Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Machine
Transféré par
ashu099Description originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Machine
Transféré par
ashu099Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Explain the V curves of synchronous motors.
What types of motor would you employ for the following types of loads? State reasons for your choice: (i) Hoist (ii) Rolling mill (iii) Textile mill (iv) Refrigeration and Air-conditioning Briefly enumerate the different types of starters used for induction motors. A d.c. shunt motor, whose armature resistance is 0.5 ohm, is to be starred by a controller which keeps the armature current between the limits of 60 A and 80 A, the supply voltage being 400 V. Calculate the number and values of the resistance steps. Prove the theory of the method of calculation you employ. 15 Explain, with the help of neat sketches, how interpoles improve commutation in a d.c. machine. How are the interpole windings connected in (i) d.c. motors, (ii) d.c. generator? Explain why asynchronous motor does not start by itself. Using synchronous-impedance method, determine the voltage regulation of a 2000-volt single-phase alternator supplying a load current of 100 A at rated voltage and a power factor of (i) unity, (ii) 0.8 leading, and (iii) 0.707 lagging. The test results available are as follows: The full- load current of 100 A is produced on short-circuit by a field excitation of 2.5 A, an e.m.f of 500 V is produced on open circuit by the same excitation, and the armature resistance is 0.8 ohm. Describe briefly the construction of (i) woundrotor, (ii) deep-bar and (iii) double-cage type induction motors and explain how in each case a high starting torque is obtained Using double-revolving-field theory, develop an equivalent circuit for single-phase induction motor. Explain Techniques adopted for braking of d.c. motors Hunting phenomenon in synchronous machines. Purpose and action of a delta-connected tertiary winding in Y-Y connected transformers A 400-V. 3-phase, 50-Hz 6-pole Y-connected induction motor, when running light at normal voltage and frequency takes power input of 1.2 kW and the line current is 8.25 A. With the rotor locked and 180 V applied to the stator, the power input is 5.25 kW and the line current is 45 A. The stator resistance measured between two line terminals when hot is 0.9 . Draw the approximate equivalent circuit of the motor and calculate the net mechanical power output and torque when working at a slip of 4%. Distinguish the torque-speed characteristics of induction motors meant for (i) continuous running under full-load and (ii) a.c. servomotor Indicate, in each case, the design criteria and the means adopted for achieving the desired performance.
Derive the expression for the synchronizing power of a synchronous generator with a cylindrical rotor when connected to an infinite bus-bars. Discuss the effect of an excitation failure. What is understood by synchronous condenser? Explain its operation and application Explain how a salient pole machine can develop torque without field excitation Explain what is meant by Synchronous Impedance of an alternator. Find the synchronous impedance and reactance of a single- phase alternator in which a given field current produces an armature current of 250 amperes on short-circuit and a generated e.m.f. of 1500 volts on open circuit. The armature resistance is 2 ohms. Hence calculate the terminal p.d. when a load of 250 amperes at 6.6 kV and lagging power factor 0.8 is switched off. A 3-phase alternator having a reactance of 10 ohms has art armature current of 220 amperes at unity power factor when running on 11 kV constant frequency bus-bars. If the steam admission be unchanged and the e.m.f. raised by 25% determine graphically or otherwise the new value of machine current and power factor Discuss the relative merits and disadvantages of single cage and double cage induction motors. If the standstill impedance of the outer cage of a double cage machine is 0.3 + j 0.4 ohm and of the inner cage is 0.1 + j 1.5 ohms, compare the relative currents and torques of the two cages (i) at standstill; (ii) at a slip of 5%. An induction motor with a star-delta starter is supplied through a feeder from V volts, 50 Hz mains. Coming to line drop, the starling current is found to be the same with star as well as delta connections. From a short-circuit test on the motor, when delta connected, the following data were obtained; V = 200 V; I = 125 A; power factor = 0.4 (line values). Determine the resistance of the feeder. If a second feeder of the same cross-section be rim in parallel with the original feeder, find the percentage increase in the starting torque obtained with each connection What is on load tap changing facility in a power transformer? What is its application in power system control? Two identical synchronous machines of rating 100 MW, 50 Hz operating in parallel have the following characteristics: Machine 1 : Speed droop R = 4% Speed changer set to give 50% rated load at rated speed. Machine 2 : Speed drop R = 4% Speed changer set to give 75% rated load at rated speed. (i) Determine the load taken by each machine for a total load of 150 MW and the frequency of operation. (ii) What adjustment should be made by the speed changers of the machines to share the load as in (i) but with a frequency of 50Hz? With proper circuit diagram, explain the working of shaded pole single phase induction Motor
Describe the star-delta method of starting a three-phase induction motor A 100 HP induction motor is coupled to an industrial drive whose torque varies directly as the square of the speed. An e.m.f. of 100 V per phase is induced in the rotor winding of the induction motor at standstill. The full-load slip of the induction motor is 5 per cent. Calculate the resistance to be added in the rotor circuit to reduce the speed by 20 per cent. Neglect the mechanical losses and rotor reactance The maximum efficiency of a 100 kVA single phase transformer is 98 per cent and occurs at 80 per cent full load at 0.8 p.f. If the leakage impedance of the transformer is 5 per cent, find the voltage regulation at rated load at 0.75 p.f. lagging A synchronous motor is receiving 30 per cent of the power that is capable of receiving from an infinite bus. If the load on it is doubled, calculate the maximum value of the rotor angle during swinging of the motor around its new equilibrium position. Explain the speed-current torque-current and speed-torque characteristics of DC series motor A three phase star connected synchronous generator is rated at 1.5 MVA, 11 KV. The armature effective resistance and synchronous reactance are 1.2ohm and 25 ohms respectively per phase. Calculate the percentage voltage regulation for a load of 1.4375 MVA at (i) 0.8 p.f. lagging and (ii) 0.8 p.f. leading. Also find out the p.f. at which the regulation becomes zero In the case of three phase induction motor derive the ratio of maximum torque to full load torque as Tm / TF1 = (2+sFL2)/SFL where = y2/x2
With necessary circuit diagram briefly describe Sumpners test. Explain how the test results are useful in determining equivalent circuit and efficiency of the transformer The following two synchronous machines arc operating in parallel. Machine A 50 MW 6% speed regulation Machine B 50 MW 3% speed regulation (i) Determine the load taken by each machine for a total load of 80 MW when the speed changers are set to give rated speed at 100% rated output. (ii) The speed changers of machine A is so adjusted that 80 MW is equally shard. Find the output of machine A for rated speed and also its percentage speed at no load. A 220 V D.C. shunt motor takes 22 A at rated voltage and runs at 1000 rpm. Its field resistance is 100 and armature circuit resistance is 0.1 . Compute the value of additional resistance required in the armature circuit to reduce the speed to 800 rpm when (i) the load torque is proportional to speed (ii) the load torque varies as the square of the speed Two identical D.C. machines when tested by Hopkinson method gave following test results: Field currents are 2.5 A and 2 A. Line voltage is 220 V. Line current including both the field currents is 10 A. Motor armature current is 73 A. The armature resistance of each machine is 0.05 . Calculate the efficiency of both the machines
Explain the working of a transformer at no load and loaded conditions. A 10 KVA, 440 V, 50 Hz, 3 phase alternator has the following O.C.C. Field current 1.5 3.0 5.0 8.0 11.0 (Amp) Terminal voltage (vol) 150 300 440 550 600
15.0 635
With full load zero p1 load applied, an excitation of 14 A produced a terminal voltage of 500 V. On short circuit, 4A excitation was required to circulate full load current. Using MMF method determine the full load percentage regulation for 0.8 p.f. lagging and 0.8 p.f. leading When a three phase supply is given to a three phase winding a rotating magnetic field of constant amplitude will be produced. Justify the above statement Explain how the parameters of 3 phase induction motor can be obtained from the test results Explain the speed-current, torque-current and speed- torque characteristics of DC shunt Motor A 3.5 MVA, slow-speed, 3phase synchronous generator rated at 6.6 kV has 32 poles. Its direct and quadrature axis synchronous reactances as measured by the slip test are 9.6 and 6 respectively. Neglecting armature resistance determine the regulation and the excitation emf needed to maintain 6.6 kV at the terminals when supplying a load of 2.5 MW a 0.8 pf lagging. What maximum power can the generator supply at the rated terminal voltage, if the filed becomes open-circuited?
A 3-phase induction motor has a starting torque of 100% and a maximum torque of 200% of the full-load torque. Find slip at maximum torque. Describe a series (universal) motor. Give its cross-sectional view when connected to ac supply. Describe its performance characteristics
A squirrel-cage induction motor has a slip of 4% at full load. Its starting current is five times the full-load current. The stator impedance and magnetising current may be neglected; the rotor resistance is assumed constant. (i) Calculate the maximum torque and the slip at which it would occur. (ii) Calculate the starting torque. Express torques in pu of the full-load torque.
What do you understand by a synchronous condenser? Explain with the help of phasor diagrams its operation and application. The emf per turn of a 1-phase 2200/220 V, 50 Hz transformer is approximately 12 V. Calculate (i) the number of primary and secondary turns, and (ii) the net cross-sectional area of core for a maximum flux density of 1.5 T.
Find the resistance of the load which takes a power of 5 kW from a dc shunt generator whose external characteristic is given by the equation V = 250 0.5 IL . Briefly describe the phenomenon of hunting in a synchronous machine. How is it remedied?
A single phase transformer has percentage regulation of 4 and 4.4 for lagging power factor of 0.8 and 0.6 respectively. The full load copper loss is equal to iron loss. Calculate (i) The lagging power factor at which full load regulation is maximum. (ii) The full lead efficiency at unity power factor.
Why are the compensating winding and the Interpole winding used in a universal motor for ac operation? Draw the schematic connection diagram of all the stator windings and the armature or an ac-operated series (universal) motor. Derive the torque equation of a dc machine The following test results were obtained on a 7.5 kW, 400 V, 4 pole, 50 Hz, delta-connected induction motor with a stator resistance of 2.1 /phase. No load 400 V, 5.5 A, 410 W Rotor blocked 140 V, 20 A, 1550 W Obtain the approximate equivalent circuit model. Also estimate the breaking torque developed when the motor running with a slip of 0.05. has two of its terminal suddenly interchanged. What is meant by similar polarity ends of the two windings of a single phase transformer ? How are these ends identified?
A is 15 kVA, 2300/230 V, 50 Hz single phase transformer gave the following test data: Open Circuit Test V0 = 2300 V, I0 = 0.21 A, W0 = 50 W Short Circuit Test VS = 47 V, IS = 6.0 A, WS =160 W (i) Find the equivalent circuit referred to high voltage side. (ii) Calculate the full load voltage regulation at 0.8 pf lagging when the load voltage is held at 220 volts. (iii) What is the efficiency at half the rated load at unity of ? (iv) Find the maximum efficiency and corresponding output power.
State reasons of using tertiary windings in a transformer. Explain with the help of suitable diagrams, how rotating magnetic field is produced in a 3phase induction motor. A 25 hp, 400 V, 50 Hz four pole star connected induction motor has the following impedances per phase in ohms referred to the stator side: RS = 0.641, Rr = 0.332
XS = 1.106, Xr = 0.464 and Xmag = 26.30 Rotational losses are assumed constant and are 1.1 kw and core losses are assumed negligible. If the slip is 2.2% at rated voltage and frequency, find: (i) speed (ii) Stator current (iii) Power factor (iv) Output and input power (v) Efficiency of the motor Show that the starting torque of a single phase induction motor is zero. Sketch and explain the Open Circuit and Short Circuit characteristics of a synchronous machine. Two synchronous generators are supplying a common load. Generator 1 has a no load frequency of 51.5 Hz and regulation of 1 MW/Hz. The total load is 2.5 MW at 0.8 pf lagging. (i) At what frequency, are the generators supplying this load and how much power is supplied by each generator? (ii) An additional load of 1 MW is attached to this system. What will be the new frequency and power generation of each alternator? (iii) How much is the governor set-point of generator 2 to be adjusted to bring the system frequency at 50 HZ for 3.5 MW system load? Compare the speed-current characteristics of various types of D.C. motors. Describe Sumpners (back to back) test used for transformer. Indicate its advantages. A 1-phase, 30 KVA, 2300/230 V. 50 Hz transformer gave the following results on tests: Leakage impedance in the high voltage (HV) winding = 0.55 + j 0.65 . Leakage impedance in the low voltage (LV) winding = 0.0055 + j 0.0065 . Shunt branch admittance as seen from LV side = (0.003 j 0.02) . (i) Draw the equivalent circuits of the transformer referred to HV and LV sides. (ii) The transformer is connected to 2200 volts at the sending end and delivers rated current at 0.8 p.f. lagging to a load of 0.3 + j2 on the LV side. Draw the phasor diagram and hence or otherwise determine the voltage at the load end and the efficiency of the transformer. Assume core lossed to be 160 W and ignore voltage drops due to exciting current. Describe with the help of a neat sketch and phasor diagrams a system through which a 2phase supply can be obtained from a 3-phase system. Explain the Torque-Slip characteristics of a 3-phase induction motor. Starting with the expression for torque as a function of slip. Show that the value of maximum torque is independent of rotor resistance. A 3-phase, 400 V, 50 Hz star connected induction motor gave the following test results: No load : 400 V, 7.5 A, 0.135 power factor Blocked rotor : 150 V, 35 A, 0.44 power factor The ratio of standstill leakage reactances of stator and rotor is estimated as 2. If the motor is running at a speed of 960 rmp, determine
(i) the net mechanical power output (ii) the net torque (iii) slip and (iv) efficiency of motor Assume stator and rotor copper lossed to be equal. What is the need of starters for induction motors? Briefly describe various techniques used for the starting of 3-phase induction motors. What is meant by infinite bus bars? State the conditions required to be satisfied for connecting a synchronous generator to an infinite bus bar. Explain how the instant of synchronizing can be determined. A generator has synchronous reactance of 1.7241 p.u. and is connected to a very large system. The terminal voltage of the generator is 1/2 00 p.u. and the generator is supplying to the system a current of 0.8 p.u. at 0.9 p.f. lagging. Neglecting resistance. Calculate: (i) internal voltage (ii) active and reactive power output of the generator (iii) the power angle and reactive power output of the generator if the excitation of the generator is increased by 20% keeping active power constant. A 5 KW, 230 V, shunt motor has an armature resistance of 0.5 and a field resistance of
230 . At no load the motor runs at a speed of 1000 rpm and draws a current of 3 A. At full load and rated voltage, the current drawn in 23 A and the armature reaction causes a drop of 2% in the flux. Determine: (i) full load speed (ii) full load torque
SECTION A
1. (a) With necessary circuit diagrams explain the open-circuit test and short circuit test conducted on single. Phase transformer. Justify that the copper loss in the open-circuit test condition and the iron loss in the short circuit test condition are normally neglected 12 (b) A 500 kVA single phase transformer with 0.012 p.u. resistance and 0.06 p.u. reactance, is connected in parallel with a 250 kVA single phase transformer with 0.014 p.u. resistance and 0.045 p.u. reactance to share a load of 600 kVA at 0.8 power factor logging. Find the 2VA and power factor shared by each transformer. 12 (c) A 220 V d.c. shunt motor takes 20A at rated voltage and runs at 1000 rpm. Its field circuit resistance is 100 and armature circuit resistance is 0.1 . Compute the value of additional resistance required in the armature circuit to reduce the speed to 800 rpm when (i) the load torque is proportional to speed (ii) the load torque varies as the square of the speed. 16 2. (a) What are the conditions to he satisfied for a d.c. shunt generator to built up? Explain the process of building up of emf in a d.c. shunt generator. 10 (b) A 10 kVA, 440 V, 50 Hz. three phase alternator has the following OCC:Field current (amp.) Terminal voltage (Volts) 1.0 100 3.0 300
5.0 440 8.0 550 11.0 600 15.0 635 With full load zero power factor load applied, an excitation of 14 A produced a terminal voltage of 500 V On short circuit, 4 A excitation was required to circulate the full load current. Using MME method, determine the full load percentage regulation for 0.6 p.f. lagging and 0.6 p.f. leading. 20 (b) Explain how to determine the direct and quadrature axis reactances of a salient pole synchronous machine. 10 I.E.S-(Conv.) - 1999
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
3. (a) Describe with the help of an appropriate diagram the Star-Delta method of starting a threephase induction motor. 10 (b) A 400 V 6 pole, 50Hz, three phase star connected induction motor running at rated voltage lakes 7.5 A with a power input of 700W. With the rotor blocked and 150 V applied to the stator the input current is 35 A and the power input is 5000W. The rotor and the stator copper losses are equal under the blocked rotor condition. The standstill leakage reactance of the stator and rotor as seen from the stator are estimated to be in the ratio of 1:0.5. Obtain the equivalent circuit of the induction motor. Calculate the net mechanical power output, torque, input power and the efficiently at a slip of 4%. 20 (c) Explain the operation of single phase capacitor start motor. 10 2. (a) Two d.c. generators having rectilinear external characteristics operate in parallel. One machine has the terminal voltage of 270 V on no load and 220 V at the load current of 30 A. The other has a voltage of 280 V at no load and 220 V at the load current of 30 A. Calculate the output current and the bus voltage of each machine when (i) the total load current is 50 A (ii) the load resistance of 10 ohms 16 (b) A 5 KVA, 220/110 V single phase transformer has the maximum efficiency of 96.97% at power factor logging. Its core loss is 50 W and full load regulation at 0.8 p.f. lag is 5%. Find the efficiency and regulation at 3/4 th full load, 0.9 p.f. lagging. At what p.f. at full load the regulation will be (i) maximum (ii) minimum, and (iii) zero? Calculate the maximum and minimum regulation? 16 (c) What do you understand by the term vector group of a transformer? Show the terminal connections pf a 3-phase transformer having vector groups. (i) DY11 (ii) Dd6, and the corresponding phasor diagrams 8 3. (a) Discuss about the open circuit and short circuit characteristics of a synchronous generator. Draw the phasor diagram under short circuit condition. What do you understand by the term short circuit ratio? Discuss how the short circuit ratio can be calculated from the two
characteristic curves. 12 (b) A 2000 KVA, 11 KM 3-phase star connected alternator has a resistance of 0.3 ohm and reactance of 5 ohms per phase. It delivers full load current at a p.f. of 0.8 lagging and normal rated voltage. Compute the terminal voltage for the same excitation and load current at a 0.8 p.f. leading. 10 (c) A 50 Hz, 3-phase induction motor designed for voltage V1 is switched on to 40 Hz supply of voltage V2. Find (i) the ratio of starting torques, starting currents and maxi- mum torques when V2 = 1.5 V1. (ii) the ratio of V1 to V2 to give equal values of starting torques both at 40 Hz and 50 Hz. Ignore stator impedance and neglect rotor resistance. 18 Why does the external characteristic of a d.c. shunt generator turn back as it is overloaded? (b) What are the terms air-gap powers, internal mechanical power developed and shaft power? How are these terms related with, each other? 2. (a) (i) What are the no-load rotational losses in electrical machines? How can these be determined? (ii) Which of the losses in rotating electrical machines are influenced by the magnitude of the flux the load and the square of the load? Write a general expression for all the losses occurring in rotating electrical machines and prove there from that maximum efficiency occurs when losses proportional to square of current = constant losses, 14 (b) Explain the effect of armature reaction on the main field flux by using the developed view of armature-current sheet and poles of a d.c. machine. Hence, outline the bad effects of armature reaction. Discuss how the resultant flux density waveform obtained above gets modified with the use of interpoles. 18 (c) A 2200/220 1-phase transformer has maximum possible voltage regulation of 6% and it occurs at a p.f. of 0.3, Find the toad voltage at full-load at p.f. at 0.8 lead. 8 3. (a) A star-connected alternator is synchronized with an infinite bus of 11kV; its steam input is then increased till its output power is 15 MW. Now, when its excitation e.m.f. is increased to 130%, the synchronous machine starts operating at a p.f. of 0.8 lagging. Compute the synchronous reactance of the machine. Neglect armature resistance. Determine the power factor, load angle and armature current of the machine before the excitation e.m.f. is increased. 16 (b) Explain how the desirable features of high-starting torque and low-operating slip are obtained in a double-cage polyphase induction motor A double-cage motor has standstill impedance of 1 + j 1 and 0.3 + j 5 for its two cages. Compare the relative torques of the two cages (i) at standstill and (ii) at a slip of 0.05 12 (c) Why is it advantageous to use double revolving field theory for determining the running performance of a single-phase induction motor? Draw torque - speed characteristics of a single - phase induction motor based on double - revolving field theory and discuss about the magnitude of torque at zero speed and
synchronous speed. Sketch waveform of rotor current under normal running conditions of the single-phase induction motor. 2. (a) The efficiency at unity PF of a 6600/384 V, 200 kVA single-phase transformer is 98%, both at full-load and at half full-load. The PF at no-bad is 0.2 lagging and the full-load regulation at a lagging PE of 0.8 is 4%. Draw the equivalent circuit referred to LV side and insert all values. 20 (b) A 500 V, 25 HP DC shunt motor takes a current of 2.4 A while running light. The field and armature resistances are 650 ohms and 0.57 ohm, respectively. Calculate full-load efficiency, assuming a brush drop of 2 V. 10 (c) Why is the starting current high in a DC motor? Explain the working of a four-point starter for a DC machine. 10 3. (a) A cylindrical rotor hydro-generator is feeding an active power of 0.25 p.u. into a large network bus which is held at 1.0 p.u. voltage. The generator is overexcited the an induced voltage of 1.5 p.u. The synchronous impedance of the generator and the connecting link are j 0.725 p.u./ phase and j0.11 p.u., phase respectively. Calculate the percent change in reactivepower output measured at the network bus in each of the following cases: (i) If the turbine torque is increased by 100%, keeping the excitation of the generator constant (ii) If the turbine torque is held constant at the initial value, but the excitation is increased by 20% (neglect saturation) 20 (b) Using double revolving field theory explains the working of a single-phase induction motor. 10 (c) A squirrel-cage induction motor has a starting current of six times the lull-load current at a slip of 0.04. Calculate the line current and starting torque in p.u. of full-load values for the following methods of starting (i) Direct switching (ii) Auto-transformer starting with motor current limited to2.0 p.u. (iii) Star-Delta starting 10 A 3-phase induction motor draws 1000 kVA at a p.f. of 0.8 lag. A synchronous condenser is connected in parallel to draw an additional 750 WA at a p.f. of 0.6 lead. The p.f. of the total load supplied by the mains is: (i) Unity (ii) 0.707 lead (iii) 0.6 lag (iv) zero A 3-phase synchronous motor has (i) High starting torque (ii) No starting torque (Hi) Low starting current (iv) Low starting torque 2. (a) Find the synchronous impedance and reactance of a single-phase alternator in which a given field current produces an armature current of 250 A, on short circuit and a generated e.m.f. of 1500 V on open circuit. The armature resistance is 2.0 ohms. Calculate the terminal potential
difference when a load of 250 A at 6.6 kV at a lagging p.f. of 0.8 is switched off. 15 (b) A series motor of resistance 1.0 ohm between the terminals runs at 1000 r.p.m. at 220 V with a current of 15 A. Find the speed at which it will run when connected in series with a 4.5 ohms resistance and taking a current of 10 A at the same supply voltage. Assume linear magnetization characteristic. (c) Discuss briefly the different methods used for electrical braking of d.c. motors. 10 3. (a) A 100 kVA transformer has its maximum efficiency of 98% at full load and unity p.f. During the day it is loaded as follows 12 hrs 20 kW at a p.f. of 0.5 lag 6 hrs 20 kW at a p.f. of 0.9 lag 6 hrs 20 kW at a p.f. of 0.8 lag. Calculate the all day efficiency of the transformer. 16 (b) A 1200 V, 50 Hz star connected induction motor has a star connected slipring rotor with a transformation ratio of 3.75. The rotor resistance per phase is 0.016 ohm and leakage inductance of 0.8 mH/Phase. Neglect stator impedance. Find: (i) rotor starting current per phase with slip ring short circuited, (ii) the rotor p.f. at starting, (iii) the external resistance per phase required to obtain a starting current of 125 An the stator, (iv) the rotor current of 4% slip and (v) the rotor p.f. at 4% slip. 16 (c) Discuss the relative merits and demerits of single cage and double cage induction motors. 2. (a) A transformer is connected to a 1000 V. 50 Hz supply The total core loss is 1000 W, of which 700 W are hysteresis and 300 W are eddy current loss, If the applied voltage is raised to 2000 V and the frequency to 100 Hz, find the new core loss. 15 (b) An alternator has an armature resistance of 0.3 and leakage reactance of 1.22 . The alternator supplies 100 A current to a feeder of resistance 1.512 and reactance 20 . The voltage at the far end of the feeder is 3000 V. The load current having a p.f. of 0 8 lagging with respect to this voltage. Find the terminal voltage of the alternator and the emf generated. 10 (c) A star connected squirrel-cage induction motor has following parameters and rating Rs = 2 , Rv = 3 , Xs = Xv = 3.5 . V = 400 V, 50 Hz. 1380 RPM It is driven by a voltage source inverter which gives constant V/f control to IM. If the inverter frequency is variable from 10% of rated frequency to base frequency, calculate (a) frequency for a speed of 1000 RPM and full mad torque (b) torque for a frequency of 35 Hz and speed of 950 RPM. 15 3. (a) Derive the condition for maximum efficiency of a transformer. 15 (b) A series generator of total resistance 0.5 ohm is running at 1000 RPM and delivering 5 kW at a terminal p.d. of 100 V If the speed is raised to 1500 RPM and the power is adjusted to 8 kW, find the new current and terminal voltage. Assume that the m/c is working on the straight portion of the characteristic such that the flux is proportional to the current and the emf generated is proportional to product of flux and speed
15 (c) A shunt wound motor runs at 500 RPM on a 200 V supply. Ra = 0.5 ohm, the current drawn is 30 A in addition to field current. What resistance must be placed in series with the armature in order that the speed may be reduced to 300 RPM, the current in the armature remaining same? If the load s channel so that the inserted resistance, the armature current reduces to 15 A what wilt he the speed? 10 2. (a) A 220 V d.c. compound generator has resistances of the armature, shunt and series windings as 0.1 ohm, 50 ohms and 006 ohm, respectively. The load current is 100 A at 220 V. Find the induced e.m.f. and armature current when the machine is connected as a (i) long shunt, (ii) short shunt. (iii) how will the ampere-\turn of the series winding will change if in (i) a diverter resistance of 0.1 ohm be connected in parallel with series winding? Ignore armature reaction. 12 (b) Calculate efficiency, voltage at the secondary terminals and primary input current when supplying full load secondary current at power factor (i) unity (ii) 0.8 lag, for a 4 kVA, 230/460 V single phase transformer. The following are test results Open circuit with 230 V applied to LV side 0.6 A, 75 W Short circuit with 20 V applied to HV side - 10 A, 60 W. 20 (c) Summarize the conditions for proper parallel operation of (i) single-phase transformers, and (ii) 3-phase transformers. 8 3. (a) A synchronous generator supplies rated power at 0.8 p.f. lagging. Its resistance and synchronous reactance are 0.01 and 1.0 pu. Calculate the terminal voltage if the open circuit voltage is 2.1 p.u. What is the minimum allowable excitation voltage? 14 (b) From the short circuit test on a 50 H.P., 440 V, 50 Hz, 6 pole star connected, 3-phase induction motor, the following data were obtained V = 230 V, I = 140 A, cos = 035 (line values). The motor drives a load having a constant torque of 300 N.m. Estimate the maximum percentage reduction in the supply voltage possible before the motor stalls. Assume that the copper losses are equally divided between the stator and the rotor. Neglect magnetizing current. 14 (c) Name the chief methods of speed control of a 3-phase induction motor. Explain briefly one of the most modem methods of speed control of an induction motor namely (v/f) control. 12 2. (A) A 1500 kVA, 6.6/1.1 kV, 3 phase delta-star connected transformer has the following test result: S.C. test: (Instruments placed on h.v. side) 300 V, 131.21 A, 30 kw Calculate its percentage resistance, percentage reactance drops, percentage efficiency and percentage regulation on full load at 0.8 power factor lagging. The iron loss during O.C. test with rated voltage supplied is 25 kW. 14 (b) A star-connected 3-phase alternator delivers a 3-phase star- connected load at a power factor of 0.8 lagging. A wire connects the load and the alternator. The terminal voltage at no-load is 2500 V, and at full-load of 1460 kW it is 2200 V. Determine the terminal voltage when it
delivers a 3 phase star-connected load having a resistance of 6 Q and reactance 8 (2 per phase respectively. Assume constant current and field excitation. 14 (c) (i) Interpret the following instructions and mention their addressing mode and flag affected, if any XRA A; DAA; DCR M; ADD B. 8 (ii) What is the difference between Accumulator (ACC) and Instruction Register (IR)? 4 3. (a) (i) With connection diagrams for both shunt and separately excited D.C. generators, draw the important characteristics of these generators. 6 (ii) Calculate the rms value of the induced emf per phase of a 10 pole, three phase, 50 Hz alternator with 2 slots per pole per phase and 4 conductors per slot in two layers. The coil span is 150. The flux per pole is 0.12 wb. 8 (b) Two alternators working in parallel supply a lighting load of 3000 kW and a motor load aggregating to 5000 kW at a p.1 of 0.72. One machine is loaded up to 5000 kW at 0.8 p.f. lagging. What is the load and power factor of the other machine? 14 (c) Consider a two stage synchronous counter (both stages receive the pulses at the CK input). In each counter K = 1. If Q1 and J1 Q0, draw the circuit. From a truth table of Q0 and Q1 after each pulse, demonstrate that this is a 3 : 1 counter. 12 2. (a) A 3 phase load of 40 kW, 380 V having a p.f. of 0.8 (lagging) receives its power through a 3 phase auto transformer from a 3 phase 440 V 3 supply. The auto transformer is connected in star. The neutral is NOT grounded. Neglect exciting current and impedance of the transformer winding. (i) Draw the diagram depicting the above situation. (ii) Calculate the currents entering the load from the auto transformer. (iii) Calculate the currents entering the transformer from the supply side. (iv) Show the currents flowing in the transformer windings along with directions. 3+4+4+4 (b) A 230 V, D.C. Machine has Ra = 0.3 and Rsh 160 respectively. It is running as a motor on NO LOAD at 1000 RPM taking an armature current of 3.3 A at rated voltage. When the motor is run on FULL LOAD at rated voltage, the line current has a value of 40 Amps. Calculate the speed and torque developed for this condition, assuming that armature reaction weakens the no load flux by 4%.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- R410A Split Systems Air Conditioner Technical ManualDocument100 pagesR410A Split Systems Air Conditioner Technical ManualHenry Phan75% (4)
- Analysis and Design of Transmission TowersDocument50 pagesAnalysis and Design of Transmission Towersadnan-651358Pas encore d'évaluation
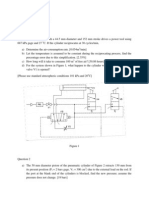
- A Feedwater Heater Operating at Steady State Has Two Inlets and One ExitDocument1 pageA Feedwater Heater Operating at Steady State Has Two Inlets and One ExitAhmed MasoudPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheet 3Document3 pagesSheet 3geo_bi100% (1)
- R7310305 Design of Machine Members - IDocument1 pageR7310305 Design of Machine Members - IsivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture18 FM SD IitgDocument11 pagesLecture18 FM SD IitgmyidmaranPas encore d'évaluation
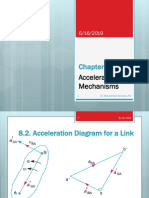
- Acceleration in MechanismsDocument38 pagesAcceleration in Mechanismsmurali_330Pas encore d'évaluation
- SE 2003&2008 Pattern PDFDocument799 pagesSE 2003&2008 Pattern PDFBenigno Tique Jonasse100% (1)
- Assignment-5 (Gear Train)Document2 pagesAssignment-5 (Gear Train)Mohd Javed IqbalPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Engineering Faculty Insulator GuideDocument33 pagesElectrical Engineering Faculty Insulator GuideEnyewPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Transmission SystemsDocument3 pagesDesign of Transmission SystemsSaravanan KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanical Engineering Turbomachinery Assignment QuestionsDocument2 pagesMechanical Engineering Turbomachinery Assignment QuestionsAbebe AyingdaPas encore d'évaluation
- R7210202 Fluid Mechanics & Hydraulic MachineryDocument1 pageR7210202 Fluid Mechanics & Hydraulic MachinerysivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Vehicle Motor TypesDocument20 pagesElectric Vehicle Motor TypesRahulPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial Questions Me405Document1 pageTutorial Questions Me405Blessed ZiyambePas encore d'évaluation
- Theory of Machines - Josh Ampofo KNUSTDocument60 pagesTheory of Machines - Josh Ampofo KNUSTfanpop botherPas encore d'évaluation
- Pumps: A Guide to Classification, Components, Working Principles, and EfficienciesDocument27 pagesPumps: A Guide to Classification, Components, Working Principles, and EfficienciesMuhammad UsmanPas encore d'évaluation
- V2 ECU For AMT TurbinesDocument26 pagesV2 ECU For AMT TurbinesAmin Anjom100% (1)
- Tutorial Sheet No 1 On Spur GearDocument3 pagesTutorial Sheet No 1 On Spur GearChirayuPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial Pneumatic CircuitDocument5 pagesTutorial Pneumatic CircuitMuhammad Abdullah0% (1)
- ME 363 - Fluid MechanicsDocument5 pagesME 363 - Fluid MechanicsMostafa Mohamed0% (1)
- Taif Sheet 2&3 Shaft Design and BearingsDocument2 pagesTaif Sheet 2&3 Shaft Design and BearingsBen Ahmed100% (1)
- GL 112 CAM ANALYSISDocument6 pagesGL 112 CAM ANALYSISNathi Dan MasekoPas encore d'évaluation
- Control TheoryDocument2 pagesControl Theorycjdbbt1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Aços Carbono Construção CivilDocument5 pagesAços Carbono Construção CivilIrvin WilliamPas encore d'évaluation
- Adama University School of Engineering and Inforamation Technology Bottle Jack Design Design of Hydraulic Bottle JackDocument56 pagesAdama University School of Engineering and Inforamation Technology Bottle Jack Design Design of Hydraulic Bottle JackMintePas encore d'évaluation
- Torsional Vibration HandoutsDocument3 pagesTorsional Vibration HandoutsjaycobsmillanPas encore d'évaluation
- Dom Assignment 1Document2 pagesDom Assignment 1Praveen KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- 4-SPEED GEAR BOXDocument17 pages4-SPEED GEAR BOXKhanna Dhinesh100% (1)
- Mom - 18me32 AssignmentDocument4 pagesMom - 18me32 AssignmentS KousikPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 31 Thermal Engineering II (23.09.2020) .Document47 pagesLecture 31 Thermal Engineering II (23.09.2020) .Dr. BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANPas encore d'évaluation
- Equilibrium of Floating BodiesDocument18 pagesEquilibrium of Floating BodiesMuneeb Rehman100% (1)
- Lecture in Machine ElementsDocument30 pagesLecture in Machine ElementsMark Angelo PagadorPas encore d'évaluation
- GATE 2023 Mechanical Engineering Question Paper SolutionDocument29 pagesGATE 2023 Mechanical Engineering Question Paper SolutionTG ManduuPas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamics of Machinary - Question BANKDocument17 pagesDynamics of Machinary - Question BANKS A ABDUL SUKKURPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 - IntroductionDocument53 pagesChapter 1 - IntroductionSiraj MohammedPas encore d'évaluation
- Upto 2010 KomDocument36 pagesUpto 2010 KomRajueswarPas encore d'évaluation
- RAC Assignments 24062016 091508AMDocument37 pagesRAC Assignments 24062016 091508AMsakalidhasavasanPas encore d'évaluation
- MEM 404 Mechanics of Machines Question BankDocument12 pagesMEM 404 Mechanics of Machines Question BankRohit DiwakarPas encore d'évaluation
- Geneva MechanismDocument12 pagesGeneva Mechanismsarodesarang4750Pas encore d'évaluation
- CIRT, Bhopal Turbo Machinery (ME 502) Tutorial/Assignment Sheet 4 (Water Turbine)Document1 pageCIRT, Bhopal Turbo Machinery (ME 502) Tutorial/Assignment Sheet 4 (Water Turbine)AnkurTripathiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter - 1 - Static Force Analysis PDFDocument29 pagesChapter - 1 - Static Force Analysis PDFSourabh JangraPas encore d'évaluation
- Achieving static and dynamic balanceDocument13 pagesAchieving static and dynamic balanceTuanbk NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- UnkulunkuluDocument62 pagesUnkulunkuluTsegawbeztoPas encore d'évaluation
- Angular velocity and forces in reciprocating enginesDocument39 pagesAngular velocity and forces in reciprocating enginesrajashekar reddy nallalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Exam - Thermo Fluids Lab - 2013Document1 pageFinal Exam - Thermo Fluids Lab - 2013Siraj MohammedPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.epicyclic Gear TrainDocument3 pages1.epicyclic Gear TrainRishi ShuklaPas encore d'évaluation
- ME6703 CIM Important Questions Unit 1Document2 pagesME6703 CIM Important Questions Unit 1raja30gPas encore d'évaluation
- Circuito NeumaticoDocument13 pagesCircuito NeumaticoJulio A. López BárcenasPas encore d'évaluation
- 9a01308-Fluid Mechanics & Hydraulic MachineryDocument4 pages9a01308-Fluid Mechanics & Hydraulic MachinerysivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- University of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 5 (Chapter 5)Document4 pagesUniversity of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 5 (Chapter 5)Vivin MathewPas encore d'évaluation
- AUTO400 Homework Assignment 1 SOLUTIONDocument16 pagesAUTO400 Homework Assignment 1 SOLUTIONVinoliaEdwin100% (1)
- AC Series MotorsDocument8 pagesAC Series Motorsゞ『HaiDerツ98〆Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Manual 1 (Gyroscope)Document3 pagesLab Manual 1 (Gyroscope)Muhammad FarhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Marcet Boiler ExperimentDocument13 pagesMarcet Boiler ExperimentSatiah WahabPas encore d'évaluation
- Solved Problems: Single Degree Free VibrationDocument14 pagesSolved Problems: Single Degree Free Vibrationprem adhikariPas encore d'évaluation
- Impulse and reaction turbine velocity diagramsDocument5 pagesImpulse and reaction turbine velocity diagramsdevang_panchal899600Pas encore d'évaluation
- Short Questions ECDDocument7 pagesShort Questions ECDNanda Kishore RayPas encore d'évaluation
- EE2006D Assignments 1-2 2020Document2 pagesEE2006D Assignments 1-2 2020vinodPas encore d'évaluation
- Part BDocument10 pagesPart BVenkat ManiPas encore d'évaluation
- Written QuestionsDocument18 pagesWritten QuestionsGokul RajPas encore d'évaluation
- DC Motor Assignment QuestionsDocument6 pagesDC Motor Assignment QuestionsSaurav SomeshPas encore d'évaluation
- List of 3287 Eligilble Candidates Under CSSS-2010Document132 pagesList of 3287 Eligilble Candidates Under CSSS-2010ashu099Pas encore d'évaluation
- CourseDocument56 pagesCourseAshutosh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDocument593 pagesHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- Untitled PageDocument2 pagesUntitled Pageashu099Pas encore d'évaluation
- EENG224 DSCRDocument2 pagesEENG224 DSCRashu099Pas encore d'évaluation
- List of Power Projects Used in Plexos Modelling of Generation Capacity Expansion Planning - REMB&EPIMB 0616 - FINALDocument12 pagesList of Power Projects Used in Plexos Modelling of Generation Capacity Expansion Planning - REMB&EPIMB 0616 - FINALCamz RoxasPas encore d'évaluation
- Lead Times Rockwell Automation 2023-03-29Document3 pagesLead Times Rockwell Automation 2023-03-29Omar Alfredo Del Castillo QuispePas encore d'évaluation
- Thermodynamics LabDocument8 pagesThermodynamics Labmohammad. 21Pas encore d'évaluation
- Simplicity Plus Installation ManualDocument47 pagesSimplicity Plus Installation ManualMo MeMesPas encore d'évaluation
- DatasheetDocument5 pagesDatasheetStuxnetPas encore d'évaluation
- WPQTDocument18 pagesWPQTMuhammad Fitransyah Syamsuar PutraPas encore d'évaluation
- F01S100 cabinet holds MA5610 MA5616 telecom equipmentDocument12 pagesF01S100 cabinet holds MA5610 MA5616 telecom equipmentmoaz ELZANATYPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit-1 DC CircuitsDocument44 pagesUnit-1 DC CircuitsLatha BarlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Multiband Microstrip Patch Antenna For Wireless ApplicationDocument3 pagesDesign of Multiband Microstrip Patch Antenna For Wireless ApplicationAnonymous CUPykm6DZPas encore d'évaluation
- Low Voltage Ower CapacitorsDocument18 pagesLow Voltage Ower Capacitorsrajpre1213Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tps 54240Document48 pagesTps 54240Maria KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2 - Drawing PackageDocument198 pagesModule 2 - Drawing PackageAlif PrayogaPas encore d'évaluation
- PDF Philips 26610Document11 pagesPDF Philips 26610ecsa tallerPas encore d'évaluation
- FEKO. Script ExamplesDocument182 pagesFEKO. Script ExamplesLaz GsodfjxPas encore d'évaluation
- Diesel Generator Set Specifications SheetDocument2 pagesDiesel Generator Set Specifications SheetManmadhan MadhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Certa-Flow DATA SHEET OkDocument4 pagesCerta-Flow DATA SHEET OkJAIME HERNANDEZ HERNANDEZPas encore d'évaluation
- ECG With DRL-SCH - Completa+Sim-TexIn - Slau516Document5 pagesECG With DRL-SCH - Completa+Sim-TexIn - Slau516Lulu Sweet ThingPas encore d'évaluation
- En Data Sheet 2236Document6 pagesEn Data Sheet 2236Equipe FCPas encore d'évaluation
- CM SL Commissioning Report 0811Document2 pagesCM SL Commissioning Report 0811Waqar Ul HaqPas encore d'évaluation
- Article 99Document7 pagesArticle 99Hoàng Nguyễn BáPas encore d'évaluation
- Các kí hiệu trong bản vẽ thiết kế nhà máy nhiệt điệnDocument6 pagesCác kí hiệu trong bản vẽ thiết kế nhà máy nhiệt điệnthanhphong2782Pas encore d'évaluation
- Power Quality Analysis of Traction Supply SystemsDocument5 pagesPower Quality Analysis of Traction Supply SystemsHershal RockksPas encore d'évaluation
- NT Converter 1.1Document8 pagesNT Converter 1.1George BarsoumPas encore d'évaluation
- Predicting Radiated Emissions From Cables in The RE02/RE102/DO-160/SAE J113-41 Test Set Up, Using Measured Current in NEC and Simple TX EquationsDocument49 pagesPredicting Radiated Emissions From Cables in The RE02/RE102/DO-160/SAE J113-41 Test Set Up, Using Measured Current in NEC and Simple TX EquationsdasdfsadPas encore d'évaluation
- Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis (IVDocument35 pagesSinusoidal Steady-State Analysis (IVPhan Phuong NgocPas encore d'évaluation
- Transient Characteristics of Electrical Loads With DC SourceDocument7 pagesTransient Characteristics of Electrical Loads With DC SourceEloykerz CahyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Whitepaper: by Richard A. Scholl of Advanced Energy Industries, IncDocument0 pageWhitepaper: by Richard A. Scholl of Advanced Energy Industries, IncAngel DemianPas encore d'évaluation
- Price List - SSD90 LED, SST-300, Luminus, CBT-140 Driver... Etc For LED Light Source or Medical or Stage Light (Mo-Light) 2024Document7 pagesPrice List - SSD90 LED, SST-300, Luminus, CBT-140 Driver... Etc For LED Light Source or Medical or Stage Light (Mo-Light) 2024mahfoudPas encore d'évaluation