 2mantaray_09Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fourier SeriesDocument12 pagesFourier SeriesChrysanthos KoutsoyiannisPas encore d'évaluation
- Solutions: MATH 214-2 - Fall 2001 - Final Exam (Solutions)Document11 pagesSolutions: MATH 214-2 - Fall 2001 - Final Exam (Solutions)Patrick ManzanzaPas encore d'évaluation
- SAT Subject Math Level 2 Facts & Formulas Numbers, Sequences, FactorsDocument11 pagesSAT Subject Math Level 2 Facts & Formulas Numbers, Sequences, FactorsneenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Solving Cubic Equations PDFDocument8 pagesSolving Cubic Equations PDFHaariniPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.continuity and Differentiability Assignment SolutionsDocument15 pages5.continuity and Differentiability Assignment SolutionsOlagunju AbdulmalikPas encore d'évaluation
- 8.2 Table of Derivatives: D y D X !Document2 pages8.2 Table of Derivatives: D y D X !Sahil GouthamPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematical Methods For Business, Economics & FinanceDocument67 pagesMathematical Methods For Business, Economics & FinanceHareen JuniorPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.6 Limits at InfinityDocument15 pages1.6 Limits at InfinityHamza MamarintaPas encore d'évaluation
- List of FormulaDocument3 pagesList of FormulaAnggun AureolaPas encore d'évaluation
- AEMx CH05Document83 pagesAEMx CH05林茂泉Pas encore d'évaluation
- Quadratic Equations 2022 2023Document32 pagesQuadratic Equations 2022 2023Edward Kenneth PantallanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Differentiations of Inverse Hyperbolic FunctionsDocument16 pagesDifferentiations of Inverse Hyperbolic FunctionscikguhafidzuddinPas encore d'évaluation
- 2020 - 07. Sistem Persamaan LinierDocument35 pages2020 - 07. Sistem Persamaan LiniersindunugrohoPas encore d'évaluation
- IndicesDocument3 pagesIndicesPratik ShresthaPas encore d'évaluation
- The International University (Iu) - Vietnam National University - HCMCDocument4 pagesThe International University (Iu) - Vietnam National University - HCMCDiệu Vi NguyễnPas encore d'évaluation
- Trig Inverse TrigDocument7 pagesTrig Inverse Trigashenafihenok400Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3 SolDocument3 pages3 SolnamanPas encore d'évaluation
- Rational ExpressionsDocument9 pagesRational ExpressionsShinePas encore d'évaluation
- Algebra Chap 1Document74 pagesAlgebra Chap 1ᜎᜒᜌᜓᜈᜒᜎ᜔ ᜄ᜔ᜏᜇᜒᜈ᜔Pas encore d'évaluation
- Calculus Notes-T.CochranDocument14 pagesCalculus Notes-T.CochranguntursrinivasPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 2Document8 pagesWeek 2ng0934325Pas encore d'évaluation
- AlgebraicDocument16 pagesAlgebraiczohabnoor63Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ch8 - More About Equations - EX8CDocument17 pagesCh8 - More About Equations - EX8CWayne TsoiPas encore d'évaluation
- List of Formulae Trigo-Sscm1023Document3 pagesList of Formulae Trigo-Sscm1023aieyinHengPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.0 The Derivatives 3.1 Derivative and GradientDocument5 pages3.0 The Derivatives 3.1 Derivative and Gradientsolomon okechukwuPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecuaciones Con Coeficientes Constantes.-: Am e Bme Ce e Am BM C 0 e Am BM CDocument7 pagesEcuaciones Con Coeficientes Constantes.-: Am e Bme Ce e Am BM C 0 e Am BM CGustavo Villalba UñoPas encore d'évaluation
- Gen MathDocument7 pagesGen MathHG Mejia ECPas encore d'évaluation
- AA Mathematics ReviewerDocument6 pagesAA Mathematics ReviewerJo Louis CamiguingPas encore d'évaluation
- VJC 2023 H2 Math CT SolutionsDocument13 pagesVJC 2023 H2 Math CT SolutionsVenkateswaran Gayathri (Bbss)Pas encore d'évaluation
- WWW - Yoquieroaprobar.es: Resolver Las Siguientes Ecuaciones: 1) X + 3x - X - 3 0Document2 pagesWWW - Yoquieroaprobar.es: Resolver Las Siguientes Ecuaciones: 1) X + 3x - X - 3 0TaniaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gauss Quadrature MethodDocument12 pagesGauss Quadrature MethodMirza Shahzaib ShahidPas encore d'évaluation
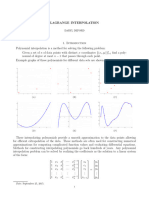
- Lagrange InterpolationDocument3 pagesLagrange InterpolationMacloud KamulaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1101M1 (06-12) Mid (Solution)Document9 pages1101M1 (06-12) Mid (Solution)Leni ApriyantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes LinearSystemsDocument33 pagesNotes LinearSystemsRenu KoshalPas encore d'évaluation
- Stress Strain TensorDocument44 pagesStress Strain Tensorעוז אושרי100% (1)
- Department of Education: Republic of The Philippines Region IV-A (CALABARZON) Division of Rizal Table of SpecificationDocument3 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The Philippines Region IV-A (CALABARZON) Division of Rizal Table of SpecificationODETTE GENOVA100% (1)
- Mathematical Language and SymbolsDocument18 pagesMathematical Language and SymbolsMarvin Idos (Marbxs)100% (1)
- Combinatorics Exercises Stephan WagnerDocument8 pagesCombinatorics Exercises Stephan WagnerAli ErginPas encore d'évaluation
- Matlab SImulink Collate 130121Document234 pagesMatlab SImulink Collate 130121Tini100% (1)
- How To Identify Conic Sections PDFDocument31 pagesHow To Identify Conic Sections PDFkaskaraitPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment V: SolutionDocument2 pagesAssignment V: SolutionMiliyon TilahunPas encore d'évaluation
- FCM 2 CW 2 April 2023Document4 pagesFCM 2 CW 2 April 2023Maliq MorrisPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 KYP Lemma: N M N N MDocument4 pages8 KYP Lemma: N M N N MAlli-Oke Olusegun RazakPas encore d'évaluation
- 2-Computing LimitsDocument5 pages2-Computing LimitsGabriel LinaresPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise - 01 Quadratic Equation: Check Your GraspDocument8 pagesExercise - 01 Quadratic Equation: Check Your Grasponline pathshalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics-I - Bridge CourseDocument30 pagesMathematics-I - Bridge CourseSINNAPPARAJ SPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch01 - SE 1.4Document12 pagesCh01 - SE 1.4GeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- Project 1 NarrativeDocument2 pagesProject 1 Narrativeapi-263994578Pas encore d'évaluation
- Prof. Dr. Bartel Leenert Van Der Waerden (Auth.) - A History of Algebra - From Al-Khwārizmī To Emmy Noether-Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg (1985) PDFDocument279 pagesProf. Dr. Bartel Leenert Van Der Waerden (Auth.) - A History of Algebra - From Al-Khwārizmī To Emmy Noether-Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg (1985) PDFPaulina CiudadPas encore d'évaluation
- Merged Modules MATHS For IGCSEDocument143 pagesMerged Modules MATHS For IGCSElittlegus100% (2)
- Answer / Skema Jawapan Peperiksaan Percubaan SPM 2011 Additional Mathematics (Paper 1)Document7 pagesAnswer / Skema Jawapan Peperiksaan Percubaan SPM 2011 Additional Mathematics (Paper 1)Sim Ping Ping0% (1)
- 9709 s03 Ms 1+2+3+4+5+6+7Document42 pages9709 s03 Ms 1+2+3+4+5+6+7Roukaiya Peerkhan50% (4)
- Automorphic Functions: Daniel Nicks May 16, 2006Document31 pagesAutomorphic Functions: Daniel Nicks May 16, 2006will bPas encore d'évaluation
- Math104 Chapter 2 Permutation and CombinationDocument11 pagesMath104 Chapter 2 Permutation and Combinationzam cayetanoPas encore d'évaluation
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Math1314.501.10f Taught by Brady McCary (bcm052000)Document6 pagesUT Dallas Syllabus For Math1314.501.10f Taught by Brady McCary (bcm052000)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupPas encore d'évaluation
- Stable Manifold TheoremDocument7 pagesStable Manifold TheoremRicardo Miranda MartinsPas encore d'évaluation
- Math For EEDocument280 pagesMath For EEvinodlifePas encore d'évaluation
- PDF Resize 4Document5 pagesPDF Resize 4Madzlina IbrahimPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.3 Inverse of A Matrix PDFDocument23 pages4.3 Inverse of A Matrix PDFjokydin92Pas encore d'évaluation
- Modeling Input/Output Data: Partial Least Squares (PLS)Document18 pagesModeling Input/Output Data: Partial Least Squares (PLS)Kerwin ManiaulPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Algebra - Foundations To Frontiers PDFDocument903 pagesLinear Algebra - Foundations To Frontiers PDFlicks.vinicius1649Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mathmission For Xii (2023-24) - O.P. GuptaDocument192 pagesMathmission For Xii (2023-24) - O.P. GuptaSathviki DasariPas encore d'évaluation
- Cbjemacq 02Document13 pagesCbjemacq 02Raman Deep DarochPas encore d'évaluation
- Review MAT102Document6 pagesReview MAT102Sanjana BulusuPas encore d'évaluation