Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
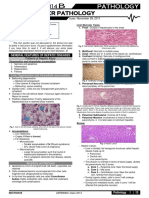
Pathology Slides in English (Little Bit Bulgarian Too:)
Transféré par
Fırat GüllüTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
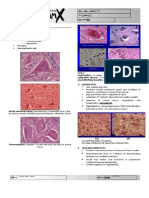
Pathology Slides in English (Little Bit Bulgarian Too:)
Transféré par
Fırat GüllüDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
1
1-Necrosis renis / 34. Infarctus anaemicus renis/. Anemic infarction of the kidney develops in blockage of some of the branches of renal areteriya - obiknovino of embolism, resulting in ischemia occurs with subsequent necrosis of the renal parenchyma in the relevant section. It is a coagulation necrosis, presented in a section of the body with preserved structure in which the visible shadows of glomeruli and tubules. In cells lacking nuclei tubes and homogenized cytoplasm, intense pink colored XE. Disappear cellular details can be seen only vaguely delineated cell borders. Morphological features of necrosis are different phases of nuclear fission: homogenization (compaction) of the nuclear chromatin - karyopycnosis, degradation of nuclei presented in the form of pellets - karyorrhexis and complete disappearance in necrotic cells - karyolysis. Affected cell and tissue structures are homogenized granular cytoplasm and stained more intensely than eozina. Around the area of necrosis is hiperemichnohemoragichnata area consisting of dilated blood vessels and bleeding. Near it there is segmented shaft of leukocytes, which may be missing in early stages. Adjacent renal tissue is found with a fully preserved structure.
2. Necrosis pulmonis / 58 Bronchopneumonia tbc caseosa./ Kazeozna necrosis of the lung is most commonly seen in kazeozna bronchopneumonia or in the center of granulomas formed in tuberculosis. It is represented by nonstructural, drebnozarnisti areas completely deleted sinkavorozov alveolar structure and color of stain H & E. Among the nonstructural fields can be monitored and blue colored remnants of nuclear
chromatin resulting from karyorrhexis. Around the necrotic zone are macrophages, monocytes that migrated from the blood flow in relation to the cellular response to chronic irritation. They are formed epiteloidni cells with oval nuclei and pale pink cytoplasm. With its form and arrangement they resemble epithelial cells, where labeled cells si.Sred epiteloidnite meet multicore type giant cells "Langhans" resulting from the merger of several epiteloidni cells. Their nuclei are located along the periphery of the cell in the form of a horseshoe with an opening to the central necrosis of the periphery of the granuloma are described T lymphocytes forming etc. lymphocyte shaft.
Giant type cells Langhans
3. Necrosis lymphonodi. (=58 Tuberculosis lymphonodi) The process is represented by a centrally located area of necrosis in kazeozna lymph node - a large, structureless, rose-colored mass, which one can see the blue colored drebnozarnisti fragments of nuclear chromatin. About kazeoznata necrosis are characteristic features of spindle cell epiteloidni ordered palisades / boards as a fence /. Among them are found Multinucleated giant cell type "Langhans. Under the fibrous capsule of the lymph node on the periphery of the necrotic area is visible reserved lymph follicles.
Giant type cells "Langhans"
4. Necrosis myocardii /=35 Infarctus anaemicus myocardii). This study demonstrates the preparation ischemic / anemic / coagulation necrosis in the myocardium as a result of stopping the blood flow, due mostly to the blockage of coronary artery by a clot or prolonged vasoconstriction. In anemic / white / myocardial infarction was observed well homogenized limited area of cardiomyocytes, which have lost their transverse nabrazdenost and stained more intensely than eozina. Nuclei are not clearly visible. Among the necrotic cardiomyocytes reserved visible elements of the interstitial connective tissue and blood vessels from the shadows. After 6 to 8 hours of initial clinical manifestation of myocardial necrotic fields are separate from the surrounding tissue through etc. hyperemic-hemorrhagic area represented by dilated blood vessels and bleeding, and later by inflammatory leukocytes segmented shaft.
5. Necrosis cerebri /= 36. Infarctus anaemicus cerebri encephalomalacia. It is for anemic infarction due to obturation of the thrombus or thromboembolism artery in the brain. Necrosis is kolikvatsionen type, characteristic of cells and tissues poor in protein and rich in water and lipids. When hypoxia occurs the death of brain cells, which is manifested by "softening" of brain matter, etc. encephalomalacia. Microscopy in the area of necrosis is seen stretch of pale pink colored, homogeneous, structureless granular matter with a view or as a single thread veins. Gangliyni and glial cells, and nevrofibrili not observed. On the border with preserved tissue are very large cells with bright nuclei and sometimes piknotichni swollen, vacuolated cytoplasm, which detect lipids and brown pigment / hemosiderin. The same is formed by the disintegration of erythrocytes in the hearth of necrosis and their phagocytic glial cells. These cells are ingested and dissolved lipids of myelin sheath. They are marked as lipofagi (psevdoksantomni cells) and cells derived from mikrogliyata. When staining for lipids in Sudan III kriostatni cuts on their cytoplasm are stained yellow-orange. If fatalities occur after receiving the attack (stroke), the process of necrosis ends with the formation of glial scar formation or a pseudocyst. Years later when an autopsy can be found psevdokistata attesting spent cerebral infarction.
pseudocyst
6. Emphysema pulmonis. Pulmonary emphysema is a process of destruction and dilation of the airways distal to terminal bronchioles. In the most common form panatsinaren histological picture of emphysema in the lung is represented by: - Advanced respiratory bronchioles, alveolar moves alveoli and pores of Cohn. - Destroyed mezhdualveolarni baffle. - Thin alveolar walls, poor in elastic fibers. - Reduced number and poor alveolar capillary wedge kravonapalneni. - In the alveoli and alveolar interstitial macrophages are loaded with pigment antrakotichen / koniofagi /.
7. Atrophia fusca hepatis. Brown atrophy of the liver is observed in the course of diseases associated with failure and inferiority of nutrition: idiopathic pyloric stenosis or gastric / doudenalna ulcer, cancer of the stomach and esophagus, cachexia, incl. and senile, diseases of the endocrine glands etc.. Macroscopically, the liver is reduced in size to brownish, thickened and sharp edge. Histological picture is represented by thin gredichki liver, mainly in centrilobular areas. Delchetata are reduced in size and portal spaces appear dilated. Hepatocytes around v. centralis are reduced in size (atrophic) in the cytoplasm, perinuklearno, there is accumulation of
yellow-brown pigment - lipofuscin.
8. Cell swelling / Dystrophia parenchymatosa renis / Home of the cell damage due to most of the effects of hypoxia, toxic or infectious factors. It is for intracellular edema. The process is reversible upon removal of etiopatogenetichniya factor. With persistence, the impact goes into a severe severe cellular or tissue damage, incl. and necrosis. Most often this process occurs in the epithelial cells of proximal convoluted tubule of the kidney. The boundaries between cells are not well visible. Ducts are enlarged, and their lumens are irregular because they prominirane of swollen epithelial cells that stained intensely for XE are colored pink. In the process progresses in the cytoplasm may form vacuoles representing dilated cisterns of endoplazmatichniya reticulum. Hence the name or vakuolerna hidropichna dystrophy - a more advanced stage of intracellular edema.
9.Corpus albicans ovarii. It is a physiological delay in involyuiralite yellow hyaline bodies in the fibrous stroma of the ovary. Because macroscopic deposition of hyaline in them they become white, and where bear its name. White bodies are final phase in the evolution of the Graafian follicle. Under the microscope appear as homogeneous pink-colored eozina of nonstructural forms. Their bodies are well-demarcated from the surrounding tissue folded in the form of swag border, tend to lobubirane.
10. Fibrinoidna necrosis (bottom of a stomach ulcer). The product is an example of local deposition of fibrinoid necrosis in the mucous membranes in the case at the bottom of chronic stomach ulcer. The
process is referred to as fibrinoidna necrosis and is a sign of exacerbation of the ulcer. Pathological findings is the result of changes in collagen fibers under the influence of end-of-vessels plazmenni protein albumin, globulin and fibrinogen. In this process, receive solid, insoluble compounds, stained pink from eozina who perished together with local cells form a layer fibrinoidnata necrosis. There remain four areas of the plague - surface, consisting of cellular detritus and inflammatory exudate of segmented leukocytes, fibrinoidna necrosis zone, represented by pink and blue uniform stripe layer of granulation tissue which is located in a mature fibrous tissue.
Fibrinoid Necros(Fibrinoid)
10
11. Hyalinosis arteriolarum renis The process is subendotelno hyaline deposition in the walls of arterioles as a result most of arterial hypertension. In preparation is presented in the deposition of hyaline walls of small arteries and arterioles of the kidneys. Vascular walls are unevenly thickened, homogeneously pink colored HE. Depending on the severity of their lumens process with varying degrees of narrowing. The worst injured were the walls of glomeruli privodyashtite vessels - arterioles in their vascular pole (vasa afferens), which can be seen in cross-section as pink rings.
10
11
12. Amyloidosis renis (HE). Amyloid appears as a homogeneous, pink colored by eozina, structureless substance in renal structures. Glomeruli are affected to varying degrees - from the homogenization of individual capillaries in the early stage, to cover all the glomeruli of the process. Damaged glomeruli are larger than normal as a result of their accumulation of abnormal protein. Shows the preparation and accumulation of pink colored protein in the walls of vessels of medium and small caliber and in the basal membrane of the seminiferous that are thickened. The process leads to fatty degeneration in epithelial cells them due to chronic hypoxia associated with reduction in glomerular blood flow. Fatty degeneration of the epithelial cells of proximal tubules is the cause of macroscopic findings "ren albus".
11
12
13. Amyloidosis renis (MV). In preparation for staining with metilviolet property is used to amyloid metahromatichno colors of some aniline dyes. The process is called metahromaziya violet paint colors metilviolet amyloid selectively in red and other tissues retain its main blue-violet color. Histologically all structures, with enlarged size of the amyloid deposits are stained red. / Parts or whole glomeruli glomeruli, vessel walls and basement membrane of ducts /.
12
13
14. Amyloidosis lienis (HE). Deposition of amyloid in the spleen may be focal in the form of homogeneous pink-colored lymph follicles with eozin / t.n.sagova spleen / or as diffuse deposits in the walls of the sine wave and connective network of the red pulp / Ham-derson spleen /. The name derives from the spleen Sagova its macroscopic appearance - when she cut dotted with small whitish nodules, like grains of sago. In preparation demonstrate hearth deposition in follicles that are enlarged. Centrally located follicular arteries affected by the process are also homogenized, thickened with pink colored walls.
13
14
15. Amyloidosis lienis (MV). Stained with metilviolet deposits in lymph follicles and their central arteries amyloid is red, and other tissues are blue-violet. This method is used for proof of amyloidosis in differential diagnosis with other processes.
14
15
16.Carcinoma gelatinosum (HE). The presented case is a demonstration of glandular cancer / adenocarcinoma / intracellular and extracellular sluzoobrazuvane. In the malignant transformation of glandular cells due to impaired metabolism of glikoproteidite they occur nekotroliruema production of mucus. In the early form intracellular mucus vacuoles. Later they merged to form a mucus drop, forcing the core to the periphery of the cell. It begins to look like a "ring with a stone." Thoroughly congested with mucus cells die and form lakes of mucus, dyeing basophilic - in sinkavovioletov color. Among them. visible single cell type "ring with a stone."
15
16
17.Carcinoma gelatinosum (alcian blau ). Glikoproteidite are complex organic compounds of proteins with polymerized hydrocarbons. Depending on their location, in violation of their metabolism accumulate neutral or acidic mucopolysaccharides. An example is again zhelatinozniyat, mucus producing adenocarcinoma. Preparation indicates the presence of acid mucopolysaccharides in tumor cells and lakes of mucus around them has been used to color blue altsianovo their demonstration. Histologically visible blue-green mucus sections and single cancer cells with blue stained mucus droplets.
16
17
18. Mucoviscidosis pancreatis. Cystic Fibrosis / cystic fibrosis / a hereditary disorder of epithelial transport of chloride ions in mucus secretion in exocrine glands and the lining of the respiratory, gastrointestinal tract and pancreas In this case, the process affects pancreatic ductal cells from which the component produced exceptionally phlegm, blocked outgoing channels of the gland. They are expanding due to fluid retention with subsequent formation of retention cysts. The process is coupled with glandular atrophy and fibrosis around the canals. The preparation is described seeing changes - mostly dilated ducts filled with mucus retention periduktalnata fibrosis and cysts containing mucus pink homogeneous material.
17
18
19. Nevus pigmentosus. Pigment nevus is congenital or acquired benign neoplasm originating from dendritic melanocytes localized in the basal layer of epidermis. In this case it is seen as an example of impaired metabolism of aboriginal pigment melanin produced by dendritic melanocytes. Nevus can occur in various forms but the most common are: border, dermal, complex, spitz nevus, and nevus dizplastichen. In this case demonstrates dermal nevus. In melanocytes proliferate as it shaped nests in the epidermis. Usually they contain brown granules of melanin, the pigment but may not be evident. The nests are composed of uniform round or polygonal cells drained, with homogeneous or slightly granular cytoplasm and large round or oval nucleus. Nevus can give early malignant pigmented tumors - malignant melanoma.
20. Induratio fusca pulmonis (HE) The process demonstrates the local deposition of haemosiderin in the lungs in chronic left heart failure (especially in congenital or acquired in later defects of the mitral valve). As a result of chronic venous stasis in the alveolar capillary wedge there is hypoxia, which leads to damage of endothelial cells and their permeability to increase. By diapedeza erythrocytes appear in the lumen of the alveoli, where phagocytosed by macrophages located there, in this case denoted as hemosiderofagi. In their hemoglobin is converted into ferritin, which aggregates in zlatistokafenikavite hemosiderin granules. Meanwhile, hypoxia leads to proliferation of fibroblasts to produce collagen and thickening of the
18
19
alveolar walls. In the alveoli and the interstitial are many hemosiderofagi. Hemosiderofagite can be found in the sputum of patients as a diagnostic test and therefore are called cells of the heart defect (Hertzfehlercellen).
19
20
21.Induratio fusca pulmonis (Histochemical reaction to demonstrate the Fe + + in the structure of hemosiderin). To prove the nature of the postponed in brown induration of lung pigment / hemosiderin / used histohimichnata Max Perls reaction and with ferotsiankalii tsolna kitselina etc. Berlin blue. Hemosiderinat turns sinkavozeleno. Histologically observed glaucous granules in the cytoplasm of siderofagite located in the lumen of the alveoli.
20
21
22.Icterus renis. With increased level of bilirubin was observed in the deposition of the seminiferous epithelium, Henle's loop and more rarely in these legal and collecting tubules of the kidney. In the affected cells are found small greenish-brown grains. In the later stage these cells in the lumen of husked and ducts with bile acids and bile salts form cylinders. The epithelial cells of the proximal part of nephron develop dystrophic and necrotic changes, which represent the morphological equivalent etc. hepato-renal syndrome.
21
22
23.Anthracosis pulmonis The product is an example of exogenous pigment deposition in the lung coal dust. Inhaled dust particles smaller than 5 microns mukotsiliarnata overcome the barrier of traheobronhialnoto tree and reach the alveoli where phagocytosed by alveolar macrophages. Phagocytosed dust particles, they are called macrophages koniofagi and the process is referred to as antrakoza. Histologically visible koniofagi whose cytoplasm contained black powder inclusions. After the death of koniofagite antrakotichniyat pigment is deposited in the interstitial connective tissue in the walls of the alveoli, in the course of Sep subplevrano, peribronchially.
24. Steatosis hepatis = Dystrophia adiposa hepatis (HE). Otlaganeto at lipidi under the format trigliceridi in erni CE nabldava when fraction uvredani toksini hipoksini sstoni, zaharen, diabetes, zatlstvane, etc. and CE oznaava Kato steatoza. Kasai Xie nayfrequently for natrupvaneto in hepatocitite under the format kapici, koito when ocvetvane with hemalaun eozin se vidat Kato optically prazni vacuoles, tj Kato with his SA ekstrahirani parafinovata processing of alkohola. In zavisimost from goleminata, Breu and razprostranenieto in hepatocitite ernodrobnata steatoza se podrazdel to ognina and difuzna, drebnokapesta and edrokapesta. Histologino strukturata to erni fraction (e) well. In the portalnite space hepatocitite zonite about fatty vacuoles and sdrat tezi at centralnite at deletata near centralnite CA Veni a comparatively shraneni. Zonalnoto otlagane to mazninite dependence of procest, kojto go e predizvikal. When hipoksi obiknoveno SA zasegnati centrolobularnite zone, toksini vzdejstvi, buying uvredait on the krvni current agent idva e steatozata periportalnite zone at deletata. Obilnoto natrupvane to dovede to trigliceridi can obrazuvaneto on Yes
22
23
fatty brushes and smrt at hepatocitite. Nekrozata predizvikva vzpalitelna format hronien response under hepatit, kojto Mauger da premine in cirrhosis. Takv process nabldava with hronien alkoholizm CE. Hepatociti steatoza ss da CE srenat when you can virusen with hepatit and razlini uvredani, toksini and lekarstveno included obusloven hepatit.
25. Dystrophia adiposa hepatis (Sudan III ). Demonstration of lipids in hepatocytes is implemented using kriostatni cuts only on fresh or fixed in formalin material, but not on vlklyucheni histologically in paraffin processed tissue fragments. Thus, the material does not pass into alcoholic solutions, lipids do not dissolve and can be colored with lipoboi. The most commonly used method is coloring Sudan III, where the lipids are visualized as orange-drops in the cytoplasm of hepatocytes.
23
24
26.theromatosis aortae (H) It is for cholesterol deposition, holesterinovite esters and neutral fat in the arteries of the intimate. Etc. are formed atherosclerotic plaques, which have three main components: A. cellular composition - mainly smooth muscle, macrophages and T lymphocytes 2. extracellular matrix including collagen, elastic fibers, proteoglycans and 3. intra-and extracellularly deposited lipids, cholesterol crystals These components are found in different proportions and configurations for different lesions. Most often the surface of plaques in the aorta ateromatoznite visible fibrous layer ("top") composed of smooth muscle cells and relatively dense collagen. Below it is the necrotic core of plaque, etc.. etc. athera, containing lipids, cholesterol and cholesterol esters, detritus from dead cells and foam cells. In the periphery of the lesion is an area of neovascularisation, proliferation of small blood vessels. In advanced atherosclerotic plaques are found in calcifications. On histological preparation of the aorta is seen splitting cadovata wall between intimate and media blanks and optical processing of soluble holesterinovite crystals and
24
25
lipids.
27. Atheromatosis aortae (Sudan III). Suspended lipids in the aortic wall was demonstrated to freezing kriostatni cuts on non-fixed formalin material. In the artery wall are displayed orange-drops and crystals in place of suspended cholesterol and cholesterol esters.
25
26
28. Thrombus mixtus . Thrombosis is the process of prizhizneno clotting of blood formation in the lumen of the vessels and cavities of the heart stoppers composed of elements of blood. On histological preparation is seen transversely cut vascular wall and anchor the thrombus located in the lumen her very clear ivitsestiyat construction of thrombi due to delay stratification of blood is so elementi.Vizhdat lines of Zahn. Adjacent to the vessel wall are pale pink colored uniform tables drebnozarnista structure containing razpadnati platelets. Between platelet layers are deposited segmented leukocytes, whose nuclei are stained blue by hemalauna. Erythrocytes are distributed unevenly in different parts of mixed thrombus and stained by eozina in reddish color. In addition to blood cells in the mixed thrombus contains fibrin and deposited in the form of fine threads between cellular elements stained with hemalaun eozin they are clearly seen among erythrocyte masa.Fibrinat can easily be proved if the product is colored by Weigert, demonstrate is a sinkavovioletov color.
Free Wall
29. Thrombus organisatus canalisatus. A favorable outcome of vascular thrombosis, organization and sanitation of thrombotic mass. From the vascular wall starts sprouting of young mesenchymal cells and newly formed capillaries with endothelial juicy. Along with the organization in thrombus occurring processes of decay and destruction of its components: the lysis of leucocyte nuclei, hemolysis of erythrocytes, homogenization and dissolution of fibrin fibers. In thrombus forming slits in which the periphery enter mesenchymal cells and capillaries. He became
26
27
multicellular, richly vascularised young granulation tissue which matures later, with the growth of collagen fibers. Part of obliterating the capillaries, the other extended. The functional load leads to thickening of capillary walls and endoteliziranite slits, resulting in vascular walls are formed with smooth muscle and elastic fibers, ie be designed structurally and functionally complete vessels that restore blood flow interrupted.
27
28
31. Infarctus haemorrhagicus pulmonis.
Hemorrhagic infarction is necrosis, which develops in organs with dual blood supply in terms of blood zastoy.Takav example is hemorrhagic infarction of the lung. It is an illustration of necrosis of the lung occurring as a result of embolism of thrombi in the branches of the pulmonary artery, originating mostly from the veins of the leg or pelvic venous plexuses. Histologically visible necrotic cavity with walls filled with erythrocytes, and kravonapalneni broken capillaries. Besides interstitial alveoli is also covered by the hemorrhage. The center of the infarct structure of the alveoli may completely disappear, to talk about what occurred difinitivno nekroza.Otkrivat are blood vessels with thrombi in the lumen im.V border areas of infarction and preserved lung tissue alveoli are filled with erythrocytes, desquamation epithelial cells and siderofagi showing previous chronic venous, stasis, and swollen technost.Ako heart attack at the periphery of the lung pleural reaction occurs with deposition of inflammatory infiltrate rich in fibrin.Razviva fireplace is fibrinous pleurisy.
28
29
32. Cyanosis hepatis. Venous hyperaemia or cyanosis hepatis is a brief stagnation of blood in the venous system of the liver. Etiological factors involved in the development of congestive plethora may be presented raznoobrazni.V case preparation for circulatory disturbances of cardiac origin, which occurs due to stagnation of blood in the liver, initially in v.hepatica, and later in still smaller branches, including in vv. centrales The central veins are dilated in delchetata and kravonapalneni.Poradi expiry of blood elements still making material for histological examination some central veins remain completely free, but highlighted changes in form and goleminat of lumens. Venous stasis leading to urinary erythrocytes and in adjacent capillary wedge, pushing against the liver cells and cause moderate atrophic changes in tyah.Drugi morphological changes in liver parenchyma are not, which means that the process is stagnant at the beginning of its development and has a short duration .
29
30
33. Hepar muschatum. In progressive right heart weakness due to prolonged venous stasis in the central veins of liver delcheta occurs centrilobular dystrophy and atrophy of hepatocytes. These changes are due to developing hypoxia. Relatively preserved only hepatocytes around portal prostranstva.Makroskopski picture resembles the cut surface of moskatovo nutmeg, hence the name. Dark red congestive areas change with areas of dystrophic yellow hepatocytes loaded with lipids. In continuation of chronic venous stasis congestive centrilobular zones Dead zones merge with the neighboring delcheta and form stagnant paths connecting the two adjacent central veni.Poluchava be so Muscat liver, reverse type, where the center of zones of preserved hepatocytes is portal space / not the central vein / surrounded by dystrophic and atrophic hepatocytes with congestive landscaped walkways between them.
E.g: congestive paths
30
31
34. Oedema pulmonis. Lung edema may be cardiogenic or not cardiogenic. Cardiogenic occurs in acute left heart failure. not cardiogenic observed in shock, leading to the development of respiratory distress sindrom.Firstly swelling occurs in the alveolar walls, which expand, interstitial edema develops after excessive accumulation of fluid in interstitial lung began filling the alveoli with fluid Picture intraalveolaren edema. Histologically shows homogeneous and pink colored eozina of matter, filling alveoli, alveolar moves bronchi and bronchioles. Between alveolar spacers appear thickened. In the accompanying prolonged chronic venous stasis are thickened fibrosing alveolar walls, the presence of siderofagi in them and in the alveoli, dilated capillaries and fully blood.
31
32
41. Haemorrhagiae punctatae cerebri. Pinpoint hemorrhages in the brain occur with damage to small blood vessels due to a number of infectious-toxic effects, trauma, tumors and dr.Makroskopski they are represented by scattered dark red spotting polentsa in white brain matter, which disappears when wipe im.Te result most of diapedezni bleeding in increased permeability of vascular wall. On histological preparations appear yellowish or tan circular or elliptical groups of erythrocytes outside the vessels in the vicinity or in the form of sleeves around them. Detected data is swelling around the cells and vessels and nekrobiotichni dystrophic changes in the surrounding neurons and glial elements ..
32
33
42.Pneumonia loblaris. It is for acute focal inflammation of the lung, engaging in varying degrees delcheta individual or groups of delcheta due mostly to bacterial infection. On histological preparations appear larger or smaller groups of alveoli filled to varying degrees with serous exudate mixed with neutrophil leukocytes, macrophages, erythrocytes, alveolar epithelial desquamation and some fibrin. Among the inflammatory foci are no alveoli or little quantity of exudate. From the pathological process are affected bronchi and bronchioles located in pneumonic outbreak. Their lumen is full of mucus material containing cell desquamation and neutrophil leukocytes.
43. Pneumonia crouposa. (Croupy - fibrinous, lobar pneumonia). It is about an acute infectious disease with a picture of fibrinous inflammation which occurs in four stages and covers fully one or more parts of the lungs. Inflammatory process begins with the stage of active hyperemia expansion and engorgement of the vessels in the interstitial and alveolar capillary wedge and release scarce and interstitial fluid in the alveoli (first stage). In the second stage becomes fibrinous exudates rich in red blood cells resulting in macroscopic lung parenchyma is compacted, there is red and resembles liver. This is the stage of red hepatizatsiya. Fibrin strands pass through the pores of Cohn and histologically shows that all the respiratory bronchioles, alveoli and alveolar moves are made from delicate fibrin network coloring in pale pink color. In reaction to Weigert it violetoovosinkav colors in color. In the third stage, which was presented to the preparation, the number of leukocytes in the alveolar exudate increases znachitelno.Osven among leukocytes and exudate are macrophages. The color of the affected lobe becomes macroscopic off-white
33
34
(gray hepatizatsiya stage). Interstitial is extended to kravonapalneni vessels infiltrated by neutrophil leukocytes. In Weigert stain shows how fibrin fibers pass through the pores of Cohn from one socket to another, and cell nuclei dyed in cherveno.Pri favorable outcome exudates completely absorbed, and this is the fourth stage of the process if it becomes affected areas of the parenchyma organize and fibrosing.
34
35
44. Pericarditis fibrinosa. It is a fibrinous inflammation affecting mainly epicardium and subepikardnata takan.Sreshta fat is common in end-stage chronic renal failure / uremia / Trauma, inflammation in the myocardium and others. On histological preparations shows that the epicardium is covered with different thick layer of fibrin exudation, colored by eozina in pale pink. In the deeper part of the layer and are neutrophil leukocytes in moderate amounts. Underlying adipose tissue with dilated vessels and kravonapalneni, infiltration of leukocytes and macrophages, mainly located perivazalno.
35
36
46. Pleuritis fibrinosa. Fibrinous pleurisy is the most reactive - a place corresponding to a subject a pathological process in the lung parenhim.Lokalizira is a visceral and parietal pleura it affects only the surface layer of cells without passing border membrane. Histological deposition occurs mainly serofibrinozen exudate on serosal moderate absolute neutrophil counts when it comes to inflammation in the neighborhood. Fibrinous pleurisy can be sterile - with hemorrhagic infarction in the lung, the relevant pleural cover accumulated fibrin. Under favorable conditions exudates can be absorbed, but more often to organize and form adhesions between the visceral and parietal pleura.
36
37
47.Leptomeningitis purulenta. In abscess meninges are infiltrated by diffuse large amount of neutrophil leukocytes accumulated mainly around the dilated vessels and kravonapalneni. Nuclei of leukocytes or hipersegmentirani or are at different stages of dystrophic-necrotic changes. In the underlying gray matter vessels are dilated and kravonapalneni with the presence of a significant amount of round cells and leukocytes around single tyah.Nalitse is swelling around the cells and vessels.
37
38
48. Nephritis purulenta (abscedens). Purulent inflammation of the kidneys may develop infection hematogenously arrived by road or ascending urinary mehur.Hematogennite abscesses are scattered evenly in kidney cortex and astsenedntnite may be single larger one of the poles of the body into sections corresponding to the damaged cups of the basin.Histologically in the renal parenchyma, mainly in the cortex are different sizes outbreaks in which the bulk was destroyed and accumulated neutrophil leukocytes, residues razpadnati cells and structureless necrotic material. Renal structures in the periphery of the abscess are infiltrated by neutrophil leukocytes, which fill many lumens and kanalcheta.Nalitse are dystrophic changes in cells of proximal convoluted tubule, which are eosinophilic granular cytoplasm and the boundaries between them are not well visible.
38
39
49. Abscessus cerebri . The most characteristic pathological changes in brain abscess are: destruction of brain tissue and forming a cavity with purulent exudate accumulation in it of segmented leukocytes. In the process of development in the wall of the abscess formed three layers .. The inner layer, etc. "pyogenic membrane" necrotic tissue is infiltrated with neutrophil leucocytes. Around it are clustered macrophages, plasma cells, lymphocytes and young capillaries. Most macrophages were foamy, cytoplasm mesh resulting from routine paraffin processing of brain tissue, where they fagiranite lipids ekstrahirat.Yadrata they are eccentric. These macrophages loaded with lipids by razpadnatoto brain substance called lipofagi psevdoksantomni or cells that give macroscopic yellow color of the second layer of wall abstsesa.Kogato to become chronic abscess is encapsulated and is distinct from brain tissue with a wall of mature connective tissue containing collagen fibroblesti, fibrocytes and blood vessels, representing a third outer layer of abscess wall.
39
40
50. Granulatio. By the term to mean granulatsio young granulation tissue that develops in various processes in regenerators organizma.Formiraneto of granulation tissue is an expression of chronic inflammation nespetsifichchno, as seen in wound healing and in various toksoinfektsiozni effects .. This process is characterized by: 1 / growth of young connective tissue rich in cells and 2 / neoplasms of capillary wedge. Cellular elements in tissue novorazrastvalata differentiate well in large increases in mikroskopa.Ot haraktertni them most are the young connective tissue cells called fibroblasti.Tova are large cells with highly elongated spindle formats bright oval or slightly drained yadra.Drugi cells found in tissue are neutrophil and eosinophilic leukocytes with characteristic segmentation of nuclei, lymphocytes almost naked hiperhromni nuclei or scant cytoplasm, plasma cells with eccentric nuclei available in which the chromatin is arranged in the form of spokes of a wheel epiteloidni cells - oval, slightly drained, bright blister nuclei poor in chromatin and macrophages - large cells with abundant cytoplasm and oval or kidney yadro.Mogat to meet and giant cells most often a "foreign body" with many randomly located nuclei in the cytoplasm. Ssred this cellular composition seen many young capillary wedge, giving macroscopic granular appearance of newly formed tissue, and hence its name - are upholstered granulatsio.Kapilarite juicy endothelial whose nuclei are marked indentation whose penetration in education im.This construction is inherent in newly formed blood vessels young characterizing granulation tissue ..
40
41
51.Granuloma typus corporis alieni. With the entry of foreign objects into the body or outside in the formation of unusual for normal body bodies in his / due to a variety of inflammatory / tissue immediately surrounding the foreign body granulation tissue develops, which means the name granuloma type "foreign body" The process is a productive inflammation in the body seeks to limit and defuse it become trapped foreign bodies. Most often these are sutures, paraffin, silicone, gauze, cellulose materials, oil solutions, bone sekvestri, parasites, and other metal particles. Around them proliferate young granulation tissue containing capillaries, fibroblasts fibrocytes, lymphocytes, plasma cells, lymphocytes and segmented most characteristic for this tissue type giant cells "foreign body". They are multi-core, their cores are almost identical and are located in the cell pole opposite the foreign body. The cells congregate around the foreign body, surrounding it, and sometimes when it is small enough it "swallow." In cases where foreign bodies can be removed through absorption, then located around granulation tissue gradually matures and becomes a mature fibrous takan.Po thus foreign body remains difinitivno included encapsulated in tsikatrisialna formed tissue.
Giant Multinucleated cells a "foreign body"
41
42
52.Cicatrices myocardii / / Scarring in the myocardium are areas of mature connective tissue, which develops due to hypoxia or myocardial infarction. This tissue is rich in cell elementi.Sastoi mainly of fibrocytes, fibroblasts and a small number of blood vessels, surrounded by collagen fibers. When staining hemalaun eozin scar turns pale pink. Peripheral myofibres atrophic or hypertrophied.
42
43
53. Cicatrices myocardii (V.G.) With Van Gieson staining scar tissue turns rozovocherveno because it is rich in collagen and muscle tissue environment - in yellow
43
44
54. Cirrhosis hepatis (HE). Liver cirrhosis is the end stage of many pathological processes in the liver. Characteristics: 1.razrastvane of scar tissue at the site of the destroyed hepatocytes, which also distorts the structure and circulation in the body. Histologically observed fibrotic septa connecting two adjacent portal areas, two neighboring central veins or portal areas with neighboring central vein surrounding so different sized islands of relatively preserved hepatocytes. This leads to 2.Razrushavane normal architectonics of the liver and formation etc. psevdodelcheta 3.Kraglokletachna infiltration of lymphocytes and plasma cells in portal areas and fibrous septa. 4.Proliferatsiya of bile ducts in fibrous septa. 5.Distrofichni changes in hepatocytes in the form of vakuolerna or fatty degeneration and necrosis of the same. 6.Regeneratorni processes in hepatocytes, which are larger, lighter cytoplasm, larger and darker colored form yadra.Te regenerators nodes are visible macroscopically on the surface of Liver drob.Imat different sizes depending type of cirrhosis-mikronodularna nodes with a diameter of 3 mm. and makronodularna significantly larger / more than 3 mm. /
44
45
55.Cirrhsis hepatis (V.G.) In this preparation is used histochemical staining Van Gieson, which proves the presence of collagen in connective tissue grew surrounding the newly formed psevdodelcheta.Toy colors are red and the remaining liver tissue - the yellowish color.
45
46
56. Tuberculosis miliaris pulmonis. Miliary is a chronic granulomatous tubelkuloza, specific inflammation. Histologically among lung parenchyma seen many tubercles with typical construction. In the center of the granuloma is homogeneous, structureless, pinkcolored zone of eozina kazeozna necrosis around it are arranged next to one another palisading (such as boards of a fence), drained epiteloidni cells, which include light cytoplasm and round, low-chromatin core . Among them are giant multi-type cells "Langhans", which together with epiteloidnite cells specific for tuberculous granuloma. Their cytoplasm is abundant, but their cores are round or oval, situated on the periphery of the cell in the form of a horseshoe with the opening to the central necrosis. Most peripherally around epiteloidnite cells located shaft T-lymphocytes. Another specific characteristic of tubers is the lack of blood vessels and plasma cells in it, unlike syphilis granuloma.
Tuberculo
46
47
57. Leptomeningitis tuberculosa. Mycobacterium tuberculosis most often causes chronic meningitis or meningoencephalitis. Inflammation of the meninges are usually localized at the base of the brain on hiazmata, bridge pins and Silvievite cerebral sulci. The most significant finding is the presence of foci of necrosis kazeozna in which the structure of the meninges is completely removed and is surrounded by epiteloidni cells, giant cell type "Langhans" and lymphocytes. Formed typical tuberkuli.V underlying gray matter to rub swelling, bleeding and scant lymphocytic infiltration around blood vessels.
Tuberculosa
47
48
58.Mesoaortitis luetica. Is one of the serious complications of syphilis in its third stage. It is a chronic inflammatory process involving primarily the media of the aorta, which expressed no specific character. Histologically characterized by: 1. / Vascularity of mediyata.Normalno expressed in the media of the aorta vessels do. 2. / Perivascular infiltrates in the media kraglokletachni and adventitsiyata of lymphocytes and plasma cells 3. / Proliferation of vessels in intimate adventitsiyata to complete occlusion of their lumen (endarteriitis obliterans), which alone has a specific character. The development of pathological changes in the media accompanied by destruction of elastic fibers and increase of fibrous tissue that forms small fields of vascular fibrosis stena.Mozhe to form and aneurysm, most often in the ascending aorta.
48
49
59. Morbus Hodgkin Hodgkin's disease has four forms: nodular sclerosis, mixed tselularitet, lymphocyte predominance and lymphocyte depletion. Typical cells are pathognomonic for the diagnosis of cells Reed-Sternberg. They are large cells with multi-core diameter 15-45 micrometers in prominirashti nucleons and abundant lightly eosinophilic cytoplasm. Especially characteristic are the dual cells with mirror images of nuclei containing acidophilic nucleons surrounded by clear zone. In nodular sclerosis razraztvaneto of connective tissue gives nodular type tumor takan.Pri it most often found, etc. lakunarni cells, which are considered a special variant of the cells in Reed - Sternberg. They are large single lobulirani nuclei and abundant pale cytoplasm. The combined tselularitet which is the most common form of the disease is heterogeneous infiltrate of lymphocytes, plasma cells and eosinophils are found histiotsiti.Trudno cells of classic Reed Sternberg. They are so lymphocytic variant - with a gentle lobulirani nuclei, resembling popcorn / popcorn cells .The diagnosis of Hodgkin's disease is based on the finding of Reed Sternberg cells or their variants among heterogeneous cellular composition of inflammatory lymphocytes, plasma cells, eosinophils and histiocytes epiteloidni.
49
50
60. Myoarditis rheumatica. It is a chronic inflammation specifically, in developing cyclic interstitial infarction near blood vessels and subendotelno. In the early phase was observed histologically mucoid edema and swelling of the interstitial tissue in the myocardium and its impregnation with acidic mucopolysaccharides. They are basophilic in staining hemalaun eozin and give metahromaziya tuloidinovo with blue. Later came fibrinoidno swelling of collagen fibers and the main substance formed zone fibrinoidna necrosis. In it Van Gieson stain ceases to be positive for kolagen.Okolo necrotic foci are found predominantly neutrophil leukocytes, scattered lymphocytes, plasma cells and histiocytes. In the second phase of the process demonstrated on histological preparation, the specific form of rheumatism granuloma of Aschoff-Talalaev. It is presented with central necrosis located around it and ordered Anichkov cells having abundant slightly basophilic cytoplasm. . Their nuclei are large, in longitudinal section shows the central location of their chromatin (bar wavy appendages, like a caterpillar) and in cross-section similar to the "eye of the owl." The second type of cells are specific granuloma of giant cells Ashoff, which have abundant cytoplasm and centrally located 1 to 4 cores. Around them are lymphocytes, plasma cells and rare neutrophil leukocytes. In the third phase cells gradually disappear and be replaced by granulomas mature connective scar takan.Obrazuva is a fusiform shape.
50
51
61. Hyperplasia mucosae uteri glandularis cystica It is a hormonally driven process to an imbalance between estrogen and progesterone - continuous prevalence of estrogen in relative or absolute reduction . factors are menopause, prolonged administration of estrogenic drugs, estrogen - producing tumors and polycystic ovarian syndrome, the same. These conditions can lead to endometrial hyperplasia zhlezi.Te grow in proliferative phase are different in size, some are cystic dilated .. upholstered them cylindrical epithelial cells with nuclei hiperhromni located close to each other. Hyperplasia of the glands is accompanied by hyperplasia and endometrial stromal cells, which are also compressed. Among Hyperplastic structures can sometimes be seen swollen pink colored liquid or kravoizlivi.Hiperplaziyata may be atypical or complex, where the glands are closely back to back and they are epithelial multilayer with signs of atipizam.Bazalnite membranes of the glands are preserved, unlike glandular endometrial cancer, in which they razrushavat.Tova condition is precancerous and may lead to the development of endometrial cancer, usually occurring in older age.
51
52
62.Hypertrophia glandulae prostatae. Prostatic hypertrophy is the result of a hormonal deficiency - loss of gonadal function in mazhete.Protsesat develops gradually over years after the age of 50 and 70 year olds were observed in 90% of mazhete.Kasae to diffuse enlargement zhlezata.Histologichno characterized by hyperplasia of the glandular and stromal structures. The process is represented by the proliferation of glands located close to each other, but with preserved basal membrani.Zhlezite are larger, upholstered with two rows of cells - the same basal cylindrical and cubic mioepitelni cells that showed no signs of atypia. Some of the glands were dilated with cystic vatrezhlezna proliferation of tubular epithelial cells, having basal located yadra.Hipertrofiyata may be glandular proliferation only in glandular structures and adenomiomatozna when expanding and smooth muscle fibers of stromal gland.
52
53
63.Struma colloides. It is about increasing the size of the thyroid gland, resulting in expansion and enlargement of the follicles with abundant colloid accumulation in them. When colloidal accumulate in large quantities, it depresses follicular epithelial cells of cubic and they become flat. Process is referred as histological accommodation. / adaptation to changed conditions / Histologically observed sizes of follicles, sometimes forming large cysts from the merger of several follicles, filled with pink eozina of homogeneous koloid.V depending on the size of folikulitei goitre is referred to as micro or makrofolikularna .
53
54
64. Fibroma cutis. Benign tumor of mature connective tissue composed of fibroblasts, fibrocytes and collagen fibers, consist mostly subcutaneous. Histologically characterized by the appearance of spindle cells and collagen bundles of fibers crossing each other in different directions. In longitudinally cut bundles of nuclei of the cells are elongated with sharp edges in the cross - they are round. Between the cells are deposited collagen fibers which are stained a pale eozin with cellular components of the tumor. When the tumor is dominated by collagen fiber texture is denser and is called a hard fibroma (fibroma durum), where the predominant cellular component is soft and is called soft fibroma (fibroma molle). If it shows scant stroma, carrying blood vessels and merging in separate sections of the tumor parenchyma.
54
55
68 Lipoma Wen is a benign tumor of mature adipose tissue and is the most common tumor of soft tissue in vazrastni.Histologichno is well encapsulated, contains delcheta surrounded by soft connective tissue network, which carries blood vessels and form a stromal tumor. Bulk of the tumor consists of lipotsiti large cells containing in their cytoplasm different in size fat droplets which after routine paraffin processing appear optically empty. As a result of accumulation of fatty droplets lipotsitite nuclei are pushed to the periphery of the cells.
55
56
69 Leiomyoma (HE). Benign tumor of smooth muscle., Which can develop anywhere there is smooth muscle, but is - in honor of her matkata.V it is often multiple and the diagnosis was uterus myomatosus. Bulk of the tumor consists of bundles of different thickness smooth muscle cells, which are intertwined in different directions. Cytoplasm of muscle cells are stained more intensely red than eozina compared with cells of the connective tissue that forms the capsule and stromal tumor. Because vortical arrangement of smooth muscle bundles, cell nuclei in histological preparations were cut in different planes, so we have a round, oval or rod shape with cut corners, unlike fusiform nuclei of the fibrocytes.
56
57
70 Leiomyoma (V.G.) When staining hemalaun-eozin, muscle cells and the stromal collagen fibers are stained a pale pink. Histological finding in fibroid and Leiomyoma is relatively uniform and sometimes difficult to differentiate between both tumors. To differentiate between fibroid Leiomyoma of using histochemical staining Van Gieson, in which collagen is colored in red and muscle cells - in yellow.
57
58
71 Chondroma. Hondromat a benign tumor of hyaline hrushtyal.Kogato develops in the bone canal enhondroma, if the surface - is referred to as ekhondroma Outside tumor was covered with perichondrium, from which connective tissue strands start separating tumor delcheta and shaping tumor stroma. Bulk of the tumor consists of various size cartilage cells (chondrocytes), which are scattered in groups included 2-3 cells per capsule, located unevenly colored matrix.
58
59
72 Hemangioma cavernosum hepatis. Hemangiomas are common benign tumors characterized by the growth of normal and abnormal vessels filled with blood. Most common are cavernous and capillary wedge hemangiom.Kavernozniyat haemangioma, which was presented to the preparation, an interconnected voids surrounded by thin bands of connective tissue, upholstered in endothelial cells. Cavities are among the liver tissue in the form of poorly demarcated from the liver parenchyma cavernous bodies, filled with krav.Can be seen intravascular thrombosis and calcification.
59
60
73 . Fbrosarcoma. Fibrosarcomas a malignant tumor, composed of fibroblasti.Sreshta is in adults in the deep tissues of the hip, knee and . with hipertselularitet - tightly packed, spindle cells with polymorphism, which are arranged like a fish bone is heringa.Chesto found atypical mitozi.Tumorat a positive expression of vimentin. Stromal is underdeveloped and is represented mainly by collagen fibers. Metastasize through blood.
60
61
74 .Leiomyosarcoma. Leiomyosarcoma is a malignant tumor of smooth muscle tissue, representing 10% -20% of soft tissue tumors sarkomi.Povecheto of this type originate from the uterine muscle or the gastrointestinal tract .. may be encountered in women with localization in the deep soft tissues of the extremities and retroperitoneum . Histologically its cells are characterized by marked cellular atypia and form tufts, intertwined in different directions. Stromal relatively less represented by mature fibrous tissue. Tumor parenchyma is stained yellow by the method of Van Gieson, and in stromal rozovocherven tsvyat.Osven obiknoveniyag vretenovidnokletachen leyomoosarkomat type can be epiteloiden and pleomorphic tip.Pri last polymorphism is also characteristic of high mitotic activity.
61
62
75. Sarcoma osteogenes. Osteogenic sarcoma is the most common primary malignant tumor of bone. It occurs in all age groups, but 75% of cases are in young people under 20 godini.Razviva in long bones and affects men more often. The bulk are usually composed of large polygonal, sometimes oval or spindly cells with pronounced atypia, giant cells and numerous atypical mitozi.Produktsiyata of mineralized or non-mineralized bone / osteoid / form of primitive bone gredichki is the hallmark of tumora.Dopalnitelna finding in osteosarcoma can be vascular proliferation, the presence of cartilage matrix and fields of fibrous connective tissue. According to the prevalence of some of these elements are defined and some types of . and staining with antibody against vimentin gives chervenokafenikava reaction in the cytoplasm of tumor expression of vimentin kletki.Pozitivnata is characteristic of many types of sarcomas..
osteoid
76. Fibroadenoma glandulae .ammae.
62
63
Fibroadenoma is the most common benign tumor of gardata.Schita that its development is related to increased activity of estrogen. Usually occurs in young zheni.Toy well encapsulated with a diameter of 1 to 10 cm Bulk of it consists of two tissue components: 1.adenomatozna component representing tumor growth of canals and 2. scar - fibrous tissue derived from the gland. When scar tissue grows around the canals, it is a fibroadenoma perikanalikularen. If the connective component enters and pushes almost complete obliteration glandular ducts talk about intrakanalikularna form. Stromal oskadno.V case presents two types of fibrous tissue, one element of the parenchyma of the tumor is located immediately around glandular structures, - a poor collagen and colors sinkavorozovo while stromal tumor is a mature connective tissue, rich collagen and intense red color of eozina.Taka shows that the tumor parenchyma contained in their epithelial and mesenchymal / fibrotic /Component.
77. Cystadenoma papilliferum ovarii.
63
64
Serous tumors are the most common ovarian neoplasms constitute 20% to 60% of all ovarian tumors .. Sixty percent of them are benign, 15% have low malignant potential - with borderline malignancy and 25% are malignant. Benign serous tumors may be endophytic and tsistadenomi ekzofitni / surface papillomas / or dvete.Serozniyat tsistadenom is composed of cysts containing serous fluid light, upholstered with a single layer of cylindrical epithelium, partly with cilia, partially secreted. Without signs of atypia . epithelium resembles that of the fallopian tube, proliferate into the lumen of the cyst and formed papillary strukturi.V papillae can be seen concentric laminar cells containing calcium - etc psamomni cells, which help to differentiate between tumor of neoplasms of different origin in this oblast.Kogato the cover is a multilayer epithelium with signs of atypia without invasion of epithelial cells in stromal tumor is referred to as serous tumor of borderline malignancy / low malignant potential /. . In serous carcinoma mnogorednostta atipizmat and are even more pronounced and there is a massive invasion of the tumor stromal cells, and the surface of the ovary.
Pappilary Structures
cystic cavity
64
65
78. Adenoma leomorphe glndulae parotis (.. tumor mixtus gl. parotis). Eighty percent of neoplasms of the salivary glands are the parotid gland, 70 /% - 80% of them are honor-dobrokachestveni.Nay pleomorphic adenoma, indicated that because of his heterogennost.Izgraden is of two types of cells - epithelial ducts of the glands and mioepitelni.Te form channels, glandular epithelial structures and drags .. Parenchymal cells are cylindrical or cubic in shape, surrounded by different sized areas of mucoid substance whose quantity in some areas is quite large and the epithelial cells appear as islands among them. The type of the parent compound is different: basophilic mucus, type of cartilage is rarely a case of bone tissue. This diverse type of tumor is given ground in the past to be called mixed tumor.Dnes believe that the compound is a product of epithelial cells. "
65
66
79..Papilloma vesicae urinariae. Papilloma of the bladder is a benign tumor originating in the urothelium, occurs rarely and has dimensions of 0.2 - 1.0 cm. It is built with a tender of papillae fibrovaskularna stroma, Branching Tree. Histologically there are papillary structures are covered in multi prehodnokletachen epithelium without signs of atypia, with very little stroma, sometimes stromal blood vessels lie almost kletki.Za among parenchymal contrast papilloma prehodnokletachniyat bladder cancer is characterized by a coarse papillary structures, more mnogorednost epithelium with marked cellular atypia and invasion of tumor cells into the subepithelial fibrous tissue and muscle tissue in the wall of mehura.Otkasnati papillae in these tumors can be detected in urine of patients with concomitant hematuria and are important for setting the diagnosis.
66
67
80.Carcinoma planocellulare Squamous cell carcinoma is a malignant tumor originating in a multilayered squamous epithelium. Can be found everywhere in the body where there is such epithelium - oral cavity, esophagus, cervix, vagina and dr.i is particularly frequent in armor developed on the basis of metaplasia of filamentous cylindrical multilayered epithelium in flat, mainly in smokers. Histologically composed of nests of a multilayered squamous epithelium with typical construction, are located outside the cylindrical cells with dark nuclei, characteristic of the basal layer, followed inside the other cell layers (Spinoza, granulosa and light). Spinoza often dominated by layer, so the tumor mean as spinotselularen. All layers are marked cellular and nuclear atypia, especially spinozniyat.V center of nests, depending on the degree of differentiation in more mature tumors detected output horn / horn beads etc /. Stromal is represented by broad strands of connective tissue, among which the stroma reaction - infiltration by lymphocytes, plasma cells and lymphocytes
cancer pearls
tumor clusters
67
68
81. Carcinoma basocellulare. Basal cell carcinoma is the most common cancer in choveka.Sreshta is on skin areas exposed to sunshine and slightly pigmented individi.Toy grows slowly in the form of plaque, which razyazvyava and forms etc. ulcus rodens.Ryadko metastasize .. It originates from the basal layer of the multilayered squamous epithelium, mainly the face and exposed areas, and entering into the subcutaneous tissue. Bulk of it consists of clusters of cells similar to the basal layer of the epidermis - with scant cytoplasm and elongated, hiperhromni nuclei. Of dystrophic changes in tumor cells sometimes acquire psevdozhlezist strands form. The tumor may be multifocal growth - the type of surface or grows in depth, forming a knot structures among the connective tissue or mucinous matriks.V connective tissue stroma appears stroma reaction by lymphocytes and plasma cells.
68
69
82.Adenocarcinoma ventriculi. Midst of malignant tumors of the stomach adenocarcinoma is the most common and most - important / 90-95% / .. It originates from the gland epithelium of gastric mucosa and classified according to the depth of invasion, macroscopic type and histological podtip.Tumorat two histological forms - intestinal variant, which is typical gastric adenocarcinoma, composed of atypical glands located next to each other with broken basement membrane, forming strands and gland resembling Bowel cancer The second is the diffuse type in which tumor cells infiltrating the mucosa and deeper layers of the wall stomach. Cells resemble stone ring with the inside wall of the ring and contain sluz.Poslednata is dakazva with PAS reaction and staining with altsianovo blue according to the nature of mukopolizapharidite located in sluzta.Tazi form called linitis plastica and is characterized by diffuse thickening of the without the formation of gastric tumor in its lumen.
69
70
83.Adenocarcinoma uteri. The most common form of endometrial cancer is endometroidniyat type of adenocarcinoma, one of the most commonly occurring malignant tumors in the female reproductive sistema.Sreshta are mostly between the ages of 55 and 65 godini.Razvitieto it is associated with increased estrogen stimulation and is often based on atypical endometrial hiperplaziya.Tumorat may be infiltrative or predominantly ekzofiten rastezh.Toy infiltrates myometrium and gives metastases in lymph regionarnite vazli.Histologichno is represented by glandular structures lying back to back, forming epithelial strands with damaged basal membrane between them with cells arranged in multiple rows with marked atypia. . In some glands and papillary growths observed in the lumen of the glands im.Atipizmat is expressed in varying degrees, depending on the degree of differentiation of the tumor, it can be: high, moderate or low differentiated.
70
71
84.Adenocarcinima gelatinosum(HE) View slide 17, where the described the same tumor.
85. Invasive ductal breast cancer with dezmoplastichna stromal reaction (skirozen cancer etc.). It is a carcinoma with abundant stroma, predominantly from the parenchyma. The bulk is presented as individually arranged or small groups of cells, solid nests, tubular structures and others.
tumor nests
71
72
86. Medullary breast cancer - carcinoma with scant stroma. The structure of this cancer is completely opposite to the structure of skirozniya cancer. Medullary carcinoma with abundant parenchyma, composed of cells with basophilic cytoplasm and vesicular nuclei with oval or polygonal shape. Tumor parenchyma is nest building, sometimes the cells are arranged in strands (syncytial growth). Is extremely scarce stromal vessels and it can not supply the necessary nutrients to all cells, resulting in often visible necrosis and hemorrhage.
Tumor outbreaks of syncytial type
72
73
89. Glioblastoma multiforme Glial brain tumors are subdivided into astrocytomas, ependymoma and oligodendrotgliomi. Astrocytoma subtypes are different, but most common are fibrilerniyat / 80% / pilotsitniyat tip.Spored and degree of differentiation fibrilerniyat astrocytoma is divided into astrocytoma, anaplastic astrocytoma and glioblastoma multiforme. Glioblastoma multiforme is the lowest diferentsiran.Toy spongioblastite comes from representing the earliest phase of the glia. Histologically there are cells with a strong cellular and nuclear atypia. Are characteristic giant cells with single nuclei and ugly large number atypical mitoses in tumor .. there are many blood vessels with endothelial cells and areas of hemorrhage and necrosis. There are areas with palisading arrangement of tumor cells ..
73
74
90.Astrocytoma. The tumor is derived from mature astrocytes. Histologically composed of large cells with pale cytoplasm, with fewer fibrils in protoplazmatichniya type astrocytes or more gliofibrili - in fibrous astrocytoma .. The cells resemble one another and have a little nuclear polymorphism. Growths of cells in the form of delicate fibrils show a positive immunohistochemical reaction for glial acidic protein fibrileren / GFAP /. Fibrils form a fine network around the blood vessels. Rarely seen dystrophic-necrotic changes in tumor tissue and eventually forming cysts.
74
75
91. Neurinoma (schvanoma). Nevrinomat is a benign tumor that develops from Schwann sheaths nervite.Toy is common in the cranial cavity and comes from the eighth craniocerebral nerve. Histologically consists of elongated cells arranged in strands, intertwined in various posoki.Razlichavat are two subtypes of the tumor - Antoni A type that meet the so-called Lewy Verokay in which cells with elongated cytoplasmic their spines are arranged in bundles around area in which only appendages without nuclei. Rodlike nuclei of the cells are arranged parallel to each other, like soldiers on parade, forming a blue colored hemalaun eozin bands around the area free of nuclei. In Antoni type B cells lacking a Verokay, the cells are arranged in loose, show miksoidni changes and can form a positive mikrokisti.Tumorat immunohistochemical reaction for S - 100 protein. Stromal often contain dilated blood vessels. Has been shown between nevrinoma cells can form collagen fibers
75
76
92.Meningioma. Tumors of the meninges / meningioma / are benign neoplasms and occur in adults they come from meningotelnite arahnoideyata cells and are usually secured to durata.Podrazdelyat on the following / in the presence of PAS positive droplets in cells / s mikrokistichen. presented syncytial tumor type and is composed of oval and spindle cells. which are arranged concentrically as bulbs, separated by connective tissue stroma. Sometimes in these cell layers occurs hialinizatsiya or deposition of calcium and form etc. psamomni teltsa.Kogato dominated psamomnite tumor cells is defined as psamomatozen option.
Psamomni cells
76
77
93.Melanoma malignum. Malignant melanoma is a pigmented malignant tumor that timely diagnosis can be treated with wide surgical incisions. The main histological types of malignant melanoma are superficial spreading melanoma, melanoma lumpy, akralno lentigiozen melanoma and lentigo maligna melanoma.Tumorat contains two types of parenchymal cells: 1) cells with extremely epitelopodobni polymorphism arranged in clusters like cancer and 2) spindle cells forming fascicles, with some diffuse structure similar to sarkoma.Kletkite usually have large nuclei with irregular contour and contained chromatin at the nuclear periphery membrana.Harakterni eosinophilic their nucleons are described as "cherry red". tumor may have horizontal or vertical growth, which determines its shape. melanin content also shows great diversity, it may be lacking in so-called achromatic melanoma. The depth of vertical growth determines the biological behavior of melanoma.Spored classification of Clark - when the tumor is confined to the epidermis is level I, leaching into the surface of the papillary layer II level of the entry of tumor cells in the superficial vascular plexus III is - it level with invasion into the reticular layer of dermis - IV level. V-th level is when the tumor has entered into the subcutaneous tissue. Forecast and the possibility of metastatic tumor is determined by the depth of invasion in millimeters for vertical growth of the tumor from the granular layer of the epidermis proper. /
77
78
94. Choriocarcinoma / chorionepithelio / Horiokartsinomat highly aggressive malignant tumor growing from the trophoblastic elements platsentata.Makroskopski is represented by multiple hemorrhagic masses filling the uterine kuhina.Kletachnite components include horiokartsinoma sintsitiotrofoblasti, tsitotrofoblasti and intermediate / intermediate / trophoblastic . Multinucleated cells are finally differentiated and show no mitotic aktivnost.Te are pathognomonic for tumora.Tsitoplazmata their thick and stained intensely eosinophilic bazofilno.Chesto to contain many vacuoles of advanced tanks endoplazmatichniya reticulum. Tsitotrofoblastnite cells are small to moderate sized single-cells with scant pale to bright granular . trophoblastic cells have characteristics of both. They are large, polygonal with one or more nuclei and abundant cytoplasm that is dense eosinophilic, without vacuoles. The chorionic villi are not a component of horiokartsinoma, except in rare cases where it comes from a normally developing placenta.
78
79
95. Carcinoma Renis ( hypernephroma). Renal cell carcinoma originates from the seminiferous epithelium and is localized mainly in korata.Toy represents 80% to 85% of all primary malignant tumors of the kidney and 2% to 3% of all malignant neoplasms in adults. It occurs most frequently in the sixth - seventh decade and is twice as frequent in mazhete.Svetlokletachniyat carcinoma is the most common type and is 70% to 80% of all kidney cancers. The bulk is made up of cells with pale granular cytoplasm rich in glycogen and lipids, which give a yellowish color macroscopic tumor there, because his likeness with adrenal gland and its previous name hypernephroma. Nuclei of light cells are small, round and hiperhromni, mostly located in the center of kletkite.Granuliranite cells resemble the seminiferous epithelium have small round nuclei and granular cytoplasm pink. The tumor has nest building, there are also atsinarni structures surrounded by thin bands of connective tissue and thin-walled blood vessels, which are due to hemorrhage and necrotic areas.
79
80
96.Seminoma testis. Seminoma represents 50% of all testicular tumors and germinativnokletachni occurs in men 40 years vazrast.Makroskopski zhaltenikavorozova lobulirana tumor mass with necrosis and hemorrhage. It is a malignant tumor growing from the seminiferous epithelium. Histologically seen large cells with pale eosinophilic cytoplasm and centrally located round nucleus with one or two . stroma is represented by bands sprouting in the tumor parenchyma and dividing irregular strands and nests .. A characteristic feature of seminoma is the presence of lymphoid infiltrates in stromal that can form lymph follicles and germinativnokletachni tsentrove.Mozhe occur granulomatous reaction epiteloidni cells and giant cells type "Langhans." Most seminoma contain glycogen in parenchymal cells and give your PAS positive reaction.
80
81
97.Carcinoma hepatocellulare. Hepatocellular cancer predsavlyava 5.4% of all malignant tumors in humans as the frequency varies in different parts of sveta.Razvitieto is related largely to infection by hepatitis B and hepatitis C viruses. Macroscopically, the tumor has three forms: can be a single node , multifocal or diffuse growing. In well differentiated forms its cells reproduce and form a liver gredichki zhlezistopodobni strukturi.Te are large, polygonal with acidophilic cytoplasm and large hiperhromni yadra.V them can be found zhaltozelenikav bile pigment. In low differentiated cancer cells are large, multi .. Stromal tumor is scarce and is represented only by sinusoidal vessels. Histology of hepatocellular carcinoma is quite diverse and, depending on cell arrangement the following types: - Trabecular where atypical hepatocytes are arranged as trabeculae and gredichki with different orientations. - Atsinozen (psevdoglandularen) with formation of kanalikuli zhlezistopodobni or structures whose lumen can sometimes be found bile. - Clear-option when tumor cells are rich in glycogen and lipids.
81
82
98. Myelosis hepatis. Preparation demonstrated extramedullary hematopoiesis in the liver in chronic mielolevkoza. Histologically sinusoidal in highly advanced izpulneni with myeloid cell line, which are at different stages of maturity (blasts). The accumulation of immature white blood cells is most pronounced in sinusoidal central parts of delchetata. In severe exacerbation of leukemia (blast crisis) proliferation of immature elements are observed in portal spaces.
82
83
99.Lymphadenosis hepatis. Preparation illustrates the morphological substrate of chronic hepatic limfolevkoza drob.Patologichniyat process develops in portal spaces and consists primarily perivazalna proliferation of lymphocytes and fewer lymphoblasts. Lymphocyte proliferation is lumpy in nature and locates perivazalno. During prolonged treatment of patients with cytostatics may occur growths of connective tissue collagen and development of cirrhosis.
83
84
100. Mastopathia chronica fibrosa cystica. Fibrokistichnata breast disease is hormonally driven process resulting in hiperestrogenemiya. Violation occurs in the ratio between connective and epithelial components of breast cancer. The process refers to mamarnata dysplasia. It consists in marked expansion of periduktalnata perilobularnata and connective tissue that is coupled with hyperplasia of ductal and lobular epithelium and formation of single or multiple cysts. Lining the cysts is upholstered single-breasted or double-breasted cube, often epithelial cells have acidophilic cytoplasm, similar to the epithelium of sweat glands - case for hidroadenoidna / apocrine / epithelial metaplasia. There are sections vatrekistichni papillary growths of epithelial / ductal papilomatoza /. The contents of the cysts is a homogeneous pink-colored fabric with eozina. Sometimes, there is atypical lobular hyperplasia, which resembles the cytological carcinoma in situ, but the cells do not fill more than 50% in atsinite lobula.Tazi hyperplasia is a risk of developing in situ or invasive carcinoma. Another element of fibrokistichnata disease can be sclerotic adenoza.Tya is characterized by proliferation of roofing and mioepitelni epithelial cells in small ducts located back to back with significant stromal fibrosis, which forces them. Overgrowth of scar tissue pressing on atsinite lumens and channels and they look as solid strands of cells. Differential diagnosis of invasive carcinoma is difficult. Immunohistochemical demonstration of intact smooth muscle cells mioepitelni actone in favor of the diagnosis sclerosing adenosis.
Fibrose
Adenose
101. Actinomycosis. Actinomycosis is a chronic purulent inflammation caused by fungi aktinomitseti.Glavniyat cause of human actinomycosis eu is Actinomyces Israeli. Actinomycosis has four forms according to its localization tservikofatsialna, thoracic, abdominal and tazova.Histologichno it is characterized by the formation of abscesses which appear aktinomitsetni Druze surrounded by a large number of segmented leukocytes and macrophages loaded with lipids of phagocytosed dead cell is elementi.Harakterno finding of granules with a diameter of 1 micrometer in exudate, and aggregates of filaments of the fungus with a diameter of 30 to 3000 micrometers in diametar.Aktinomitsetnite Druze give a positive PAS-
84
85
reaction.
actinomycosis druse
102.Adenoma villosum recti. Adenomas of the colon are three basic forms, tubular, and vilozen tubulovilozen.Te occur most often in rektosgmoidnata oblast.Vilozniyat adenoma may reach larger sizes. - Up to 10 cm in diametar.Toy looks like a cauliflower growths with one to three centimeters above ligavitsata.Papilarnite structures are often covered by single-breasted or multilayer cylindrical epithelium with mild to moderate and severe dysplasia. In 40% of the lesions can be found invasive carcinoma.
85
86
103. Carcinoma papillare gl. hyreoideae Thyroid cancer has four main histological types: papillary carcinoma / 75% -85% of cases / follicular carcinoma / 10% to 20% /, medullary carcinoma / 5% / and anaplastic carcinoma / less than 5%. . papillary cancer may be solitary or multifocal type. Macroscopically can be encapsulated or have invasive growth to surrounding tissues. Histological type is characteristic of the nuclei of cells constituting the tumor. Their chromatin is finely dispersed and they look optically transparent "ground glass" papillary structures are present, although some tumors are largely composed of follicles. These follicular variants biologically related as papillary tumors if they have previously described nuclei in vid.V papillary structures can be seen concentric laminar calcified structures, denoted as psamomni cells..
104./Hronichen lymphocytic Hashimoto's thyroiditis Hashimoto's Hashimoto e autoimmune disease characterized by progressive reduction of epithelial cells tireoideyata which gradually replaced by mononuclear cell infiltration and fibroza.Toy is the most common cause of hypothyroidism in parts of the world where there is no shortage of yod.Makroskopski gland is diffusely and symmetrically enlarged with sivkavorozova surface at srez.Histologichno picture is represented by abundant mononuclear inflammatory infiltration of small lymphocytes, plasma cells and lymphoid germinal formed tsenvtrove folikuli.Tireoidnite lymph follicles are atrophic and are often seen covered in cells with abundant eosinophilic granular cytoplasm, denoted as oksifilni cells or Hurthle. ultrastructure of these cells are rich in mitochondria. Less gland is reduced in size, compact and fibrosing /
86
87
atrophic variant of Hashimoto
87
88
105 .Metastases carcinomatosae lymphonodi. Malignant tumors of epithelial origin metastasize initially lymph channels in the lymph regionernite vazli.Metastatichniyat process begins first in the peripheral sinuses of the node that is gradually filled with tumor kletki.Po later formed last pockets are separated from each other lymphoid cells. aggression leads to tumor filling the entire lymph node with tumor nests by the cancer, with germination in the capsule of the node and even perinodalnata tissue.
88
89
107. Liposarcoma. Liposarcoma is a malignant tumor originating from adipose takan.Toy is one of the most common sarcomas in adults in the fourth - fifth decade, rarely occurring in detsa.Obiknoveno develops in deep soft tissues of the extremities and abdomen / retroperitoneal /. Histologically there are following types of tumor: welldifferentiated, miksoiden, kraglokletachen pleomorfen.Tumorat and usually consists of lipotsiti lipoblasti and which mesh with cytoplasm and centrally located place yadro.Na of fat extracted in the cytoplasm are vacuoles. Grease prove to freezing kriostatni cut stained with Sudan III and dyed in oranzhevozhalt tsvyat.Tumornite cells are expressed in varying degrees polimorfizam.Posledniyat becomes particularly demonstrative in pleomorphic type tumora.Stromata usually scarce - fibrous strands of blood vessels but it can be quite pronounced and the case is described as fibrosing liposarcoma
89
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Pathology Slides 1Document28 pagesPathology Slides 1SydPas encore d'évaluation
- Patho4-6 - Liver (Dr. Dy)Document13 pagesPatho4-6 - Liver (Dr. Dy)miguel cuevas100% (1)
- Hematologic Pathology p65-87Document23 pagesHematologic Pathology p65-87zeroun24100% (1)
- Microscopic Slides Pathology-2Document135 pagesMicroscopic Slides Pathology-2Justin JannatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathology StudyGuide 2011 KAAUDocument83 pagesPathology StudyGuide 2011 KAAUKamila Anna Jakubowicz100% (1)
- L6-PATHO-Neoplasia (Sept2821)Document12 pagesL6-PATHO-Neoplasia (Sept2821)Erald PaderangaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 11 Blood Vessels 8th Ed NotesDocument7 pagesChapter 11 Blood Vessels 8th Ed NotesKyle Christopher SiaPas encore d'évaluation
- General Pathology PDFDocument201 pagesGeneral Pathology PDFAbdirahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Neoplasia I - RecordingDocument6 pagesNeoplasia I - RecordingIS99057Pas encore d'évaluation
- WBC Pathology: Lecturer: Associate Professor T. A. GrekovaDocument49 pagesWBC Pathology: Lecturer: Associate Professor T. A. GrekovaFaheem MusthafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gastrointestinal PathologyDocument14 pagesGastrointestinal PathologyRahul ShuklaPas encore d'évaluation
- Patho A 1. 5 Hemodynamic Disorders (Bongat, 2015)Document12 pagesPatho A 1. 5 Hemodynamic Disorders (Bongat, 2015)Grant GarcesPas encore d'évaluation
- I. Cellular Adaptations:: Cellular Injury, Cell Adaptation & Cell Death 1. Hyperplasia 3. AtrophyDocument4 pagesI. Cellular Adaptations:: Cellular Injury, Cell Adaptation & Cell Death 1. Hyperplasia 3. AtrophyShuaib SiddiquiPas encore d'évaluation
- 120-Nr-M.D. Degree Examination - June, 2008-Pathology-Paper-IDocument16 pages120-Nr-M.D. Degree Examination - June, 2008-Pathology-Paper-IdubaisrinivasuluPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 10 - Diseases of Infancy and ChildhoodDocument17 pagesChapter 10 - Diseases of Infancy and ChildhoodAgnieszka WisniewskaPas encore d'évaluation
- Endocrine Pathology p17-32Document16 pagesEndocrine Pathology p17-32zeroun24Pas encore d'évaluation
- Neoplasia MG Vs Bg2010Document122 pagesNeoplasia MG Vs Bg2010bilinda_butcherPas encore d'évaluation
- Cellular Injury, Adaptation and Cell DeathDocument8 pagesCellular Injury, Adaptation and Cell DeathJessica Febrina Wuisan100% (1)
- Hemodynamic Disorders, Thromboembolic Disease, and ShockDocument87 pagesHemodynamic Disorders, Thromboembolic Disease, and Shockgifty100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - The Cell As A Unit of Health and DiseaseDocument14 pagesChapter 1 - The Cell As A Unit of Health and DiseaseMon Dominguez100% (2)
- Top 100 Pathology Secrets List W/ NotesDocument6 pagesTop 100 Pathology Secrets List W/ NotesPA2014100% (4)
- General Pathology 1Document39 pagesGeneral Pathology 1Muheto100% (2)
- 2021 Systemic Pathology S4T1 - RBC and Bleeding Disorders PDFDocument27 pages2021 Systemic Pathology S4T1 - RBC and Bleeding Disorders PDFAlexis Bondad100% (1)
- MBBS PBL Problems Yr 1-4Document79 pagesMBBS PBL Problems Yr 1-4Keithtra HepburnPas encore d'évaluation
- 200 Points in Special PathologyDocument15 pages200 Points in Special Pathologyjihadeqitaal100% (1)
- Robbin's SummariesDocument98 pagesRobbin's SummariesnopedontsuemepleasePas encore d'évaluation
- Pathology 3Document33 pagesPathology 3Lorenzo FrancisPas encore d'évaluation
- Robbins Questions Chp1-10Document28 pagesRobbins Questions Chp1-10verbatimmt100% (1)
- Chapter 13 Neoplastic Proliferations of White CellsDocument16 pagesChapter 13 Neoplastic Proliferations of White CellsOmar100% (1)
- 14 Patho Head and Neck PathologyDocument10 pages14 Patho Head and Neck PathologyMartin TanPas encore d'évaluation
- Gallbladder and Pancrease PathologyDocument4 pagesGallbladder and Pancrease Pathologyjohn smithPas encore d'évaluation
- Robbins Ch. 20 The Kidney Review QuestionsDocument10 pagesRobbins Ch. 20 The Kidney Review QuestionsPA2014100% (4)
- Mbbs PBL BibleDocument76 pagesMbbs PBL Biblejoshy2211960% (1)
- Pathology A - The Cell As A Unit of Health and DiseaseDocument13 pagesPathology A - The Cell As A Unit of Health and DiseaseYui VainPas encore d'évaluation
- 18 Lymphoma - Libre PathologyDocument13 pages18 Lymphoma - Libre PathologyfadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch.1 Baby Robbins OutlineDocument11 pagesCh.1 Baby Robbins OutlinePA2014100% (3)
- Renal - PathologyDocument38 pagesRenal - Pathologyjmosser3102100% (2)
- Divergent Differentiation, Creating So-Called Mixed Tumors: Seminoma Are Used For Malignant Neoplasms. TheseDocument6 pagesDivergent Differentiation, Creating So-Called Mixed Tumors: Seminoma Are Used For Malignant Neoplasms. TheseSherwin Kenneth Madayag100% (1)
- GI PathologyDocument22 pagesGI Pathologyzeroun24100% (5)
- CNS PathologyDocument10 pagesCNS Pathologysarguss1483% (6)
- CH 7 Genetic and Pediatric Diseases (P. 243-272, Nature of Genetic Abnormalities Contributing To Human DiseaseDocument16 pagesCH 7 Genetic and Pediatric Diseases (P. 243-272, Nature of Genetic Abnormalities Contributing To Human DiseaseJustine HungPas encore d'évaluation
- DR Nilukshi Perera Consultant HaematologistDocument68 pagesDR Nilukshi Perera Consultant HaematologistThaveeshaLindsayWhitePas encore d'évaluation
- Case Scenarios University DR - NerveDocument24 pagesCase Scenarios University DR - NerveSREE NITHINPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Injury RobbinsDocument44 pagesCell Injury RobbinsAnastasia DosiPas encore d'évaluation
- Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease, 9th Ed (2015) Notes 1Document6 pagesRobbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease, 9th Ed (2015) Notes 1Joan Timbol0% (2)
- Robbins Chapter 1 DiagramsDocument18 pagesRobbins Chapter 1 DiagramsYoja GarzonPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Injury & AdaptationDocument22 pagesCell Injury & AdaptationUmam LoyalPas encore d'évaluation
- Grossing Templates (S)Document51 pagesGrossing Templates (S)Jack GuccionePas encore d'évaluation
- Pulmonary PathologyDocument6 pagesPulmonary PathologyjamesjaanPas encore d'évaluation
- Robbin's Chapter 20 Kidney PathologyDocument4 pagesRobbin's Chapter 20 Kidney Pathologynbaumgartner0100% (1)
- Robbins Ch. 18 Liver and Biliary Tract Review QuestionsDocument12 pagesRobbins Ch. 18 Liver and Biliary Tract Review QuestionsPA2014Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pathology QuestionsDocument67 pagesPathology QuestionsRedentor MagdayaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathology of The Lung: C.Murtono Demo Pada Blok Respirasi FkuajDocument54 pagesPathology of The Lung: C.Murtono Demo Pada Blok Respirasi Fkuajsetiawan_sukmadjayacPas encore d'évaluation
- Lung PathologyDocument101 pagesLung Pathologyhm3398Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Injury, Death, and Adaptation: DefinitonsDocument37 pagesCell Injury, Death, and Adaptation: Definitonsyasobaby100% (1)
- OSPE 4th Yr PathoDocument144 pagesOSPE 4th Yr PathoMuhammadShahzadPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathology Solved Papers 2015Document35 pagesPathology Solved Papers 2015Lakshmi Venkataraman100% (3)
- Master Plan Patho!Document94 pagesMaster Plan Patho!chiarastanziola01Pas encore d'évaluation
- Demographics of RussiaDocument19 pagesDemographics of RussiaFırat GüllüPas encore d'évaluation
- Part III Internal Medicine Examination AnswersDocument91 pagesPart III Internal Medicine Examination AnswersFırat GüllüPas encore d'évaluation
- Demographics of Finland: SourceDocument18 pagesDemographics of Finland: SourceFırat GüllüPas encore d'évaluation
- Part II Internal Medicine Examination AnswersDocument16 pagesPart II Internal Medicine Examination AnswersFırat Güllü100% (2)
- Internal MedicineDocument5 pagesInternal MedicineFırat GüllüPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology Examination AnswersDocument205 pagesPathophysiology Examination AnswersFırat Güllü67% (6)
- Internal Medicine SynopsisDocument6 pagesInternal Medicine SynopsisFırat GüllüPas encore d'évaluation
- 27.surgical OsteomylitisDocument2 pages27.surgical OsteomylitisFırat GüllüPas encore d'évaluation
- 26.surgical Inflammation. (Skeletal and Muscular Tenosynovitis)Document2 pages26.surgical Inflammation. (Skeletal and Muscular Tenosynovitis)Fırat GüllüPas encore d'évaluation
- Surgical Infection and Inflammation: 4. SepsisDocument3 pagesSurgical Infection and Inflammation: 4. SepsisFırat GüllüPas encore d'évaluation
- Patofisiologi StrokeDocument14 pagesPatofisiologi Strokenatalia alexandraPas encore d'évaluation
- Carotid ArteryDocument5 pagesCarotid ArteryAsif AyazPas encore d'évaluation
- Sudden DeathDocument26 pagesSudden DeathAbang AzharPas encore d'évaluation
- Hipertension ArticuloDocument8 pagesHipertension ArticuloAngie CalderónPas encore d'évaluation
- Abstract Book INAACCDocument83 pagesAbstract Book INAACCrodtobingPas encore d'évaluation
- Disfunctional Vascular Endothelium As A Driver of Atherosclerosis - Emergind Insights Into Pathogenesis and Treatment 2021Document18 pagesDisfunctional Vascular Endothelium As A Driver of Atherosclerosis - Emergind Insights Into Pathogenesis and Treatment 2021Camila VidigalPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of MI, COPD and BPHDocument10 pagesPathophysiology of MI, COPD and BPHSarah Lim100% (1)
- HEARTDocument11 pagesHEART1NC21IS038 POLATHALA MOUNIKAPas encore d'évaluation
- January 2011 MS - Unit 1 Edexcel Biology A-LevelDocument24 pagesJanuary 2011 MS - Unit 1 Edexcel Biology A-LevelAyse KerimPas encore d'évaluation
- Imaging Thoracic Aortic AneurysmDocument11 pagesImaging Thoracic Aortic AneurysmHector Hernandez-SoriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Atherosclerosis and ThrombosisDocument6 pagesAtherosclerosis and Thrombosisstudy with mainePas encore d'évaluation
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument17 pagesMyocardial InfarctionJoshua ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- General Pathology NotesDocument29 pagesGeneral Pathology NotesMohd Syaiful Mohd ArisPas encore d'évaluation
- LocholDocument6 pagesLocholKashif FarooquiPas encore d'évaluation
- Bulacan State UniversityDocument19 pagesBulacan State UniversityIana Khrys GodoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology-II NIRALIDocument244 pagesPharmacology-II NIRALIRock Patel93% (29)
- 17 - OET Online Test 4Document20 pages17 - OET Online Test 4Abdullah Mohammad Ibne Haider100% (1)
- cILOSTAZOL 2Document10 pagescILOSTAZOL 2Muslih KerenPas encore d'évaluation
- Handbook of Indexing Techniques A Guide For Beginn... - (Chapter 3 Writing The Index)Document16 pagesHandbook of Indexing Techniques A Guide For Beginn... - (Chapter 3 Writing The Index)joseph jaalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis A Review: Imedpub JournalsDocument6 pagesPathogenesis of Atherosclerosis A Review: Imedpub JournalsHaydee RocaPas encore d'évaluation
- ARTERISCLEROSISDocument46 pagesARTERISCLEROSISAdilla Edi AriefPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiac Rehab BookletDocument32 pagesCardiac Rehab BookletAbu Bakr Siddique100% (1)
- CT BR SureSubtraction CT DSADocument11 pagesCT BR SureSubtraction CT DSAWALVRadiologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Coronary Calcium ScoreDocument49 pagesCoronary Calcium ScoreBinod KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Matthew J. Budoff, Jerold S. Shinbane (Eds.) - Cardiac CT Imaging - Diagnosis of Cardiovascular Disease (2016, Springer International Publishing)Document565 pagesMatthew J. Budoff, Jerold S. Shinbane (Eds.) - Cardiac CT Imaging - Diagnosis of Cardiovascular Disease (2016, Springer International Publishing)Dr Sebastian GraciasPas encore d'évaluation
- Tnok 71712Document199 pagesTnok 71712hola123456789jgPas encore d'évaluation
- TO USE ESVS 35th Annual Meeting Programme Detailed Update 30.07 6Document44 pagesTO USE ESVS 35th Annual Meeting Programme Detailed Update 30.07 6Alexandru PredenciucPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiovascular Disorders: Coronary AtherosclerosisDocument6 pagesCardiovascular Disorders: Coronary AtherosclerosisHazel BandayPas encore d'évaluation
- CVD Q's & A'sDocument9 pagesCVD Q's & A'sAlan TaylorPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Limb IschemiaDocument18 pagesAcute Limb Ischemiakarl abiaadPas encore d'évaluation