Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Coal-Fired Electricity Generation
Transféré par
Teja BhogadiDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Coal-Fired Electricity Generation
Transféré par
Teja BhogadiDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Coal-fired electricity generation
1. Accounts for 39% of world electricity production the most important source of electricity in OECD and non-OECD. 2. Accounts for more than 50% of electricity generation in Australia, China, India, Australia, Eastern Europe and the USA. 3. Coal expected to remain the most important source of electricity through to 2030. Capacity will grow by 120% (twothirds of this in developing countries) $1.3 trillion of investment.
4. Predominantly domestic good: 3% traded.
Projected world electricity production to 2030, by fuel source
TWh
Solar/Wind Combustible Renewables & Waste Geothermal
30 000
25 000
20 000
Hydro
15 000
Nuclear
10 000
Gas
5 000
Liquid Fuels
0
2002
2010
2020
2030
Source: World Energy Outlook 2004, IEA
Coal
Coal-fired electricity emissions
1. 70% of all power sector electricity and heat emissions. 2. 15.8% of global anthropogenic GHG emissions (22% for electricity and heat).
3. Projected to rise 60% by 2030 with developing countries accounting for 90% of this growth.
4. Higher plant thermal efficiencies are the key to achieving lower emissions intensities. 5. CO2 emissions intensities vary significantly: Japans is 35% lower than Indias.
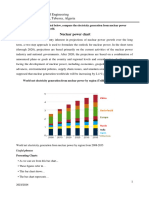
Coal-fired electricity generation CO2 emissions intensities by region, 2002
kg CO2/ MWh 1 200
1 100
1 000
900
800
700
Aus/NZ USA S&E Asia FSU Japan Latin America Africa Middle East Canada Korea West Europe China East Europe India
Scope for progress
1. In 2002, average thermal efficiency in the OECD was 36%, in developing countries it was 30%. In 2030, expected to rise to 40% and 36% respectively. 2. State-of-the-art pulverised plants have efficiencies as high as 47%. IGCC (gasification) plants 50%. Thermal efficiencies of up to 56% is believed to be possible. 3. If all regions were to achieve the same efficiency level of Japan emissions could be reduced by 17% in 2020. 4. Major barrier to reducing emissions: capital costs. 5. Capture and storage technologies is probably 10 years off. Major technical and cost challenges.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Renewable Energy Market UpdateDocument63 pagesRenewable Energy Market UpdatedemonsPas encore d'évaluation
- Elep Financial Model For DGDocument11 pagesElep Financial Model For DGjoshua surbaktiPas encore d'évaluation
- India Energy Outlook 2021Document251 pagesIndia Energy Outlook 2021Niraj Kumar100% (1)
- CCUS in Clean Energy TransitionsDocument174 pagesCCUS in Clean Energy TransitionsLong NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Solar EnergyDocument19 pagesSolar EnergyhellPas encore d'évaluation
- Technology Roadmap Wind EnergyDocument63 pagesTechnology Roadmap Wind EnergyEdgard Leonardo Castaneda GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- IEA Renewables2022Document159 pagesIEA Renewables2022rtjoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Generation From CoalDocument114 pagesPower Generation From CoalOral KarahanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Future of PetrochemicalsDocument132 pagesThe Future of PetrochemicalsRayden79100% (1)
- TechnologyRoadmapSolarPhotovoltaicEnergy 2014edition PDFDocument60 pagesTechnologyRoadmapSolarPhotovoltaicEnergy 2014edition PDFbia9193Pas encore d'évaluation
- Indus TowersDocument2 pagesIndus TowersAniruddh Singh ThakurPas encore d'évaluation
- Renewable Power Generation Costs in 2020D'EverandRenewable Power Generation Costs in 2020Pas encore d'évaluation
- Carbon Capture and Storage:: The Solution For Deep Emissions ReductionsDocument12 pagesCarbon Capture and Storage:: The Solution For Deep Emissions ReductionsWenKhai LimPas encore d'évaluation
- CO Emissions From Fuel Combustion: Statistics ReportDocument13 pagesCO Emissions From Fuel Combustion: Statistics ReportArude AmagawaPas encore d'évaluation
- Renewables 2021 - Analysis and Forecast To 2026 - IeaDocument175 pagesRenewables 2021 - Analysis and Forecast To 2026 - IeaMohammad ShofiePas encore d'évaluation
- GE Aeroderivative Vietnam Sep 22 FinalDocument36 pagesGE Aeroderivative Vietnam Sep 22 Finaltuanpham100% (1)
- Scaling up biomass for the energy transition: Untapped opportunities in Southeast AsiaD'EverandScaling up biomass for the energy transition: Untapped opportunities in Southeast AsiaPas encore d'évaluation
- India's Journey Towards Excellence & Certified Photovoltaic Systems & Qualified PeopleDocument19 pagesIndia's Journey Towards Excellence & Certified Photovoltaic Systems & Qualified PeopleRajeev KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- English Future Petrochemicals ESDocument11 pagesEnglish Future Petrochemicals ESsanjayshah99Pas encore d'évaluation
- GT2005-68014 Axial Compressor MaintenanceDocument48 pagesGT2005-68014 Axial Compressor MaintenanceRaden MasPas encore d'évaluation
- WEO2017 Launch BrusselsDocument14 pagesWEO2017 Launch Brusselssanjayshah99Pas encore d'évaluation
- 25 Niti Aayog Report PDFDocument305 pages25 Niti Aayog Report PDFSiddharth ModiPas encore d'évaluation
- Greening Asia's Economic DevelopmentDocument19 pagesGreening Asia's Economic Developmentaffif syah muahammadPas encore d'évaluation
- ECE3072 Sp21 Lecture 8Document23 pagesECE3072 Sp21 Lecture 8Nik ChoPas encore d'évaluation
- Global+Steel+Production+Costs+ +jan2022Document35 pagesGlobal+Steel+Production+Costs+ +jan2022pricks_kerPas encore d'évaluation
- WEO 2017 Executive Summary English VersionDocument13 pagesWEO 2017 Executive Summary English VersionadanasporPas encore d'évaluation
- IEA - Renewables 2023Document143 pagesIEA - Renewables 2023Никита МузафаровPas encore d'évaluation
- Coal Supply DemandDocument40 pagesCoal Supply DemandJuragan BiasaPas encore d'évaluation
- Smart GridDocument90 pagesSmart Gridjose girotPas encore d'évaluation
- Faculty of Mechatronics and Electronics, Lac Hong University, Bien Hoa, VietnamDocument23 pagesFaculty of Mechatronics and Electronics, Lac Hong University, Bien Hoa, VietnamMạnh KhangPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethiopia Energy Outlook - Analysis - IEADocument16 pagesEthiopia Energy Outlook - Analysis - IEAAbraham L ALEMUPas encore d'évaluation
- THTHDocument12 pagesTHTHCaptain HendoPas encore d'évaluation
- Role of Ongc in The India's Road Map For Energy SecurityDocument65 pagesRole of Ongc in The India's Road Map For Energy SecuritynanimbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hubbert S PeakDocument53 pagesHubbert S Peakjbalbas6307Pas encore d'évaluation
- European Union 2020 Energy Policy ReviewDocument310 pagesEuropean Union 2020 Energy Policy ReviewFenhia RivasPas encore d'évaluation
- National Energy Map For India: Technology Vision 2030 and Low Carbon PathsDocument29 pagesNational Energy Map For India: Technology Vision 2030 and Low Carbon PathsRaveesh SrinivasPas encore d'évaluation
- Oil 2020Document120 pagesOil 2020Sandy TyasPas encore d'évaluation
- Transforming Construction For The Digital AgeDocument24 pagesTransforming Construction For The Digital Agetarzoon1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Key World Energy Statistics 2020Document81 pagesKey World Energy Statistics 2020Amin DehghaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Korea 2020 Energy Policy ReviewDocument204 pagesKorea 2020 Energy Policy ReviewSunderjit SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- The Netherlands 2020 Energy Policy ReviewDocument258 pagesThe Netherlands 2020 Energy Policy ReviewFiorella AvalosPas encore d'évaluation
- Renewables 2018 Analysis and Forecasts To 2023 IEADocument210 pagesRenewables 2018 Analysis and Forecasts To 2023 IEAdarkestmatterPas encore d'évaluation
- Germany 2020 Energy Policy ReviewDocument229 pagesGermany 2020 Energy Policy ReviewCristin CorelliPas encore d'évaluation
- RE MOOC W5 Wind EnergyDocument189 pagesRE MOOC W5 Wind EnergyMaximiliano TaubePas encore d'évaluation
- World Energy Outlook 2008 Key GraphsDocument12 pagesWorld Energy Outlook 2008 Key GraphsJonathan MouettePas encore d'évaluation
- MIT2 60s20 Lec22Document32 pagesMIT2 60s20 Lec22ahmed aliPas encore d'évaluation
- Global Energy ConsumptionDocument67 pagesGlobal Energy ConsumptionjuoyjePas encore d'évaluation
- ETM forASEANwebinarDocument14 pagesETM forASEANwebinarTiara SyPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Sector Overview 2023Document24 pagesPower Sector Overview 2023Rakesh MahtaPas encore d'évaluation
- Wood Pellets Business 11 Feb 2020Document16 pagesWood Pellets Business 11 Feb 2020Aljazari FoundationPas encore d'évaluation
- Nuclear Power ChartDocument2 pagesNuclear Power Chartboudraaokba77Pas encore d'évaluation
- World Energy Outlook: Executive SummaryDocument12 pagesWorld Energy Outlook: Executive SummaryformemslPas encore d'évaluation
- IEA-Clean Energy MFGDocument36 pagesIEA-Clean Energy MFGManokaran KPas encore d'évaluation
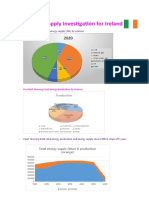
- Energy Supply Investigation 2022Document4 pagesEnergy Supply Investigation 2022Amaya CembellinPas encore d'évaluation
- Market Report Series Oil 2018Document138 pagesMarket Report Series Oil 2018AmrPas encore d'évaluation
- IEA 2022 - Canada Policy ReviewDocument261 pagesIEA 2022 - Canada Policy ReviewJose CondorPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2Document23 pagesChapter 2upper paunglaungPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy India 2020Document17 pagesEnergy India 2020Deepak Saheb Gupta50% (2)
- Financing Renewables Energy Projects in India: Global Renewable Energy ForumDocument32 pagesFinancing Renewables Energy Projects in India: Global Renewable Energy Forumchinmay_antaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Coal Information Overview 2020 EditionDocument28 pagesCoal Information Overview 2020 EditionS. Deep DasPas encore d'évaluation
- Oil 2021 PDFDocument167 pagesOil 2021 PDFsdfghPas encore d'évaluation
- Making Better Energy ChoicesDocument33 pagesMaking Better Energy ChoicesDaisyPas encore d'évaluation
- Coal Use in India and China Platts ReportDocument32 pagesCoal Use in India and China Platts ReportkiritiguharoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chevening EssaysDocument3 pagesChevening EssaysAngga AprilianPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Solar Energy Audit ServicesDocument8 pages4 Solar Energy Audit ServicesVi TranPas encore d'évaluation
- Moroccan Ministry of EnergyDocument2 pagesMoroccan Ministry of EnergySiyuan SunPas encore d'évaluation
- Aean Super 8 MPIA Brochure A4 1Document4 pagesAean Super 8 MPIA Brochure A4 1Dave EACPas encore d'évaluation
- 03 Liteature ReviewDocument8 pages03 Liteature ReviewSayp dPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 OnlineDocument12 pages1 OnlineabdoualhinnawiPas encore d'évaluation
- Source of EnergyDocument16 pagesSource of EnergyOmoso KeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Up 1Document4 pagesUp 1Renz BonPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy Resources (Case Study On Ethiopia)Document8 pagesEnergy Resources (Case Study On Ethiopia)Andiga Nagata100% (1)
- 2X4 (SEASONAL TILT) STRUCTURE ASSEMBLY LAUOUT, BOQ & DesignDocument3 pages2X4 (SEASONAL TILT) STRUCTURE ASSEMBLY LAUOUT, BOQ & DesignYashwant Raj VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Thesis Photovoltaic SystemDocument5 pagesThesis Photovoltaic Systemfjgjdhzd100% (2)
- DNV GL Energy Transition Outlook 2020 Main Report Lowres SingleDocument306 pagesDNV GL Energy Transition Outlook 2020 Main Report Lowres SinglekhairulPas encore d'évaluation
- Lot EPCDocument8 pagesLot EPCTayeb KazemiPas encore d'évaluation
- Luzon Committed 2021 June 01Document2 pagesLuzon Committed 2021 June 01asiancutiePas encore d'évaluation
- SG Series: Solar Gel Deep CycleDocument2 pagesSG Series: Solar Gel Deep CycleJosé Luis González MartínezPas encore d'évaluation
- MITEI Energy Futures Spring 2023Document48 pagesMITEI Energy Futures Spring 2023Jose PulidoPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy in Sweden 2020 - An OverviewDocument18 pagesEnergy in Sweden 2020 - An OverviewigoralcPas encore d'évaluation
- Renewable Energy Powered Water Supply System in Uganda A Critical ReviewDocument8 pagesRenewable Energy Powered Water Supply System in Uganda A Critical ReviewKIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparison of Various Power PlantsDocument5 pagesComparison of Various Power PlantsShiva H. AdhikariPas encore d'évaluation
- Natural ResourcesDocument1 pageNatural ResourcesAndrea AndaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Solar Energy: Compiled By: Ashwani KumarDocument19 pagesSolar Energy: Compiled By: Ashwani KumarAniket NagpalPas encore d'évaluation
- Ocean Thermal, Wave & Tidal EnergyDocument49 pagesOcean Thermal, Wave & Tidal EnergyAni TaPas encore d'évaluation
- DURVA SHETYE - International Oil Companies Betting On Renewables - A Right StrategyDocument4 pagesDURVA SHETYE - International Oil Companies Betting On Renewables - A Right StrategyDurva ShetyePas encore d'évaluation
- Energy, Environment & SustainabilityDocument37 pagesEnergy, Environment & SustainabilityStrings AIPas encore d'évaluation
- ON Grid-Connected Wind-Photovoltaic Cogeneration Using Back-To-Back Voltage Source ConvertersDocument11 pagesON Grid-Connected Wind-Photovoltaic Cogeneration Using Back-To-Back Voltage Source ConvertersThulasi PrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Soorya Bala Sangramaya LECO Loan LECO ApplicationDocument2 pagesSoorya Bala Sangramaya LECO Loan LECO ApplicationnavindraPas encore d'évaluation