Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Assessment
Transféré par
OPsssl0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
25 vues2 pagesThe patient is experiencing a dry mouth and throat, indicating fluid volume deficit likely due to intestinal obstruction. Intestinal obstruction occurs when blockage obstructs normal intestinal contents flow, causing the intestine to become vulnerable to ischemia and damage. This allows intestinal bacteria to invade and cause fluid exudation and dehydration. The nursing plan includes monitoring the patient, keeping them in a semi-fowler's position, and looking for signs of dehydration. The goal is for the patient's discomfort to decrease and fluid imbalance to stabilize within a few days with nursing intervention.
Description originale:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThe patient is experiencing a dry mouth and throat, indicating fluid volume deficit likely due to intestinal obstruction. Intestinal obstruction occurs when blockage obstructs normal intestinal contents flow, causing the intestine to become vulnerable to ischemia and damage. This allows intestinal bacteria to invade and cause fluid exudation and dehydration. The nursing plan includes monitoring the patient, keeping them in a semi-fowler's position, and looking for signs of dehydration. The goal is for the patient's discomfort to decrease and fluid imbalance to stabilize within a few days with nursing intervention.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
25 vues2 pagesAssessment
Transféré par
OPssslThe patient is experiencing a dry mouth and throat, indicating fluid volume deficit likely due to intestinal obstruction. Intestinal obstruction occurs when blockage obstructs normal intestinal contents flow, causing the intestine to become vulnerable to ischemia and damage. This allows intestinal bacteria to invade and cause fluid exudation and dehydration. The nursing plan includes monitoring the patient, keeping them in a semi-fowler's position, and looking for signs of dehydration. The goal is for the patient's discomfort to decrease and fluid imbalance to stabilize within a few days with nursing intervention.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
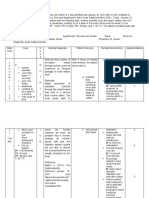
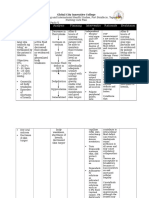
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS INFERENCE PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
Subjective: Fluid volume Intestinal obstruction Short term: Independent:
“ Pengeng tubig tuyong tuyo deficit related occurs when a After 2 hours Kepp the To promote After 1 day of nursing
na lalamunan ko as verbalized to abnormal blockage obstructs the of nursing patient in pulmonary intervention the
by the patient” loss of normal flow of intervention semi-fowler’s ventilation client
gastrointestin contents through the patient position To see if Feeling on his or her
Objective: al fluids. intestinal tract. feeling Look for their a Discomfortabity will
Pale complexion Obstruction of the becomes sign’s of sudden loss Become comfortable.
Dry mouth intestine causes the to comfortable. dehydration of fluid
Dry skin become vulnerable to After 1 hour Monitor V/S To see if After 1 day of
Pain scale is 8/10 ischemia. The nursing Monitor there is nursing intervention
V/S taken: intestinal mucosal intervention Intake other the patient
BP: 110/70 barrier can be the patient and Output complicatio verbalized the
TEMP: 36.3 damaged, thus pain scale Health n information about his
PR: 94 allowing intestinal will Teaching To observe or her disease.
RR: 21 bacteria to invade the decreased to about the the fluid
intestinal wall and 4/10 disease balance of
causing fluid Long Term: Dependent: the patient
exudation, which After 3 days Maintain the To orrient
leads to hypovolemia of nursing client in NPO the patient
and dehydration. intervention as ordered about the
About 7 L of of fluid the fluid Insertion of disease
per day is secreted imbalance of NGT as Dependent:
into the small the patient ordered To examine
intestine and stomach will become Maintain the further the
and ussually stable. IV therapy as obstruction
reabsorbed. During ordered To
obstruction however, Administer decompress
fluid accumulates, analgesic, the bowel
causing abdominal broad To maintain
distension and spectrum the fluid
pressure on the anti-biotic as balance of
mucosal wall, which ordered the patient
can leads to For pain
peritonitis and
perforation.
Obstructions can be
partial and complete/
the most common
type of intestinal
obstruction in one of
the small intestine
from fibrous adhesion.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Intestinal Ills: Chronic Constipation, Indigestion, Autogenetic Poisons, Diarrhea, Piles, Etc. Also Auto-Infection, Auto-Intoxication, Anemia, Emaciation, Etc. Due to Proctitis and ColitisD'EverandIntestinal Ills: Chronic Constipation, Indigestion, Autogenetic Poisons, Diarrhea, Piles, Etc. Also Auto-Infection, Auto-Intoxication, Anemia, Emaciation, Etc. Due to Proctitis and ColitisPas encore d'évaluation
- Cues/Needs Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term Independent Short TermDocument3 pagesCues/Needs Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term Independent Short TermLatrell GelacioPas encore d'évaluation
- Diverticulosis, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesD'EverandDiverticulosis, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesÉvaluation : 1 sur 5 étoiles1/5 (1)
- Risk NCP - PESCADERO 4CDocument1 pageRisk NCP - PESCADERO 4COrlando VillanuevaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rules and Directions for the Employment of Injections in Various DiseasesD'EverandRules and Directions for the Employment of Injections in Various DiseasesPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan For Peritonitis NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Peritonitis NCPyamie sulongPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan Diarrhea Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan Diarrhea Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationKrah100% (1)
- Volume 1Document2 pagesVolume 1roxybiscantePas encore d'évaluation
- Salva, R.D NCP & Drug Study (Isph - Gs Pediaward)Document7 pagesSalva, R.D NCP & Drug Study (Isph - Gs Pediaward)Rae Dominick Aquino SalvaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Case Analysis GastritisDocument7 pagesNCP Case Analysis GastritisSteffi GolezPas encore d'évaluation
- Borata Nursing Process RleDocument11 pagesBorata Nursing Process Rlefiel borataPas encore d'évaluation
- Intussuception Is A Condition in Which Part of The Intestine Folds Into The Section Next To ItDocument3 pagesIntussuception Is A Condition in Which Part of The Intestine Folds Into The Section Next To ItEduard GarchitorenaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP FinalDocument18 pagesNCP FinalHelen GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Diarrhea Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesDiarrhea Nursing Care PlanKrizha Angela NicolasPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan Diarrhea Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan Diarrhea Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationKrahPas encore d'évaluation
- Constipation: Patient Name: Shehzad Age: 45 Ward: Emergency BDocument2 pagesConstipation: Patient Name: Shehzad Age: 45 Ward: Emergency BShafiq Ur RahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesFinal Nursing Care PlanKatherine BellezaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term Goal Independent: Short Term GoalDocument5 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term Goal Independent: Short Term GoalJobelle AcenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Subjective: Nephrolithiasis Is STO: After 8 Diagnostics: STO: Fully MetDocument3 pagesSubjective: Nephrolithiasis Is STO: After 8 Diagnostics: STO: Fully MetSebastianPas encore d'évaluation
- Renal Concept MapDocument1 pageRenal Concept MapShaira Ann CalambaPas encore d'évaluation
- Post-Partum Care Plan NCPDocument2 pagesPost-Partum Care Plan NCPRap De la CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Ate Gabs Nyo Pagod NaDocument3 pagesAte Gabs Nyo Pagod NaGabrielle EvangelistaPas encore d'évaluation
- JVJV NCP Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDocument2 pagesJVJV NCP Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitvicenteturasPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 NCP Formulated From Case Study LUCI DONNA MAE V.Document8 pages2 NCP Formulated From Case Study LUCI DONNA MAE V.Harlene Joyce ReyPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Scenario 1: Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Aldrin M. Paulino BSN 3ADocument4 pagesCase Scenario 1: Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Aldrin M. Paulino BSN 3A24 PAULINO ALDRIN MUJARPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan: IndependentDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: IndependentAdhaPas encore d'évaluation
- F. NCP ProperDocument4 pagesF. NCP ProperAle SandraPas encore d'évaluation
- Mirana BSN2-7 NCPDocument3 pagesMirana BSN2-7 NCPCrystal MiranaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP AppendicitisDocument2 pagesNCP Appendicitismnms0708100% (2)
- Group-5 NCM-107 NCPDocument4 pagesGroup-5 NCM-107 NCPbulok netflakes100% (1)
- Case Scenario: Prostate CancerDocument5 pagesCase Scenario: Prostate Cancer24 PAULINO ALDRIN MUJARPas encore d'évaluation
- V. Drug Study: Dat e Ord Ere D Drug Action Indication Nursing Responsibilities & ConsiderationDocument6 pagesV. Drug Study: Dat e Ord Ere D Drug Action Indication Nursing Responsibilities & Considerationronnie023Pas encore d'évaluation
- XIV. TreatmentDocument2 pagesXIV. TreatmentCharlemagne Louise BuadaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Post PartumDocument2 pagesNCP Post PartumsteffiPas encore d'évaluation
- Dipolog Medical Center College Foundation Inc.: A Case Study OF AppendicitisDocument11 pagesDipolog Medical Center College Foundation Inc.: A Case Study OF AppendicitisTiffany AdriasPas encore d'évaluation
- DS - Senokot ForteDocument1 pageDS - Senokot ForteMarjorie Dela RosaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP-fluid Volume DeficitDocument4 pagesNCP-fluid Volume DeficitChrissa Mae Aranilla MayoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pleural Effusion Case PresentationDocument16 pagesPleural Effusion Case PresentationDhindee OmahoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan: Histolytica, ADocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Histolytica, AkristennemariePas encore d'évaluation
- Advincula NCP LiverDocument2 pagesAdvincula NCP LiverErryl Justine AdvinculaPas encore d'évaluation
- Deficient Fluid Volume (AGEDocument2 pagesDeficient Fluid Volume (AGENursesLabs.com83% (6)
- NCP FluidDocument4 pagesNCP FluidSofronio OmboyPas encore d'évaluation
- Simulation 1 Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term Goal Independent: Short Term GoalDocument7 pagesSimulation 1 Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term Goal Independent: Short Term GoalBianca CabatayPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment Scientific Analysis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term GoalDocument4 pagesAssessment Scientific Analysis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term GoalJayson OlilePas encore d'évaluation
- Funda Sample ScenarioDocument2 pagesFunda Sample ScenarioGadez JeanpelPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan - FormatDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan - FormatKyle VargasPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP UTI (Artillo)Document3 pagesNCP UTI (Artillo)Al TheóPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study 5Document6 pagesCase Study 5Anthony jesusPas encore d'évaluation
- Larceña Sic Rot 7Document11 pagesLarceña Sic Rot 7noemilauPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Desired Outcome Nursing Intervention Justification EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Desired Outcome Nursing Intervention Justification EvaluationDan MandigPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP - AgeDocument5 pagesNCP - Ageunsp3akabl386% (7)
- Acute Abdominal Pain CareplanDocument12 pagesAcute Abdominal Pain Careplanbenardnyakundi99Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan AmebiasisDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plan AmebiasisCarl Simon CalingacionPas encore d'évaluation
- Evaluation of ConstipationDocument8 pagesEvaluation of ConstipationAndrea GallegoPas encore d'évaluation
- Capacio Case#1 RevisedDocument4 pagesCapacio Case#1 RevisedLorenz CapacioPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP of GlomerularnephritisDocument6 pagesNCP of GlomerularnephritisSimran JosanPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument3 pagesNCP Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceVitha100% (1)
- HydroceleDocument10 pagesHydroceleRyan RePas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care PlanDocument12 pagesNursing Care Plankeishaaa29100% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan - UtiDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan - Utisweet_karisma05100% (6)
- Apraxia 2Document25 pagesApraxia 2Vellardo AlbayPas encore d'évaluation
- 9 ECG Strips On The NCLEXDocument1 page9 ECG Strips On The NCLEXSibel ErtuğrulPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Surgical Exam Part 1Document16 pagesMedical Surgical Exam Part 1api-382250888% (42)
- Healthcare Waste Management System ReportDocument30 pagesHealthcare Waste Management System ReportLevi GasparPas encore d'évaluation
- Patricia Nicole Y.Cruz 2BSA-4 Module 2: Lesson 1-Assignment #1Document4 pagesPatricia Nicole Y.Cruz 2BSA-4 Module 2: Lesson 1-Assignment #1Patricia CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Prostate cancerPRIMERDocument27 pagesProstate cancerPRIMERLuan MarcosPas encore d'évaluation
- Cytogenetics - Prelim TransesDocument15 pagesCytogenetics - Prelim TransesLOUISSE ANNE MONIQUE L. CAYLOPas encore d'évaluation
- Signs of Respiratory Distress in Your Child: Signs To Look ForDocument2 pagesSigns of Respiratory Distress in Your Child: Signs To Look ForMa GynPas encore d'évaluation
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Worker-Related Musculoskeletal Disorders of The Upper Extremity OmbroDocument705 pagesDiagnosis and Treatment of Worker-Related Musculoskeletal Disorders of The Upper Extremity OmbroDouglas GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Preeclampsia and EclampsiaDocument23 pagesPreeclampsia and Eclampsiaapi-3705046100% (6)
- Smog Evs ProjectDocument17 pagesSmog Evs Projectshrey narulaPas encore d'évaluation
- RRLDocument12 pagesRRLEmilyne Joy Mendoza CabayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Breast Cancer Thesis SampleDocument6 pagesBreast Cancer Thesis Sampleanngarciamanchester100% (2)
- Oncology Nursing NotesDocument12 pagesOncology Nursing Notesjoyrena ochondra100% (6)
- Oral Mucosal Ulceration - A Clinician's Guide To Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument9 pagesOral Mucosal Ulceration - A Clinician's Guide To Diagnosis and TreatmentAnonymous pvuOXZPas encore d'évaluation
- Reading ComprehensionDocument27 pagesReading ComprehensionNguyen MinhPas encore d'évaluation
- Dental Caries & GeneticsDocument13 pagesDental Caries & GeneticsRenuka PiddennavarPas encore d'évaluation
- Test: Total Hemoglobin (HGB or HB)Document38 pagesTest: Total Hemoglobin (HGB or HB)Angiela JauriguePas encore d'évaluation
- Kidd Blood Group LawickiDocument54 pagesKidd Blood Group LawickiAlfrey PuebloPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Anthropology Plagues and People (ANTH 2240, A01/CRN18650)Document13 pagesDepartment of Anthropology Plagues and People (ANTH 2240, A01/CRN18650)jakejnfhfbPas encore d'évaluation
- Causes and Consequences of The American Civil WarDocument5 pagesCauses and Consequences of The American Civil WarNhân PhanPas encore d'évaluation
- TotilacDocument4 pagesTotilacOliver Tabag100% (2)
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) : Pop Ariana Narcisa Class XI-B Colegiul Tehnic Ana AslanDocument12 pagesObsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) : Pop Ariana Narcisa Class XI-B Colegiul Tehnic Ana AslanAriPopPas encore d'évaluation
- CPE239 Demonstration 411Document11 pagesCPE239 Demonstration 411Hong Jun TeePas encore d'évaluation
- Nemeroff Et Al. 2013 - Dsm-5 2013 Collection Psychiatrist Views (Word Drop)Document19 pagesNemeroff Et Al. 2013 - Dsm-5 2013 Collection Psychiatrist Views (Word Drop)DestriPas encore d'évaluation
- Amy L. Lansky - Impossible Cure - The Promise of HomeopathyDocument295 pagesAmy L. Lansky - Impossible Cure - The Promise of Homeopathybjjman88% (17)
- Growtallerwithshinlengthening ComDocument28 pagesGrowtallerwithshinlengthening ComManu MohanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lens and Cataract - Dr. Angbue-Te (2023)Document4 pagesLens and Cataract - Dr. Angbue-Te (2023)Patricia ManaliliPas encore d'évaluation
- Instant Download Solution Manual For Moneybanking and Financial Markets Cecchetti Schoenholtz 4th Edition PDF ScribdDocument32 pagesInstant Download Solution Manual For Moneybanking and Financial Markets Cecchetti Schoenholtz 4th Edition PDF ScribdSharonYoungeizr100% (13)
- 382 FullDocument23 pages382 FullRahma WirdaPas encore d'évaluation