Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Practice Naming Hydrocarbons
Transféré par
Jun Yu LiuTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Practice Naming Hydrocarbons
Transféré par
Jun Yu LiuDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Name: _____________________ Period: ___
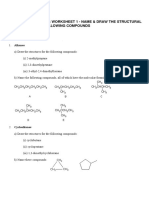
I. Alkanes (1) Name the following alkanes. (a) (g)
CH3 CH3CH2CHCH 2CH2CH3
(b)
CH2CH2CH2CH3 CH3CH2CHCH 2CHCH 2CHCH 3 CH3CH2 CH3
CH2CH3 CH3CH2CHCHCH 2CH2CH3 CH3
(c)
(h)
CH3 CH2 CH2 CH CH2 CH2
CH3 CH3CH2CHCH 2CHCH 3 CH3
(d) (i)
CH2
CH2CH3
CH3
CH2CH3
CH2
CH CH CH2 CH3
CH3CHCH 2CHCHCH 2CH2CH3 CH3
(e)
CH2
(j)
CH3
CH2CH2CH3
CH2
CH3 C CH2CH3
CH3CHCH 2CHCHCH 2CH2CH2CH3 CH2CH3
CH2
(f) (k)
CH2
CH2CH3
CH2CH3 CH CH CH3 CH CH3
(2) Draw the following alkanes. (a) 2-Methylpropane (g) 3-Ethyl-2-methyl-5,6-dipropylnonane
(b) 3-Ethyl-2-methylhexane
(h) 1-Ethylcyclopropane
(c) 2,2-Dimethylbutane
(i) 1-Propyl-2,3-dimethylcyclobutane
(d) 3-Ethyl-2,5-dimethylheptane
(j) 1,2-Diethyl-3-methylcyclopentane
(e) 3,3,5-Trimethyloctane
(k) 1,3-Dimethylcyclohexane
(f) 5-Butyl-2,3,6-trimethyldecane
(3) Name and draw the five structural isomers of C6H14.
II. Alkenes (1) Name the following alkenes. (a) (d)
CH2 CH3 CH CH
(e)
CH3CH2CH=CHCH 2CH3
(b)
CH CH
CH3
CH3CH=CHCHCH 2CH2CH3 CH2CH3
(c)
CH3
CH3
CH3CHCH=CHCHCHCH 2CH3
CH3
CH2CH2CH3
(f)
CH3CHCHCH=CHCH 3 CH3
CH2CH3 CH CH2 CH2 CH CH CH2
(2) Draw the following alkenes. (a) 2-Methylpropene (d) 1-methylcyclopentene
(b) 3-Ethyl-4-methyl-2-pentene
(e) 6-Ethyl-3,3-dimethyl-4-nonene
(c) 3-Ethyl-2,4-dimethyl-3-heptene
(f) 3-Ethyl-4,5-dimethylcyclohexene
(3) (a) Name the two stereoisomers of 2-hexene. #1 #2
CH3 C=C H
CH3 CH2CH2CH3 C=C H H
CH2CH2CH3
(b) Name and draw the two stereoisomers of 3-hexene.
III. Alkynes (1) Name the following alkynes. (a) CH2C CCH2 CH3 (c)
CH3
(b)
CH3C = CCCH2CH3
CH3
CH3
(d)
CH3CH2C= CCHCH 2CH3
CH2CH3 CH3CH2C= CCHCHCH 2CH3 CH3
(2) Draw the following alkynes. (a) 4-Ethyl-2-heptyne (c) 2,5,6-Trimethyl-3-octyne
(b) 3-Ethyl-5-methyl-1-hexyne
(d) 3,8-Dimethyl-5-decyne
(d) Answers: I. Alkanes (1) (a) 3-Methylhexane (b) 3-Ethyl-4-methylheptane (c) 2,4-Dimethylhexane (d) 4-Ethyl-2,5-dimethyloctane (e) 5-Ethyl-2-methyl-4-propylnonane (f) 4-Ethyl-3,8-dimethyldecane (g) 4,6-Diethyl-2-methyldecane (h) 1-Methylcyclohexane (i) 1-Ethyl-2-methylcyclopentane (j) 1,2-Diethyl-1-methylcyclobutane (k) 1-Ethyl-2,3-dimethylcyclopropane (f) (e)
(i)
CH2CH3 CH3CHCHCH 2CHCH 2CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3CH2CCH2CHCH 2CH2CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3
CH3 CH
CH3 CH
CH2
(j)
CH
CH2CH2CH3
CH2CH3 CH CH2 CH CH2CH3 CH CH3
CH3
CH2CH2CH2CH3
CH3CHCHCH 2CHCHCH 2CH2CH3 CH3
(g)
CH2
(k)
(2) (a)
CH3
CH2CH2CH3
CH2 CH2 CH2
CH3 CH CH2 CH CH3
CH3 CH3CHCH 3
(b)
CH3
CH3CHCHCH 2CHCHCH 2CH2CH3 CH2CH3 CH3CH2
(h)
CH2CH2CH3
CH3CHCHCH 2CH2CH3 CH3
(c)
CH2CH3 CH
CH3 CH3CH2CCH3 CH3
(3) 1. Hexane CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2 CH3 2. 2-Methylpentane 3. 3-Methylpentane 5. 2,2-Dimethylbutane
CH2
CH2
CH3 CH3CH2CHCH 2CH3
4. 2,3-Dimethylbutane
CH3 CH3CCH2CH3 CH3
CH3 CH3CHCH 2CH2CH3
CH3 CH3CHCHCH 3 CH3
II. Alkenes (1) (a) 3-hexene (b) 4-Ethyl-2-heptene (c) 4,5-Dimethyl-2-hexene (d) 3,5-Dimethylcyclopentene (e) 2,6-Dimethyl-5-propyl-3-octene (f) 3-Ethylcyclohexene (d) (c) (e)
CH3 CH3 CH3CHC=CCH 2CH2CH3 CH2CH3
(f)
CH3 CH3CH2CCH=CHCHCH 2CH2CH3 CH3 CH2CH3
(2)(a)
CH2 CH2 C CH2 CH
CH2CH3 CH CH3 CH CH CH3 CH CH CH2
(b)
CH3
CH3
CH3CH=CCHCH 3 CH2CH3
(3) (a) #1: trans-2-hexene (or (E)-2-hexene) #2: cis-2-hexene (or (Z)-2-hexene)
(b) trans-3-hexene (or (E)-3-hexene)
cis-3-hexene (or (Z)-3-hexene)
III. Alkynes (1) (a) 2-pentyne (b) 5-Methyl-3-heptyne (c) 4,4-Dimethyl-2-hexyne (d) 5-Ethyl-6-methyl-3-octyne (b) (d)
CH2CH3 CH= CCHCH 2CHCH 3 CH3
(a)
CH2CH3 CH3C= CCHCH 2CH2CH3
(c)
CH3 CH3CHC = CCHCHCH 2CH3 CH3 CH3
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 15 Naming and Drawing Functional Groups Practice WorksheetDocument4 pages15 Naming and Drawing Functional Groups Practice WorksheetCorey Becker33% (6)
- Organic Chemistry Woorksheet On Nomenclature Chemistry 112 I. Alkanes A. Give The IUPAC Name For Each of The FollowingDocument3 pagesOrganic Chemistry Woorksheet On Nomenclature Chemistry 112 I. Alkanes A. Give The IUPAC Name For Each of The FollowingDatu Nasthur TalipasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Naming and Drawing Alkenes Worksheet and KeyDocument6 pagesNaming and Drawing Alkenes Worksheet and Keyhaniiman100% (1)
- Naming Hydrocarbons Worksheet and Key: Write The Name of Each of The Hydrocarbon Molecules Shown Below: 1) 8)Document2 pagesNaming Hydrocarbons Worksheet and Key: Write The Name of Each of The Hydrocarbon Molecules Shown Below: 1) 8)Yoshua YanottamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Naming Esters Practice WorksheetDocument2 pagesNaming Esters Practice WorksheetBrianna Malcolm100% (1)
- Thermochemistry Module 1Document9 pagesThermochemistry Module 1PavithiranPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 35Document3 pagesLesson 35MarcTnnPas encore d'évaluation
- Algebraic Method To Balance Chemical EquationDocument3 pagesAlgebraic Method To Balance Chemical EquationBruce WalkerPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Colligative Properties of SolutionsDocument3 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson: Colligative Properties of SolutionsMarcTnnPas encore d'évaluation
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 21 Answer SchemeDocument9 pagest2 Chem Revision Ex 21 Answer SchemeNicholas OwPas encore d'évaluation
- Drawing and Naming AlkanesDocument3 pagesDrawing and Naming AlkanesNastya Kats100% (1)
- Naming Alkanes Ws 1 and Ws 2Document4 pagesNaming Alkanes Ws 1 and Ws 2Kristoff AvilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Alkenes TutorialDocument8 pagesAlkenes TutorialVarshLokPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Form 6 Sem 2 01Document69 pagesChemistry Form 6 Sem 2 01Febian HenryPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic Chemistry - Worksheet 1Document10 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Worksheet 1Prakas PalanychamyPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: D-Block Elements (II)Document3 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson: D-Block Elements (II)MarcTnnPas encore d'évaluation
- ProteinDocument16 pagesProteinRosnadia RosliPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 41Document3 pagesLesson 41MarcTnnPas encore d'évaluation
- A1 Alcohols Ws 1Document21 pagesA1 Alcohols Ws 1GyaanPas encore d'évaluation
- Enthalpy ChangesDocument17 pagesEnthalpy ChangesDoc_Croc100% (1)
- Lesson 38Document3 pagesLesson 38MarcTnnPas encore d'évaluation
- Covalent Bond Worksheet PDFDocument4 pagesCovalent Bond Worksheet PDFHelma Jabello AriolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Answer All Questions in This Section. Indicate The Correct Answer On The Space Provided in Page 2Document5 pagesAnswer All Questions in This Section. Indicate The Correct Answer On The Space Provided in Page 2seanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Semester 3 DefinitionDocument1 pageChemistry Semester 3 DefinitionYong ChoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Quick Revision Paper 3 Section B Physics SPMDocument7 pagesQuick Revision Paper 3 Section B Physics SPMTeoh MilayPas encore d'évaluation
- Moles Stoichiometry Olevels Only MCQs Complete 2014 Protected PDFDocument24 pagesMoles Stoichiometry Olevels Only MCQs Complete 2014 Protected PDFAli AshrafPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 39Document3 pagesLesson 39MarcTnnPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry 120: Experiment 3 Preparation of Standard Sodium Thiosulfate Solution and Determination of Hypochlorite in A Commercial Bleach ProductDocument4 pagesChemistry 120: Experiment 3 Preparation of Standard Sodium Thiosulfate Solution and Determination of Hypochlorite in A Commercial Bleach ProductamitmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry STPM Sem 3 MSAB Pre-Trial QuestionDocument6 pagesChemistry STPM Sem 3 MSAB Pre-Trial QuestionKenneth Chan43% (7)
- Chemistry Paper 3 SampleDocument3 pagesChemistry Paper 3 Samplerihdus2100% (2)
- Rate of Reaction 2Document12 pagesRate of Reaction 2Baskaran ManogaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Amines and Amides AnswersDocument2 pagesAmines and Amides AnswersKristine Sumalinog0% (1)
- Chemistry Form 4 Definition ListDocument3 pagesChemistry Form 4 Definition ListAliif IsmailPas encore d'évaluation
- GCE A Levels H2 Chemistry Prelim Paper 2Document20 pagesGCE A Levels H2 Chemistry Prelim Paper 2Chong56Pas encore d'évaluation
- Short Note Chemistry Form 5-Chapter 5 Chemical For ConsumerDocument4 pagesShort Note Chemistry Form 5-Chapter 5 Chemical For Consumersalamah_sabri100% (1)
- CHEMISTRY FORM 6 SEM 3 Chapter 6 PDFDocument32 pagesCHEMISTRY FORM 6 SEM 3 Chapter 6 PDFYuzamrah Awang NohPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 41Document4 pagesLesson 41MarcTnn100% (1)
- Oxidation - Reduction Choice QuestionsDocument5 pagesOxidation - Reduction Choice QuestionsMirza Bilal Mughal100% (1)
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: D-Block Elements (I)Document3 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson: D-Block Elements (I)MarcTnnPas encore d'évaluation
- Naming Alkanes Worksheet 2Document2 pagesNaming Alkanes Worksheet 2Kamariah Ismail100% (1)
- 04 Alkane Nomenclature 343 AnsDocument6 pages04 Alkane Nomenclature 343 AnsSileshi TerefePas encore d'évaluation
- Thermochemistry (Answers)Document17 pagesThermochemistry (Answers)Venessa BlingBling ChunPas encore d'évaluation
- Half Life ALLDocument24 pagesHalf Life ALLRafaelCarneiroPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2 - Matter and Energy Fuels: Learning ObjectivesDocument6 pagesUnit 2 - Matter and Energy Fuels: Learning ObjectivesNiña Viaña BinayPas encore d'évaluation
- Rates of Chemical Reactions - NewDocument13 pagesRates of Chemical Reactions - Newsam100% (1)
- Chemical EquationsDocument37 pagesChemical Equationssinung waluyojatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Complex Ions Naming Chemistry STPM Sem 2Document4 pagesComplex Ions Naming Chemistry STPM Sem 2Chong Yin PingPas encore d'évaluation
- PPP Enthalpy ChangesDocument39 pagesPPP Enthalpy ChangesHenryLim9100% (1)
- Stoichiometry For ChemistryDocument11 pagesStoichiometry For ChemistryWONG TSPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 40Document3 pagesLesson 40MarcTnnPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Le Chatelier's Principle (II)Document4 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson: Le Chatelier's Principle (II)MarcTnnPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan: Some of Their PropertiesDocument3 pagesLesson Plan: Some of Their PropertiesMarcTnnPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic Chemistry WorksheetDocument72 pagesOrganic Chemistry Worksheetgkawsar22Pas encore d'évaluation
- Speed of Reaction SummaryDocument3 pagesSpeed of Reaction Summarychong5660% (5)
- NomenDocument4 pagesNomensushil kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- 13 DPP 2 New Batch A-N +ans For StudentsDocument32 pages13 DPP 2 New Batch A-N +ans For StudentskljPas encore d'évaluation
- I UpacDocument19 pagesI UpacJay DodiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Esr Nomenclature Test OasisDocument4 pagesEsr Nomenclature Test OasisAnamika Barnwal100% (1)
- 1.intro To Organic Chem-PracticeDocument2 pages1.intro To Organic Chem-PracticeZul Abror Bin Ya'akopPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Manual FSI 12803 Exp 3 7.11.2022Document4 pagesLab Manual FSI 12803 Exp 3 7.11.2022alyea atiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Cultivando Suncor Status UpdateDocument56 pagesCultivando Suncor Status UpdateCBS News ColoradoPas encore d'évaluation
- Approved Welding Consumables R14 Aug 2011Document32 pagesApproved Welding Consumables R14 Aug 2011Akhilesh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- United States Patent: (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of PatentDocument7 pagesUnited States Patent: (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patentnur mxPas encore d'évaluation
- Demo Table of Prediction Methods For Feed Oil and Biodiesel PropertiesDocument9 pagesDemo Table of Prediction Methods For Feed Oil and Biodiesel PropertiesJessicalba LouPas encore d'évaluation
- PMI ProcedureDocument9 pagesPMI ProcedureKarrar TalibPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise BM With Chemical ReactionDocument2 pagesExercise BM With Chemical ReactionSergio Rugerio TorresPas encore d'évaluation
- Boiler Water Testing ProcedureDocument17 pagesBoiler Water Testing ProcedureGuruPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To TitrationDocument57 pagesIntroduction To TitrationSoumi ChoudhuryPas encore d'évaluation
- Day 1 AnswersDocument31 pagesDay 1 Answershaoues23100% (2)
- SSPDocument16 pagesSSPRaghunath Veeramani100% (1)
- 2021 Master CatalogDocument330 pages2021 Master Cataloggeetha raniPas encore d'évaluation
- Why DistilledDocument2 pagesWhy DistilledDr. Varah SiedleckiPas encore d'évaluation
- MMS-How To Make It-By Jim HumbleDocument9 pagesMMS-How To Make It-By Jim Humblephilalethes2456Pas encore d'évaluation
- Evaluation of Thermoplastic Polyurethane Solids and Solutions For Biomedical ApplicationsDocument4 pagesEvaluation of Thermoplastic Polyurethane Solids and Solutions For Biomedical ApplicationsROHITPas encore d'évaluation
- Bioseparation Dr. Kamal E. M. Elkahlout An OverviewDocument30 pagesBioseparation Dr. Kamal E. M. Elkahlout An OverviewKemal ELkahloutPas encore d'évaluation
- Karty CharakterystykDocument6 pagesKarty CharakterystykekoherwantoroPas encore d'évaluation
- (Polymer Science and Technology 15) Raymond B. Seymour (Auth.), Raymond B. Seymour (Eds.) - Conductive Polymers-Springer US (1981) PDFDocument235 pages(Polymer Science and Technology 15) Raymond B. Seymour (Auth.), Raymond B. Seymour (Eds.) - Conductive Polymers-Springer US (1981) PDFRizmahardian Ashari KurniawanPas encore d'évaluation
- JSPL Hard PlateDocument3 pagesJSPL Hard PlateKrishna KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- SCHB032 - Memo - Test 1 2022Document5 pagesSCHB032 - Memo - Test 1 2022emjayPas encore d'évaluation
- Effect of Boiled Cassava Leaves (Manihot Esculenta Crantz) On Total Phenolic, Flavonoid and Its Antioxidant ActivityDocument12 pagesEffect of Boiled Cassava Leaves (Manihot Esculenta Crantz) On Total Phenolic, Flavonoid and Its Antioxidant ActivityOxide HelixPas encore d'évaluation
- Article-106-Spc Waxes Used in The Cosmetics IndustryDocument3 pagesArticle-106-Spc Waxes Used in The Cosmetics IndustryVictor Lopez100% (1)
- 2012 Katalisis OganologamDocument64 pages2012 Katalisis OganologamJodhi Hartono PutraPas encore d'évaluation
- Pickering Emulsion Polymerization Kinetics of StyreneDocument44 pagesPickering Emulsion Polymerization Kinetics of StyreneAnonymous 9bc25fDPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemsheets A2 1025 Reactions of AromaticsDocument5 pagesChemsheets A2 1025 Reactions of AromaticsdodoPas encore d'évaluation
- 9 Welding Processes Cwip 3.1Document12 pages9 Welding Processes Cwip 3.1Jawed AkhterPas encore d'évaluation
- Iron Making Course - Blast FurnaceDocument51 pagesIron Making Course - Blast FurnaceSurendra Panda100% (4)
- JSRNBR eDocument8 pagesJSRNBR eDevender KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Demineralisation Plant CalculationDocument14 pagesDemineralisation Plant Calculationsmbhat25100% (2)
- CP-29 Carbopol Aqua SF-1 Product SummaryDocument2 pagesCP-29 Carbopol Aqua SF-1 Product SummaryadrianaPas encore d'évaluation