Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Xa 2 GT 1 Pdaf
Transféré par
Subrahmanyam Sana0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
10 vues1 pageTitre original
xa2gt1pdaf
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
10 vues1 pageXa 2 GT 1 Pdaf
Transféré par
Subrahmanyam SanaDroits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 1
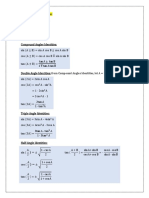
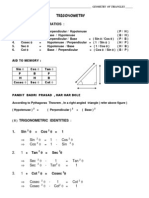
Trigonometry Section 1: Trigonometric identities
Proof of double-angle formulae
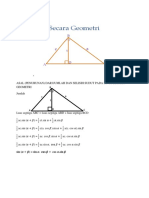
You can prove these by putting B = A in the compound-angle formula. From: Putting B = A: So:
sin( A + B) = sin A cos B + cos A sin B sin( A + A) = sin A cos A + cos A sin A sin 2 A = 2sin A cos A
From: Putting B = A: So:
tan A + tan B 1 tan A tan B tan A + tan A tan( A + A) = 1 tan A tan A 2 tan A tan 2 A = 1 tan 2 A tan( A + B ) =
From: Putting B = A: So:
cos( A + B) = cos A cos B sin A sin B cos( A + A) = cos A cos A sin A sin A
cos 2 A = cos 2 A sin 2 A
There are two more alternative forms for
Using the Pythagorean identity: Rearranging: Substituting this into gives: So:
sin 2 A + cos 2 A 1 sin 2 A 1 cos 2 A cos 2 A = cos 2 A (1 cos 2 A) cos 2 A = 2 cos 2 A 1
Using the Pythagorean identity: Rearranging: Substituting this into gives: So:
sin 2 A + cos 2 A 1 cos 2 A 1 sin 2 A cos 2 A = (1 sin 2 A) sin 2 A cos 2 A = 1 2sin 2 A
MEI, 20/09/05
1/1
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Formula Sheet GeometryDocument2 pagesFormula Sheet Geometrykenneth_fvPas encore d'évaluation
- Trigonometry: All in One Formulas List !Document10 pagesTrigonometry: All in One Formulas List !Rohit Ghere50% (2)
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsD'EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankD'EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankPas encore d'évaluation
- Parabola (Exercise+ Solved Example)Document16 pagesParabola (Exercise+ Solved Example)The ChampionPas encore d'évaluation
- Trigonometric Identities GuideDocument15 pagesTrigonometric Identities GuideНеизвестный НечитаемыйPas encore d'évaluation
- Formulae of TrigonometryDocument3 pagesFormulae of TrigonometryManoj Khandelwal100% (1)
- Formula SheetDocument1 pageFormula SheetSaleem SheikhPas encore d'évaluation
- Trigonometric Identities and Equation EngDocument33 pagesTrigonometric Identities and Equation Engchirag2796100% (1)
- Wikimama Class 11 CH 2 TrigonometryDocument6 pagesWikimama Class 11 CH 2 TrigonometryWikimamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesD'EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesÉvaluation : 1.5 sur 5 étoiles1.5/5 (2)
- H2 Mathematics - TrigonometryDocument12 pagesH2 Mathematics - TrigonometryMin YeePas encore d'évaluation
- Maths Summer Vacation Assignment Package Solution: Trigonometric Ratios & IdentitiesDocument31 pagesMaths Summer Vacation Assignment Package Solution: Trigonometric Ratios & IdentitiesaijazmonaPas encore d'évaluation
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageD'EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguagePas encore d'évaluation
- Angle-Sum and Difference Identities: Sin A/2 (1 - Cos A) / 2 Cos A/2 (1 + Cos A) / 2Document2 pagesAngle-Sum and Difference Identities: Sin A/2 (1 - Cos A) / 2 Cos A/2 (1 + Cos A) / 2carry2 pandeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Tan A Tan B 1 Tan A Tan BDocument2 pagesTan A Tan B 1 Tan A Tan BibrahimPas encore d'évaluation
- Publication 12 5352 477Document7 pagesPublication 12 5352 477Mohammad FaizanPas encore d'évaluation
- Trigonometry Worksheet on Identities and ExpressionsDocument1 pageTrigonometry Worksheet on Identities and ExpressionsIshwarya SivakumarPas encore d'évaluation
- FormulasDocument14 pagesFormulasPragya Gupta100% (1)
- Trigonometry Formula SheetDocument2 pagesTrigonometry Formula Sheetkusumathirumalesh19Pas encore d'évaluation
- Trigonometric Formulas GuideDocument1 pageTrigonometric Formulas GuideGutium CristiPas encore d'évaluation
- CSC A CSC A : Trigonometric Formulas and IdentitiesDocument2 pagesCSC A CSC A : Trigonometric Formulas and IdentitiesTeo Mark De JesusPas encore d'évaluation
- Trigonometric Formulae: C+ D C D C D C+ D C+ D C D C+ D D CDocument3 pagesTrigonometric Formulae: C+ D C D C D C+ D C+ D C D C+ D D CtraePas encore d'évaluation
- Split 4026815802256091763Document5 pagesSplit 4026815802256091763vidyakumari808940Pas encore d'évaluation
- Angle Relationships in TrigonometryDocument10 pagesAngle Relationships in Trigonometrydahlai dahlia oktaviani gintingPas encore d'évaluation
- Tugas MTKDocument4 pagesTugas MTKJackPas encore d'évaluation
- Thumbnail HereDocument115 pagesThumbnail HereFor 3rd Party signupsPas encore d'évaluation
- Compound Angles: Definitions and FormulaeDocument19 pagesCompound Angles: Definitions and FormulaeRon HartPas encore d'évaluation
- Review Trigonometric IdsDocument1 pageReview Trigonometric IdsGabby LabsPas encore d'évaluation
- MathsDocument6 pagesMathsmangalaprasadojhaPas encore d'évaluation
- TR 3Document13 pagesTR 3Nadya AnandaPas encore d'évaluation
- EMATH 4th Quarter Week 4 ModuleDocument7 pagesEMATH 4th Quarter Week 4 ModuleB - HERRERA, Jhian Carlo G.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Trig IdentitiesDocument1 pageTrig IdentitiesHeena PasrichaPas encore d'évaluation
- A2 Maths QuestionsDocument2 pagesA2 Maths QuestionsIshwarya SivakumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Solutionbank: Edexcel AS and A Level Modular MathematicsDocument159 pagesSolutionbank: Edexcel AS and A Level Modular MathematicsMaruf_007Pas encore d'évaluation
- QB - M2E05 Trigonometry 2Document48 pagesQB - M2E05 Trigonometry 2AllyLauPas encore d'évaluation
- Byjus Com Maths Trigonometry Questions 1 15 - RemovedDocument6 pagesByjus Com Maths Trigonometry Questions 1 15 - RemovedVikas PratikPas encore d'évaluation
- Useful Trigonometry ResultsDocument1 pageUseful Trigonometry ResultsfreudianslipjrPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 1 - Double Angle FormulaeDocument9 pagesLesson 1 - Double Angle Formulaeiminathi ndlovuPas encore d'évaluation
- Trigonometry 2Document5 pagesTrigonometry 2Jehan B KothariPas encore d'évaluation
- Calg t6 5Document13 pagesCalg t6 5api-261379705Pas encore d'évaluation
- Solution of Triangle Theory - EDocument14 pagesSolution of Triangle Theory - EthinkiitPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheet - 01 - Compound AngleDocument17 pagesSheet - 01 - Compound AngleNoob Game PlayPas encore d'évaluation
- Trig Identities - Cosine Law and Addition FormulaeDocument2 pagesTrig Identities - Cosine Law and Addition FormulaemousypusaPas encore d'évaluation
- Trig Formulas & IdentitiesDocument2 pagesTrig Formulas & IdentitiesChristian AlonzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics Trigonometry Summary 1. Basic Trigonometric RatiosDocument2 pagesMathematics Trigonometry Summary 1. Basic Trigonometric RatiosSimran GillPas encore d'évaluation
- Properties of Triangle-1Document58 pagesProperties of Triangle-1jmunjalPas encore d'évaluation
- Trigonometry Formula PDFDocument1 pageTrigonometry Formula PDFNaitikPas encore d'évaluation
- Adobe Scan 16 Mar 2021Document2 pagesAdobe Scan 16 Mar 2021Neha EdwinPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 Trigonometry UpdatedDocument60 pagesChapter 3 Trigonometry Updatedanita khimaPas encore d'évaluation
- Plane and Spherical TrigonometryDocument76 pagesPlane and Spherical TrigonometryAlyssa Marie AsuncionPas encore d'évaluation
- Trigonometric FormulaeDocument9 pagesTrigonometric FormulaeButik Chantek KamiPas encore d'évaluation
- Triangle FormulasDocument3 pagesTriangle FormulasFrancia BalondoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lessson 9 TrigonometryDocument11 pagesLessson 9 Trigonometryjamesmorara3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cosine Sum and Difference IdentitiesDocument26 pagesCosine Sum and Difference IdentitiesVilDomPas encore d'évaluation
- The Addition FormulaeDocument8 pagesThe Addition FormulaeNitish BhardwajPas encore d'évaluation
- c3 Trigonometry Notes PDFDocument2 pagesc3 Trigonometry Notes PDFWandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Formula SheetDocument1 pageFormula SheetAbi RajasingamPas encore d'évaluation
- Proofs and applications of sine and cosine formulaeDocument22 pagesProofs and applications of sine and cosine formulaeMeenakshi ChaudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Double AngleDocument10 pagesDouble AngleKishore RameshPas encore d'évaluation
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesD'EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesPas encore d'évaluation
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledSubrahmanyam SanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Trigonometry - I: Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsDocument37 pagesTrigonometry - I: Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsSubrahmanyam SanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Conceptual QnsDocument6 pagesConceptual QnsSubrahmanyam SanaPas encore d'évaluation
- IMOMATH - Functional EquationsDocument18 pagesIMOMATH - Functional EquationsDijkschneierPas encore d'évaluation
- Complex NumbersDocument24 pagesComplex NumbersSubrahmanyam SanaPas encore d'évaluation
- VAT (VELOCIITY ADVANCED TESTDocument13 pagesVAT (VELOCIITY ADVANCED TESTSubrahmanyam SanaPas encore d'évaluation
- L No 01Document38 pagesL No 01Annas Equity AnalystPas encore d'évaluation
- SequencesDocument68 pagesSequencesSubrahmanyam SanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Velociity : Junior Kalam CampusDocument3 pagesVelociity : Junior Kalam CampusSubrahmanyam SanaPas encore d'évaluation
- VAT (VELOCIITY ADVANCED TESTDocument13 pagesVAT (VELOCIITY ADVANCED TESTSubrahmanyam SanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Parabola (Theory)Document8 pagesParabola (Theory)The Champion100% (1)
- Probability DPP PDFDocument32 pagesProbability DPP PDFSubrahmanyam SanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Integration 1Document49 pagesIntegration 1Subrahmanyam SanaPas encore d'évaluation
- 35 Integration Full Part 1 of 5Document16 pages35 Integration Full Part 1 of 5rappycatPas encore d'évaluation
- 35 Integration Full Part 1 of 5Document16 pages35 Integration Full Part 1 of 5rappycatPas encore d'évaluation
- 35 Integration Full Part 1 of 5Document16 pages35 Integration Full Part 1 of 5rappycatPas encore d'évaluation
- Pair of Straight Lines PDFDocument23 pagesPair of Straight Lines PDFSubrahmanyam Sana100% (1)
- 35 Integration Full Part 1 of 5Document16 pages35 Integration Full Part 1 of 5rappycatPas encore d'évaluation
- Definite Integral and Area Under Curves: FXDX y FXDocument2 pagesDefinite Integral and Area Under Curves: FXDX y FXSubrahmanyam SanaPas encore d'évaluation
- TimetableDocument1 pageTimetableSubrahmanyam SanaPas encore d'évaluation