Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
DRAW10W - Drawing Instruments and Its Uses
Transféré par
Paolo GochingcoCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
DRAW10W - Drawing Instruments and Its Uses
Transféré par
Paolo GochingcoDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
1
Drawing Instruments and Its Uses
The traditional method of creating technical drawings is with drawing instruments. Since the eighteenth century, precision instruments have been the tools of drafters. Today, CAD software is another tool used by many drafters. The basic concepts of drawing and measuring is the same for traditional and CAD drawing. By understanding the basic principles of drawing, the properly trained drafter can create and modify any type of drawing. For many years, the essential equipment for students in technical schools and for engineers and designers in professional practice remained unchanged. This equipment included a drawing board, T-square, triangles, an architects or engineers scale, and a professional-quality set of drawing instruments. Now, however, other equipment has come into general use, including the
drafting machine, parallel-ruling straightedge, technical fountain pen and, of course, the computer. Typical pens used for technical drawing are pencils and technical pens. Usually used are mechanical pencils with a standard lead thickness. General line widths are 0.18 mm, 0.25 mm, 0.5 mm and 0.7 mm. Hardness varies usually from HB to 2H. Softer lead gives a better contrast, but harder lead gives more accurate track. Paper or plastic surfaces do require their own lead types. In most cases, the final drawings are drawn with ink. The pen is generally Rapidograf-type technical pen, a marker pen that draws lines of consistent width (so-called steel marker pen). The pen has an ink container which contains a metal tube, inside which is a thin metal needle or wire, the soul. Ink is absorbed between the needle and the tube wall, preventing an excessive amount of ink from being released. The needle has a
weight and by waving the pen back and forth the needle is released and the ink can run. Previously, the tank was filled from an ink bottle, newer styluses use ink cartridges. Each line width has its own stylus. Width of the line is standardized. In Finland, the most commonly used set is 0.13 mm, 0.18 mm, 0.25 mm, 0.35 mm, 0.50 mm and 0.70 mm. There are their own stylii for tracing paper and plastic, because plastic requires a harder pen tip. The drawing board is an essential tool. Paper will be attached and kept straight and still, so that the drawing can be done with accuracy. Generally, different kinds of assistance ruler are used in drawing. The drawing board is usually mounted to a floor pedestal in which the board turns to a different position, and also its height can be adjustable. Smaller drawing boards are produced for table-top use.
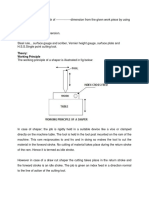
Drafting machine is a device which is mounted to the drawing board. It has rules that can be adjusted by controlling mechanism. There are two main types of apparatus: a parallelogram apparatus based on a hinged arm; and a "wagon apparatus" which moves on rails mounted to the top of the drawing board. The accuracy of the parallelogram apparatus is better in the middle of the board, decreasing towards the edges, whereas a wagon apparatus has a constant accuracy over the whole board. Parallelogram apparatus are often equipped with a ballast, with the intention to make the device lighter to handle. The drawing-head of a wagon apparatus slides on bearings in a vertical trail, which in turns is moving along a horizontal, top-mounted rail. Both apparatus types do have a movable drawing-head and the rules attached to it so that the angle between the rules may be adjusted. Drawing apparatus enables easy drawing of parallel lines over the paper. The adjustable angle between the rulers lets the
lines to be drawn in varying angles. Rulers may also be used as a support for separate special rulers and letter templates. The rules are replaceable and they can be for example scale-rules. Drawing apparatus has evolved from a drawing board mounted parallel ruler and a pantograph, a device copying the ratios. Rulers used in technical drawing are usually made of polystyrene. Rulers come in two types according to the design of their edge. Straight edge can be used with lead and felt pens, whereas when technical pen is used the edge must be grooved to prevent the spread of the ink. The basic tool in technical drawing is a triangular set square, either 90/60/30 or 90/45/45 degree. Also in use are a continuously adjustable 0-90 degrees protractor and a separate T-square - a straightedge which can use the edge of the drawing board as a support.
Architect's scale is a scaled, threeedged ruler which has six different scales marked to its sides. A typical combination for buildings details is 1:20, 1:50, 1:100, 1:25, 1:75 and 1:125. There are their own rulers for zoning work as well as for inch units. Today scale rulers are made of plastic, formerly of hardwood. A pocket-sized version is also available, with scales printed on flexible plastic stripes. A parallel ruler is a movable ruler used on the drawing board. Its angle stays constant and with it the horizontal lines can be easily be drawn all over the board. It is also used as a support for protractor and letter templates. The parallel ruler is usually connected to the board with strings, which allow the ruler to be positioned in a small angle. For drawing of curves, rulers of various designs are used: solid curved rulers
and "parrot rulers" or a curved ruler the shape of which can be modified. Templates contain pre-dimensioned holes in the right scale to accurately draw a symbol or sign. Letter templates will deliver the text, as well number as letter characters. For drawing circles and circle-arcs, circle templates are used, containing a suitable set of holes in certain dimensions with suitable sized holes in them. Models are also available for other geometric shapes such as squares and for drawing ellipses. Drafting paper is silk-like and translucent. It is primarily suitable for pencils and felt tip pens. Pencil marks can be corrected to some extent with an eraser. Tracing paper is polished sandwich-like sheet which is suitable for lead and pens. Eraser or scraping is used for correcting. Translucent plastic films are commonly used in photocopying. They have higher mechanical strength than translucent paper.
Drawing inks can be divided into two groups: soot inks and "plastic inks". Soot ink suits in drawing to paper and most drawing plastics. The most commonly used black soot ink is a colloidal mixture of water and carbon black. Plastic inks used on polyester sheets are non-corrosive. Corrosive inks are mainly used in map drawing. Draftsmen who practice and learn correct manipulation of their drawing instruments should strive to attain accuracy, speed, legibility and neatness. As technical drawing requires thought and concentration, mastery of technical drawing tools will promote efficient and effective drawing.
Reference: Technical Drawing Tools. (n.d.). In Wikipedia. Retrieved July 20, 2011, from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ Technical_drawing_tools
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Engineering Drawing Tools and EquipmentDocument4 pagesEngineering Drawing Tools and EquipmentKim OpenaPas encore d'évaluation
- CIPET GUWAHATI TECHNICAL DRAWINGDocument45 pagesCIPET GUWAHATI TECHNICAL DRAWINGKamal Krishna Kashyap100% (1)
- Drawing Instruments and Their UsesDocument9 pagesDrawing Instruments and Their UsesBlue MonsterPas encore d'évaluation
- Technical DrawingDocument15 pagesTechnical DrawingChristian PatricePas encore d'évaluation
- 1.drawing Instruments and Accessories PDFDocument5 pages1.drawing Instruments and Accessories PDFMAZHAR ALAMPas encore d'évaluation
- Drafting InstrumentsDocument6 pagesDrafting InstrumentsMaria RicPas encore d'évaluation
- Silverglide, Targeting SegmentsDocument11 pagesSilverglide, Targeting SegmentsTushar BallabhPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheet Metal Shop ToolsDocument18 pagesSheet Metal Shop ToolsAnandPas encore d'évaluation
- Rumex New Instruments ENGDocument34 pagesRumex New Instruments ENGAdonias de OliveiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Building Material and Construction-Iii: Lecture By: Prof. Dr. Sajjad MubinDocument44 pagesBuilding Material and Construction-Iii: Lecture By: Prof. Dr. Sajjad MubinAleena AsifPas encore d'évaluation
- A Concise Note On Workshop Technology: Nepal Students' Union Purwanchal Campus CommitteeDocument14 pagesA Concise Note On Workshop Technology: Nepal Students' Union Purwanchal Campus CommitteeAashiz PoudelPas encore d'évaluation
- Fitting Workshop Manual2014Document35 pagesFitting Workshop Manual2014Sachi DhanandamPas encore d'évaluation
- Marking OutDocument2 pagesMarking OutOladimeji TaiwoPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.2.2 Types of Lines and Letters Part 2Document25 pages1.2.2 Types of Lines and Letters Part 2ethan philasia100% (1)
- Workshop Lab: ManualDocument75 pagesWorkshop Lab: ManualNaga KiranPas encore d'évaluation
- Screw ThreadsDocument18 pagesScrew ThreadsMohamed Doweir100% (1)
- Working Drawing GuideDocument63 pagesWorking Drawing GuideLhen Mediante AsuncionPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Drawing 1Document49 pagesEngineering Drawing 1Thorne Adam Danor100% (1)
- Lecture-1 Introdution To Machine DrawingDocument23 pagesLecture-1 Introdution To Machine DrawingGurpreet MeeluPas encore d'évaluation
- Intersection of SurfacesDocument4 pagesIntersection of Surfacesrashik072Pas encore d'évaluation
- BE - 1 Lecture Notes 4 LetteringDocument12 pagesBE - 1 Lecture Notes 4 LetteringRaymund Joshua Pre�aPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Drawing by Jhole, Chapter 01Document32 pagesEngineering Drawing by Jhole, Chapter 01Abhishek KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Geometric TolerancesDocument23 pagesGeometric TolerancesSameer shaikhPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 CastingDocument77 pagesChapter 3 CastingGaurav Kumar Badhotiya100% (1)
- Brickmasonrytools 151127123349 Lva1 App6891Document14 pagesBrickmasonrytools 151127123349 Lva1 App6891Kiata WayuyabPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Two Axis Drill JigsDocument3 pagesLinear Two Axis Drill Jigsnilesh_092Pas encore d'évaluation
- Aligning Machines GuideDocument3 pagesAligning Machines Guidejonalthan1987Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Technical DrawingDocument41 pagesIntroduction To Technical Drawingnormanjames966Pas encore d'évaluation
- SSM Institute of Engineering & TechnologyDocument3 pagesSSM Institute of Engineering & TechnologyDhileepan KumarasamyPas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Development of FRUIT PLUCKER For Small Scale FarmingDocument5 pagesDesign and Development of FRUIT PLUCKER For Small Scale FarmingArjun RaghavPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanical Drafting and DesignDocument21 pagesMechanical Drafting and DesignVinod BhaskarPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual 13Document114 pagesManual 13JAINTONYPas encore d'évaluation
- UAP Arch Graphics I Course OutlineDocument2 pagesUAP Arch Graphics I Course OutlinemunimPas encore d'évaluation
- ES 114ea Engineering DrawingsDocument3 pagesES 114ea Engineering DrawingsMelchor Jaramilla OronosPas encore d'évaluation
- S.1 Technical Drawing Holiday Notes and ExerciseDocument7 pagesS.1 Technical Drawing Holiday Notes and Exerciseleticia karungi100% (1)
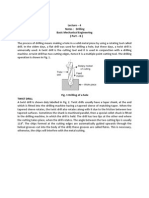
- Lecture - 4 Notes: Drilling Basic Mechanical Engineering (Part - B) 1Document5 pagesLecture - 4 Notes: Drilling Basic Mechanical Engineering (Part - B) 1Roop LalPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheet Metal WorkingDocument23 pagesSheet Metal WorkingSujit MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 Hand ToolsDocument22 pagesChapter 1 Hand ToolsMohd HapisPas encore d'évaluation
- Tools, Jigs and Die Design GuideDocument2 pagesTools, Jigs and Die Design GuideTamirat Nemomsa100% (1)
- Introduction To DFMA: Objectives of This CourseDocument37 pagesIntroduction To DFMA: Objectives of This Coursevenkat4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Good Practices in Civil WorksDocument33 pagesGood Practices in Civil Worksமாறன் செங்கேணிPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Drawing Course OverviewDocument27 pagesEngineering Drawing Course OverviewAhmad JuttPas encore d'évaluation
- Technical Drawing Course OverviewDocument94 pagesTechnical Drawing Course OverviewgodliefmesinPas encore d'évaluation
- Drafting Symbols and StandardsDocument4 pagesDrafting Symbols and StandardsResu LeirPas encore d'évaluation
- Ceramics RubricDocument1 pageCeramics Rubricapi-235894881Pas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Sustainable Design TasksDocument25 pages4 Sustainable Design TasksBeth HintonPas encore d'évaluation
- Peer Evaluation Form Group WorkDocument3 pagesPeer Evaluation Form Group WorkYamunaa PalaniPas encore d'évaluation
- 156 180Document181 pages156 180Kurnia Adi WibowoPas encore d'évaluation
- Aim: To Prepare A V Block of - Dimension From The Given Work Piece by UsingDocument4 pagesAim: To Prepare A V Block of - Dimension From The Given Work Piece by UsingSubodh ShrivPas encore d'évaluation
- Drafting ToolsDocument6 pagesDrafting ToolsErvi Jann GantalaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Polaris Total Station NotesDocument6 pagesPolaris Total Station NotesMushtaq AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- DFMA Intro LectureDocument36 pagesDFMA Intro LectureHajiasifAliPas encore d'évaluation
- Contruction Materials and EquipmentDocument31 pagesContruction Materials and EquipmentKristian RocaforPas encore d'évaluation
- Eco-Boards: A Green Building Material From Residues and WasteDocument26 pagesEco-Boards: A Green Building Material From Residues and WasteJaybesPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Drawing GuideDocument50 pagesEngineering Drawing GuideBhuwan JoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification of HandtoolsDocument1 pageClassification of Handtoolslanie a. bagapuroPas encore d'évaluation
- Plumbing Theory NotesDocument133 pagesPlumbing Theory NotesAustine OtienoPas encore d'évaluation
- Technical Drawing Tools: Ruling PenDocument4 pagesTechnical Drawing Tools: Ruling PenYeager GaryPas encore d'évaluation
- Module - 2 - Drawing Instruments. Uses and Care - OROQUEITADocument10 pagesModule - 2 - Drawing Instruments. Uses and Care - OROQUEITADarren Andrew LiosPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Drafting 1Document11 pagesIntroduction To Drafting 1lanced022710Pas encore d'évaluation
- Surfactants, Soaps and DetergentsDocument14 pagesSurfactants, Soaps and DetergentsPaolo GochingcoPas encore d'évaluation
- ENG13 Stop Communicating IneffectivelyDocument2 pagesENG13 Stop Communicating IneffectivelyPaolo GochingcoPas encore d'évaluation
- Soap and DetergentsDocument25 pagesSoap and DetergentsPaolo GochingcoPas encore d'évaluation
- Life Cycle Inventories For The Production of Detergent IngredientsDocument109 pagesLife Cycle Inventories For The Production of Detergent IngredientsPaolo GochingcoPas encore d'évaluation
- CHM142 ReviewerDocument3 pagesCHM142 ReviewerPaolo GochingcoPas encore d'évaluation
- Sulfur Products: Ariziel Ruth D. MarquezDocument12 pagesSulfur Products: Ariziel Ruth D. MarquezPaolo Gochingco50% (2)
- MATH23 Project - QuadricsDocument2 pagesMATH23 Project - QuadricsPaolo GochingcoPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution Manual Himmelblau Basic Principles and Calculations in Chemical EngineeringDocument244 pagesSolution Manual Himmelblau Basic Principles and Calculations in Chemical EngineeringNilson BispoPas encore d'évaluation
- Worktext in Differential EquationsDocument148 pagesWorktext in Differential EquationsJeff MacabitasPas encore d'évaluation
- CHE112P Lecture 4Document13 pagesCHE112P Lecture 4Paolo Gochingco100% (1)
- MATH30 Meaning From Data - Statistics Made ClearDocument2 pagesMATH30 Meaning From Data - Statistics Made ClearPaolo GochingcoPas encore d'évaluation
- Nitrogen Products: Ariziel Ruth D. MarquezDocument9 pagesNitrogen Products: Ariziel Ruth D. MarquezPaolo GochingcoPas encore d'évaluation
- ENG13 Reporting Research FindingsDocument8 pagesENG13 Reporting Research FindingsPaolo GochingcoPas encore d'évaluation
- Combustion Gaseous Fuel Liquid FuelDocument18 pagesCombustion Gaseous Fuel Liquid FuelPaolo Gochingco33% (3)
- Chapter 12 (Reactive Process) : Recycle Product Separation PurgeDocument20 pagesChapter 12 (Reactive Process) : Recycle Product Separation PurgePaolo GochingcoPas encore d'évaluation
- ENG13 Current Workplace IssuesDocument6 pagesENG13 Current Workplace IssuesPaolo GochingcoPas encore d'évaluation
- CHE112P Lecture 5Document7 pagesCHE112P Lecture 5Paolo GochingcoPas encore d'évaluation
- ENG13 SW Test PreparationDocument28 pagesENG13 SW Test PreparationPaolo GochingcoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9 and 10Document22 pagesChapter 9 and 10Paolo GochingcoPas encore d'évaluation
- ENG13 Business ReportsDocument14 pagesENG13 Business ReportsPaolo GochingcoPas encore d'évaluation
- ENG13 Technical DocumentsDocument9 pagesENG13 Technical DocumentsPaolo Gochingco100% (1)
- ENG13 How To Describe MechanismsDocument3 pagesENG13 How To Describe MechanismsPaolo GochingcoPas encore d'évaluation
- BIO99 GattacaDocument1 pageBIO99 GattacaPaolo GochingcoPas encore d'évaluation
- CHE111P Gas MixturesDocument20 pagesCHE111P Gas MixturesPaolo GochingcoPas encore d'évaluation
- BIO99 SCNT Therapy Vs EnhancementDocument4 pagesBIO99 SCNT Therapy Vs EnhancementPaolo GochingcoPas encore d'évaluation
- BIO99 JatrophaDocument5 pagesBIO99 JatrophaPaolo GochingcoPas encore d'évaluation
- CHE111P Material Balance: Multiple UnitsDocument11 pagesCHE111P Material Balance: Multiple UnitsPaolo Gochingco100% (2)
- BIO99 Cellular Reprogramming - Pluripotent Stem Cells (Yamanaka)Document11 pagesBIO99 Cellular Reprogramming - Pluripotent Stem Cells (Yamanaka)Paolo GochingcoPas encore d'évaluation
- CHE111P Material BalanceDocument36 pagesCHE111P Material BalancePaolo GochingcoPas encore d'évaluation
- Process VarDocument27 pagesProcess VarEdin AbolenciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Maneklal and Sons (Exports) : H S A W N M MDocument3 pagesManeklal and Sons (Exports) : H S A W N M MhattaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Keyboard Usb Catalog: 14 February 2022 - UserDocument11 pagesKeyboard Usb Catalog: 14 February 2022 - UserkarimsopyPas encore d'évaluation
- DIY Texas Star InstructionsDocument10 pagesDIY Texas Star InstructionsEd NunezPas encore d'évaluation
- Quick Locator Guide Fixture and Cab Products: SeesincDocument18 pagesQuick Locator Guide Fixture and Cab Products: SeesincFrancisco Javier BurgosPas encore d'évaluation
- SysLogic GBDocument18 pagesSysLogic GBsamir hacibPas encore d'évaluation
- 48 Standardization Parts List Liste DesDocument48 pages48 Standardization Parts List Liste DesBasriPas encore d'évaluation
- TIC Catalog de HerramientasDocument408 pagesTIC Catalog de HerramientasWilsonPuertasPas encore d'évaluation
- Best Japanese Sushi Knife in 2020Document48 pagesBest Japanese Sushi Knife in 2020T ChenPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Valves Product OverviewDocument18 pagesManual Valves Product OverviewYashodhan RajwadePas encore d'évaluation
- MyfordDocument1 pageMyfordPeanut d. DestroyerPas encore d'évaluation
- D-Series Catalogue PDFDocument64 pagesD-Series Catalogue PDFandresboy123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bhel Bhopal em Division: REF No.: EM/ PMD-WC /001 DATE: 15/03/2011Document5 pagesBhel Bhopal em Division: REF No.: EM/ PMD-WC /001 DATE: 15/03/2011Raj SherwaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Infantometro BABYHR 101614 - WebDocument8 pagesManual Infantometro BABYHR 101614 - WebDulfary VallejoPas encore d'évaluation
- Fresadora Makita 710w Pinza 6 8mm SarDocument104 pagesFresadora Makita 710w Pinza 6 8mm SarAlvaro GordilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Vernier Calliper Screw Gauge and SpherometerDocument6 pagesUnderstanding Vernier Calliper Screw Gauge and SpherometerAnonymous vRpzQ2BLPas encore d'évaluation
- LaporanThermograf Blowdown Valve #1Document13 pagesLaporanThermograf Blowdown Valve #1Engineering PLTU BanjarsariPas encore d'évaluation
- EP3107776A4Document1 pageEP3107776A4BubblePas encore d'évaluation
- Cca-1112a-Ce BrochureDocument6 pagesCca-1112a-Ce BrochuretswPas encore d'évaluation
- Egypt Mep Supplier - Rev02Document15 pagesEgypt Mep Supplier - Rev02Karim Galal Ismail0% (1)
- Argenta - Oreana Elementary Supplies ListDocument1 pageArgenta - Oreana Elementary Supplies ListNewsTeam20Pas encore d'évaluation
- NOITECH Catalogue 2013Document427 pagesNOITECH Catalogue 2013SergPas encore d'évaluation
- Options & Modifications FTA1100J: M Diesel Engine Fire Pump ControllerDocument3 pagesOptions & Modifications FTA1100J: M Diesel Engine Fire Pump ControllersnonumPas encore d'évaluation
- Browning M1919A4 Machine Gun.30 Caliber, Complete Set of Ordnance Blueprints - TextDocument207 pagesBrowning M1919A4 Machine Gun.30 Caliber, Complete Set of Ordnance Blueprints - TextMadison Rogers100% (1)
- Powder Measure: Auto-DrumDocument2 pagesPowder Measure: Auto-DrumFernando Passon CasagrandePas encore d'évaluation
- Knoxhult: Kitchen SeriesDocument3 pagesKnoxhult: Kitchen SeriesAkmal JasmanPas encore d'évaluation
- 2012 Reflex Web ManualDocument32 pages2012 Reflex Web Manualalcides interianoPas encore d'évaluation
- K To 12 Welding Learning Module PDFDocument139 pagesK To 12 Welding Learning Module PDFAlano JoPas encore d'évaluation
- XCOM 2 Classes and Abilities OverviewDocument55 pagesXCOM 2 Classes and Abilities OverviewThrowaway JimPas encore d'évaluation
- GANESH Precision GT-1340 Geared-Head Engine Lathe: 13" Swing Over Bedways, 40" Center DistanceDocument3 pagesGANESH Precision GT-1340 Geared-Head Engine Lathe: 13" Swing Over Bedways, 40" Center DistancemattnificentPas encore d'évaluation
- BAST Jasa Curug MekarDocument41 pagesBAST Jasa Curug Mekarsurijanti447Pas encore d'évaluation