Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Lasers, A Basic Science Experiment
Transféré par
Sam TelfordTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Lasers, A Basic Science Experiment
Transféré par
Sam TelfordDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Introduction:
Lasers
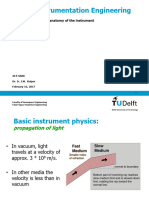
A laser (Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation) is an object capable of producing an incredible beam of monochromatic light (single colour or wavelength) that is capable of traveling kilometers in dark conditions. This laser light is also able to travel through various transparent and translucent materials. This amazing feat is called refraction and occurs in everyday life. A once famous man created a formula to express to what degree light is refracted by certain substances. Its quite a simple equation that says when the refractive index of a material is multiplied the sine of the angle of incidence the answer obtained will equal the refractive index of a second material multiplied by the sin of the angle of refraction. Or,
Where is the angle of incidence measured from the normal and measured from the same.
is the angle of refraction
Aim: To investigate the refractive properties of differently shaped transparent materials. Hypothesis: It is expected that the laser light that passes through the glass prism will be
bent or refracted the most.
Independent variable: The substance or material which the laser light is aimed at. Dependant variable: The angles of refraction and incidence. Constant variables:
Temperature of the piece of graph paper Wind speed and direction Distance of materials or substances from laser generator Type, brand etc of laser pointer
Materials:
1mw green laser Transparent glass rectangular prism Rectangular prism (perspex)
Triangular prism (perspex) semicircular prism (perspex) Plastic cup (small) light prism Graph paper Digital camera
Method:
1. Place a piece of graph paper upon a clean, dry surface, this will act as the testing surface 2. Place the material or object being tested upon the graph paper, centrally located 3. Darken the room as much as possible 4. (optional): create a mount that holds the laser just above the surface of the paper 5. Turn on the laser making sure to avoid peoples eyes at all costs and trace the path of the laser light as it travels through the various materials and substances 6. Calculate the refractive indices
Results:
Material: Diagram of Lights path: Refractive Index calculations: Appearance of light after refraction/Observatio ns:
Medium perspex triangle Large perspex triangle Perspex small triangle Glass rectangle Perspex rectangle small biconvex lens Semi Circular perspex block Large biconvex lens biconcave lens Graph of refractive indices?/angles of refraction?/dispersion of light?
Discussion: Conclusion:
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- SpectrometerDocument7 pagesSpectrometerranaateeqPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic tools and techniquesDocument33 pagesBasic tools and techniquesAditi MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- PhysicsDocument8 pagesPhysicsVinay Vinay Ranjan JaiswalPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Project Class 12th 'E' Anupam GuptaDocument36 pagesPhysics Project Class 12th 'E' Anupam Guptaguptaanupam552Pas encore d'évaluation
- Optics Egt22460Document14 pagesOptics Egt22460vimukthi gunasinghaPas encore d'évaluation
- Answer KeyDocument2 pagesAnswer KeySansen ColipanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Project File Sample - ED-2Document22 pagesProject File Sample - ED-2Shikhar Trivedi100% (5)
- Refractive Index Measurement Using a Traveling MicroscopeDocument11 pagesRefractive Index Measurement Using a Traveling Microscopeakash singh50% (2)
- Diffraction of Light: Using Vernier Labquest, and Vernier Light Sensor (LS-BTA)Document3 pagesDiffraction of Light: Using Vernier Labquest, and Vernier Light Sensor (LS-BTA)surya narayanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Reflection/Refraction: Transparent Equal To Density Normal Towards ReflectionDocument6 pagesReflection/Refraction: Transparent Equal To Density Normal Towards Reflectiontony jammerPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio G11-5Document34 pagesBio G11-5BataricitraPas encore d'évaluation
- Index of Refraction LabDocument2 pagesIndex of Refraction LabKhari HarperPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 2: Ray Theory - Part 1: Optical Fiber Communication (EEE 4175)Document20 pagesLecture 2: Ray Theory - Part 1: Optical Fiber Communication (EEE 4175)creed60Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ophthalmic Dispensing Revision Guide: First Year Part OneD'EverandOphthalmic Dispensing Revision Guide: First Year Part OneÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (3)
- Lab # 2 RefractionDocument11 pagesLab # 2 RefractionAsim SarfrazPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics 72.1 Peer ReviewDocument12 pagesPhysics 72.1 Peer Reviewviviene24Pas encore d'évaluation
- MicrosDocument264 pagesMicrospriya100% (1)
- Basic Concept of PhotographyDocument6 pagesBasic Concept of PhotographyKyla RodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Light Waves HSDocument9 pagesLight Waves HSroychan919.2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Microscope & Its Parts & History of MicroscopeDocument48 pagesMicroscope & Its Parts & History of Microscopebushra mahnoorPas encore d'évaluation
- Junior Research PaperDocument28 pagesJunior Research Paperapi-353022478Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Report 2Document5 pagesLab Report 2puja saha50% (2)
- L Principles MicrosDocument60 pagesL Principles MicrosRasul AmirovPas encore d'évaluation
- Liquid PrismDocument16 pagesLiquid PrismPrathap KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- DocumentDocument14 pagesDocumentAnjali RajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Snell's Law: Measuring Glass Refraction IndexDocument3 pagesSnell's Law: Measuring Glass Refraction IndexZayed AlmheiriPas encore d'évaluation
- Isc Physics ProjectDocument15 pagesIsc Physics ProjectBhoomi DhokaPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Work 5Document12 pagesProject Work 5GAGAN NPas encore d'évaluation
- Reflect Ance SpectrosDocument3 pagesReflect Ance SpectrosRoss JonesPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 - The MicroscopeDocument42 pages01 - The MicroscopeKyra Gayle H. PaudPas encore d'évaluation
- Determination of Refractive Index On Three MediumsDocument7 pagesDetermination of Refractive Index On Three MediumsArya AnggoroPas encore d'évaluation
- MiriaasdDocument52 pagesMiriaasdCreatia PertokiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Optical Properties Laboratory ActDocument1 pageOptical Properties Laboratory ActCamille F. ManlapigPas encore d'évaluation
- IndexDocument17 pagesIndexcocindiazaPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Pages XRD AssignmentDocument5 pages5 Pages XRD AssignmentZia ud din KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 28 - Optics Part 1Document19 pagesLecture 28 - Optics Part 1Mircea PanteaPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction MicroscopeDocument19 pagesIntroduction MicroscopeNikky NamdeoPas encore d'évaluation
- Archivos PASCO - CA-6787 PDF Files - 3 Thermo., WavDocument8 pagesArchivos PASCO - CA-6787 PDF Files - 3 Thermo., WavChess ManPas encore d'évaluation
- 7a MicrosDocument52 pages7a MicrosYong AlbertoPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Optics Lab at SJSUDocument16 pagesAdvanced Optics Lab at SJSUAli KhumaeniPas encore d'évaluation
- FTIRDocument14 pagesFTIRFaisal IqbalPas encore d'évaluation
- X-Ray DiffractionDocument26 pagesX-Ray DiffractionZain Ali KidwaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ellipsometry Jordan KuhnDocument4 pagesEllipsometry Jordan Kuhnjordan5kuhnPas encore d'évaluation
- Prism SpectrometerDocument12 pagesPrism SpectrometerFerariPas encore d'évaluation
- Optical Fiber Communication FundamentalsDocument20 pagesOptical Fiber Communication FundamentalsSaikat MahmudPas encore d'évaluation
- Nano Material Characterisation Techniques: Mathews K. Manayani Assistant Professor Nirmala College, MuvattupuzhaDocument67 pagesNano Material Characterisation Techniques: Mathews K. Manayani Assistant Professor Nirmala College, MuvattupuzhaJump BunnyPas encore d'évaluation
- Optical Fiber Structure & Light TransmissionDocument83 pagesOptical Fiber Structure & Light Transmissionece Ms.G.Bhargavi100% (1)
- Michelson-Morley Experiment Index RefractionDocument7 pagesMichelson-Morley Experiment Index RefractionJosephine ChenPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.8. Refraction LessonDocument23 pages2.8. Refraction Lesson6h4gxcf7jbPas encore d'évaluation
- LASER Cutting, Printing and Scanning ExplainedDocument7 pagesLASER Cutting, Printing and Scanning ExplainedFauzan LuqmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Light MicrosDocument39 pagesLight MicrosNabanita ChatterjeePas encore d'évaluation
- Testing Reflection Laws with MirrorsDocument2 pagesTesting Reflection Laws with MirrorsErica ObrienPas encore d'évaluation
- EENG 292 NotesDocument30 pagesEENG 292 NotesSimion OngoriPas encore d'évaluation
- Instrument Physics 2017Document24 pagesInstrument Physics 2017Sergio LPas encore d'évaluation
- PHOTOGRAPHYDocument8 pagesPHOTOGRAPHYCARANTO, JAE HANNE G.Pas encore d'évaluation
- ProposalDocument7 pagesProposalrairaicute100% (3)
- Explain X Ray Diffractometer With The Help of Schematic DiagramDocument2 pagesExplain X Ray Diffractometer With The Help of Schematic DiagramGirdhar GopalPas encore d'évaluation
- Laboratory ReviewDocument1 pageLaboratory ReviewVasin DumrongprechachanPas encore d'évaluation
- BaiganDocument14 pagesBaiganfightfortarget25Pas encore d'évaluation
- Microscope HistoryDocument4 pagesMicroscope HistoryYanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Light: Architectural Science IiiDocument53 pagesLight: Architectural Science IiiRodas YemanePas encore d'évaluation
- Refraction of Light (Answers)Document5 pagesRefraction of Light (Answers)keyur.galaPas encore d'évaluation
- KME 061 Non-Destructive Testing: Rajkiya Engineering College, BandaDocument32 pagesKME 061 Non-Destructive Testing: Rajkiya Engineering College, BandaHarsh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Class Xii Physics Set A PDFDocument10 pagesClass Xii Physics Set A PDFJ NPas encore d'évaluation
- Virtual Retinal Display: by Harish.S 1DS07CS403Document26 pagesVirtual Retinal Display: by Harish.S 1DS07CS403Harish SrinivasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Lab Manual GuideDocument77 pagesBiology Lab Manual Guideyohans100% (1)
- Chhattisgarh Dental College projection geometry guideDocument32 pagesChhattisgarh Dental College projection geometry guidevishal tiwary100% (2)
- Kim Lighting Type 5 Brochure 1996Document22 pagesKim Lighting Type 5 Brochure 1996Alan MastersPas encore d'évaluation
- Natural Lighting at The Kimbell Museum: Gifford Pierce of IdahoDocument5 pagesNatural Lighting at The Kimbell Museum: Gifford Pierce of IdahoBtn SayadPas encore d'évaluation
- PTC - BSR.RVI.01 - BoreScope Visual Inspection Procedure (Rev.1)Document9 pagesPTC - BSR.RVI.01 - BoreScope Visual Inspection Procedure (Rev.1)Sang Nguyen QuangPas encore d'évaluation
- LED LED CTLG EN 052012 PG47 APAC - tcm281 33329Document47 pagesLED LED CTLG EN 052012 PG47 APAC - tcm281 33329FreddyOlanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Specimen Bmat 2014 Section 2 Question PaperDocument24 pagesSpecimen Bmat 2014 Section 2 Question PaperAaron NanooPas encore d'évaluation
- E111 - AgustinDocument20 pagesE111 - AgustinSeth Jarl G. AgustinPas encore d'évaluation
- BAC151C: Raman Video Microsampling SystemDocument2 pagesBAC151C: Raman Video Microsampling SystemWalter Ricardo BritoPas encore d'évaluation
- HF SystemDocument44 pagesHF Systemmarwan khalilPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Bank For Sensation and Perception Second EditionDocument19 pagesTest Bank For Sensation and Perception Second Editionmrssamanthagutierrezxwojrqntcg100% (19)
- Colour Blind Justin BroackesDocument106 pagesColour Blind Justin BroackesSucharita BeniwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Physics - G. AruldhasDocument99 pagesEngineering Physics - G. Aruldhassubho0% (1)
- Utilizing The VNA As GPRDocument8 pagesUtilizing The VNA As GPRعمر الشيباني100% (1)
- AM11 Chapter 7Document21 pagesAM11 Chapter 7Xavier ValladaresPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Photoelectric ProjectDocument22 pagesPhysics Photoelectric ProjectAnonymous 3CivXAHALi100% (1)
- Spectral Signature eDocument3 pagesSpectral Signature eRahul DekaPas encore d'évaluation
- Jif 212 - Final Exam 1516Document6 pagesJif 212 - Final Exam 1516Sharuvindan NairPas encore d'évaluation
- Roxtec CatalogDocument41 pagesRoxtec Catalogvux004Pas encore d'évaluation
- CUNANAN LENS AND MIRRORS FinalDocument7 pagesCUNANAN LENS AND MIRRORS Finalvcunanan20ur0411Pas encore d'évaluation
- LSI Esquire Series Fluorescent Spec Sheet 1990Document2 pagesLSI Esquire Series Fluorescent Spec Sheet 1990Alan MastersPas encore d'évaluation
- Secret BankingDocument8 pagesSecret BankingberryberryPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 5Document7 pagesLecture 5sivamadhaviyamPas encore d'évaluation
- PHY4 January 2004Document3 pagesPHY4 January 2004api-3726022Pas encore d'évaluation
- PH 0143.20 - Ajuan Alat Farmasi Muhamadiyah 1Document11 pagesPH 0143.20 - Ajuan Alat Farmasi Muhamadiyah 1Subhan RullyansyahPas encore d'évaluation