Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Motoneuron Output Is Conduction of Signals From The
Transféré par
Tanvir AhmedDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Motoneuron Output Is Conduction of Signals From The
Transféré par
Tanvir AhmedDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
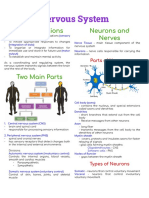
NERVOUS SYSTEM
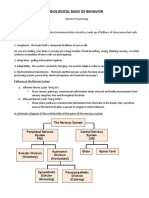
The nervous system is an organ system containing a network of
specialized cells called neurons that coordinate the actions of
an animal and transmit signals between different parts of its
body.
Nervous system performs three overlapping functions of
- sensor input
- integration and
- motor output
The sensory input is sensing the environment and changes
around an organism, and is carried out by sensory organs like
eyes, ears, nose, tongue, and skin, some of them performing
simultaneously.
The integration involves processing of information, and is
carried out by the central nervous system (CNS), which consists
of brain and spinal cord.
Motoneuron output is conduction of signals from the
integration center, the CNS, and is carried out by a group of
effector cells, the muscle cells or gland cells, which actually
carry out body’s responses to external stimuli.
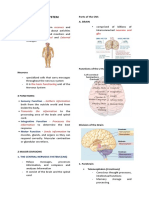
Fig: Overview of a vertebrate nervous system
Both sensory input and motor output signals are carried through
nerves, which are long ropelike structures made from nerve
cells. Nerve cells are two types:
- neurons (carry through signals)
- glia (provide supporting structures and maintenance
of neuronal cells.)
The nerves that communicate sensor and motor signals between
the central nervous system and rest of the body are collectively
referred to as peripheral nervous system (PNS).
Sensory inputs are received by receptor
cells located in sensory organs
Signals are carried through sensory
neurons of the PNS into the CNS
Processi
ng
instructions are communicated through the
motor neurons of the PNS to effector cells
Communication from the receptor cells to effector cells is
carried in two forms – chemical and electrical.
Since communication of information involves more than one
cells, the communication is through special chemicals called
neurotrasmitters or a specialized form of electric signal called
action potential.
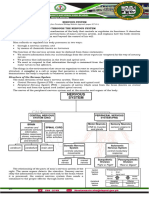
Organization:
Nervous
System
Central Nervous Peripheral Nervous
System System
Motor Sensory
Brain Spinal Cord
Division Division
- -
Information Communicati (Efferent) (Afferent)
processing on between
- Memory brain and
PNS
External Internal
Environmen Environme
t nt
Autonomous Somatic Nervous
Nervous System System
Sympathetic Parasympathetic
Division Division
- Increase - Conserve and
energy gain energy
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Unit III Nervous System and ElectromyographyDocument100 pagesUnit III Nervous System and ElectromyographymanasiPas encore d'évaluation
- An Introduction To Nervous SystemDocument27 pagesAn Introduction To Nervous Systemprasun_v100% (2)
- The Nervous SystemDocument37 pagesThe Nervous SystemNo NamePas encore d'évaluation
- Nervous Tissues HandoutsDocument6 pagesNervous Tissues HandoutsKelly TrainorPas encore d'évaluation
- Nervous SystemDocument18 pagesNervous SystemArianne Jen GenotivaPas encore d'évaluation
- AnaPhy Unit 5 Notes ReviewerDocument16 pagesAnaPhy Unit 5 Notes Reviewer쥬얼이Pas encore d'évaluation
- HAPL12M Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesHAPL12M Nervous SystemCarl Axel AzurPas encore d'évaluation
- ??????? ?????? H. Idris N. Macmod A. Mangondato M. OmarDocument70 pages??????? ?????? H. Idris N. Macmod A. Mangondato M. OmarHestia GreyertPas encore d'évaluation
- NERVOUS AND ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Notes and ActivityDocument9 pagesNERVOUS AND ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Notes and ActivitySamantha SaavedraPas encore d'évaluation
- Functions of The NS (Midterms)Document4 pagesFunctions of The NS (Midterms)initaygracileshaynePas encore d'évaluation
- Biological Basis of BehaviorDocument6 pagesBiological Basis of BehaviorLyanna MormontPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Reviewer 3rd Quarter For Grade 10 BiologyDocument19 pagesScience Reviewer 3rd Quarter For Grade 10 Biologylesterjohns150Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 3 The Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesLecture 3 The Nervous SystemJanvi MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Nervous System: DR - Arshad Ali DPT Ipm&R Kmu Ms NMPT RiphahDocument24 pagesThe Nervous System: DR - Arshad Ali DPT Ipm&R Kmu Ms NMPT RiphahAzhar MehmoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Nervous SystemDocument54 pagesNervous SystemNathaniel BudayPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit-Two Biological Bases of BehaviorDocument27 pagesUnit-Two Biological Bases of Behaviorरोशन सिग्देलPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit-Two Biological Bases of BehaviorDocument27 pagesUnit-Two Biological Bases of Behaviorरोशन सिग्देलPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy Lecture On Nervous SystemDocument172 pagesAnatomy Lecture On Nervous SystemandreabreePas encore d'évaluation
- AnaPhy Lab Nervous NotesDocument7 pagesAnaPhy Lab Nervous NotesDING ANG BATOPas encore d'évaluation
- Nervous System 2Document23 pagesNervous System 2TinPas encore d'évaluation
- Oral Exam ReviewerDocument48 pagesOral Exam ReviewerFayena JosePas encore d'évaluation
- Neuron Part IDocument15 pagesNeuron Part IjohnathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Science-Reviewer-3rd-Quarter For Grade 10 BiologyDocument19 pagesScience-Reviewer-3rd-Quarter For Grade 10 BiologyIce Cold94% (86)
- Oral Exam ReviewerDocument39 pagesOral Exam ReviewerFayena JosePas encore d'évaluation
- Human Bio - Divofnervoussystem - 091123Document2 pagesHuman Bio - Divofnervoussystem - 091123Nicole MercadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 12 - An Introduction To The Nervous System: Peripheral Nerves)Document7 pagesChapter 12 - An Introduction To The Nervous System: Peripheral Nerves)tomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayPas encore d'évaluation
- Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesNervous SystemPogi BearPas encore d'évaluation
- NCM 106 Module 2MDocument59 pagesNCM 106 Module 2MAlyssa Claire TumulakPas encore d'évaluation
- G10 Science Q3 Week 3 Nervous SystemDocument29 pagesG10 Science Q3 Week 3 Nervous Systemhimotoumaruchan009Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Physical Self: Brain and The Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesThe Physical Self: Brain and The Nervous System2022105340Pas encore d'évaluation
- 15) Central Nervous SystemDocument96 pages15) Central Nervous SystemyohdeforemostPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7 AnaphyDocument11 pagesChapter 7 AnaphySymonette OcturaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anaphy Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesAnaphy Nervous SystemAndrea SaldivarPas encore d'évaluation
- 8.1 The Nervous and Endocrine Systems: Neurones (Or Neurons)Document14 pages8.1 The Nervous and Endocrine Systems: Neurones (Or Neurons)KasspapPas encore d'évaluation
- Nervous System 1Document13 pagesNervous System 1wasim akhtarPas encore d'évaluation
- FINALS 2 5-Nervoustissue-161014172642Document56 pagesFINALS 2 5-Nervoustissue-161014172642Maika Ysabelle RavaloPas encore d'évaluation
- Control and Coordination PDFDocument24 pagesControl and Coordination PDFMUZEER PASHAPas encore d'évaluation
- Neuro HandoutDocument13 pagesNeuro HandoutFatima Shaira PulahongPas encore d'évaluation
- Organization, Neurons, Basic Functions of Synapses, and NeurotransmittersDocument3 pagesOrganization, Neurons, Basic Functions of Synapses, and Neurotransmitters22 - Fernandez, Lyza Mae D.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Anaphy - The Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesAnaphy - The Nervous SystemYo1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nervous System 2023Document31 pagesNervous System 2023Rayjie G RulePas encore d'évaluation
- G10 Science Q3 Nervous SystemDocument28 pagesG10 Science Q3 Nervous SystemEvadine LeePas encore d'évaluation
- At The Base of The Brain Stimulates Growth and Controls The Functions of Other Glands Below The Voice Box Thyroxin, CalcitoninDocument8 pagesAt The Base of The Brain Stimulates Growth and Controls The Functions of Other Glands Below The Voice Box Thyroxin, CalcitoninAubrey Jen MañasPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7Document15 pagesChapter 7Bea SeloterioPas encore d'évaluation
- Body System II 1 Nerv 1Document77 pagesBody System II 1 Nerv 1rrq8cwk2gnPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2 Biological Foundations of Behaviour - Student OutlineDocument43 pagesModule 2 Biological Foundations of Behaviour - Student OutlineDweep BajajPas encore d'évaluation
- Describe The Structure and Function of Each Component of The Nervous SystemDocument29 pagesDescribe The Structure and Function of Each Component of The Nervous Systemsiska yantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesNervous SystemChristine Joanne CelendroPas encore d'évaluation
- Nervous System Class 10Document35 pagesNervous System Class 10Just JaenPas encore d'évaluation
- The Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesThe Nervous Systemhajra0325Pas encore d'évaluation
- Neurological System Assessment Part 1 - NCM 101 H.ADocument5 pagesNeurological System Assessment Part 1 - NCM 101 H.ALexie KepnerPas encore d'évaluation
- Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesNervous SystemJake SimPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2 - Nervous SystemDocument49 pagesUnit 2 - Nervous SystemAbdullah MohammedPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Regulatory SystemDocument37 pagesHuman Regulatory SystemRudolfPas encore d'évaluation
- 2) NeurophysiologyDocument81 pages2) NeurophysiologyyohdeforemostPas encore d'évaluation
- Gen Bio 4 Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesGen Bio 4 Nervous SystemKaela Beatrice Sy LatoPas encore d'évaluation
- BioPsychology Chapter 34Document10 pagesBioPsychology Chapter 34Johnreih BanggaPas encore d'évaluation
- PChapter 12 Nerve Tissue PDFDocument3 pagesPChapter 12 Nerve Tissue PDFRuel MateoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Nervous System - NotesDocument12 pagesThe Nervous System - NotesLol lol100% (2)
- Mind at Rest: How Neuron Structure Evolves in the Sleep Cycle.D'EverandMind at Rest: How Neuron Structure Evolves in the Sleep Cycle.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Stress! Can Interfere With Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesStress! Can Interfere With Endocrine SystemInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Histology of The EyeDocument91 pagesHistology of The EyeFazira EkmaPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQs TBIDocument9 pagesMCQs TBIAkbar Ali100% (3)
- FR Radius UlnaDocument49 pagesFR Radius UlnaEkha SaraswatiPas encore d'évaluation
- 00 Neuro Cheat SheetDocument2 pages00 Neuro Cheat SheetFranz LibrePas encore d'évaluation
- Shavasana ScriptDocument3 pagesShavasana Scriptstiliyanstoyanov28Pas encore d'évaluation
- Radical Neck Dissection: (RND) Classification, Indication and TechniquesDocument42 pagesRadical Neck Dissection: (RND) Classification, Indication and TechniquesPatrycyaPas encore d'évaluation
- CTCB in Mandibular ParesthesiaDocument3 pagesCTCB in Mandibular ParesthesiaAdrian OlveraPas encore d'évaluation
- Splints For The NBCOT: Stephanie Shane OTR/L NBCOT TutorDocument29 pagesSplints For The NBCOT: Stephanie Shane OTR/L NBCOT TutorMarina EskandrousPas encore d'évaluation
- Step 1: Reverse Out Knee PainDocument11 pagesStep 1: Reverse Out Knee PainGrant Cherry100% (3)
- Kuis Modul 1.2 1Document5 pagesKuis Modul 1.2 1Wijoyo KusumoPas encore d'évaluation
- Orthodontic Treatment of A Severe Combined Anterior and Posterior Open Bite Case, Involving AnkylosisDocument8 pagesOrthodontic Treatment of A Severe Combined Anterior and Posterior Open Bite Case, Involving Ankylosisgifar ihsanPas encore d'évaluation
- Thoracic and Prothoracic Leg Neuromuscular System of The Praying Mantid, Sphodromantis Lineola (Burmeister)Document14 pagesThoracic and Prothoracic Leg Neuromuscular System of The Praying Mantid, Sphodromantis Lineola (Burmeister)JoPas encore d'évaluation
- PrinciplesofOsteopathicMedicine PDFDocument5 pagesPrinciplesofOsteopathicMedicine PDFsuso73Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cat Vs Dog Anatomy Anatomical DifferencesDocument2 pagesCat Vs Dog Anatomy Anatomical DifferencesAlliPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomi Jurnal PDFDocument13 pagesAnatomi Jurnal PDFHelda AudyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Traumatic Tympanic Membrane PerforationDocument7 pagesTraumatic Tympanic Membrane PerforationNada ZultiPas encore d'évaluation
- Core Knowledge in Orthopaedics - SpineDocument330 pagesCore Knowledge in Orthopaedics - Spinedexx12780% (5)
- Neurological Examination in Spinal Cord Injury NewDocument18 pagesNeurological Examination in Spinal Cord Injury NewPratyush RanjanPas encore d'évaluation
- Checkley's Natural Method of Physical TrainingDocument234 pagesCheckley's Natural Method of Physical TrainingCullen O'Gorman100% (2)
- Upper Limb McqsDocument48 pagesUpper Limb McqsFarhad Ali100% (2)
- Chapter04 Massage TechniquesDocument40 pagesChapter04 Massage TechniquesRonn LlavePas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment Skeletal Tabalba DoneDocument4 pagesAssignment Skeletal Tabalba DoneShane V. TabalbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Get Anatomy On Occupational StandardDocument39 pagesGet Anatomy On Occupational StandardmisawPas encore d'évaluation
- Ornac Standards PositioningDocument7 pagesOrnac Standards PositioningAndika X NandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Serratus Anterior Muscle Strength and Endurance TestsDocument12 pagesSerratus Anterior Muscle Strength and Endurance Testsrudhras22Pas encore d'évaluation
- Taste and SmellDocument22 pagesTaste and SmellabdirizakPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy of The GI TractDocument174 pagesAnatomy of The GI TractBenjamin Prabhu100% (1)
- Anatomy & Physiology Unit 1Document29 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Unit 1Priyanjali SainiPas encore d'évaluation
- An Electromyographic Analysis of Trunk and Hip Extensor Muscles During Bridging Exercises - Effect of Voluntary Control of The Pelvic TiltDocument3 pagesAn Electromyographic Analysis of Trunk and Hip Extensor Muscles During Bridging Exercises - Effect of Voluntary Control of The Pelvic TiltNicolás ManonniPas encore d'évaluation