Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Abstract
Transféré par
Nayeem ArkDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Abstract
Transféré par
Nayeem ArkDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
ABSTRACT iOS is Apple's mobile operating system developed originally for the iPhone, and later deployed on the
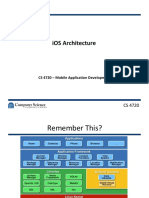
iPod Touch and iPad as well. It is derived from Mac OS X, with which it shares the Darwin foundation, and is therefore a Unix-like operating system, by nature. In iOS, there are four abstraction layers: the Core OS layer, the Core Services layer, the Media layer, and the Cocoa Touch layer. The operating system uses roughly 500 megabytes of the device's storage. Version 4, announced in April 2010, introduced multitasking as well as several business-oriented features, including encryption for email and attachments. At the WWDC 2010 keynote on June 7, 2010, Apple announced that iPhone OS had been renamed iOS. Apple licenses the trademark for "iOS" from Cisco Systems (who own IOS), the same company with which Apple had earlier settled a dispute over the "iPhone" trademark. iOS 4 was released on
June 21, 2010, three days before the iPhone 4. Staggering product launches reduces strain on Apple's servers. iOS 4 is the first version of the OS to be a free upgrade on the iPod touch; Apple had charged $9.99 for earlier upgrades. Apple previously announced that iPad users with 3.x software would receive a free upgrade to the next major (4.x) release. New features of ios4 are: Multitasking Face time Folders Performance and stability Reception strength CHAPTER: INTRODUCTION iOS is Apple's mobile operating system. Developed originally for the iPhone, it has since been shipped on the iPod Touch and iPad as well. Apple does not permit the OS to run on third-party hardware. As of June 7, 2010, Apple's App Store contained more than 225,000 iOS applications, which had collectively been downloaded more than five billion times. The user interface of iOS is based on the concept of direct
manipulation, using multi-touch gestures. Interface control elements consist of sliders, switches, and buttons. The response to user input is immediate and provides a fluid interface. Interaction with the OS includes gestures such as swiping, tapping, pinching, and reverse pinching. Internal accelerometers are used by some applications to respond to shaking the device (one common result is the undo command) or rotating it in three dimensions (one common result is switching from portrait to landscape mode). iOS is derived from Mac OS X, with which it shares the Darwin foundation, and is thereforea Unix-like operating system by nature. In iOS, there are four abstraction layers: the Core OS layer, the Core Services layer, the Media layer, and the Cocoa Touch layer. The operating system uses roughly 500 megabytes of the device's storage. CHAPTER: 2 OVERVIEW OF APPLE iOS iOS comprises the operating system and
technologies that you use to run applications natively on devices, such as iPad, iPhone, and iPod touch. Although it shares a common heritage and many underlying technologies with Mac OS X, iOS was designed to meet the needs of a mobile environment, where users needs are slightly different. If you have previously developed applications for Mac OS X, you will find many familiar technologies, but youll also find technologies that are available only on iOS, such as the Multi-Touch interface and accelerometer support. The iPhone SDK contains the code, information, and tools you need to develop, test, run, debug, and tune applications for iOS. The Xcode tools provide the basic editing, compilation, and debugging environment for your code. Xcode also provides the launching point for testing your applications on an iOS device, and in iPhone Simulatora platform that mimics the basic iOS environment but runs on your local Macintosh computer. CHAPTER: 3
ORIGIN OF iPHONE Comments made by Jobs in April 2003 at the "D: All Things Digital" executive conference expressed his belief that tablet PCs and traditional PDAs were not good choices as highdemand markets for Apple to enter, despite many requests made to him that Apple create another PDA. He did believe that cell phones were going to become important devices for portable information access, and that what cell phones needed to have was excellent synchronization software. At the time, instead of focusing on a follow-up to their Newton PDA, Jobs had Apple put its energies into the iPod, and the iTunes software (which can be used to synchronize content with iPod devices), released January 2001. On September 7, 2005, Apple and Motorola released the ROKR E1, the first mobile phone to use iTunes. Jobs was unhappy with the ROKR, feeling that having to compromise with a non-Apple designer (Motorola) prevented Apple from
designing the phone they wanted to make. In September 2006, Apple discontinued support for the ROKR and released a version of iTunes that included references to an as-yet unknown mobile phone that could display pictures and video. On January 9, 2007, Jobs announced the iPhone at the Macworld convention, receiving substantial media attention, and on June 11, 2007 announced at the Apple's Worldwide Developers Conference that the iPhone would support third-party applications using the Safari engine on the device. Third-parties would create the Web 2.0 applications and users would access them via the internet. Such applications appeared even before the release of the iPhone; the first being "OneTrip", a program meant to keep track of the user's shopping list. On June 29, 2007, Apple released version 7.3 of iTunes to coincide with the release of the iPhone. This release contains support for iPhone service activation and syncing
HISTORY OF iOS: The operating system was unveiled with the iPhone at the Macworld Conference & Expo on January 9, 2007, and released in June of that year. At first, Apple marketing literature did not specify its name, stating simply that the "iPhone uses OS X". Initially, third-party applications were not supported. Steve Jobs argued that developers could build web applications that "would behave like native apps on the iPhone". On October 17, 2007, Apple announced that a native SDK was under development and that they planned to put it "in developers' hands in February". On March 6, 2008, Apple released the first beta, along with a new name for the operating system: iPhone OS. Brisk sales of Apple mobile devices kindled interest in the SDK. The previous September, Apple had released the iPod Touch, which had most of the non-phone capabilities of the iPhone. Apple also sold more than one million iPhones during the 2007 holiday season. On January
27, 2010, Apple announced the iPad, featuring a larger screen than the iPhoneand iPod Touch, and designed for web browsing, media consumption, and reading iBooks. FEATURES: Home screen: The home screen (rendered by "SpringBoard") with application icons, and a dock at the bottom of the screen where users can pin their most frequently used apps, is presented whenever the device is turned on or the home button pressed. The screen has a status bar across the top to display data, such as time, battery level, and signal strength. The rest of the screen is devoted to the current application. Double pressing the home button activates the application switcher. A scrollable dock-like interface appears from the bottom, moving the contents of the screen up. Choosing an icon switches to an application. To the far left are icons which function as music controls, and a rotation lock. Holding the icons makes them wiggle (similarly to the homescreen) and
allows the user to quit
Reference: http://www.seminarprojects.com/Thread-apple-ios-4-full-report#ixzz1irO5kEiI
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Apple HistoryDocument4 pagesApple HistoryKarthikPillaiPas encore d'évaluation
- IOS - WikipediaDocument49 pagesIOS - WikipediaMike MikkelsenPas encore d'évaluation
- iOS Architecture, Features, Pros and ConsDocument19 pagesiOS Architecture, Features, Pros and Consshantanu.4234633100% (1)
- The Ridiculously Simple Guide to iOS 14 and WatchOS 7: Getting Started With the Newest Generation of iPhone and Apple WatchD'EverandThe Ridiculously Simple Guide to iOS 14 and WatchOS 7: Getting Started With the Newest Generation of iPhone and Apple WatchPas encore d'évaluation
- Wondershare Recoverit Data Recovery بحثDocument14 pagesWondershare Recoverit Data Recovery بحثomerPas encore d'évaluation
- xz1 Compact Root Instructions v3Document42 pagesxz1 Compact Root Instructions v3FernandoGuillenGamarraPas encore d'évaluation
- -Repeater: 展开 尺 寸: 3 6 0 x 2 4 0 mm 成品 尺 寸: 1 2 0 x 9 0 mmDocument2 pages-Repeater: 展开 尺 寸: 3 6 0 x 2 4 0 mm 成品 尺 寸: 1 2 0 x 9 0 mmhelmoz100% (1)
- Modify IP ManualDocument7 pagesModify IP ManualFerdi IrawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Debt or Equity-Which One Is Better For Your Business?: Name-Avani Shah Roll No-Pgdmrba019Document2 pagesDebt or Equity-Which One Is Better For Your Business?: Name-Avani Shah Roll No-Pgdmrba019avani shahPas encore d'évaluation
- Changing Ip CucmDocument2 pagesChanging Ip Cucmsenthil0% (1)
- Cydia Download iOS 15Document8 pagesCydia Download iOS 15xamoraPas encore d'évaluation
- WhatsNewIn iPhoneOS5Document74 pagesWhatsNewIn iPhoneOS5Gb ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- iOS ArchitectureDocument14 pagesiOS Architectureevenciomendes1861Pas encore d'évaluation
- Step-by-step guide to flash TWRP, install LineageOS and GApps (no rootDocument6 pagesStep-by-step guide to flash TWRP, install LineageOS and GApps (no rootHariSetiawan100% (1)
- SRS Atm FinalDocument4 pagesSRS Atm FinalArmaanPas encore d'évaluation
- Amlogic Burn Card Maker and How To Use ItDocument5 pagesAmlogic Burn Card Maker and How To Use Its.s.r.k.m. gupta100% (1)
- Moblie Virus DescriptionsDocument49 pagesMoblie Virus DescriptionsDozdiPas encore d'évaluation
- Pirni Sniffer On iOSDocument11 pagesPirni Sniffer On iOSahdanizarPas encore d'évaluation
- iOS Hacking: Advanced Pentest & Forensic TechniquesDocument60 pagesiOS Hacking: Advanced Pentest & Forensic TechniquesÖmer Coşkun100% (1)
- Xcode 11 Beta 2 Release NotesDocument59 pagesXcode 11 Beta 2 Release NotesDigital NomadPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Phone Cloning: Methods, Impact and PreventionDocument21 pagesCell Phone Cloning: Methods, Impact and PreventionBASBUSPas encore d'évaluation
- Getting Started With iOSDocument50 pagesGetting Started With iOSMominPas encore d'évaluation
- Installing One Click AdbDocument8 pagesInstalling One Click AdbIgnatiusPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Change IP Address Using A Batch File Script OnDocument2 pagesHow To Change IP Address Using A Batch File Script Onkamakom78Pas encore d'évaluation
- Android App Development (Content)Document25 pagesAndroid App Development (Content)VipulPas encore d'évaluation
- TrainingmanualsdDocument14 pagesTrainingmanualsdapi-550014854Pas encore d'évaluation
- DocuNet Viewer IOSDocument52 pagesDocuNet Viewer IOSIlluga Ta Phrom100% (1)
- Summary and Analysis of Federal CARES Act Eviction MoratoriumDocument4 pagesSummary and Analysis of Federal CARES Act Eviction MoratoriumKaran MorbiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Apple iOS Security Framework ReferenceDocument74 pagesApple iOS Security Framework Referencej123smithPas encore d'évaluation
- IOSGods No Jailbreak App Store - Hacked Apps - No Cydia or Computer Required!Document1 pageIOSGods No Jailbreak App Store - Hacked Apps - No Cydia or Computer Required!marcelino100% (1)
- Iphone OS Programming Guide - IntroductionDocument3 pagesIphone OS Programming Guide - IntroductionNigel HarperPas encore d'évaluation
- Fix Windows Issues with SFC and DISMDocument3 pagesFix Windows Issues with SFC and DISMjws mitsuyoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Course Objectives: PrerequisitesDocument12 pagesCourse Objectives: PrerequisitessandeepPas encore d'évaluation
- Android Practical QuestionsDocument4 pagesAndroid Practical QuestionsRashika JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Root & Unroot I9082 v4.2.2Document11 pagesRoot & Unroot I9082 v4.2.2duytrung2121Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To AndroidDocument27 pagesIntroduction To AndroidSeemalPas encore d'évaluation
- Iphone App DevelpmentDocument110 pagesIphone App DevelpmentprogrammerPas encore d'évaluation
- HeimdallDocument10 pagesHeimdallJasmin SelimovićPas encore d'évaluation
- Android Remoting 101: Exploring Applications for Fun & ProfitDocument30 pagesAndroid Remoting 101: Exploring Applications for Fun & ProfitfoosaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Workshop 04 - Android Development PDFDocument26 pagesWorkshop 04 - Android Development PDFvandemberg_silvaPas encore d'évaluation
- Best Custom RomDocument5 pagesBest Custom RomCarlo MolinaPas encore d'évaluation
- MY Miko iOS Setup GuideDocument8 pagesMY Miko iOS Setup GuideEmotixPas encore d'évaluation
- Blue JackingDocument24 pagesBlue JackingkaranPas encore d'évaluation
- IOS ArchitectureDocument15 pagesIOS ArchitectureManiPas encore d'évaluation
- Android (Operating System)Document18 pagesAndroid (Operating System)My ChannelPas encore d'évaluation
- Android Forensics: Mobile Forensics World 2009Document29 pagesAndroid Forensics: Mobile Forensics World 2009jamessouthPas encore d'évaluation
- Windows 10 - WikipediaDocument37 pagesWindows 10 - WikipediamjdiaznoveloPas encore d'évaluation
- Device Control Through Bluetooth PDFDocument23 pagesDevice Control Through Bluetooth PDFSamit TandukarPas encore d'évaluation
- User Manual DFS 2015 ENG PDFDocument56 pagesUser Manual DFS 2015 ENG PDFtheodore_praset5954Pas encore d'évaluation
- SnapTools Installation GuideDocument4 pagesSnapTools Installation GuideStVinc100% (1)
- Eye OSDocument17 pagesEye OSVizay SoniPas encore d'évaluation
- Red Tacton Project Report in Ieee FormatDocument8 pagesRed Tacton Project Report in Ieee FormatBharath Sai100% (2)
- Ios Printer SDKDocument5 pagesIos Printer SDKDenny Widyianto0% (1)
- Adb CommandsDocument7 pagesAdb CommandsMartin banaPas encore d'évaluation
- iOS Security White Paper Feb 2014Document33 pagesiOS Security White Paper Feb 2014Mikey CampbellPas encore d'évaluation
- Android Programming Cookbook by Exelixis Media P CDocument151 pagesAndroid Programming Cookbook by Exelixis Media P CAdib AzzPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.4 Useful Utils and ToolsDocument15 pages1.4 Useful Utils and Toolsjesus llumpoPas encore d'évaluation
- Methods to Increase the Internal Storage Space of Android DevicesD'EverandMethods to Increase the Internal Storage Space of Android DevicesPas encore d'évaluation
- Methods to Increase the Internal Storage Space of Android DevicesD'EverandMethods to Increase the Internal Storage Space of Android DevicesPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Fundamentals FinalDocument15 pagesComputer Fundamentals FinalanilperfectPas encore d'évaluation
- United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,249,892 B2Document14 pagesUnited States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,249,892 B2david19775891Pas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Software: A. What Is A Software?Document4 pagesComputer Software: A. What Is A Software?Dienizs Labini TadenaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Impact of Assistive Technology Use For Students With Disabilities in Higher Education: A Systematic ReviewDocument15 pagesThe Impact of Assistive Technology Use For Students With Disabilities in Higher Education: A Systematic ReviewEstante de CoresPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson-1 - INFORMATION AGEDocument24 pagesLesson-1 - INFORMATION AGE12 ABM 2A-BORRES, JEAN ROSEPas encore d'évaluation
- Keyspan:USB Serial Adapter For Windows-V3.4 ManualDocument40 pagesKeyspan:USB Serial Adapter For Windows-V3.4 ManualNo PromisesPas encore d'évaluation
- Hardware Basics:: Hardware Refers To The Tangible Electronic Components That Make Up A Computer SystemDocument16 pagesHardware Basics:: Hardware Refers To The Tangible Electronic Components That Make Up A Computer SystemsrichoPas encore d'évaluation
- An Analysis of Augmented Reality SystemsDocument6 pagesAn Analysis of Augmented Reality SystemsAlba Albert Garrido0% (1)
- LSI gs550 PDFDocument85 pagesLSI gs550 PDFIvan ivan budiPas encore d'évaluation
- Mobile OS and PlatformsDocument6 pagesMobile OS and PlatformsHem RameshPas encore d'évaluation
- HP Photosmart 420Document61 pagesHP Photosmart 420Sici0001Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tuy Municipal Health Center Information SystemDocument10 pagesTuy Municipal Health Center Information SystemCK MandericoPas encore d'évaluation
- Information Age TimelineDocument8 pagesInformation Age TimelineZPads0% (1)
- Rajni SHDocument50 pagesRajni SHsaurabhPas encore d'évaluation
- M CommerceDocument23 pagesM CommerceAnkit Makkar100% (1)
- WizCom Quick Link PenDocument158 pagesWizCom Quick Link Penoychap123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Newton Toolkit User's GuideDocument202 pagesNewton Toolkit User's Guidepablo_marxPas encore d'évaluation
- Network Gaming Utilizing Ubiquitous Computing: by Marcus SmithDocument20 pagesNetwork Gaming Utilizing Ubiquitous Computing: by Marcus SmithjadhavbabasahebPas encore d'évaluation
- DL2310GGR335BSC3143Document3 pagesDL2310GGR335BSC3143himanshujangra8930Pas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Digital Monitoring System: Is A Multi-Function Digital Power MeterDocument3 pagesAdvanced Digital Monitoring System: Is A Multi-Function Digital Power MeterparyshaanPas encore d'évaluation
- Mobile Testing Interview QuestionsDocument4 pagesMobile Testing Interview QuestionskudahmtyPas encore d'évaluation
- Freedom Universal Keyboard User ManualDocument28 pagesFreedom Universal Keyboard User ManualmuskystoatPas encore d'évaluation
- MOEPS Agency Portal ManualDocument20 pagesMOEPS Agency Portal ManualAde DarmawanPas encore d'évaluation
- X-MET5000 PMI Broch SpecDocument12 pagesX-MET5000 PMI Broch SpecAlvialvarezPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of ComputersDocument248 pagesFundamentals of ComputersRaj Kumar DevarPas encore d'évaluation
- Bcs Lab New Syllabus Manual 15CS11P PDFDocument65 pagesBcs Lab New Syllabus Manual 15CS11P PDFSudh ZsamgPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Profiler EMP-400 Manual-DRAFTDocument102 pagesManual Profiler EMP-400 Manual-DRAFTMartin Alberto Pacheco CorreaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ttool - For StudentsDocument15 pagesTtool - For StudentsNaveen KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Smartphone and Academic Performance of Grade 12 Students of Santo Tomas Catholic SchoolDocument37 pagesSmartphone and Academic Performance of Grade 12 Students of Santo Tomas Catholic SchoolSharmaine CarreraPas encore d'évaluation
- Putra Habib D-1304681 - Paper Journal - Smartphone Usage in Islamic PerspectivesDocument11 pagesPutra Habib D-1304681 - Paper Journal - Smartphone Usage in Islamic PerspectivesPutra Habib DhitarekaPas encore d'évaluation