Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Answers 2009-10
Transféré par
Yoga RasiahDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Answers 2009-10
Transféré par
Yoga RasiahDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
1
MPZ4230 Final Examination
Model Answer 2010
(01). (a). r r
x
x
u r v
r
y y
u u x u y
x y
= +
---------------- (1)
v v x v y
r x r y r
= +
---------------- (2)
By (1)
u u u
r sin r cos
x y
= +
------------- (3)
(2) r
v v v
r r cos + r sin
y x y
=
------------- (4)
(3) + (4)
u v v u u v
r rsin + r cos
r y x y x
| | | |
+ = +
| |
\ . \ .
Given that
u v u v
&
x y y x
= =
u v
r 0
r
+ =
v 1 u
r r
=
(ii). u = x
4
6x
2
y
2
+ y
4
3 2
u
4x 12xy
x
2
2 2
2
u
12x 12y
x
----------------- (1)
3 2
u
4y 12x y
y
2
2 2
2
u
12y 12x
y
------------------ (2)
2
2
P + P + x =a
1
x P
2 1
P
y
h
(1) + (2)
2 2
2 2
u u
0
x y
+ =
(b). (i).
( )
2 2 2 3
i j k
x y z
4xy 3x z 2x 2x z
( ) ( )
2 2
0 i 6x z 6x z j 4x 4x k + +
= 0
F is conservative
(ii).
2 2
4xy 3x y
x
--------------- (1)
2
2x
y
---------------- (2)
3
2x z
z
-------------- (3)
by (1) ( )
2 3 2
4x y 3x z
f y, z
2 3
= + -------------- (4)
( )
2
2f y, z
2x
y y
= +
Comparing (2)
( ) f y, z
0
y
f (y, z)=0
= 2x
2
y x
3
z
2
+c
c)
p
1
+ p
2
+ x = a
If the area of the rectangle maximum then the rest of area is minimum
3
rest of Area B = ( )
1 2
1 1 1
p y p y x h y
2 2 2
+ +
( )
1 2
1 1
p p y x(h y)
2 2
= + +
( ) ( )
1 1
a x y x h y
2 2
= +
B 1
h y
x 2
B 1
a x
y 2
When B is minimum
1 1
h y 0 y= h
2 2
=
1 1
a x 0 x= a
2 2
=
Area of the rectangle =
1 1
a h
2 2
ah
4
=
(2). (a).
(i). f(z) = u(x . y) + v(x . y)
Polar form f(z) = u(r, ) + v(r, )
1 u v u 1 v
&
r r r r
= =
(ii). f(z
1
) = (z a)
n
= (x - a + iy)
n
= (r cos + i r sin )
n
x a = r cos & y = r sin
r
2
= (x a)
2
+ y
2
f(z
1
) = r
n
(cos + i sin)
n
r(z) = r
n
e
in
f(z) = r
n
(cos n + i sin n)
= r
n
cos n + i r
n
sin n
= u + i v
n 1
u
nr cos n
r
------------------ (1)
n
u
nr sin n
------------------ (2)
n 1
v
nr sin n
r
------------------ (3)
n
v
nr cos n
------------------ (4)
4
(1) (4)
1
r
u 1 v u 1 v
0
r r r r
= =
1 1 u v 1 u v
(3) (4) 0
r r r r r
+ + = =
( )
( ) ( )
2 n n
1 1
f z
z a x a iy
= =
+
x a = r cos & y
=
r sin
r
2
= (x a)
2
+ y
2
( )
2 n
n
1
f (z )
r cos i sin
=
+
= r
-n
e
-in
= r
n
(cos n - i sin n)
u = r
-n
cos n , v = -r
-n
sin n
n 1
u n
cos n
r r
+
------------------- (5)
n
u n
sin n
r
------------------- (6).
n 1
v n
sin n
r r
+
------------------- (7)
n
v n
cos n
r
=
------------------- (8)
1
(5) + (8)
r
u 1 v u 1 v
0
r r r r
= =
1 v 1 u v 1 u
(7) (6) 0
r r r r r
+ + = =
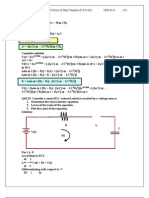
b) z = a is an interior point in the region bounded by C. The function ( )
( )
2
n
1
f z
z a
=
is
analytic in the region except at the point z = a. Let c
1
be a circle of radius r having the centre at
z = a as shown in figure. Then (z a)
-n
is analytic within and on the boundary of the region
bounded by C and C
1
. Hence by Cauchys first integral theorem, moving anticlockwise.
5
1
C
C
a
=
x
y
( ) ( )
1
n n
c c
dz dz
I
z a z a
= =
Now on the circle
1
C z-a r =
z a = re
i
Then the integral
( )
n
c
dz
I
z a
=
2 i
n in
c
re d
r e
( )
2
1 n i
n 1
0
i
e d
r
( )
( )
2
j
n 1
0
e 1 n
1
r j 1 n
If n 1 = 0
If n = 1 , the integral becomes,
1
2x
C 0
dz
I i d 2 i
z 1
= = =
Thus
0 all positive integres axcept unity
I
2 i for n = 1
Now at n = 0 the integral is
( )
n
c c
dz
I dz
z 1
= =
2
i
0
ir e d
= 0
For n = -1, -2, . the corresponding integral becomes (z a), (z a)
2
respectively which are
analytic every where in side c
1
including z = a. Therefore by Cauchys first integral theorem the
value of the line integral is zero for all negative integers.
(03). N = 100
P =0.04
x = number of computers which have software problem
(i). p(x > 6) = 1 [p(x=0) + p(x=1) + p(x=2) + p(x=3) + p(x = 4) + p(x=5) + p(x=6)
6
( )
x n x
n!
p(x) p (1 p)
x! n x !
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
0 100 1 99 3 97
2 98
4 5 95 6 94
96
100 ! 100 ! 100 ! 100!
0.04 0.96 0.04 0.96 (0.04) (0.98) 0.04 0.96
100 ! 1! 99 ! 2!98! 3!97!
1
100 ! 100 ! 100 !
0.04 (0.96) 0.04 0.96 0.04 0.96
4!96! 5! 95! 6!94!
+ + + +
=
+ +
(ii). mean () = n
= 100 0.04
= 4
Variance (x) = np(1 p)
= 100 0.04 0.96
= 3.84
(iii). = n
= 100 0.04
= 4
Variance (x) =
= 4
(b). = 15,
2
= 2.89
x = miles per galloon
(i). p (x < 13) =
13 15
z
2.89
| |
=
|
\ .
= p (z < -1.1765)
= 1 0.881
= 0.119
(iii). p(x > 17.5) =
17.5 15
p z
2.89
| |
>
|
\ .
= P(z > 1.4705)
= 1 0.9292
= 0.708
(iii).
13.5 15 18 15
p(13.5 x 18) = p z
2.89 2.89
| |
|
\ .
1.5 3
p z
2.89 2.89
| |
=
|
\ .
7
= p (-0.8823 z 1.764)
= 0.9608 [1 0.8106]
= 0.9608 0.1894
= 0.7714
(iv). p (x > 20) =
20 15
p z
2.89
| |
>
|
\ .
= p (z > 2.94)
= 1 0.9984
= 0.0016
(04).a)
n = 40 ( n > 30)
x 137 =
= 30.2
H
0
: = 150
H
a
: 150
0
cal
x 137 150
z
30.2
n 40
=
= -2.722
cal
z 2.722 =
Z
tab
= z
/2
If = = 0.1 If = 0.05
0.05
2
z z 1.65
= =
0.025
2
z z
=
cal tab
z z > = 1.96
H
0
is rejected
cal tab
z z >
H
0
is rejected
H
a
accepted 150
the mean sales at grocery store is not $150
(b). Sample 1 Sample 2
n
1
= 9 n
2
= 16
1
= 2
2
= 3.2
1
S 0.75 = S
2
= 1
H
0
=
1
=
2
8
C
( x , y )
2 2
1 1
( x , y )
x
y
H
a
=
1
2
( )
cal
2 3.2 0
t
1 1
S
9 16
=
+
( ) ( )
2 2
1 1 2 2
1 2
n 1 s n 1 s
S
n n 2
+
=
+
8 0.75 15 1
9 16 2
+
=
+
21
23
=
= 0.913
cal
1.2 1.2 12
t 3.154
0.913 5 16 9
0.913
144
= = =
+
cal
t 3.154 =
1 2
tab n n 2, / 2
T t
+
=
= t
23
,
0.025
= 2.068
c tab
t t >
H
0
is rejected
H
a
is accepted
There is a difference in the average amount of time that the boys and girls age between 7 & 11
play sports each day.
(05). (a).
(i).
9
x
a+1 a
x
y
a
a+1
y
x
(x)
(ii).
2 1
2 1
y y
m
x x
y = mx + c
(b). y = ax + b
( )
2
2
n xy x y
b
n x x
=
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
2
10 2480.5 479 47.8
10 26125 479
=
= 0.06
y b x
a
n
=
47.8 0.06 479
10
=
= 1.906
y = 0.06x + 1.906
(b).
( )
( )
( )
( )
2 2
2 2
n xy x y
r
n x x n y y
=
( )
( )( )
2 2
10 2480.5 479 47.8
10 26125 479 10 259.96 47.8
=
1908.8
31809 314.76
=
1908.8
10012200.84
=
= 0.60324
r 1
x & y are correlated
60% of data represented by the regression equation.
06)(a).
(i). y
n+1
= y
n
+ hf (x
n
, y
n
)
10
n 1 n
x 1 n
y y dy
dx x x
+
+
=
=
y
n+1
y
n
= ( )
n 1 n
dy
x x
dx
+
n 1 n
dy
y y h
dx
+
=
[ ]
x 1 n
where x x h
+
=
n 1 n
hdy
y y
dx
+
= +
= y
n
+ hf (x
n
, y
n
)
(ii). f(x, y) = 1 y
y
1
= y
0
+ 0.1 f (x
0
, y
0
)
= 1 + 0.1 (1-1)
= 1
y
2
= y
1
+ 0.1f(x
1
, y
1
)
= 1 + 0.1 (1 1)
= 1 + 0
= 1
y
3
= y
2
+ 0.1f (x
2
, y
2
)
= 1 + 0.1 (1 1)
= 1 + 0
y
3
= 1
(iii).
dy
1 y
dx
=
dy
dx
1 y
=
-log(1-y) = x +c
1 y = e
-x+c
Given that y(0)=1 1-0=e
0+c
So that c = 0
y = 1 e
-x
y(0.1) = 1 + e
-(0.1)
=1 .09
y (0.2) = 1 + e
-(0.2)
=1. 18
y(0.3) = 1 + e
-(0.3)
=1 .27
(b). y = xy + y
2
y xy y 2yy = + +
y xy y y 2yy 2y y = + + + +
y xy y 2y 2yy 2y y 4y y = + + + + +
xy 3y 2yy 6y y = + + +
11
y
n+1
= y
n
+ n
2 3 4 iv
n n n
n
h y h y h y
y .......
21 3! 4!
+ + + +
step 1
y
0
= 1
0
y 1 =
0
y 1 2 3 = + =
0
y 2 6 2 10 = + + =
iv
0
y 9 20 18 47 = + + =
2 3 iv
0 0 0
1 0 0
h y h y hy
y y hy
2! 3! 4!
= + + + +
= 1.1168625
1
y = 1.359068094
11
y = 4.2888553687
1
y = 16.42057337
iv
1
y = 89.23714802
y
2
= 1.277320662
07.
2
i 1, j i, j i 1, j
2 2
u 2u 2u
u
x h
+
+
2
i, j 1 i, j i, j 1
2 2
u 2u u
u
y k
+
+
2 2
i 1, j i 1, j i, j i, j 1 i, j 1 i, j
2 2 2 2
u u 2u u u 2u
u u
+ 0
x y h k
+ +
+ +
+ = =
Here h = k = 1
2
2 2
i 1. j i 1 j i, j 1 i, j 1 i, j 2
u u
u u u u 4u 0
x
y
+ + +
+ = + + + =
u
2
+ u
4
4u
1
= 0
u
1
+ u
3
+ u
5
4u
2
= 0
u
2
+ u
6
4u
3
= 0
2u
1
+ u
5
4u
4
= 0
2u
2
+ u
4
+ u
6
4u
5
= 0
2u
3
+ u
5
-4u
6
= 0
u
4
= 10.188
u
5
= 0.5
u
6
= 1.188
u
1
= 0.25
u
2
= 0.625
u
3
= 1.25
12
(08). V
C
+ V
R
+ V
C
= 100 cos 2t
dq
d
dq q dt
L + R 10 cos 2t
dt dt C
| |
|
\ .
=
2q + 8q + 10q = 10 cos 2t
q 4i 5q 5 cos 2t + + =
Complementary function is q
c
= Ae
t
t
c
q Ae
=
2 t
c
q Ae
2
Ae
t
+ 4 Ae
t
+ 5 Ae
t
= 0
A(
2
+ 4 + 5) = 0
= -2 i
Complementary function is
q
c
= e
-2t
(A cos t + B sin t)
let
q
p
= cos 2t + m sin 2t
q
p
= -2 sin 2t + 2m cos 2t
q
p
= -4 cos 2t 4m sin 2t
-4( cos 2t + m sin2t) + 4(-2 sin 2t + 2 cos 2t) + 5 ( cos 2 t + m sin 2t) = 5 cos 2t
(-4m + 5m - 8 ) sin 2t + (-4 + 5 + 8m) cos 2t = 5 cos 2t
m - 8 = 0
+ 8m = 5
p
1 8
q cos 2t sin 2t
13 13
= +
General solution is q = q
p
+ q
c
q =
2t
1 8
cos 2t sin 2t e (Acos t Bsin t)
13 13
+ + +
When t = 0 q(0) = 0
1
A 0
13
+ =
( ) ( )
2t 2t
q 2e A cos t B sin t e Asin t B cos t
= + + + +
1 8
2sin 2t 2cos 2t
13 13
+
when t = 0 q= 0
16
0 2A B 0
13
= + + =
13
1 -1
(t)
x
1 16
2 B 0
13 13
| |
= + + =
|
\ .
18
B
13
=
2t
1 18 1 8
q e cos t sin t cos 2t sin 2t
13 13 13 13
| |
= + +
|
\ .
(b). (i). charge at any time
2t
1 18 1 8
q e cos T sin T cos 2T sin 2T
13 13 13 13
| |
= + +
|
\ .
(ii).
dq
i
dt
=
2T
16 37 2 16
e cos T sin T sin 2T cos 2T
13 13 13 13
= + +
(iii).
c
q
v
c
=
2T
1 18 10 8
10e cos T sin T cos 2T sin 2T
13 13 13 13
= + +
(a).
0
n n
n 1
a n x n x
f (x) a cos b sin
2 L L
=
| | | |
= + +
| |
\ . \ .
L
0
L
1
a f (x).dx
L
L L
n n
L L
1 n x 1 n x
a f (x) cos dx b f (x) sin dx
L L L L
| | | |
= =
| |
\ . \ .
(b).
f(t) is symmetric equation
so f(t) even function
b
n
= 0
14
1
0
1
1
a t dt
1
0 1
1 0
tdt t dt
= +
0 1
2 2
1 0
t t
2 2
= +
1 1
2 2
= +
= 1
1
n
1
a t cos n t dt
0 1
1 0
t cos n t dt t cos n t dt
= +
[ ] [ ]
0 01
0 1
1 0
1 0
1 1
t sin n t sin n t + t sin n t sin n t
n n
= +
( )
0 1
1 0
1 cos n t 1 cos n t
sin n t sin n t-
n n n n
= +
2 2 2
1 cos n cos n 1
n n n n
= +
( )
2
4
n odd
n
0 n even
( )
2
2
4
for all n
2n 1
=
+
( )
( )
( )
2 2
m 0
1 4 1
f t cos 2n 1 t
2
2n 1
=
= +
Substituting in to differential equation, Then the general solution for f(t)
( )
( )
2 2
m 0
1 4 1
x 10x cos 2n 1 t
2
2n 1
=
+ = +
------------ (A)
Then P.I
x
n
= A
0
+ A
n
cos(2n + 1) t
n
x = -(2n+1)A
n
sin (2n + 1)t
n
x = -(2n+1)
2
A
n
cos (2n + 1)t
15
n n n
x , x , x substitute in to (A)
( ) ( ) ( )
( )
( )
2
n n n 2 2
n 0
1 4 1
10 A A cos 2n 1 t m 1 A cos 2n 1 t cos 2n 1 t
2
2n 1
=
+ + + + + = +
+
( )
( )
2
2
n 2 n 2 2
n 0
1 4 1
10 A 10 a n 1 x A cos(2n 1)t
2
2n 1
=
+ + = +
a
1
10A
2
=
0
1
A 16
20
=
( )
n
n 2
2
a
A
10 2n 1
=
+
( )
2
2
n
2 2
4
A 2n 1
10 (2n 1)
= +
+
10.
(a). If W is a set of vectors form a vector space V, then W is a subspace of V if and only if, u
& v are vectors in W
Then u + v W
k u w ; k is any scalar
(i). let u & v are two rectors in W
u= (x
1
, y
1
, z
1
) W ; x
1
+ y
1
+ z
1
= 0
v = (x
2
, y
2
, z
2
) W ; x
2
+ y
2
+ z
2
= 0
u + v = [x
1
+ x
2
, x
2
+y
2
, z
1
+ z
2
] = [x
1
+ x
2
+ y
1
+ y
2
+ z
1
+ z
2
)
= (x
1
+ y
1
+ z
1
) B(x
2
+ y
2
+ z
2
) = 0
W is a sub space of V
(ii). (x, y, z) W ; x
2
+ y
2
+ z
2
= 1
(x, y, z) = (x, y, z) but (x)
2
+ (y)
2
+(z)
2
=
2
(x
2
+ y
2
+ z
2
)
W is not a vector space over R
3
(b).
(i). (1, 0, 1) = -1(-1, 0, -1)
given vectors not linearly independent
(ii). (1, 0, 1) + (1,1,0) = (2, 1, 1)
given vectors are not linearly independent
16
(iii). (1, 1,1) + (1, 0 ,0) + r (0, 1, 0) = 0
+ = 0
+ = 0
= 0
Then = 0
= 0
Given set of vectors are linearly independent.
c) u
1
= (1, 1, 1),u
2
= (0, 1, 1), u
3
= (0, 0, 1)
1 1 0
0 1 0
0 0 1
| |
|
|
|
\ .
Using row operation cant find zero rows
u
1
, u
2
, u
3
are linearly independent vectors.
u
1
, u
2
, u
3
are basis for R
3
.
Step 1
( )
1
1
1
1,1,1
u 1 1 1
v , ,
u 3 3 3 3
| |
= = =
|
\ .
Step 2
u
2
proj w
1.
u
2
= (0, 1,1) -
2 1 1 1
, ,
3 3 3 3
| |
|
\ .
2 1 1
, ,
3 3 3
| |
=
|
\ .
2
2 1 1
, ,
2 1 1 3 3 3
v , ,
6 6 6 6
3
| |
|
| |
\ .
= =
|
\ .
Step 3
u
3
proj w
2
u
3
= u
3
(u
3.
v
1
). v
1
(u
3
, v
2
) .v
2
( )
1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1
0, 0,1 , , , ,
6 3 3 3 3 6 6 6
| | | |
=
| |
\ . \ .
1 1
0, ,
2 2
| |
=
|
\ .
17
3
1 1
0, ,
1 1 2 2
v 0, ,
1
2 2
2
| |
|
| |
\ .
= =
|
\ .
v
1
, v
2
, v
3
form an orthogonal basis for V
3
(R)
(ii).
2 1 0
A 1 3 1
0 1 2
| |
|
=
|
|
\ .
2 1 0
A I 1 3 1
0 1 2
| |
|
=
|
|
\ .
Characteristic equation= (2 - ) [(3 - ) (2 - ) 1] -1 [(2 - )]
= (2 - ) [(3 - ) (2 - ) -1 -1]
= (2 - ) [4 - 5 +
2
]
= (2 - ) [ (4 - ) ( 1 - )
= 1 or =2 or = 4
When = 1
1 1 0 x
A I= 0 2 1 y 0
0 1 1 z
| | | |
| |
=
| |
| |
\ . \ .
x + y = 0
x + 2y + z = 0
y + z = 0
z = t, y = t, x = t
1
x 1
y 1 v
z 1
| | | |
| |
= =
| |
| |
\ . \ .
v
1
is the eigon vector for 1 =
When = 2
0 1 0 x
A I 1 1 1 y 0
0 1 0 z
| | | |
| |
= =
| |
| |
\ . \ .
y = 0
18
x + y + z = 0
x = t z = -t
2
x 1
y 0 v
z 1
| | | |
| |
= =
| |
| |
\ . \ .
v
2
is the eigon vector for 2 =
When = 4
2 1 0 x
1 1 1 y 0
0 1 2 z
| | | |
| |
=
| |
| |
\ . \ .
-2x + y = 0
x y + z = 0
y 2z = 0
let x = t ,y = 2t,z = t
3
x 1
y 2 v
z 1
| | | |
| |
= =
| |
| |
\ . \ .
v
3
is the eigon vector for 4 =
1 1 1
2 3 1
3 2 6
1
1 2
p 0 2 0 2
3 6
6
2 3 1
1 1 1
3 2 6
| |
| | |
| |
| = = |
| |
|
|
\ .
|
\ .
T
2 2 3
2 1 0
1
P AP 3 0 3 1 3 1
6
1 2 1 0 1 2
| |
| |
|
|
= |
|
|
|
|
\ .
\ .
P
2 2 2 2 3 1
1 1
2 3 0 2 3 2 0 2
6 6
4 8 4
2 3 1
| | | |
| |
= | |
| |
| |
\ . \ .
19
6 0 0
1
0 12 0
6
0 0 24
| |
|
=
|
|
\ .
1 0 0
0 2 0
0 0 4
| |
|
=
|
|
\ .
S = P
T
AP
1 T
P p
=
S
2
= P
T
APP
T
AP
= P
T
A
2
P
S
3
= P
T
A
2
P P
T
AP
= P
T
A
3
P
Similarly
S
n
= P
T
A
n
P
(e). Given Quadratic form is Q (x) = (x
1
, x
2
, x
3
)
1
2
3
1 2 0 x
2 1 0 x
0 0 3 x
| |
|
|
|
\ .
Q(x) = x
T
Ax
= x
T
PP
T
APP
T
x
= x
T
PP
T
A
= y
t
y
= Q (y)
The new Quadratic form is Q (y) = (y
1
, y
2
, y
3
)
1
2
3
1 0 0 y
0 2 0 y
0 0 4 y
| |
|
|
|
\ .
(f). Relationship y = P
T
x
y
T
= (P
T
x)
T
= x
T
P
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Ux VX : Função Derivada Da Função Fórmulas de IntegraçãoDocument2 pagesUx VX : Função Derivada Da Função Fórmulas de IntegraçãoJosierBaiottoPas encore d'évaluation
- 2007 Ajc h2 Prelims Paper 1 SolutionsDocument9 pages2007 Ajc h2 Prelims Paper 1 Solutionsvincesee85Pas encore d'évaluation
- Math ReferenceDocument24 pagesMath ReferenceSujib BarmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Formula2 (1) UpdatedDocument3 pagesFormula2 (1) UpdatedAmm RoehPas encore d'évaluation
- Math Stats Booklet 1Document20 pagesMath Stats Booklet 1Koh Boon HaoPas encore d'évaluation
- NYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1Document10 pagesNYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- MIDTERM MTH3112 Sem1!16!17 Solution Nov16Document7 pagesMIDTERM MTH3112 Sem1!16!17 Solution Nov16Nik Muhd AriffPas encore d'évaluation
- Fourier Finite TransformsDocument8 pagesFourier Finite Transformserev_20Pas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering MathsDocument8 pagesEngineering MathsSanthosh SanPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam - 2011 10 28Document5 pagesExam - 2011 10 28lieth-4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 8Document15 pagesChapter 8camiloPas encore d'évaluation
- ACJC 2014 H2 Maths Supp Exam (Solution For Students)Document9 pagesACJC 2014 H2 Maths Supp Exam (Solution For Students)RaymondZhangPas encore d'évaluation
- 2014 2 Sar Tun Abdul RazakDocument4 pages2014 2 Sar Tun Abdul RazakMasytah YazidPas encore d'évaluation
- Iit - Jee Model Grand Test - Ii Paper - 1 SolutionsDocument6 pagesIit - Jee Model Grand Test - Ii Paper - 1 SolutionsSayan Kumar KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics Sample Paper Solutions Section-ADocument19 pagesMathematics Sample Paper Solutions Section-APoonamBhardwajPas encore d'évaluation
- Formulario Calculo Dif - IntegralDocument4 pagesFormulario Calculo Dif - IntegralRocki R SebastiánPas encore d'évaluation
- Formulario de Cálculo Diferencial e Integral: Jesús Rubí Miranda (Document2 pagesFormulario de Cálculo Diferencial e Integral: Jesús Rubí Miranda (lagarto27Pas encore d'évaluation
- Solutions: S - 1 5 Mathematics-III (May-2012, Set-2) JNTU-KakinadaDocument10 pagesSolutions: S - 1 5 Mathematics-III (May-2012, Set-2) JNTU-KakinadaSri DPas encore d'évaluation
- Formule Trigonometrice Derivarea Si Integrarea Functiilor CompuseDocument2 pagesFormule Trigonometrice Derivarea Si Integrarea Functiilor Compusekissu_diana281Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2010 DHS Paper 1solDocument10 pages2010 DHS Paper 1solnothingtodo1992Pas encore d'évaluation
- F C D I: Ormulario de Álculo Iferencial E NtegralDocument2 pagesF C D I: Ormulario de Álculo Iferencial E NtegralSergio Jimenez ZarzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions PDFDocument10 pagesInverse Trigonometric Functions PDFJiung WeiPas encore d'évaluation
- Multivariable Calculus, 2007-03-15. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526Document5 pagesMultivariable Calculus, 2007-03-15. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526lieth-4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Formulario: L Ogica Matem AticaDocument10 pagesFormulario: L Ogica Matem AticaDaniel ChuquipomaPas encore d'évaluation
- X X X X Ecx Ecx: Tan - Sec Sec Cot - Cos CosDocument4 pagesX X X X Ecx Ecx: Tan - Sec Sec Cot - Cos Cossharanmit2039Pas encore d'évaluation
- Target Iit-Jee: Paper - IDocument10 pagesTarget Iit-Jee: Paper - IPritam RoyPas encore d'évaluation
- F C D I: Ormulario de Álculo Iferencial E NtegralDocument2 pagesF C D I: Ormulario de Álculo Iferencial E Ntegralpaz_aranibarPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise 1 (C) : DX DyDocument7 pagesExercise 1 (C) : DX DyGokul NathPas encore d'évaluation
- Fórmulas de Cálculo Diferencial e Integral: Jesús Rubí MirandaDocument3 pagesFórmulas de Cálculo Diferencial e Integral: Jesús Rubí MirandaAnthony GuaniloPas encore d'évaluation
- Multivariable Calculus, 2009-10-30. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526Document5 pagesMultivariable Calculus, 2009-10-30. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526lieth-4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Formula RioDocument6 pagesFormula RioJorge Laura GutierrezPas encore d'évaluation
- MJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1Document22 pagesMJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongPas encore d'évaluation
- Formula TableDocument1 pageFormula TableAho Chi- ShuenPas encore d'évaluation
- RT Solutions-22!01!2012 XIII VXY Paper II Code A SolDocument16 pagesRT Solutions-22!01!2012 XIII VXY Paper II Code A Solvishal110085Pas encore d'évaluation
- Complex Analysis 1984Document20 pagesComplex Analysis 1984Suresh KannanPas encore d'évaluation
- Math Resources Trigonometric FormulasDocument10 pagesMath Resources Trigonometric FormulasAnonymous j3w8EmJb8Pas encore d'évaluation
- Multivariable Calculus, 2008-10-31. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526Document5 pagesMultivariable Calculus, 2008-10-31. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526lieth-4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Narayana Institute Iit Jee 2008 Paper 1 2Document53 pagesNarayana Institute Iit Jee 2008 Paper 1 2Pranjal AgarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- C D I 2 L E - D: X X X F X X X X FDocument0 pageC D I 2 L E - D: X X X F X X X X Fglobaltech164768Pas encore d'évaluation
- Concept Recapitulation Test I/Advanced/PAPER-1/Answer/AnswerDocument8 pagesConcept Recapitulation Test I/Advanced/PAPER-1/Answer/Answerullasagw100% (1)
- Control 3 Calculo2Document9 pagesControl 3 Calculo2camilo_akuPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam - 2012 10 30Document5 pagesExam - 2012 10 30lieth-4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Formula SheetDocument3 pagesFormula SheetHussain JiffryPas encore d'évaluation
- Iit Jee 2004 Screening MathsDocument10 pagesIit Jee 2004 Screening MathsRahul BadwaikPas encore d'évaluation
- Model Answer For Combined Mathematics I - 2013 AL Paper PDFDocument18 pagesModel Answer For Combined Mathematics I - 2013 AL Paper PDFThiwanka De SilvaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fourier SeriesDocument26 pagesFourier SeriesPurushothamanPas encore d'évaluation
- Iit - Jee Model Grand Test - Ii Paper - 2: Solutions KEY PhysicsDocument8 pagesIit - Jee Model Grand Test - Ii Paper - 2: Solutions KEY PhysicsSayan Kumar KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Tugas Bab-I & Bab IiDocument28 pagesTugas Bab-I & Bab IiblackzmillianPas encore d'évaluation
- Formulario: L Ogica Matem AticaDocument8 pagesFormulario: L Ogica Matem AticaDiana Carolina DelgadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageD'EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguagePas encore d'évaluation
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesD'EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesPas encore d'évaluation
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesD'EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesÉvaluation : 1.5 sur 5 étoiles1.5/5 (2)
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankD'EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankPas encore d'évaluation
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsD'EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankD'EverandInverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankPas encore d'évaluation
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYD'EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex ArgumentD'EverandMathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex ArgumentPas encore d'évaluation
- TT201 - 4918Document4 pagesTT201 - 4918Yoga RasiahPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic Field Theory: A Problem Solving ApproachDocument283 pagesElectromagnetic Field Theory: A Problem Solving ApproachEkSlzrPas encore d'évaluation
- Network Analysis by Van Valkenburg Solution CHAP#6Document21 pagesNetwork Analysis by Van Valkenburg Solution CHAP#6Husnain100% (2)
- Engineering Council Register News Issue 50Document9 pagesEngineering Council Register News Issue 50Yoga RasiahPas encore d'évaluation























































![Mathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex Argument](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/282615796/149x198/febb728e8d/1699542561?v=1)