Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Body Without Providing Adequate Recovery
Transféré par
api-260522530 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
22 vues14 pagesLifestyle Factors affect our fitness levels Understanding the factors and how it affects performance is vital - increase in quality of life and (in some cases) life-span Avoiding a lifestyle that increases possibility of ill-health or injury is Stress An emotional response to situations we experience related to health problems such as heart disease, high blood pressure and lowered efficiency of immune system body needs time to relax from day-to-day exercise is beneficial to relieve stress and health related illnesses.
Description originale:
Titre original
Body Without Providing Adequate Recovery
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentLifestyle Factors affect our fitness levels Understanding the factors and how it affects performance is vital - increase in quality of life and (in some cases) life-span Avoiding a lifestyle that increases possibility of ill-health or injury is Stress An emotional response to situations we experience related to health problems such as heart disease, high blood pressure and lowered efficiency of immune system body needs time to relax from day-to-day exercise is beneficial to relieve stress and health related illnesses.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
22 vues14 pagesBody Without Providing Adequate Recovery
Transféré par
api-26052253Lifestyle Factors affect our fitness levels Understanding the factors and how it affects performance is vital - increase in quality of life and (in some cases) life-span Avoiding a lifestyle that increases possibility of ill-health or injury is Stress An emotional response to situations we experience related to health problems such as heart disease, high blood pressure and lowered efficiency of immune system body needs time to relax from day-to-day exercise is beneficial to relieve stress and health related illnesses.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 14
Lifestyle Factors
Why do we need to consider
lifestyle factors?
• Lifestyle factors affect our fitness
levels
• These factors need to be considered
if we are to perform to the best of
our ability
• Understanding the factors and how if
affects performance is vital –
increase in quality of life and (in
some cases) life-span
• Avoiding a lifestyle that increases
possibility of ill-health or injury is
Stress
• An emotional response to situations we
experience
• Related to health problems such as heart
disease, high blood pressure and lowered
efficiency of immune system
• Body needs time to relax from day-to-day
• Exercise is beneficial to relieve stress and
health related illnesses
Q. When have you been stressed and why?
Q. What were your symptoms of stress?
Q. How did you deal with it? What action did
you take?
Alcohol
• Short-term effects – dizziness, loss of
motor control, reduced ability to make
decisions, reduced perception of
movement
• Long-term effects – breathlessness,
swelling of legs, muscular fatigue, increase
in body weight, joint problems, liver
damage and heart failure (extreme cases)
Smoking
• Aerobic fitness can be reduced between 5
and 10% due to smoking
• Carbon monoxide entering the body takes
space from oxygen in the blood
• Less oxygen available during exercise
• Increases risk of cancer, heart disease and
respiratory disease
Drugs
• Drug abuse can reduce fitness levels
• Banned substances (e.g. Steroids)
are used to increase capabilities for
training and rapid recovery between
exercise sessions
• Harmful activities include: smoking,
alcohol and recreational drugs (e.g.
marajana)
Sleep Patterns
• May vary due to pattern of training, or
external demands such as family and work
• At least 8 hours is recommended per
night/day for younger people
• If training intensity is high, increased sleep
may be required
• If sleep is not balanced with work, then
positive effects of training will not be seen
Work Demands
• Work hours have increased in
modern society – time to relax or
take part in non-work activities has
decreased
• Stress levels have therefore risen –
more instances of stress related
diseases (e.g. high blood pressure)
Medical History
• Fitness levels are inherited partly
from our parents, as are some of the
health-related problems that may be
experienced through the years
• Training can increase levels of fitness
but only to the capacity that has
been passed down from generation
to generation – Is this true? Discuss
Level of Activity
• The more active you are – the greater
level of fitness you will possess
• Non-active lifestyles are related to many
diseases such as obesity, heart disease,
high blood pressure and joint/bone
problems
• Increased active lifestyle = Increased
quality of life!
Diet and Weight
• Healthy diet will ensure a balance
between the nutrient value that you
consume and energy that you use for
muscular activity
• If there is an imbalance: less food
and more exercise = weight loss;
more food and less exercise =
weight gain
Gender
• Fitness of males and females differs
due to the structures of their bodies
• These differences are most
noticeable after puberty
• The two genders are psychologically
different – high drop out rate in
physical activity of females aged
between 16-21
• This may be due to career ,
relationship and financial pressures
Culture
• Exercise may be seen as a lower
priority for some people due to
career and family pressures
Sports Participation
• Participation in competition and sport
activities can overtake the
importance of maintaining fitness
levels
• Too many competitions hinder fitness
levels and stress the body without
providing adequate recovery
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Bio-Gro HyperGrowth Lean Mass FinalDocument17 pagesBio-Gro HyperGrowth Lean Mass FinalMarcelo Calderón Cruz80% (5)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Airborne Doppler Radar Navigation of Jet Transport Aircraft-EftDocument10 pagesAirborne Doppler Radar Navigation of Jet Transport Aircraft-Eftjulio perezPas encore d'évaluation
- Tillotson HD & HR Service ManualDocument11 pagesTillotson HD & HR Service ManualBeckyPas encore d'évaluation
- Btec Diploma in Sport Unit 1 - The Body inDocument2 pagesBtec Diploma in Sport Unit 1 - The Body inapi-26052253Pas encore d'évaluation
- VolleyDocument3 pagesVolleyapi-26052253Pas encore d'évaluation
- Btec Diploma in Sport Unit 1 - The Body inDocument2 pagesBtec Diploma in Sport Unit 1 - The Body inapi-26052253Pas encore d'évaluation
- Long Term Effects of Exercise On MusclesDocument1 pageLong Term Effects of Exercise On Musclesapi-26052253Pas encore d'évaluation
- Short-Term Effects of Exercise On The Muscular SystemDocument1 pageShort-Term Effects of Exercise On The Muscular Systemapi-26052253Pas encore d'évaluation
- Joint Movement in Sport - Task 5 (M1) - Answers: Rugby Player Holding The Ball Whilst Being TackledDocument3 pagesJoint Movement in Sport - Task 5 (M1) - Answers: Rugby Player Holding The Ball Whilst Being Tackledapi-26052253Pas encore d'évaluation
- Short-Term Effects of Exercise On The Muscular SystemDocument1 pageShort-Term Effects of Exercise On The Muscular Systemapi-26052253Pas encore d'évaluation
- Btec Diploma in Sport Unit 1 - The Body inDocument2 pagesBtec Diploma in Sport Unit 1 - The Body inapi-26052253Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gymnastics Level 1: I CanDocument3 pagesGymnastics Level 1: I Canapi-26052253Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bounce Pass in NetballDocument3 pagesBounce Pass in Netballapi-26052253Pas encore d'évaluation
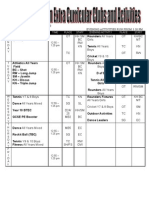
- FROM THE DATE OF September 2009: Evening Activities Run From 3:30 PMDocument1 pageFROM THE DATE OF September 2009: Evening Activities Run From 3:30 PMapi-26052253Pas encore d'évaluation
- Btec PPM AssessmentDocument3 pagesBtec PPM Assessmentapi-26052253Pas encore d'évaluation
- Skeletal SystemDocument4 pagesSkeletal Systemapi-26052253Pas encore d'évaluation
- BTEC First Sport: The Skeleton Major Bones of The BodyDocument1 pageBTEC First Sport: The Skeleton Major Bones of The Bodyapi-26052253Pas encore d'évaluation
- Analyse Psychological Factors Sports TrainingDocument3 pagesAnalyse Psychological Factors Sports Trainingapi-26052253Pas encore d'évaluation
- Make Sure That Ensure Your ClientDocument2 pagesMake Sure That Ensure Your Clientapi-26052253Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pupil Name:: Unit 1 The Body in Sport Grading Criteria For Each AssignmentDocument1 pagePupil Name:: Unit 1 The Body in Sport Grading Criteria For Each Assignmentapi-26052253Pas encore d'évaluation
- Btec Diploma in SportDocument2 pagesBtec Diploma in Sportapi-26052253Pas encore d'évaluation
- BTEC First Sport: The Skeleton Major Bones of The BodyDocument1 pageBTEC First Sport: The Skeleton Major Bones of The Bodyapi-26052253Pas encore d'évaluation
- From The Date of April 2009 Evening Activities RunDocument2 pagesFrom The Date of April 2009 Evening Activities Runapi-26052253Pas encore d'évaluation
- Btec First Certificate in Sport Unit 6 - PracticalDocument3 pagesBtec First Certificate in Sport Unit 6 - Practicalapi-26052253Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Week Food Plan For A Sports PerformerDocument3 pages2 Week Food Plan For A Sports Performerapi-26052253Pas encore d'évaluation
- Btec First Certificate in Sport Unit 6 - PracticalDocument3 pagesBtec First Certificate in Sport Unit 6 - Practicalapi-26052253Pas encore d'évaluation
- Btec First Certificate in Sport Unit 6 - PracticalDocument3 pagesBtec First Certificate in Sport Unit 6 - Practicalapi-26052253Pas encore d'évaluation
- Performer From Actually Training Progression Takes Place OverDocument9 pagesPerformer From Actually Training Progression Takes Place Overapi-26052253Pas encore d'évaluation
- Btec First Certificate in Sport Unit 6 - PracticalDocument3 pagesBtec First Certificate in Sport Unit 6 - Practicalapi-26052253Pas encore d'évaluation
- Badminton Observation ChecklistDocument3 pagesBadminton Observation Checklistapi-26052253Pas encore d'évaluation
- Btec First Certificate in Sport Unit 6 - PracticalDocument3 pagesBtec First Certificate in Sport Unit 6 - Practicalapi-26052253Pas encore d'évaluation
- Describe Four Different Lifestyle Factors That Affect Sports PerformanceDocument4 pagesDescribe Four Different Lifestyle Factors That Affect Sports Performanceapi-26052253Pas encore d'évaluation
- Roles and Responsibilities of Badminton OfficialsDocument3 pagesRoles and Responsibilities of Badminton Officialsapi-26052253Pas encore d'évaluation
- Manual DessertDocument32 pagesManual DessertDANIEL F. HERNANDEZ100% (1)
- Fuhs - Towards An Integral EpistemologyDocument39 pagesFuhs - Towards An Integral EpistemologyjmcmichaelPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Circuits 1 QPDocument7 pagesElectrical Circuits 1 QPKitty MinoguePas encore d'évaluation
- Candaza, HM Pe4l Reaction PaperDocument5 pagesCandaza, HM Pe4l Reaction Papermaria isabel candazaPas encore d'évaluation
- Envgeo D 17 00052 - R1Document42 pagesEnvgeo D 17 00052 - R1Recep AkanPas encore d'évaluation
- GIRBESDocument6 pagesGIRBESMiguel LópezPas encore d'évaluation
- Prof Budi Wiweko - Protokol Dan Pemantauan Stimulasi Ovarium SederhanaDocument36 pagesProf Budi Wiweko - Protokol Dan Pemantauan Stimulasi Ovarium SederhanaAnisanang BanjarPas encore d'évaluation
- Papr114 SpectralDocument4 pagesPapr114 Spectrallilivaca28Pas encore d'évaluation
- Shell Omala S2 GX 150: Performance, Features & Benefits Main ApplicationsDocument2 pagesShell Omala S2 GX 150: Performance, Features & Benefits Main ApplicationsVelibor KaranovicPas encore d'évaluation
- GTE LAB MANUAL Ver 4 - 1Document135 pagesGTE LAB MANUAL Ver 4 - 1akhilaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Determinants of Service Quality and Customer Satisfaction in Malaysian e Hailing ServicesDocument8 pagesThe Determinants of Service Quality and Customer Satisfaction in Malaysian e Hailing ServicesYoannisa AtinaPas encore d'évaluation
- R0221120 - Salsabilla Cindy Pratama - Daily ActivityDocument15 pagesR0221120 - Salsabilla Cindy Pratama - Daily Activitysalsabilla cindy pratamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Functional Endoscopic Sinus SurgeryDocument3 pagesFunctional Endoscopic Sinus SurgeryDanielicah CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Inhalation AnestheticsDocument27 pagesInhalation AnestheticsMarcelitaTaliaDuwiriPas encore d'évaluation
- Rangtong Shentong ViewDocument19 pagesRangtong Shentong Viewlongjim31100% (1)
- Expansion ScrewsDocument32 pagesExpansion ScrewsJomar PortadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Current Invoice No. 1: Enabling Works CeilingDocument1 pageCurrent Invoice No. 1: Enabling Works CeilingEyad RefaiPas encore d'évaluation
- MEC Threads ChartDocument12 pagesMEC Threads ChartenricoPas encore d'évaluation
- Case IH Farmall B - Brochure - 0717Document7 pagesCase IH Farmall B - Brochure - 0717nadeemmohamed555Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tech Brief 3: Digitally Control Phase Shift: Application Note 559Document6 pagesTech Brief 3: Digitally Control Phase Shift: Application Note 559Sreerag Kunnathu SugathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Safety Data Sheet: 1. IdentificationDocument7 pagesSafety Data Sheet: 1. IdentificationKhobeb MuslimPas encore d'évaluation
- Nigeria Certificate in Education Science ProgrammeDocument215 pagesNigeria Certificate in Education Science Programmemuhammadbinali77_465Pas encore d'évaluation
- Atomic Rex A Kaiju Thriller (Matthew Dennion) (Z-Library)Document163 pagesAtomic Rex A Kaiju Thriller (Matthew Dennion) (Z-Library)Strictly Aviator Amritansh VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction On Photogrammetry Paul R WolfDocument33 pagesIntroduction On Photogrammetry Paul R Wolfadnan yusufPas encore d'évaluation
- Mat11 PDFDocument13 pagesMat11 PDFRaquel Martins E SilvaPas encore d'évaluation
- Baluarte BridgeDocument1 pageBaluarte BridgeIndra MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- 4mb/01r-Que-2023 Jun Edexcel PastpaperDocument24 pages4mb/01r-Que-2023 Jun Edexcel Pastpaperaugust.shwanPas encore d'évaluation