Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Recursive Metho DS: Introduction To Dynamic Optimization Nr. 1
Transféré par
Kevin Andrew0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
34 vues7 pagesTitre original
Slides 1
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
34 vues7 pagesRecursive Metho DS: Introduction To Dynamic Optimization Nr. 1
Transféré par
Kevin AndrewDroits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 7
Recursive Methods
Introduction to Dynamic Optimization Nr. 1
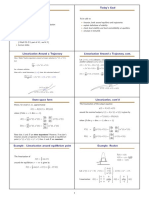
Outline Today’s Lecture
• finish Euler Equations and Transversality Condition
• Principle of Optimality: Bellman’s Equation
• Study of Bellman equation with bounded F
• contraction mapping and theorem of the maximum
Introduction to Dynamic Optimization Nr. 2
Infinite Horizon T = ∞
∞
X
V ∗ (x0 ) = sup β t F (xt , xt+1 )
{xt+1 }∞
t=0 t=0
subject to,
xt+1 ∈ Γ (xt ) (1)
with x0 given
• sup {} instead of max {}
© 0 ª∞
• define xt+1 t=0 as a plan
©© 0 ª∞ 0 0 0
ª
• define Π (x0 ) ≡ xt+1 t=0 |xt+1 ∈ Γ (xt ) and x0 = x0
Introduction to Dynamic Optimization Nr. 3
Assumptions
A1. Γ (x) is non-empty for all x ∈ X
P
A2. limT →∞ Tt=0 β t F (xt , xt+1 ) exists for all x ∈ Π (x0 )
then problem is well defined
Introduction to Dynamic Optimization Nr. 4
Recursive Formulation: Bellman Equation
• value function satisfies
(∞ )
X
V ∗ (x0 ) = max∞ β t F (xt , xt+1 )
{xt+1 }t=0
t=0
xt+1 ∈Γ(xt )
X∞
= max F (x0 , x1 ) + max∞ β t F (xt , xt+1 )
x1 ∈Γ(x0 )
{xt+1 }t=1
t=1
xt+1 ∈Γ(xt )
X∞
= max F (x0 , x1 ) + β max∞ β t F (xt+1 , xt+2 )
x1 ∈Γ(x0 )
{xt+1 }t=1
t=0
xt+1 ∈Γ(xt )
= max {F (x0 , x1 ) + βV ∗ (x1 )}
x1 ∈Γ(x0 )
continued...
Introduction to Dynamic Optimization Nr. 5
• idea: use BE to find value function V ∗ and policy function g [Principle
of Optimality]
Introduction to Dynamic Optimization Nr. 5A
Bellman Equation: Principle of Optimality
• Principle of Optimality idea: use the functional equation
V (x) = max {F (x, y) + βV (y)}
y∈Γ(x)
to find V ∗ and g
• note: nuisance subscripts t, t + 1, dropped
• a solution is a function V (·) the same on both sides
• IF BE has unique solution then V ∗ = V
• more generally the “right solution” to (BE) delivers V ∗
Introduction to Dynamic Optimization Nr. 6
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Optimization Methods (MFE) : Elena PerazziDocument28 pagesOptimization Methods (MFE) : Elena PerazziRoy SarkisPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Note SGDDocument4 pagesLecture Note SGDNishant PandaPas encore d'évaluation
- DP NoasDocument10 pagesDP Noasapurva.tudekarPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercises in Statistics Series A, No. 5: XT XTDocument3 pagesExercises in Statistics Series A, No. 5: XT XTnorman camarenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Distribusi SeragamDocument7 pagesDistribusi Seragamherlina balangsawangPas encore d'évaluation
- Probability Unit 4Document32 pagesProbability Unit 4Sayli KomurlekarPas encore d'évaluation
- MATH 2131 3.0 Section M Test Solution AnalysisDocument2 pagesMATH 2131 3.0 Section M Test Solution AnalysisveechowPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture10 - Pontryagins Minimum PrincipleDocument9 pagesLecture10 - Pontryagins Minimum PrincipleAmit BansodPas encore d'évaluation
- Math 122 Duke Day 5 NotesDocument3 pagesMath 122 Duke Day 5 NotesLuke MeredithPas encore d'évaluation
- Algebra solutionsDocument9 pagesAlgebra solutionsNandhiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Definition 2.3.6.: TX X TX X TX X TX X 0X XDocument16 pagesDefinition 2.3.6.: TX X TX X TX X TX X 0X Xdharani VPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 08-09Document6 pagesLec 08-09Alvaro Rafael MartínezPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec3 Convex Function ExerciseDocument4 pagesLec3 Convex Function Exercisezxm1485Pas encore d'évaluation
- Operaciones Repaso de OptimizacionDocument21 pagesOperaciones Repaso de OptimizacionMigu3lspPas encore d'évaluation
- Pde - T6Q9Document2 pagesPde - T6Q9Bumi BumsPas encore d'évaluation
- Moments, moment generating functions, and random variable propertiesDocument10 pagesMoments, moment generating functions, and random variable propertiestegarpradanaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 D'alembert's Solution: Weston Barger July 12, 2016Document11 pages1 D'alembert's Solution: Weston Barger July 12, 2016ranvPas encore d'évaluation
- HW3: Moment Functions - Solutions: Problem 1. Let X Be A Real-Valued Random Variable On A Probability SpaceDocument5 pagesHW3: Moment Functions - Solutions: Problem 1. Let X Be A Real-Valued Random Variable On A Probability SpaceDuc-Viet HaPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution of Ordinary Differential Equations: 1 General TheoryDocument3 pagesSolution of Ordinary Differential Equations: 1 General TheoryvlukovychPas encore d'évaluation
- UniversityDocument3 pagesUniversitySudo27Pas encore d'évaluation
- 11-Differentiation RulesDocument23 pages11-Differentiation Rulesmr abuja beyPas encore d'évaluation
- EC744 Lecture Note 3 Dynamic Programming Under Certainty: Prof. Jianjun MiaoDocument17 pagesEC744 Lecture Note 3 Dynamic Programming Under Certainty: Prof. Jianjun MiaobiniclePas encore d'évaluation
- CVX ch3Document45 pagesCVX ch3Gissela Gonzalez CubasPas encore d'évaluation
- The Classical Limit of Quantum MechanicsDocument4 pagesThe Classical Limit of Quantum MechanicsMichael ParrishPas encore d'évaluation
- Deriving the Wave Equation from Newton's LawsDocument2 pagesDeriving the Wave Equation from Newton's LawsOmaar Mustaine RattleheadPas encore d'évaluation
- Definite Integral with Variable LimitsDocument5 pagesDefinite Integral with Variable LimitsmuradPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculus2014 Lecturenote 9 30Document5 pagesCalculus2014 Lecturenote 9 30盧思宇Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cee235bpresentation PDE Intro Part 2Document13 pagesCee235bpresentation PDE Intro Part 2delaram88Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hyperbolic Equations: 8.1 D'Alembert's SolutionDocument10 pagesHyperbolic Equations: 8.1 D'Alembert's Solutionrohit singhPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Question 1: Symmetry F ( + U) F ( U) U 0 Prove The FollowingDocument4 pages1 Question 1: Symmetry F ( + U) F ( U) U 0 Prove The FollowingEmma ReinschPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercises Chapter 6Document17 pagesExercises Chapter 6BinasxxPas encore d'évaluation
- Optimization in Economic Theory (winter term 2021/22Document30 pagesOptimization in Economic Theory (winter term 2021/22Salim GhalayiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Quasi Maximum Likelihood - ApplicationsDocument17 pagesQuasi Maximum Likelihood - ApplicationsAnonymous tsTtieMHDPas encore d'évaluation
- Deterministic Continuous Time Optimal Control and The Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman EquationDocument7 pagesDeterministic Continuous Time Optimal Control and The Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman EquationAbdesselem BoulkrounePas encore d'évaluation
- Formulario PSDocument4 pagesFormulario PSCarlos RebeloPas encore d'évaluation
- Today's Goal: X U X X (T) U (T)Document5 pagesToday's Goal: X U X X (T) U (T)Abdesselem BoulkrounePas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz-6 Answers and Solutions: Coursera. Stochastic Processes December 30, 2020Document4 pagesQuiz-6 Answers and Solutions: Coursera. Stochastic Processes December 30, 2020sirj0_hnPas encore d'évaluation
- Homework 7.: Solution: Since X and Y Are Independent Poisson Distributed RandomDocument4 pagesHomework 7.: Solution: Since X and Y Are Independent Poisson Distributed RandomEni SawitriPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculus2014 Lecturenote 10 9Document8 pagesCalculus2014 Lecturenote 10 9盧思宇Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman Equation ExplainedDocument7 pagesHamilton-Jacobi-Bellman Equation ExplainedMakinita CerveraPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Probability TheoryDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Probability TheoryarjunvenugopalacharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamic Programming: Quantitative Macroeconomics (Econ 5725)Document55 pagesDynamic Programming: Quantitative Macroeconomics (Econ 5725)Lhakpa Tshering SherpaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hw3sol 21015 PDFDocument13 pagesHw3sol 21015 PDFPei JingPas encore d'évaluation
- Stopping Time Markov ProcessesDocument19 pagesStopping Time Markov Processesalvin3141Pas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation Asian OptionsDocument8 pagesPresentation Asian OptionsedemPas encore d'évaluation
- FormulaDocument1 pageFormulaGod is lovePas encore d'évaluation
- Discrete Continuous: P X X F X X P XDocument4 pagesDiscrete Continuous: P X X F X X P XKevin YauPas encore d'évaluation
- wst211 Exam 2015 MemoDocument7 pageswst211 Exam 2015 Memoyaseenayob56Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 6Document8 pagesLecture 6ranvPas encore d'évaluation
- Stochastic Calculus II Exercise Sheet 9Document2 pagesStochastic Calculus II Exercise Sheet 9DIAPas encore d'évaluation
- Convex Module BDocument29 pagesConvex Module Bchinaski06Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 5: First Order Linear Differential Equations: William Mccallum 6 September 2005Document4 pagesLesson 5: First Order Linear Differential Equations: William Mccallum 6 September 2005RaymondPas encore d'évaluation
- Classes of Operators On Hilbert Spaces Extended Lecture NotesDocument24 pagesClasses of Operators On Hilbert Spaces Extended Lecture Notestalha azanPas encore d'évaluation
- Suggested Solutions To Test: Email Address: Ymei@math - Cuhk.edu - Hk. (Any Questions Are Welcome!)Document3 pagesSuggested Solutions To Test: Email Address: Ymei@math - Cuhk.edu - Hk. (Any Questions Are Welcome!)Bryan Steve PichuchoPas encore d'évaluation
- Direct_Transcription_Using_Single_Point_Collocation__for_students_ (1)Document6 pagesDirect_Transcription_Using_Single_Point_Collocation__for_students_ (1)marion.martin031995Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 2b SolutionsDocument12 pagesAssignment 2b SolutionsArfaz HussainPas encore d'évaluation
- Properties of The Wave Equation On RDocument12 pagesProperties of The Wave Equation On RElohim Ortiz CaballeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Homework: Nonlinear RegressionDocument5 pagesHomework: Nonlinear RegressionmaxPas encore d'évaluation
- Tables of The Legendre Functions P—½+it(x): Mathematical Tables SeriesD'EverandTables of The Legendre Functions P—½+it(x): Mathematical Tables SeriesPas encore d'évaluation
- Evans Jovanovic 1989Document21 pagesEvans Jovanovic 1989Kevin AndrewPas encore d'évaluation
- Islam Panel DataDocument45 pagesIslam Panel DataKevin AndrewPas encore d'évaluation
- Cross Countrasdy CepDocument98 pagesCross Countrasdy CepKevin AndrewPas encore d'évaluation
- On The Mechanics of Firm Growth: Erzo G. J. LuttmerDocument27 pagesOn The Mechanics of Firm Growth: Erzo G. J. LuttmerKevin AndrewPas encore d'évaluation
- Answerps 1Document8 pagesAnswerps 1Kevin AndrewPas encore d'évaluation
- Economics Text BooksDocument4 pagesEconomics Text BooksKevin Andrew100% (1)
- Economics Text BooksDocument4 pagesEconomics Text BooksKevin Andrew100% (1)
- Jehle and Reny SolutionsDocument33 pagesJehle and Reny SolutionsKevin Andrew80% (10)
- Graduate Macro Theory II: Notes on Value Function IterationDocument10 pagesGraduate Macro Theory II: Notes on Value Function IterationBruno AvilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Residential Energy Scheduling For Variable Weather Solar Energy Based On Adaptive Dynamic ProgrammingDocument11 pagesResidential Energy Scheduling For Variable Weather Solar Energy Based On Adaptive Dynamic ProgrammingChaitali moreyPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy Allocation and Utilization For Wirelessly Powered Iot NetworksDocument11 pagesEnergy Allocation and Utilization For Wirelessly Powered Iot NetworksFritz FatigaPas encore d'évaluation
- Economic DynamicDocument191 pagesEconomic DynamicMarcoLesthrPas encore d'évaluation
- 2011 07 A Short Note On The Tobin Tax The Costs and Benefts of A Tax On Financial Transactions EDHECDocument72 pages2011 07 A Short Note On The Tobin Tax The Costs and Benefts of A Tax On Financial Transactions EDHECVincent_Delaru_4396Pas encore d'évaluation
- Stochastic Control PrincetonDocument14 pagesStochastic Control PrincetonSamrat MukhopadhyayPas encore d'évaluation
- A Brief Introduction To Differential GamesDocument16 pagesA Brief Introduction To Differential GamesMohamedHasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Operations Research 9th Edition Hillier Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Operations Research 9th Edition Hillier Solutions Manualcleopatrafreyane8c100% (17)
- A Reinforcement Learning Approach For Inventory ReplenishmentDocument11 pagesA Reinforcement Learning Approach For Inventory ReplenishmentSyauqi Hidayat BaihaqiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sp14 Cs188 Lecture 9 - Mdps IIDocument48 pagesSp14 Cs188 Lecture 9 - Mdps IIuser84541561Pas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamic Programming Algorithm Explained in ECE 551 LectureDocument11 pagesDynamic Programming Algorithm Explained in ECE 551 Lectureadambose1990Pas encore d'évaluation
- Singapore Institute of Management: University of London Preliminary Exam 2015Document5 pagesSingapore Institute of Management: University of London Preliminary Exam 2015viktor6Pas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamic Programming MethodDocument3 pagesDynamic Programming Methodbobo411Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chess AI: Competing Paradigms For Machine Intelligence: Shiva Maharaj Nick Polson Alex TurkDocument15 pagesChess AI: Competing Paradigms For Machine Intelligence: Shiva Maharaj Nick Polson Alex TurkDomingo IslasPas encore d'évaluation
- AE8803 Final Presentation Manan GandhiDocument23 pagesAE8803 Final Presentation Manan Gandhimgandhi4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamic Programming....Document4 pagesDynamic Programming....Nidz BhatPas encore d'évaluation
- Hubbard, R. G. (1994) - Investment Under Uncertainty Keeping One's Options Open. Journal of Economic Literature, 1816-1831 PDFDocument17 pagesHubbard, R. G. (1994) - Investment Under Uncertainty Keeping One's Options Open. Journal of Economic Literature, 1816-1831 PDFlcr89Pas encore d'évaluation
- C B C N P D M Decision Theory, Reinforcement Learning, and The BrainDocument25 pagesC B C N P D M Decision Theory, Reinforcement Learning, and The BrainGaoudam NatarajanPas encore d'évaluation
- RLbook Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesRLbook Solutions ManualmeajagunPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Operations Research 9Th Edition Hillier Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument47 pagesIntroduction To Operations Research 9Th Edition Hillier Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFchihungqo9td5100% (10)
- Dynammic Programming Shortest RouteDocument18 pagesDynammic Programming Shortest RouteJodi AkbarPas encore d'évaluation
- Forward Thinking and Family Support: Explaining Retirement and Old Age Labor Supply in IndonesiaDocument59 pagesForward Thinking and Family Support: Explaining Retirement and Old Age Labor Supply in IndonesiaDoãn Tâm LongPas encore d'évaluation
- A Dynamic Theory of Public Spending, Taxation and DebtDocument36 pagesA Dynamic Theory of Public Spending, Taxation and DebtLuis Carlos Calixto RodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- 09 Forward Differential Dynamic ProgrammingDocument18 pages09 Forward Differential Dynamic ProgrammingMuslikhudinPas encore d'évaluation
- Reinforcement Learning and Optimal Control Textbook ChapterDocument42 pagesReinforcement Learning and Optimal Control Textbook ChapterChainszzPas encore d'évaluation
- High-Dimensional Continuous Control Using Generalized Advantage Estimation-1506.02438v5Document14 pagesHigh-Dimensional Continuous Control Using Generalized Advantage Estimation-1506.02438v5scribrrrrPas encore d'évaluation
- DD Unit 5. SlidesDocument27 pagesDD Unit 5. SlidesThanos GowdaPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Literacy JEP 2014Document40 pagesFinancial Literacy JEP 2014Sindhuja BhaskaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Methods For Truck Dispatching in Open-Pit MiningDocument141 pagesMethods For Truck Dispatching in Open-Pit MiningGuilherme Bastos67% (3)
- HJB EquationsDocument38 pagesHJB EquationsbobmezzPas encore d'évaluation