Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Edison College Nursing Program Infection Risk Plan
Transféré par
Brian BracherDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Edison College Nursing Program Infection Risk Plan
Transféré par
Brian BracherDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
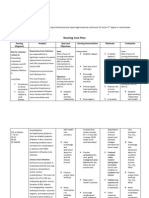
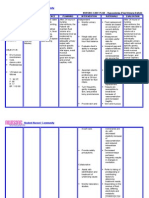
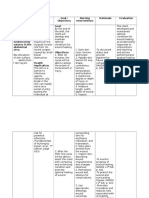
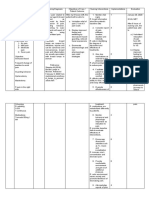
EDISON COLLEGE NURSING PROGRAMS NURSING CARE PLAN ASSESSMENT DATA (Appropriate data to support nursing diagnosis, include
subjective and objective data) NURSING DIAGNOSIS (Must include scientific rationale for the diagnosis, include references*) PLANNING Goals (include realistic short and long term client-centered goals) Short Term/Long Term Interventions Short Term: 1. At the end of the shift, patient will remain free of signs / symptoms of infection such as WBC count of 4,5003 10,000/mm , temp of < 100 F, and absence of purulent drainage wounds. Long Term: 1. At time of discharge, patient will be free of signs / symptoms of infection such as WBC count of 3 4,500-10,000/mm temp of < 100 F, and absence of purulent drainage wounds. NURSING IMPLEMENTATION (What actually was done, must include scientific rationale with references and delegation of tasks*) 1. Nurse monitored for signs and symptoms of infection, such as elevated systemic temperature, reddening of the area surrounding the wound, increased temperature of skin surrounding the wound, purulent wound drainage, and elevated WBC count multiple times throughout shift. Common assessment findings of an infected wound include purulent discharge, redness, warmth, fever, & elevated WBC. (Lemone 2011 pp.78, 288, 294-295) 2. Nurse administered antibiotics as per physicians orders. Antibiotics are medications used to treat bacterial infections and some have activity against a wide variety of bacteria. Prophylactic antibiotic treatment is effective in the prevention of postoperative complications. (Lemone 2011 p. 297) 3. Nurse provided regular EVALUATION (Actual outcome of care and appropriate follow-up actions) Goals Implementations Short Term goals evaluation: 1. At the end of shift, patient was free of signs / symptoms of infection. Temp - 98.7, 98.1. WBC was not ordered to be checked again during nurses shift. Wound characteristics were: RLL was only able to see drainage in wound vac, it remained serosanguinous. Toes (distal to injury) remained pink and not overly warm. Cranial incision did not produce any new drainage and was either excessively red or warm. Goal met. Long Term goal evaluation: 1. If client and nursing staff continue with these interventions, in all likelihood, the patient should remain free of signs / symptoms of infection. Goal on its way to being met. Evaluation of interventions: 1. Patient was monitored throughout shift for s/s of infection and none were present. Although no infection is present, continue intervention for
Subjective: Patient denies feeling febrile Patient denies malaise Patient denies history of MRSA Objective: 12cm craniotomy surgical incision on rear left of cranium, well approximated wound edges with dried serosanguinous drainage, healing by primary intention, closure with staples, granulation tissue present, skin around wound warm (normal warm) to touch Patient has a Foley urinary catheter Open fracture of right lower leg, heavily bandaged (doctors order to not remove), toenail cap refill of effected leg <3 seconds, skin on toes warm (normal warm) to the touch. Wound vac treatment on right lower leg, chamber containing serosanguinous drainage WBC: 7.1 Temp: 98.5F
Risk for infection R/T: surgical incision wound and open fracture of right lower leg Scientific Rationale: An open fracture carries significant risk for wound contamination and subsequent infection. The patient who undergoes surgery will have a postoperative wound. Any break in skin integrity must be monitored for infection. (Lemone 2011 p.1326) Pathophysiology: Infection occurs when an organism is able to colonize and multiply within a host. An infection causing microorganism must have virulence, be transmitted from its reservoir, and gain entry into the susceptible host. When the immune system is alerted that an invader has entered the body, cytokines send a message to phagocytes to attack the infection. Lymphocytes and other white blood cells also begin to attack the microorganism. The result of
Planned Nursing Interventions: 1. Throughout shift, nurse will continue to monitor for signs and symptoms of infection, such as elevated systemic temperature, reddening of the area surrounding the wound, increased temperature of skin surrounding the wound, purulent wound drainage, and elevated WBC count. 2. Nurse will administer
this activity often results in a fever and causes the blood vessels to enlarge in order to increase the amount of blood containing phagocytes and lymphocytes to the site of infection. (Lemone 2011 pp. 270-273, 292)
antibiotic drugs, as per physicians orders 3. Nurse will provide urinary catheter care & cleansing at least once per shift. 4. Nurse will observe proper hand hygiene and aseptic technique when caring for wounds. 5. Educate client on the importance of consuming adequate amounts of protein, calories, and fluids to promote wound healing.
catheter care with soap and water once during shift. *Delegated to female student nurse. Catheter care prevents access and limits bacterial ascent into, and growth in, urinary tract. (Doenges / Moorhouse / Murr 2010, p.353) 4. Nurse observed hospital policies and procedures in regard to hand hygiene and aseptic technique when caring for patients wounds. Hand hygiene remains the single most important factor in preventing the spread of infection. Standard precautions are essential in protecting the patient and the nurse from infection by preventing crosscontamination and exposure to infectious organisms. (Lemone 2011 pp.250, 302) 5. Nurse spoke to patient regarding the important role that protein, calories, and fluids play in the process of wound healing. Calories and proteins are needed to meet metabolic needs and promote wound healing. Fluids prevent dehydration and promote blood perfusion. (Doenges / Moorhouse / Murr 2010, p.679)
early detection. Goal met. 2. Patient was administered antibiotics as per physicians orders. No s/s of infection present. Goal met. Continue this intervention. 3. Patient was provided urinary catheter care once during shift. It was delegated to female nursing students. No s/s of infection present. Urinary catheter care is important in preventing contamination of the urinary tract, so continue this intervention. Goal met. 4. Adherence to hospital policy and procedure regarding hand washing and aseptic technique when providing wound care and/or observation was heeded. No s/s of infection present. Goal met. Continue this preventative intervention. 5. Nurse educated patient regarding the importance of nutrition, especially protein, calories, and adequate fluid intake in the process of healing. Patient demonstrated understanding of the concepts by restating. Goal met. Discontinue intervention.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Case Study 2Document7 pagesCase Study 2desdav100% (1)
- Risk For InfectionDocument18 pagesRisk For InfectionValiant Baybay0% (1)
- NCP - Risk For InfectionDocument6 pagesNCP - Risk For Infectionlinnaroueyak100% (1)
- NCP Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument2 pagesNCP Impaired Skin IntegrityAshley Kate SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Pain NCPDocument2 pagesAcute Pain NCPcharmaine3489% (19)
- Risk For InfectionDocument3 pagesRisk For InfectioncamziiiPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP - Risk For InfectionDocument2 pagesNCP - Risk For InfectionTarquin TomadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity Intolerance Related To Decrease Blood FlowDocument3 pagesActivity Intolerance Related To Decrease Blood FlowDarkCeades100% (3)
- NCP Risk For InfectionDocument2 pagesNCP Risk For InfectionI Am SmilingPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP For Infection !Document1 pageNCP For Infection !Clariss AlotaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Risk For InfectionDocument6 pagesNCP Risk For InfectionEllenare Racion100% (1)
- CommunicationDocument4 pagesCommunicationapi-302578028Pas encore d'évaluation
- Impaired skin integrity assessmentDocument2 pagesImpaired skin integrity assessmentJerryson Justo100% (2)
- Risk For InfectionDocument1 pageRisk For InfectionAcmihs Dequilla100% (8)
- Colostomy care assessmentDocument2 pagesColostomy care assessmentzbestgurl100% (1)
- NCP Impaired SkinDocument2 pagesNCP Impaired Skinarjay2306_obcq100% (1)
- Impaired Tissue Integrity Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesImpaired Tissue Integrity Nursing Care PlanLynnette Adams Mayotte95% (20)
- Nursing Care Plan Risk For Skin BreakdownDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Risk For Skin BreakdownShelli Miller Pryor82% (11)
- Impaired Skin Integrity Related To Surgical Incision and DrainsDocument1 pageImpaired Skin Integrity Related To Surgical Incision and DrainsGaDis MaNis100% (10)
- Nursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationPaul Cubacub100% (1)
- NCP For InfectionDocument1 pageNCP For InfectionNathaniel EllanoPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Risk For InfectionDocument3 pagesNCP Risk For InfectionXerxes Dejito0% (1)
- Infection NCPDocument1 pageInfection NCPMsOrangePas encore d'évaluation
- NCP - ConstipationDocument3 pagesNCP - ConstipationDaniel Dave KapunanPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP For Acute PainDocument2 pagesNCP For Acute PainEmman RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Risk For InfectionDocument2 pagesRisk For InfectionSuzette Rae Tate0% (1)
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Fully Met IfDocument5 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Fully Met IfLorraineAnneSantiagoCandelarioPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Pain Care PlanDocument2 pagesAcute Pain Care PlanKim Biro Turner86% (37)
- NCP Acute Pain Related To InflammationDocument3 pagesNCP Acute Pain Related To InflammationMa. Elaine Carla Tating38% (8)
- NCP For Post Op Wound and FractureDocument6 pagesNCP For Post Op Wound and FractureAlyssa Marie0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For RabiesDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan For RabiesAngel VillamorPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Pain NURSING CARE PLANDocument2 pagesAcute Pain NURSING CARE PLANMatthew Emmanuel M. Martinez100% (4)
- NCP-Risk For InfectionDocument4 pagesNCP-Risk For InfectionMarianne May Loquias100% (4)
- Risk For Infection NCP Ortho JadDocument1 pageRisk For Infection NCP Ortho JadjadpauloPas encore d'évaluation
- NURSING CARE PLAN Acute Intermittent Moderate PainDocument1 pageNURSING CARE PLAN Acute Intermittent Moderate PainDiana Laura Lei100% (3)
- NCP-Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument2 pagesNCP-Impaired Skin IntegrityMikee Ann Valdez96% (26)
- Assessme NT Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective CuesDocument3 pagesAssessme NT Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective CuesTricia100% (1)
- Post-op Nursing Care for Appendectomy PatientDocument3 pagesPost-op Nursing Care for Appendectomy Patientmichelle_celeste100% (2)
- Acute Pain Management After EpisiotomyDocument3 pagesAcute Pain Management After EpisiotomyJheanAlphonsineT.MeansPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Pain NCPDocument3 pagesAcute Pain NCPRoberto Joaquin Angeles100% (1)
- NURSING CARE PLAN On Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN On Impaired Skin Integrityapi-371817493% (30)
- Post-op Nursing Care Plan for Skin IntegrityDocument2 pagesPost-op Nursing Care Plan for Skin IntegritySharewin PulidoPas encore d'évaluation
- Constipation NCPDocument2 pagesConstipation NCPDemilyn Olofernes-Fat100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Infection.Document1 pageNursing Care Plan For Infection.Abegail Abaygar83% (12)
- GENERAL SANTOS DOCTORS’ MEDICAL SCHOOL FOUNDATION NURSING CARE PLANDocument4 pagesGENERAL SANTOS DOCTORS’ MEDICAL SCHOOL FOUNDATION NURSING CARE PLANFran LanPas encore d'évaluation
- Deficit)Document2 pagesDeficit)Lee DeePas encore d'évaluation
- Nanda 11 Edi. P. 620-621Document3 pagesNanda 11 Edi. P. 620-621Besael Baccol0% (1)
- Skin Integrity Nursing Care for ElderlyDocument2 pagesSkin Integrity Nursing Care for ElderlyRazz Domenique Reyes Escaros100% (5)
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPChrisTine M. MoralesPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan for GastroenteritisDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plan for GastroenteritisChris Denver BancalePas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Impaired Skin IntergrityDocument2 pagesNCP Impaired Skin IntergrityLaura Sansonetti100% (6)
- Assessing Skin Integrity and Preventing BreakdownDocument2 pagesAssessing Skin Integrity and Preventing Breakdowncuicuita100% (3)
- SchistosomiasisDocument92 pagesSchistosomiasisIvan Juan75% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan Acute PainDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Acute PainJonette Calix Sam100% (1)
- Care Plan Risk For Infection 2Document3 pagesCare Plan Risk For Infection 2Chander KantaPas encore d'évaluation
- Concepts of Infection ControlDocument53 pagesConcepts of Infection ControlPak Pandir0% (1)
- Patient Case Study on AppendicitisDocument19 pagesPatient Case Study on Appendicitisfarzaneh yeganehPas encore d'évaluation
- Concepts of Infection ControlDocument53 pagesConcepts of Infection ControlBimal Dey100% (1)
- NeutrotoppppcDocument10 pagesNeutrotoppppcapi-255084253Pas encore d'évaluation
- Deep Incisional SSIDocument2 pagesDeep Incisional SSIJan Michael BuragaPas encore d'évaluation
- MSDS Chemical InjectionDocument12 pagesMSDS Chemical InjectionJohnson Lopes100% (1)
- Cor PulmonaleDocument13 pagesCor PulmonaleHayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mims Indonesia - June.2015.en - SampleDocument1 786 pagesMims Indonesia - June.2015.en - SampleHendryFransiskus50% (2)
- Manifestation MeditationDocument28 pagesManifestation Meditationrajendraghugre80% (5)
- Corpening Group Exercise January: RM Time Class Instruc. RM Time Class Instruc. RM Time Class InstrucDocument1 pageCorpening Group Exercise January: RM Time Class Instruc. RM Time Class Instruc. RM Time Class InstrucymcawncPas encore d'évaluation
- Kumbaka ResearchDocument4 pagesKumbaka Researchshishai08Pas encore d'évaluation
- Kasus 2Document3 pagesKasus 2Amalia RisnaPas encore d'évaluation
- SIADH (Syndrome of Inapproperiate Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion)Document11 pagesSIADH (Syndrome of Inapproperiate Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion)itsmesubu100% (2)
- Helium Dilution Technique Rakesh Oct 2016Document61 pagesHelium Dilution Technique Rakesh Oct 2016AyePas encore d'évaluation
- Available Medicine at Pharmacy of THQ Hospital Jampur District Rajanpur Date:03.03.2020Document2 pagesAvailable Medicine at Pharmacy of THQ Hospital Jampur District Rajanpur Date:03.03.2020Kashif AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Balance System: by M K SastryDocument33 pagesBalance System: by M K SastryEdison halim100% (3)
- Mental Health Term PaperDocument8 pagesMental Health Term Paperchememartinez29100% (2)
- Nutrilab, Inc. v. Schweiker, 547 F. Supp. 880 (N.D. IllDocument4 pagesNutrilab, Inc. v. Schweiker, 547 F. Supp. 880 (N.D. Illapi-237393155Pas encore d'évaluation
- A New Understanding and A Minimalist Approach For.17Document9 pagesA New Understanding and A Minimalist Approach For.17diego.guerra.smithPas encore d'évaluation
- Policy & Procedure Ino Without Hosp Id InfoDocument11 pagesPolicy & Procedure Ino Without Hosp Id InfoKCS100% (1)
- En ModulTechnik Moduflex 2500 2600Document12 pagesEn ModulTechnik Moduflex 2500 2600Razvan PredaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cholesterol Lowering Secrets ReportDocument12 pagesCholesterol Lowering Secrets ReportSantoshKumarPas encore d'évaluation
- H MoleDocument7 pagesH MoleRaymond Christopher LimPas encore d'évaluation
- TMJ DislocationDocument56 pagesTMJ DislocationAlok BhardwajPas encore d'évaluation
- CvadDocument11 pagesCvadNjideka A.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Suicide EssayDocument4 pagesSuicide EssayTiffanyPas encore d'évaluation
- Developmental Delays in ChildrenDocument12 pagesDevelopmental Delays in ChildrenSarah Lombres Antigua MontefalcoPas encore d'évaluation
- Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing - 0.5 Mcfarland NcclsDocument14 pagesAntimicrobial Susceptibility Testing - 0.5 Mcfarland NcclsAnonymous brvvLxoIluPas encore d'évaluation
- Stop excessive sweating with a safe, affordable at-home solutionDocument2 pagesStop excessive sweating with a safe, affordable at-home solutionJohny AplleasedPas encore d'évaluation
- Food and NutritionDocument5 pagesFood and NutritionCes Blanco LicerioPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical-Surgical Nursing Care: Caring For Clients With Diabetes MellitusDocument90 pagesMedical-Surgical Nursing Care: Caring For Clients With Diabetes MellitusJonalynCollodChewacheoPas encore d'évaluation
- Dentistry exam questionsDocument38 pagesDentistry exam questionsJollnar Ahmad100% (1)
- Case Conference 011017 (Appendicitis)Document36 pagesCase Conference 011017 (Appendicitis)Lilik NatasubrataPas encore d'évaluation
- DietPlan14DayLowCarbPrimalKeto 5Document131 pagesDietPlan14DayLowCarbPrimalKeto 5josuedsneto100% (5)
- Selfassessment Nurs 151Document10 pagesSelfassessment Nurs 151api-315083210Pas encore d'évaluation
- Uncontrolled Spread: Why COVID-19 Crushed Us and How We Can Defeat the Next PandemicD'EverandUncontrolled Spread: Why COVID-19 Crushed Us and How We Can Defeat the Next PandemicPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisD'EverandSummary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (9)
- The Gut-Immune Connection: How Understanding the Connection Between Food and Immunity Can Help Us Regain Our HealthD'EverandThe Gut-Immune Connection: How Understanding the Connection Between Food and Immunity Can Help Us Regain Our HealthPas encore d'évaluation
- Epic Measures: One Doctor. Seven Billion Patients.D'EverandEpic Measures: One Doctor. Seven Billion Patients.Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (13)
- The Transformation: Discovering Wholeness and Healing After TraumaD'EverandThe Transformation: Discovering Wholeness and Healing After TraumaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (70)
- The Nocebo Effect: When Words Make You SickD'EverandThe Nocebo Effect: When Words Make You SickPas encore d'évaluation
- Do You Believe in Magic?: The Sense and Nonsense of Alternative MedicineD'EverandDo You Believe in Magic?: The Sense and Nonsense of Alternative MedicinePas encore d'évaluation
- The Wisdom of Plagues: Lessons from 25 Years of Covering PandemicsD'EverandThe Wisdom of Plagues: Lessons from 25 Years of Covering PandemicsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (5)
- The Atlas of Disease: Mapping Deadly Epidemics and Contagion from the Plague to the CoronavirusD'EverandThe Atlas of Disease: Mapping Deadly Epidemics and Contagion from the Plague to the CoronavirusÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (10)
- Deaths of Despair and the Future of CapitalismD'EverandDeaths of Despair and the Future of CapitalismÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (30)
- Arthritis Diet: Anti-inflammatory Diet for Arthritis Pain ReliefD'EverandArthritis Diet: Anti-inflammatory Diet for Arthritis Pain ReliefPas encore d'évaluation
- The War on Informed Consent: The Persecution of Dr. Paul Thomas by the Oregon Medical BoardD'EverandThe War on Informed Consent: The Persecution of Dr. Paul Thomas by the Oregon Medical BoardÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (2)
- Quick Fixes: Drugs in America from Prohibition to the 21st Century BingeD'EverandQuick Fixes: Drugs in America from Prohibition to the 21st Century BingePas encore d'évaluation
- Epidemics and Society: From the Black Death to the PresentD'EverandEpidemics and Society: From the Black Death to the PresentÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (9)
- War on Ivermectin: The Medicine that Saved Millions and Could Have Ended the PandemicD'EverandWar on Ivermectin: The Medicine that Saved Millions and Could Have Ended the PandemicÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (7)
- There Are No Accidents: The Deadly Rise of Injury and Disaster—Who Profits and Who Pays the PriceD'EverandThere Are No Accidents: The Deadly Rise of Injury and Disaster—Who Profits and Who Pays the PriceÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (15)
- Blood Runs Coal: The Yablonski Murders and the Battle for the United Mine Workers of AmericaD'EverandBlood Runs Coal: The Yablonski Murders and the Battle for the United Mine Workers of AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- Community Organizing and Community Building for Health and Social Equity, 4th editionD'EverandCommunity Organizing and Community Building for Health and Social Equity, 4th editionPas encore d'évaluation
- The HPV Vaccine On Trial: Seeking Justice For A Generation BetrayedD'EverandThe HPV Vaccine On Trial: Seeking Justice For A Generation BetrayedÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (13)
- Heat Wave: A Social Autopsy of Disaster in ChicagoD'EverandHeat Wave: A Social Autopsy of Disaster in ChicagoÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (40)
- Mama Might Be Better Off Dead: The Failure of Health Care in Urban AmericaD'EverandMama Might Be Better Off Dead: The Failure of Health Care in Urban AmericaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anti-vaxxers: How to Challenge a Misinformed MovementD'EverandAnti-vaxxers: How to Challenge a Misinformed MovementÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (12)
- Doctored: The Disillusionment of an American PhysicianD'EverandDoctored: The Disillusionment of an American PhysicianÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (11)
- The Truth about Wuhan: How I Uncovered the Biggest Lie in HistoryD'EverandThe Truth about Wuhan: How I Uncovered the Biggest Lie in HistoryÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (6)
- AIDS Activist: Michael Lynch and the Politics of CommunityD'EverandAIDS Activist: Michael Lynch and the Politics of CommunityPas encore d'évaluation