Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Thermal Power Plant
Transféré par
Shailesh Sankdasariya100%(3)100% ont trouvé ce document utile (3 votes)
5K vues8 pagesREFERANCE.
CONCLUSION.
STATUS
ADVANTAGES & DISADVANTAGES.
VARIOUS FACTOR
VARIOUS TYPES
WORKING
BLOCK DIAGRAM&IT’S COMPONANTS.
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentREFERANCE.
CONCLUSION.
STATUS
ADVANTAGES & DISADVANTAGES.
VARIOUS FACTOR
VARIOUS TYPES
WORKING
BLOCK DIAGRAM&IT’S COMPONANTS.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
100%(3)100% ont trouvé ce document utile (3 votes)
5K vues8 pagesThermal Power Plant
Transféré par
Shailesh SankdasariyaREFERANCE.
CONCLUSION.
STATUS
ADVANTAGES & DISADVANTAGES.
VARIOUS FACTOR
VARIOUS TYPES
WORKING
BLOCK DIAGRAM&IT’S COMPONANTS.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 8
Thermal Power Plant ENERGY SYSTEMS
BY SHAILESH B. PATEL -090760111025
THERMAL POWER
PLANT
CONTENTS:-
0!J BLOCK DIAGRAM & IT'S COMPONANTS. 0!J WORKING CYCLES.
0!J DETAILED PROCESS OF POWER GENERATION. 0!J TYPES OF THERMAL POWER PLANTS.
0!J ADVANTAGES & DISADVANTAGES.
0!J KEY FACTS ABOUT THERMAL POWER PLANTS. 0!J STATUS OF THERMAL POWER PLANT IN INDIA. 0!J CONCLUSION.
0!J REFERANCE.
THERMAL POWER PLANT ENERGY SYSTEMS SANKDASARIYA SHAILESH B. ENRL NO-090760 111025 SSASIT (E.C. DEPARTMENT)
SSASIT
I BY SHAILESH B. PATEL(E.C. DEPARTMENT)
Thermal Power Plant ENERGY SYSTEMS
BY SHAILESH B. PATEL -090760111025
THERMAL POWER PLANT
~AIM:- TO STUDY ABOUT THERMAL POWER PLANT.
This experiment explains the basics of the working of a coal fired thermal power plant. More than half of the electricity generated in the world is by using coal as the primary fuel.The function of the coal fired thermal power plant is to convert the energy available in the coal to Electricity.Coal power plants work by using several steps to convert stored energy in coal to usable electricity that we find in our home that powers our lights, computers, and sometimes, back into heat for our homes.
~BLOCK DIAGRAM:-
Components of a coal"flroo thermal plant
j, Coal Supply
Il~ •
~ .
.. . I ','
I
Generator
•
,~I
Sub~18tion T ran sfurm er
Truck. FA
...
Water TreBtment Plant
~.".""'.'.".' .. '.
"" , ',',' • I
, '- . ',' , .
, . .
In thermal generating plants, fuel is converted into thermal energy to heat water, making steam. The steam turns an engine (turbine), creating mechanical energy to run a generator. Magnets turn inside the generator, producing electric energy.Coal, oil and gas are used to make thermal electricity. They all work basically the same way (with a few exceptions: for example, in an oil- or gas-fired plant, fuel is piped to the boiler).
SSASIT
I BY SHAILESH B. PATEL(E.C. DEPARTMENT)
Thermal Power Plant ENERGY SYSTEMS
BY SHAILESH B. PATEL -090760111025
1-COAL SUPPLY - After haulers drop offthe coal, a set of crushers and conveyors prepare and deliver the coal to the power plant. When the plant needs coal, coal "hoppers" crush coal to a few inches in size and conveyor belts bring the coal inside.
2-COAL PULVERIZER - The belts dump coal into a huge bin (pulverizer), which reduces the coal to a fine powder. Hot air from nearby fans blows the powdered coal into huge furnaces (boilers).
3-BOILER - The boiler walls are lined with many kilometres of pipe filled with water. As soon as the coal enters the boiler, it instantly catches fire and burns with high intensity (the temperatures inside the furnace may climb to 1,300° C). This heat quickly boils the water inside the pipes, changing it into steam.
4-PRECIPITATORS AND STACK - As the coal burns, it produces emissions (carbon dioxide, sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides) and ash.The gases, together with the lighter ash (fly ash), are vented from the boiler up the stack. Huge air filters called electrostatic precipitators remove nearly all the fly ash before it is released into the atmosphere. The heavier ash (bottom ash) collects in the bottom ofthe boilers and is removed.
5-TURBINE AND GENERATOR - Meanwhile, steam moves at high speed to the turbines, massive drums with hundreds of blades turned at an angle, like the blades of a fan.As jets of high-pressure steam emerge from the pipes, they propel the blades, causing the turbine to spin rapidly. A metal shaft connects the turbine to a generator. As the turbine turns, it causes an electro-magnet to turn inside coils of wire in the generator. The spinning magnet puts electrons in motion inside the wires, creating electricity.
6-CONDENSERS AND COOLING WATER SYSTEM - Next, the steam exits the turbines and passes over cool tubes in the condenser. The condensers capture the used steam and transform it back to water. The cooled water is then pumped back to the boiler to repeat the heating process. At the same time, water is piped from a reservoir or river to keep the condensers constantly cool. This cooling water, now warm from the heat exchange in the condensers, is released from the plant.
7-WATER PURIFICATION - To reduce corrosion, plants purify water for use in the boiler tubes. Wastewater is also treated and pumped out to holding ponds.
8-ASH SYSTEMS - Ash is removed from the plant and hauled to disposal sites or ash lagoons. Ash is also sold for use in manufacturing cement.
9-TRANSFORMER AND TRANSMISSION LINES - transformers increase the voltage ofthe electricity generated. transmission lines then carry the electricity at high voltages from the plant to substations in cities and towns.
SSASIT
I BY SHAILESH B. PATEL(E.C. DEPARTMENT)
Thermal Power Plant ENERGY SYSTEMS
BY SHAILESH B. PATEL -090760111025
~WORKING CYCLES:- There are four main circuits in any thermal power plant and these are as given below:
1-COAl & ASH CYClE 2-AIR & GAS CYClE
3-FEED WATER & STEAM CYClE 4-COOLING WATER CYClE
l-COAL & ASH CYCLE -this circuit deals mainly with feeding the boiler with coal for combustion purposes and taking care ofthe ash that is generated during the combustion process and includes equipment and paraphernalia that is used to handle the transfer and storage of coal and ash.
2-AIR & GAS CYCLE - we know that a ir is one of the ma in components of the fire triangle and hence necessary for combustion. Since lots of coal is burnt inside the boiler it needs a sufficient quantity of air which is supplied using either forced draught or induced draught fans. The exhaust gases from the combustion are in turn used to heat the ingoing air through a heat exchanger before being let off in the atmosphere. The equipment which handles all these processes fall under this circuit.
3-FEED WATER & STEAM CYCLE - this section deals with supplying of steam generated from the boiler to the turbines and to handle the outgoing steam from the turbine by cooling it to form water in the condenser so that it can be reused in the boiler plus making good any losses due to evaporation etc.
4-COOLING WATER CYCLE -this part ofthe thermal power plant deals with handling ofthe cooling water required in the system. Since the amount of water required to cool the outgoing steam from the boiler is substantial, it is either taken from a nearby water source such as a river, or it is done through evaporation if the quantity of cooling water available is limited.
~DETAILED PROCESS OF POWER GENERATION IN A THERMAL POWER PLANT:
Boiler
Feed\'Vater heater
Feed pump 2
Feed pump 1
SSASIT
I BY SHAllESH B. PATEl(E.C. DEPARTMENT)
Thermal Power Plant ENERGY SYSTEMS
BY SHAILESH B. PATEL -090760111025
The conversion from coal to electricity takes place in three stages. STAGE 1:
The first conversion of energy takes place in the boiler. Coal is burnt in the boiler furnace to produce heat. Carbon in the coal and Oxygen in the air combine to produce Carbon Dioxide and heat.
STAGE 2:
The second stage is the thermodynamic process.
J-The heat from combustion ofthe coal boils water in the boiler to produce steam. In modern power plant, boilers produce steam at a high pressure and temperature.
2-The steam is then piped to a turbine.
3-The high pressure steam impinges and expands across a number of sets of blades in the turbine. 4-The impulse and the thrust created rotates the turbine.
S-The steam is then condensed and pumped back into the boiler to repeat the cycle.
STAGE 3:
In the third stage, rotation ofthe turbine rotates the generator rotor to produce electricity based of Faraday's Principle of electromagnetic induction.
~TYPES OF THERMAL POWER PLANTS .
Thermal power plants are classified by the type offuel and the type of prime mover installed.
~BY TYPES OF FUEL
l.NUClEAR POWER PLANTS 2.FOSSIL FUElLED POWER PLANTS 3.GEOTHERMAL POWER PLANTS
4.RENEWABLE ENERGY PLANTS OR BIOMASS-FUElLED POWER PLANTS 5. INTEGRATED STEEl MILLS
6.S0LAR THERMAL ElECTRIC PLANTS
l.Nuciear power plants use a nuclear reactor's heat to operate a steam turbine generator. About 20% of electric generation in the USA is produced by nuclear power plants.
2.Fossil fuelled power plants may also use a steam turbine generator or in the case of natural gas fired plants may use a combustion turbine. A coal-fired power station produces electricity by burning coal to generate steam, and has the side-effect of producing a large amount of carbon dioxide, which is released from burning coal and contributes to global warming. About 50% of electric generation in the USA is produced by coal fired power plants.
3.Geothermal power plants use steam extracted from hot underground rocks.
SSASIT
I BY SHAILESH B. PATEL(E.C. DEPARTMENT)
Thermal Power Plant ENERGY SYSTEMS
BY SHAILESH B. PATEL -090760111025
4.Renewable energy plants or biomass-fuelled power plants may be fuelled by waste from sugar cane, municipal solid waste, landfill methane, or other forms of biomass.
5.1n integrated steel mills, blast furnace exhaust gas is a low-cost, although low-energy-density, fuel. Waste heat from industrial processes is occasionally concentrated enough to use for power generation, usually in a steam boiler and turbine.
6.Solar thermal electric plants use sunlight to boil water, which turns the generator.
~BY TYPES OF PRIME MOVERS
1.Steam turbine plants 2.Gas turbine plants 3.Combined cycle plants
4.1nternal combustion reciprocating engines a re used to provide power for isolated commun ities and are frequently used for small cogeneration plants.
5.Microturbines, Stirling engine and internal combustion reciprocating engines are low-cost solutions for using opportunity fuels, such as landfill gas, digester gas from water treatment plants and waste gas from oil production.
~ADVANTAGES & DISADVANTAGES OF THERMAL POWER PLANTS:
~ADVANTAGES:
1. They can be located very conviniently near the load centres.
2. Does not require shielding like required in nuclear power plants.
3.Unlike nuclear power plants whose power production method is difficult, for thermal power plants it is easy if compared.
4. Transmission costs are reduced as they can be set up near the industry.
5. The portion of steam generated can be used as process steam in different industries.
6. Steam engines and turbines can work under 25% of overload capacity.
7. Able to respond changing loads without difficulty.
~DISADVANTAGES:
1. Large amounts of water are required.
2. Great difficulties experienced in coal handling and disposal of ash.
3. Takes long time to be erected and put into action.
4. Maintenance and operating costs are high.
5. With increase in pressure and temperature, the cost of plant increases.
6. Troubles from smoke and heat from the plant.
SSASIT
I BY SHAILESH B. PATEL(E.C. DEPARTMENT)
Thermal Power Plant ENERGY SYSTEMS
BY SHAILESH B. PATEL -090760111025
~KEY FACTS ABOUT COAL-FIRED ELECTRICITY PRODUCTION IN THERMAL POWER PLANTS
In practice to effect these three stages of conversion, many systems and sub systems have to be in service. Also involved are different technologies, like combustion, aerodynamics, heat transfer, thermodynamics, pollution control, and logistics.
As an example consider these facts for typical coal fired power plant of capacity 500 MW. Around 2 million tons of coal will be required each year to produce the continuous power.
Coal combustion in the boiler requires air. Around 1.6 million cubic meter of air in an hour is delivered by air fans into the furnace.
• The ash produced from this combustion is around 200,000 tons per year.
• Electrostatic precipitators capture almost all ofthis ash without dispersing this to the atmosphere. Pollutants from coal power plants like carbon dioxide, sulphur dioxide, and nitrogen oxide can also affect the environment. Thermal power plants are the biggest producers of Carbon Dioxide.
• The boiler for typical 500 MW units produces around 1600 tons per hour of steam at a temperature of 540 to 600 degrees Centigrade. The steam pressures is in the range of 200 bar. The boiler materials are designed to withstand these conditions with special consideration for operational safety.
• Heat transfer from the hot combustion gases to the water in the boiler takes place due to Radiation and convection.
• The Electrical generators carry very large electric currents that produce heat and are be cooled by Hydrogen and water.
• The steam leaving the turbine is condensed and the water is pumped back for reuse in the boiler. To condense all the steam it will require around 50,000 cubic meter per hour of cooling water to be circulated from lakes, rivers or the sea. The water is returned to the source with only an increase of 3 to 4 degrees centigrade to prevent any effect to the environment.
• Apart from the cooling water the power plant also requires around 400 cubic metere per day of fresh water for making up the losses in the water steam cycle.
SSASIT I BY SHAILESH B. PATEL(E.C. DEPARTMENT)
Thermal Power Plant ENERGY SYSTEMS
BY SHAILESH B. PATEL -090760111025
~STATUS OF THERMAL POWER PLANT IN INDIA:
11 UTIARPRADESH
NAME OF POWER STATION CAPACITY (MW)
Kothagndam 240
Gauhati 40
Barauni 150
Bokaro 225
Patratu 400
Rajghat 200
Indraprashstha 350
Badarpur 300
Dhuvaran 530
Ukai 240
Faridabad 200
Panipat 220
Kobra 420
Satpura 300
Nagpur (koradi) 480
Nashik 280
Paras 90
Talcher 254
Neyvelli 600
Eunose 450
Harduaganj 540
Obra 550
Samtaldih 480
Chandrapur 420
Durgapur 290 STATE
1. ANDHRA PRADESH 2 ASSAM
3 BIHAR
4 DELHI
5 GUJARAT
6 HARAYANA
7 MADHYA PRADESH
8 MAHARASH RTRA
9 ORISSA
10 TAMILNADU
12 WEST BENGAL
~CONCLUSION:
Though thermal power energy has so many advantages, the main disadvantage is thermal pollution. Water mainly gets polluted using thermal energy. The automobile industry, textile industry, thermal power plant, nuclear power plant release hot water to the water bodies.
Thermal power plant are goods that produce electricity.Morever,these plants are important to customers and are presumed to have a service life of greater than twenty years.Accordigly,thereliability of a power plant is considered most important,followed by after-sales service and then economic efficiency.
As demand for electrical power increases throught the world,varios plants intends to continue to strive to supply power plants that provide reliability,high performance and low price in accordance with the need of customers.
~REFERANCE :
WWW.CENTREOFENERGY.COM WWW. EN.WIKIPEDIA.ORG WWW.BRIGHTHUB.COM
SSASIT
I BY SHAILESH B. PATEL(E.C. DEPARTMENT)
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Mechanical Engg.: Report On Industrial TrainingDocument44 pagesMechanical Engg.: Report On Industrial TrainingSakshi SanghiPas encore d'évaluation
- Kota Thermal Power Plant Report in Standered FormDocument45 pagesKota Thermal Power Plant Report in Standered FormAbhishek Meena100% (2)
- A Report On Industrial VisitDocument15 pagesA Report On Industrial VisitChandni Bhagchandani100% (1)
- Thermal Power Plant Project ReportDocument63 pagesThermal Power Plant Project Reportasutoshjena28171% (24)
- Thermal Power PlantDocument29 pagesThermal Power PlantSiri VenniPas encore d'évaluation
- NTPCDocument33 pagesNTPCSubodh DuhanPas encore d'évaluation
- PPTDocument20 pagesPPTSriram ramsPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Power Generation Full Seminar Report 74537Document23 pagesThermal Power Generation Full Seminar Report 74537Umang Vyas88% (8)
- Project Report On Thermal PlantDocument58 pagesProject Report On Thermal Plantmenyu198964% (11)
- Training Report On Thermal Power Plant, Panki KanpurDocument30 pagesTraining Report On Thermal Power Plant, Panki Kanpurravi800150% (2)
- Boiler:: Heat Exported by Outlet Steam Heat Supplied by The FuelDocument13 pagesBoiler:: Heat Exported by Outlet Steam Heat Supplied by The FuelBrijesh SrivastavPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Power PlantDocument15 pagesThermal Power PlantAlisha251267% (6)
- Thermal Power Plant PDFDocument118 pagesThermal Power Plant PDFdance77% (22)
- Vocational Training Report On Thermal Power PlantDocument51 pagesVocational Training Report On Thermal Power PlantShubham Agrawal100% (4)
- Thermal Power PlantDocument13 pagesThermal Power PlantKD KannaPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Power Plant Training Training Report-Aniket KaushalDocument44 pagesThermal Power Plant Training Training Report-Aniket KaushalAniket Kaushal88% (16)
- Coal Thermal Power Plant REPORTDocument55 pagesCoal Thermal Power Plant REPORTOcampo Amy100% (2)
- DR - NTTPS-report Sai VivekDocument22 pagesDR - NTTPS-report Sai VivekIndra kandalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Complete NTPC ReportDocument111 pagesComplete NTPC ReportSunil Kumar SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Power PlantDocument15 pagesThermal Power PlantMathes Mano100% (3)
- Disadvantages of Supercritical BoilerDocument2 pagesDisadvantages of Supercritical Boilerpriyajsingh100% (1)
- BoilerDocument45 pagesBoilerEr Prem PrincepsPas encore d'évaluation
- Seminar Report On Captive Thermal Power PlantDocument27 pagesSeminar Report On Captive Thermal Power PlantSubham100% (1)
- Basics of Thermal Power PlantDocument35 pagesBasics of Thermal Power PlantMansoor Chowdhury100% (1)
- Boiler ParameterDocument2 pagesBoiler ParameterFiePas encore d'évaluation
- Study of Boiler Efficiency in Visakhapatnam Steel PlantDocument39 pagesStudy of Boiler Efficiency in Visakhapatnam Steel PlantPhanindra Guttula50% (2)
- Thermal Power Plant Interview Questions AnswersDocument2 pagesThermal Power Plant Interview Questions Answersrajeshkumarpuvvala50% (2)
- Boiler With Mountings and AccessoriesDocument67 pagesBoiler With Mountings and AccessoriesYashvir Singh100% (1)
- High Pressure Boiler: Course ContentsDocument11 pagesHigh Pressure Boiler: Course ContentsSheh Naz100% (2)
- Experiments of Power Plant Engineering in SPPUDocument27 pagesExperiments of Power Plant Engineering in SPPUSiddiqui Adil Adnan100% (2)
- Steam Power Plant Questions and Answers - SanfoundryDocument3 pagesSteam Power Plant Questions and Answers - SanfoundryShubhendra YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Steam Power PlantDocument56 pagesSteam Power PlantصصPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Power StatonDocument15 pagesThermal Power StatonShiv ashish sharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Boiler Operation Engineers Examination Papers Nov 2016Document10 pagesBoiler Operation Engineers Examination Papers Nov 20169766224189Pas encore d'évaluation
- Power Plant Engg (Two Mark Question With Answer, Big Question)Document19 pagesPower Plant Engg (Two Mark Question With Answer, Big Question)Lionus LeoPas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Fabrication of A Single Stage Steam Reaction TurbineDocument13 pagesDesign and Fabrication of A Single Stage Steam Reaction Turbinesalehmashrur 98Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Seminar On Damodar Valley CorporationDocument30 pagesA Seminar On Damodar Valley Corporationatul mishra100% (5)
- Steam TurbineDocument46 pagesSteam TurbineIbrahim Mostafa50% (2)
- Thermal Power Plant TrainingDocument18 pagesThermal Power Plant TrainingAnkit Surana0% (1)
- Induction Furnace ReportDocument29 pagesInduction Furnace ReportFabin Antony100% (2)
- Compounding of Steam TurbineDocument13 pagesCompounding of Steam TurbineDivya Prakash Srivastava100% (3)
- Thermal Power PlantDocument50 pagesThermal Power PlantQasim KhalidPas encore d'évaluation
- Condensate Extraction Pump: GeneralDocument5 pagesCondensate Extraction Pump: GeneralAnonymous DKv8vpPas encore d'évaluation
- Sintering Plant at A GlanceDocument72 pagesSintering Plant at A Glanceskt9560100% (1)
- Report On Jamshoro Thermal Power PlantDocument24 pagesReport On Jamshoro Thermal Power PlantSuresh Kumar100% (2)
- PUMPS 1-NotesDocument16 pagesPUMPS 1-NotesPortifer Harrison Ray Mubanga100% (1)
- Commissioning Step of The Power PlantDocument3 pagesCommissioning Step of The Power Plantssheart_mind100% (1)
- CFBC BoilerDocument7 pagesCFBC Boilerkaruna346Pas encore d'évaluation
- Report Chhabra Thermal Power PlantDocument40 pagesReport Chhabra Thermal Power PlantMangilal LovevanshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Coal Fired Thermal Power PlantDocument33 pagesCoal Fired Thermal Power Plantflorece33% (3)
- Thermal Power PlantDocument36 pagesThermal Power PlantAshvani Shukla100% (1)
- Project Report by Manish YadavDocument53 pagesProject Report by Manish Yadavmanish yaduvanshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal EngineeringDocument10 pagesThermal Engineeringlokeshdhangar842Pas encore d'évaluation
- National Capital Power Station N.T.P.C: Presented by KshitijDocument25 pagesNational Capital Power Station N.T.P.C: Presented by KshitijHarshit MittalPas encore d'évaluation
- Industrial Training PresentationDocument25 pagesIndustrial Training PresentationHarshit MittalPas encore d'évaluation
- Report On Steam Power PlantDocument5 pagesReport On Steam Power PlantBabbu Mehra100% (1)
- T Project ReportDocument63 pagesT Project ReportArif AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Power PlantDocument5 pagesThermal Power PlantAnudeep ChittluriPas encore d'évaluation
- SWITCHYARD, NTPC SIPAT Training ReportDocument35 pagesSWITCHYARD, NTPC SIPAT Training ReportSuresh Sunny80% (5)
- Me Lab 3Document27 pagesMe Lab 3Jerome Vega AndesPas encore d'évaluation
- 8051 Based Simple Digital ClockDocument7 pages8051 Based Simple Digital ClockShailesh SankdasariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- ATMEL MCS 8051 Instruct SetDocument50 pagesATMEL MCS 8051 Instruct Setand3botPas encore d'évaluation
- 8051 Based Digital ClockDocument15 pages8051 Based Digital ClockShailesh SankdasariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- 131701-1 Gtu 3rd Sem PaperDocument1 page131701-1 Gtu 3rd Sem PaperShailesh SankdasariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Matlab Finite Element Modeling For Materials Engineers Using MATLABDocument74 pagesMatlab Finite Element Modeling For Materials Engineers Using MATLABPujara ManishPas encore d'évaluation
- 130904-2 Gtu 3rd Sem PaperDocument1 page130904-2 Gtu 3rd Sem PaperShailesh SankdasariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- 131101-2 Gtu 3rd Sem PaperDocument4 pages131101-2 Gtu 3rd Sem PaperShailesh SankdasariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- 130901-1 Circuit & Networks Gtu 3rd Sem PaperDocument3 pages130901-1 Circuit & Networks Gtu 3rd Sem PaperShailesh SankdasariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- 130901-2 Circuit & Networks Gtu 3rd Sem PaperDocument2 pages130901-2 Circuit & Networks Gtu 3rd Sem PaperShailesh SankdasariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- 8051 Project LCD InterfacingDocument7 pages8051 Project LCD InterfacingShailesh Sankdasariya100% (5)
- 130904-3 Gtu 3rd Sem PaperDocument3 pages130904-3 Gtu 3rd Sem PaperShailesh SankdasariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological University: InstructionsJainish JariwalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nuclear Power PlantDocument9 pagesNuclear Power PlantShailesh Sankdasariya100% (2)
- Hydro Magnetic Power PlantDocument7 pagesHydro Magnetic Power PlantShailesh SankdasariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- 130001Document2 pages130001Ashwin PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- 130310-130701-Digital Logic Design PDFDocument2 pages130310-130701-Digital Logic Design PDFjayant_2222143Pas encore d'évaluation
- Wind Turbine Power PlantDocument8 pagesWind Turbine Power PlantShailesh SankdasariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Combined Cycle Gas Turbine.Document9 pagesCombined Cycle Gas Turbine.Shailesh Sankdasariya100% (6)
- Hydro Magnetic Power PlantDocument7 pagesHydro Magnetic Power PlantShailesh SankdasariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Combined Cycle Gas Turbine.Document9 pagesCombined Cycle Gas Turbine.Shailesh Sankdasariya100% (6)
- Wind Turbine Power PlantDocument8 pagesWind Turbine Power PlantShailesh SankdasariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Solar Power PlantDocument8 pagesSolar Power PlantShailesh Sankdasariya50% (2)
- Power DistributionDocument6 pagesPower DistributionShailesh SankdasariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- List of Gas Turbine Power Plant in IndiaDocument2 pagesList of Gas Turbine Power Plant in IndiaShailesh SankdasariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydro Power PlantDocument8 pagesHydro Power PlantShailesh Sankdasariya67% (3)
- Biogas Power PlantDocument7 pagesBiogas Power PlantShailesh Sankdasariya100% (1)
- Diesel Electric Power PlantDocument7 pagesDiesel Electric Power PlantShailesh Sankdasariya100% (5)
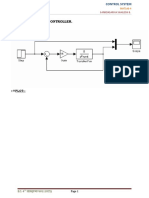
- Ex-1: Propertional Controller.: ModelDocument4 pagesEx-1: Propertional Controller.: ModelShailesh SankdasariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- POWER DISTRIBUTION CoverDocument2 pagesPOWER DISTRIBUTION CoverShailesh SankdasariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydroelectric Power PlantDocument33 pagesHydroelectric Power PlantJuselle Lopez Montemayor100% (1)
- VibrationDocument24 pagesVibrationMeiliana Cendra AsihPas encore d'évaluation
- Steam Turbine Maintenance Maintenance InstructionsDocument11 pagesSteam Turbine Maintenance Maintenance Instructionsdreamboy87Pas encore d'évaluation
- Centrif Compr Droplet ErosionDocument6 pagesCentrif Compr Droplet ErosionrossifrancescoPas encore d'évaluation
- Single or Dual Pressure Nitric Acid (R.L. Harvin)Document11 pagesSingle or Dual Pressure Nitric Acid (R.L. Harvin)Gamma OktaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bhel Report Final2Document76 pagesBhel Report Final2Anuj Lamba100% (1)
- Turbine & AuxilariesDocument64 pagesTurbine & Auxilariesulhatolkargmailcom100% (1)
- Module 2: Thermodynamics 2, Fluid MechanicsDocument2 pagesModule 2: Thermodynamics 2, Fluid MechanicsRozy MacaseroPas encore d'évaluation
- Cci Overview PDFDocument8 pagesCci Overview PDFOrkhan SeyidovPas encore d'évaluation
- Operational Cleaning and Steam Blow of Large Thermal Power Plant Boilers (Kostolac B2 Experience) PDFDocument36 pagesOperational Cleaning and Steam Blow of Large Thermal Power Plant Boilers (Kostolac B2 Experience) PDFSturovo TurboPas encore d'évaluation
- Abstract On Steam TurbineDocument2 pagesAbstract On Steam TurbineAsdfPas encore d'évaluation
- Toshiba JSW Turbine and Generators PVT LimitedDocument2 pagesToshiba JSW Turbine and Generators PVT Limitedanil_singh_62Pas encore d'évaluation
- Q&A For Main Turbine Assembly & Maintenance (Hitachi & Toshiba-800 MW Unit)Document68 pagesQ&A For Main Turbine Assembly & Maintenance (Hitachi & Toshiba-800 MW Unit)Pulkit AgarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- BEI Vol C Turbine PDFDocument302 pagesBEI Vol C Turbine PDFTony AppsPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Engineering Lab ManualDocument74 pagesThermal Engineering Lab ManualYudhisthar SainiPas encore d'évaluation
- 1916 Sothern Verbal Notes For EngineersDocument990 pages1916 Sothern Verbal Notes For EngineersReginPas encore d'évaluation
- On-Site Emergency Plan: Captive Power Plant Angul, OdishaDocument67 pagesOn-Site Emergency Plan: Captive Power Plant Angul, OdishaANILPas encore d'évaluation
- PGT 1&2Document16 pagesPGT 1&2jack27nikkPas encore d'évaluation
- Biro Klasifikasi Indonesia: Application For ClassificationDocument7 pagesBiro Klasifikasi Indonesia: Application For ClassificationJoy Arief JanuarPas encore d'évaluation
- E2 - 5 Toshiba SasakiDocument32 pagesE2 - 5 Toshiba SasakiGhulam Khairul IlhamPas encore d'évaluation
- Pipe Problems Looks Fam 2Document178 pagesPipe Problems Looks Fam 2Eep Jay0% (1)
- Thermal Power Plant RehabilitationDocument51 pagesThermal Power Plant Rehabilitationsenthil031277Pas encore d'évaluation
- Propulsion and Power Formula SheetDocument4 pagesPropulsion and Power Formula SheetArun VinthanPas encore d'évaluation
- Dme PDFDocument102 pagesDme PDFRavikiran MahendraPas encore d'évaluation
- Siemens CompressorDocument12 pagesSiemens Compressorverat81100% (1)
- Turbine Rotor Replacement PDFDocument11 pagesTurbine Rotor Replacement PDFjeya vasanthPas encore d'évaluation
- Elrctrical Power Engineering SyllabusDocument75 pagesElrctrical Power Engineering Syllabusgishi_sjdc6983Pas encore d'évaluation
- ComAp Explanatory Dictionary GuideDocument34 pagesComAp Explanatory Dictionary GuideAdnan YakoobPas encore d'évaluation
- 000 3BD Ee 01509 006Document93 pages000 3BD Ee 01509 006Samir Zaghlool100% (1)
- LP ByPass SystemDocument43 pagesLP ByPass SystemAshwani Dogra50% (2)
- Electric Motor Control: DC, AC, and BLDC MotorsD'EverandElectric Motor Control: DC, AC, and BLDC MotorsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (19)
- Well Integrity for Workovers and RecompletionsD'EverandWell Integrity for Workovers and RecompletionsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (3)
- Fire on the Horizon: The Untold Story of the Gulf Oil DisasterD'EverandFire on the Horizon: The Untold Story of the Gulf Oil DisasterPas encore d'évaluation
- Power of Habit: The Ultimate Guide to Forming Positive Daily Habits, Learn How to Effectively Break Your Bad Habits For Good and Start Creating Good OnesD'EverandPower of Habit: The Ultimate Guide to Forming Positive Daily Habits, Learn How to Effectively Break Your Bad Habits For Good and Start Creating Good OnesÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (21)
- The Journeyman Electrician Exam Study Guide: Proven Methods for Successfully Passing the Journeyman Electrician Exam with ConfidenceD'EverandThe Journeyman Electrician Exam Study Guide: Proven Methods for Successfully Passing the Journeyman Electrician Exam with ConfidencePas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Motors and Drives: Fundamentals, Types and ApplicationsD'EverandElectric Motors and Drives: Fundamentals, Types and ApplicationsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (12)
- Air Cooled Heat Exchanger Handbook: Fundamentals, Calculations, Design and Q&AD'EverandAir Cooled Heat Exchanger Handbook: Fundamentals, Calculations, Design and Q&APas encore d'évaluation
- Solar Energy: Survive Easily on Solar Power Off the GridD'EverandSolar Energy: Survive Easily on Solar Power Off the GridPas encore d'évaluation
- The Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialD'EverandThe Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialPas encore d'évaluation
- Shorting the Grid: The Hidden Fragility of Our Electric GridD'EverandShorting the Grid: The Hidden Fragility of Our Electric GridÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- Well Control for Completions and InterventionsD'EverandWell Control for Completions and InterventionsÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (10)
- Idaho Falls: The Untold Story of America's First Nuclear AccidentD'EverandIdaho Falls: The Untold Story of America's First Nuclear AccidentÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (21)
- Building Energy Management Systems and Techniques: Principles, Methods, and ModellingD'EverandBuilding Energy Management Systems and Techniques: Principles, Methods, and ModellingPas encore d'évaluation
- Renewable Energy: Physics, Engineering, Environmental Impacts, Economics and PlanningD'EverandRenewable Energy: Physics, Engineering, Environmental Impacts, Economics and PlanningÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (4)
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionD'EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Handbook on Battery Energy Storage SystemD'EverandHandbook on Battery Energy Storage SystemÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- Solar Power Demystified: The Beginners Guide To Solar Power, Energy Independence And Lower BillsD'EverandSolar Power Demystified: The Beginners Guide To Solar Power, Energy Independence And Lower BillsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- Offshore Wind Energy Generation: Control, Protection, and Integration to Electrical SystemsD'EverandOffshore Wind Energy Generation: Control, Protection, and Integration to Electrical SystemsPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical Power Distribution for IndustryD'EverandPractical Power Distribution for IndustryÉvaluation : 2.5 sur 5 étoiles2.5/5 (2)
- Global Landscape of Renewable Energy FinanceD'EverandGlobal Landscape of Renewable Energy FinancePas encore d'évaluation
- The Truth About Solar Panels The Book That Solar Manufacturers, Vendors, Installers And DIY Scammers Don't Want You To ReadD'EverandThe Truth About Solar Panels The Book That Solar Manufacturers, Vendors, Installers And DIY Scammers Don't Want You To ReadÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (10)
- Photovoltaic Solar Energy: From Fundamentals to ApplicationsD'EverandPhotovoltaic Solar Energy: From Fundamentals to ApplicationsPas encore d'évaluation
- Asset Integrity Management for Offshore and Onshore StructuresD'EverandAsset Integrity Management for Offshore and Onshore StructuresPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Power Plant: Design and OperationD'EverandThermal Power Plant: Design and OperationÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (23)