Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
d5lr Ivf Study
Transféré par
james_delicaDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
d5lr Ivf Study
Transféré par
james_delicaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
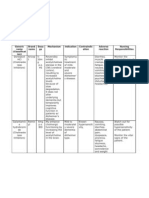
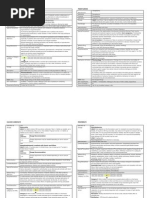
NAME OF THE FLUID 5 % dextrose in lactated ringers (D5LR) Electrolytes in 1000 ml Sodium-130mmol Potassium-4 mmol Calcium-1.
4mmol Chloride-109 mmol Lactate-28 mmol
CLASSIFICATION & ACTION Hypertonic Solution Nonpyrogenic, parenteral fluid, electrolyte and nutrient replenisher
INDICATION Replacement therapy particularly in extracellular fluid deficit accompanied by acidosis Treatment of shock Persons needing extra calories who cannot tolerate fluid overload
SIDE EFFECTS Increased serum osmolality Hypernatremia Hypokalemia Altered thermoregulatio n Pulmonary edema Cardiovascular overload
CONTRAINDICATIO N Renal failure Heart disease Dehydration Liver dysfunction Diabetes mellitus Lactic acidosis Alkalosis Hyperkalemia
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES Watch out for signs of hypervolemia Do not administer unless solution is clear and container is undamaged. Never stop hypertonic solutions abruptly. Dont give concentrated solutions IM or subcutaneously . Check vital signs frequently. Report adverse reactions. Monitor fluid intake and output and weight carefully. Watch carefully for signs and symptoms of fluid overload. Monitor patients for signs of mental confusion.
MONITORING PARAMETERS Monitor glucose level carefully. Monitor for sodium, potassium and serum osmolality.
Hypertonic solutions are those that have an effective osmolarity greater than the body fluids. These solutions draw fluid out of the intracellular and interstitial compartments into the vascular compartment, expanding vascular volume. It raises intravascular osmotic pressure and provides fluid, electrolytes and calories for energy.
Lung sounds are frequently auscultated to detect signs of fluid accumulation.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Ivf Study D5LRDocument2 pagesIvf Study D5LRmaria_boyles100% (2)
- D5LRDocument2 pagesD5LRMae Ann Bueno Castillon100% (2)
- D5LRDocument2 pagesD5LRjonoelc100% (5)
- Ivf Study d5lrDocument2 pagesIvf Study d5lrryan0% (1)
- Drug Study - D5NSSDocument1 pageDrug Study - D5NSSCerie Anne Olay100% (1)
- PNSS Drug StudyDocument2 pagesPNSS Drug Studyrain peregrinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Plain LRDocument3 pagesPlain LRlovlyPas encore d'évaluation
- Ivf PnssDocument3 pagesIvf Pnssdonlyn100% (5)
- Nursing Responsibility Adverse Effects Machanism of Action Drug NameDocument2 pagesNursing Responsibility Adverse Effects Machanism of Action Drug NameSalwa ZeinPas encore d'évaluation
- Ivf Drug StudyDocument9 pagesIvf Drug StudyRyu Bomi0% (2)
- D 5 IMBDocument2 pagesD 5 IMBAloyan Rose JoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Republic of The Philippines Puerto Princesa City: Palawan State UniversityDocument3 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Puerto Princesa City: Palawan State UniversityRosemarie EustaquioPas encore d'évaluation
- IVF Drug StudyDocument5 pagesIVF Drug StudyHannah Angelu CabadingPas encore d'évaluation
- D5imb IvDocument2 pagesD5imb IvLegendXPas encore d'évaluation
- D5WDocument1 pageD5WBreena Reubee EstillorePas encore d'évaluation
- D5LRDocument2 pagesD5LRLouiseville Ann Arcilla PilPas encore d'évaluation
- Sodium ChlorideDocument1 pageSodium ChlorideMark Christian M. GonzagaPas encore d'évaluation
- D5NMDocument3 pagesD5NMjonoelc100% (2)
- Ivf StudyDocument2 pagesIvf StudyDanePepitoPas encore d'évaluation
- Treatment/ Infusion d5lrDocument1 pageTreatment/ Infusion d5lrjbespirituPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Presentation Station 3B Drug Study Sodium ChlorideDocument4 pagesCase Presentation Station 3B Drug Study Sodium ChloridehahahahaaaaaaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Piperacillin Tazobactam Drug StudyDocument5 pagesPiperacillin Tazobactam Drug StudyKathlene Boleche100% (2)
- Lactulose Drug StudyDocument1 pageLactulose Drug StudyJhanine ArellanoPas encore d'évaluation
- D5 0.3%Document1 pageD5 0.3%Aloyan Rose Joy0% (1)
- Lactulose Drug StudyDocument4 pagesLactulose Drug StudyAgronaSlaughterPas encore d'évaluation
- Dextrose in Water (50%)Document2 pagesDextrose in Water (50%)jbambaoPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 DrugsDocument2 pages1 DrugsPatricia Lucero100% (2)
- Folic AcidDocument2 pagesFolic AcidConn_Casipe_8158100% (1)
- GlucoseDocument4 pagesGlucoseGwyn RosalesPas encore d'évaluation
- PNSS Drug StudyDocument2 pagesPNSS Drug Studyabrokenheartedgirl86% (14)
- Tranexamic Acid Drug StudyDocument1 pageTranexamic Acid Drug StudyCen Janber Cabrillos67% (3)
- Generic Name:: Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindi-Cation Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageGeneric Name:: Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindi-Cation Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesmaemalabonPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study D5W2Document3 pagesDrug Study D5W2Girlie Jane Sevillano RN100% (2)
- Tranexamic Acid Drug StudyDocument2 pagesTranexamic Acid Drug StudyFa Villarin100% (1)
- Ascorbic AcidDocument3 pagesAscorbic Acidmanelz_16Pas encore d'évaluation
- PnssDocument2 pagesPnssFrances Oscar GaviolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Aminoleban Drug StudyDocument1 pageAminoleban Drug StudyNajmah Saaban100% (1)
- ALZHEIMER's - Drug Study.Document2 pagesALZHEIMER's - Drug Study.Christian UretaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study - Acetaminophen, ParacetamolDocument1 pageDrug Study - Acetaminophen, ParacetamolmikErlh100% (2)
- Drug Study Ko ToDocument4 pagesDrug Study Ko ToGian Carlo FernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudySa Dei100% (1)
- Final Drug StudyDocument9 pagesFinal Drug StudyCherry Lou Correos Tejada100% (2)
- Senna Concentrate: The Medicine at BedtimeDocument2 pagesSenna Concentrate: The Medicine at BedtimeTempoPas encore d'évaluation
- A Drug Study On Evening Primrose OilDocument5 pagesA Drug Study On Evening Primrose OilAlexis Khalyl Y. MontejoPas encore d'évaluation
- SenokotDocument1 pageSenokotKatie McPeek100% (1)
- Drug Study 2Document3 pagesDrug Study 2Aileen Alpha100% (2)
- DS - Oral Rehydration Salts (ORS)Document2 pagesDS - Oral Rehydration Salts (ORS)Celline Isabelle ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- DRUG STUDY: Biogesic - ParacetamolDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY: Biogesic - ParacetamolYum CPas encore d'évaluation
- D5 WaterDocument3 pagesD5 WaterErnestomalamionPas encore d'évaluation
- D5IMBDocument1 pageD5IMBPrincess Garrote50% (2)
- AcetazolamideDocument2 pagesAcetazolamideLIEZEL GRACE VELAYOPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydralazine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesHydralazine Drug StudyErika Robella100% (1)
- Hary-Fluid Management Part 1Document49 pagesHary-Fluid Management Part 1Keta PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Type of Solution Classification Content Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication How Supplied Dose Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesType of Solution Classification Content Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication How Supplied Dose Nursing ResponsibilitiesAlexis TillanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Alteration in Fluid and Electrolyte Status Lecture NotesDocument11 pagesAlteration in Fluid and Electrolyte Status Lecture Notes0912247251Pas encore d'évaluation
- FLUID AND ELECTOLYTE IMBALANCE FinalDocument27 pagesFLUID AND ELECTOLYTE IMBALANCE FinalShiva BiradarPas encore d'évaluation
- Guidance For Intravenous Fluid and Electrolyte Prescription in AdultsDocument8 pagesGuidance For Intravenous Fluid and Electrolyte Prescription in AdultsfrakturhepatikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid GuidelinesDocument8 pagesFluid GuidelinesAya SalahPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid and Electrolyte - 2022Document147 pagesFluid and Electrolyte - 2022Lacangan, Thea YvonnePas encore d'évaluation
- Dka 31-05-11Document52 pagesDka 31-05-11Hussain AzharPas encore d'évaluation
- GaramycinDocument2 pagesGaramycinjames_delicaPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Event Program-InvitationDocument1 pageFinal Event Program-Invitationjames_delicaPas encore d'évaluation
- JamesdelicaDocument2 pagesJamesdelicajames_delicaPas encore d'évaluation
- Celecoxib Drug StudyDocument1 pageCelecoxib Drug StudyMan Gatuanko83% (12)
- Ra Wah Night Shift - Word Format FiniDocument17 pagesRa Wah Night Shift - Word Format FiniREHOBOTH YAMBO KAHILUPas encore d'évaluation
- Mercedes (DTC) 976990001963 20220615144147Document3 pagesMercedes (DTC) 976990001963 20220615144147YB MOTOR Nissan - Datsun SpecialistPas encore d'évaluation
- Adminstration of Intramusclar InjectionDocument3 pagesAdminstration of Intramusclar InjectionDenise CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- EQ Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesEQ Cheat SheetGabrielPas encore d'évaluation
- Leta-Leta CaveDocument5 pagesLeta-Leta CaveToniPas encore d'évaluation
- Total04 Digital Version PDFDocument52 pagesTotal04 Digital Version PDFbeatriz matos67% (3)
- Eoi QAMDocument6 pagesEoi QAMPeeyush SachanPas encore d'évaluation
- Indigo Airlines - Final ReportDocument22 pagesIndigo Airlines - Final Reportanand_lihinarPas encore d'évaluation
- Popular CultureDocument6 pagesPopular CultureAmritaPas encore d'évaluation
- Disa Match: A Match You Can Count OnDocument8 pagesDisa Match: A Match You Can Count OngPas encore d'évaluation
- AC350 Specs UsDocument18 pagesAC350 Specs Uskloic1980100% (1)
- Mathematics For Engineers and Scientists 3 PDFDocument89 pagesMathematics For Engineers and Scientists 3 PDFShailin SequeiraPas encore d'évaluation
- ONGC Buyout GOI's Entire 51.11% Stake in HPCLDocument4 pagesONGC Buyout GOI's Entire 51.11% Stake in HPCLArpan AroraPas encore d'évaluation
- ScheduleDocument1 pageScheduleparag7676Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5: Sampling Distributions: Solve The ProblemDocument4 pagesChapter 5: Sampling Distributions: Solve The ProblemEunice WongPas encore d'évaluation
- Wic ReflectionDocument3 pagesWic Reflectionapi-307029735Pas encore d'évaluation
- Scientific American Psychology 2nd Edition Licht Test BankDocument44 pagesScientific American Psychology 2nd Edition Licht Test Bankpurelychittra3ae3100% (24)
- Class 28: Outline: Hour 1: Displacement Current Maxwell's Equations Hour 2: Electromagnetic WavesDocument33 pagesClass 28: Outline: Hour 1: Displacement Current Maxwell's Equations Hour 2: Electromagnetic Wavesakirank1Pas encore d'évaluation
- CM1000 ManualDocument12 pagesCM1000 ManualyounesPas encore d'évaluation
- Infrastructure Definition:: Economic Infrastructure Includes BroadlyDocument3 pagesInfrastructure Definition:: Economic Infrastructure Includes Broadlyabraha gebruPas encore d'évaluation
- Tim Ingold - From The Transmission of Representations To The Education of Attention PDFDocument26 pagesTim Ingold - From The Transmission of Representations To The Education of Attention PDFtomasfeza5210100% (1)
- Case-Study - Decision Making Under UncertaintyDocument21 pagesCase-Study - Decision Making Under UncertaintyMari GhviniashviliPas encore d'évaluation
- Asyb 2020 2Document295 pagesAsyb 2020 2KhangPas encore d'évaluation
- EASA - Design OrganisationsDocument30 pagesEASA - Design Organisationsyingqi.yangPas encore d'évaluation
- FENA-01 - 11 - 21 - Ethernet Adapter - User's Manual - Rev BDocument388 pagesFENA-01 - 11 - 21 - Ethernet Adapter - User's Manual - Rev BQUOC LEPas encore d'évaluation
- Welding Research Council: BulletinDocument28 pagesWelding Research Council: BulletinRogerio Tropia GranjaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bluforest, Inc. (OTC: BLUF) InvestigationDocument5 pagesBluforest, Inc. (OTC: BLUF) Investigationfraudinstitute100% (1)
- TOP233YDocument24 pagesTOP233YJose BenavidesPas encore d'évaluation
- Flash Memoir RevisedDocument3 pagesFlash Memoir Revisedapi-511179803Pas encore d'évaluation
- Amies A 114 - 3Document17 pagesAmies A 114 - 3Syed Umar Farooq100% (1)