Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Avl Trees
Transféré par
Vinuta Jamakhandi0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
12 vues7 pagesAVL TREES are height-balanced trees. There is a limit placed on the amount of difference allowed between the heights of any two subtrees sharing a common root. The maximum allowalble diffrence in the AVL tree is ONE. Maintaining a tree in AVL form as new nodes are inserted involves the use of a set of four possible rotations. Each of the rotations is confined to a single, local area of the tree. The
Description originale:
Titre original
AVL_TREES
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentAVL TREES are height-balanced trees. There is a limit placed on the amount of difference allowed between the heights of any two subtrees sharing a common root. The maximum allowalble diffrence in the AVL tree is ONE. Maintaining a tree in AVL form as new nodes are inserted involves the use of a set of four possible rotations. Each of the rotations is confined to a single, local area of the tree. The
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
12 vues7 pagesAvl Trees
Transféré par
Vinuta JamakhandiAVL TREES are height-balanced trees. There is a limit placed on the amount of difference allowed between the heights of any two subtrees sharing a common root. The maximum allowalble diffrence in the AVL tree is ONE. Maintaining a tree in AVL form as new nodes are inserted involves the use of a set of four possible rotations. Each of the rotations is confined to a single, local area of the tree. The
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 7
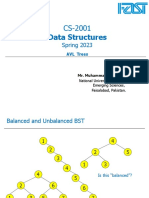
AVL TREES
Problem of indexing with binary trees:
Binary searching requires too many seeks.
Keeping an index in sorted order is expensive.
This is where AVL trees come into picture.
WHATS AN AVL TREE??
AVL tree is a height-balanced tree.
In height_balanced tree there is a limit placed on
the amount of difference allowed between the
heights of any two subtrees sharing a common
root.
The maximum allowalble diffrence in the AVL tree
is ONE.
HB(1) is an AVL tree.
Main features that make AVL trees
important :
By setting a maximum allowable difference in the
height of any two subtrees, AVL trees guarantee a
minimum level of performance in searching.
Maintaining a tree in AVL form as new nodes are
inserted involves the use of a set of four possible
rotations. Each of the rotations is confined to a
single, local area of the tree. The most complex of
the rotations requires only five pointer
reassingnments.
Simpler version of previous slide:
WHY USE AVL TREES??
To reduce the depth of the tree and hence reduce
comparisons while searching for a key or inserting
a key.
By at most five pointer reassignments a new
node is inserted.
AVL trees provide an
acceptable solution for the
problem of keeping index in
sorted order.
THANK YOU!! ;)...
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledAnand SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Research Paper On Application of Avl TreeDocument6 pagesResearch Paper On Application of Avl Treehfuwwbvkg100% (1)
- Data StructureDocument19 pagesData StructurekokigokulPas encore d'évaluation
- Data StructureDocument17 pagesData StructureFaisal JafferPas encore d'évaluation
- Research Paper On Avl TreeDocument4 pagesResearch Paper On Avl Treewtdcxtbnd100% (1)
- Data Structure Unit 3Document7 pagesData Structure Unit 3Ritik SainiPas encore d'évaluation
- DSA Ch8 Ch9 AVL TreesDocument82 pagesDSA Ch8 Ch9 AVL TreesDũng TrầnPas encore d'évaluation
- B TreeDocument16 pagesB TreeVijaya Kumar VadladiPas encore d'évaluation
- AVL TreesDocument25 pagesAVL TreesjoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Avl Tree Research PaperDocument7 pagesAvl Tree Research Papertug0l0byh1g2100% (1)
- Implementing AVL Trees - Rotations, Insertion, DeletionDocument6 pagesImplementing AVL Trees - Rotations, Insertion, Deletionprajakta kudalePas encore d'évaluation
- DS FREE WRITING 6Document3 pagesDS FREE WRITING 6abinashreddy792Pas encore d'évaluation
- AVL Trees Balanced Binary SearchDocument26 pagesAVL Trees Balanced Binary SearchArbaz AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 13 - AVL TreesDocument82 pagesLecture 13 - AVL TreesPrhna Wala BachaPas encore d'évaluation
- DS TreeDocument11 pagesDS TreeAdithya UcPas encore d'évaluation
- AVL-Trees: Advance Analysis of AlgorithmDocument17 pagesAVL-Trees: Advance Analysis of Algorithmuzma_abidi8886Pas encore d'évaluation
- Session27 (1)Document17 pagesSession27 (1)kreshmithasruthiPas encore d'évaluation
- AVL TreesDocument20 pagesAVL TreesKaranvir Kaur DhindsaPas encore d'évaluation
- Avl TreeDocument24 pagesAvl Treeharishan_sciPas encore d'évaluation
- 7376212ad158-Assignment Series 71Document6 pages7376212ad158-Assignment Series 71ANANDARAJ SPas encore d'évaluation
- Searching Pt3Document28 pagesSearching Pt3sriachutPas encore d'évaluation
- Dsa Case Study 27Document4 pagesDsa Case Study 27gokulakrishnanab2005Pas encore d'évaluation
- Research Paper On Avl TreesDocument6 pagesResearch Paper On Avl Treesjiyzzxplg100% (1)
- Data Structures and Algorithm: Avl TreeDocument42 pagesData Structures and Algorithm: Avl TreeSarah FatimaPas encore d'évaluation
- AVL Tree Definition and PropertiesDocument3 pagesAVL Tree Definition and PropertiesAkash MadanPas encore d'évaluation
- avl treeDocument10 pagesavl treeshift2cs22Pas encore d'évaluation
- Avl TreeDocument10 pagesAvl TreeMALATHY AMARNATHPas encore d'évaluation
- AVL Tree Datastructure Explained - Self Balancing Binary Search TreeDocument7 pagesAVL Tree Datastructure Explained - Self Balancing Binary Search TreeSaumya TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- AVL Tree: A Self-Balancing Binary Search TreeDocument5 pagesAVL Tree: A Self-Balancing Binary Search TreeNitul PathakPas encore d'évaluation
- Superior University LahoreDocument13 pagesSuperior University Lahorevtpvj5wpgsPas encore d'évaluation
- TreesDocument16 pagesTreesLavanya JPas encore d'évaluation
- Avl PDFDocument60 pagesAvl PDFaliPas encore d'évaluation
- BURHANDocument4 pagesBURHANZaini Pehlwan GPas encore d'évaluation
- AVLTreesDocument70 pagesAVLTreesAman Pushpinder BirdiPas encore d'évaluation
- AVL TreesDocument34 pagesAVL TreesSaleha MasoodPas encore d'évaluation
- AVL Tree OperationsDocument23 pagesAVL Tree Operationsprasad barlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 4: Balanced Binary Search TreesDocument11 pagesLecture 4: Balanced Binary Search TreesNavia RadhakrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 5, 1Document41 pagesLecture 5, 1baukaPas encore d'évaluation
- 3d3f0ef1 1603358945498Document38 pages3d3f0ef1 1603358945498Hai SuriPas encore d'évaluation
- PPT7 - AVL TreeDocument30 pagesPPT7 - AVL TreeRapik HardiantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment Data StructuerDocument5 pagesAssignment Data StructuerHaseeb ZahidPas encore d'évaluation
- AVL Tree Data StructureDocument7 pagesAVL Tree Data Structurewhisper hhmmPas encore d'évaluation
- AVL Trees: Spring 2007Document27 pagesAVL Trees: Spring 2007mukesh427Pas encore d'évaluation
- Binary Search Tree Structure and OperationsDocument22 pagesBinary Search Tree Structure and OperationsJatin ValechaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 4Document8 pagesAssignment 4Venkata Harsha Vardhan KinjarapuPas encore d'évaluation
- UntitledDocument72 pagesUntitledrohanPas encore d'évaluation
- AVL Trees: ITCS6114 Algorithms and Data StructuresDocument32 pagesAVL Trees: ITCS6114 Algorithms and Data Structuresmaven patriggePas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 9: AVL-tree 1: CSC2100 Data StructureDocument22 pagesLecture 9: AVL-tree 1: CSC2100 Data StructureMatthew John Sino CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- IT202-DS-Unit 5 - Advanced Search TechniquesDocument87 pagesIT202-DS-Unit 5 - Advanced Search TechniquesBhuvaneshwari BPas encore d'évaluation
- Árboles Binarios de Búsqueda (ABB) : ABB Árbol Binario Ordenado Según Uno o Más Criterios Cada Nodo Tiene Dos HijosDocument31 pagesÁrboles Binarios de Búsqueda (ABB) : ABB Árbol Binario Ordenado Según Uno o Más Criterios Cada Nodo Tiene Dos HijosCamilo RojasPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Structures & Algorithms: AVL TreeDocument20 pagesData Structures & Algorithms: AVL TreeDimas Maulana IshaqPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 11 Advanced Data Structures: Structure Page NosDocument17 pagesUnit 11 Advanced Data Structures: Structure Page NosSaurav JhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Avl 1Document6 pagesAvl 1dharna28gsPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Structures Tree Types and TraversalDocument12 pagesData Structures Tree Types and TraversalEsdras Benjamin Cotto RevolorioPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 16 AVL TreesDocument9 pagesLecture 16 AVL TreesAll Rounded GamerPas encore d'évaluation
- Trees: Balanced SearchDocument84 pagesTrees: Balanced SearchwircexdjPas encore d'évaluation
- AVL tree balancing algorithmDocument5 pagesAVL tree balancing algorithmepanicu2000Pas encore d'évaluation
- AVL Tree Balancing Through RotationsDocument43 pagesAVL Tree Balancing Through Rotationskinghs786Pas encore d'évaluation
- Naples, Sorrento & the Amalfi Coast Adventure Guide: Capri, Ischia, Pompeii & PositanoD'EverandNaples, Sorrento & the Amalfi Coast Adventure Guide: Capri, Ischia, Pompeii & PositanoÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Arizona, Utah & New Mexico: A Guide to the State & National ParksD'EverandArizona, Utah & New Mexico: A Guide to the State & National ParksÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- The Bahamas a Taste of the Islands ExcerptD'EverandThe Bahamas a Taste of the Islands ExcerptÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Japanese Gardens Revealed and Explained: Things To Know About The Worlds Most Beautiful GardensD'EverandJapanese Gardens Revealed and Explained: Things To Know About The Worlds Most Beautiful GardensPas encore d'évaluation
- New York & New Jersey: A Guide to the State & National ParksD'EverandNew York & New Jersey: A Guide to the State & National ParksPas encore d'évaluation
- South Central Alaska a Guide to the Hiking & Canoeing Trails ExcerptD'EverandSouth Central Alaska a Guide to the Hiking & Canoeing Trails ExcerptÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)