Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Hydroxyapatite Crystals Structural Components of Bone Matrix
Transféré par
hahaayaDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Hydroxyapatite Crystals Structural Components of Bone Matrix
Transféré par
hahaayaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
BONE
Specialized form of connective tissue composed of cells and extracellular matrix. Provide support and protection Serve as storage site for calcium and phosphate Mineralized by calcium phosphate in the form of hydroxyapatite crystals Structural components of bone matrix: a. Type I collagen 90% b. Type V collagen c. Ground subs 10% - noncollagenous proteins - bone devt, growth, remodeling, repair c.1. Proteoglycan Macromolecules - core protein with side chains of glycosaminoglycans hyaluronan chondroitin sulfate keratan sulfate - compressive strength of bone - bind growth factors - may inhibit mineralization c.2. Multiadhesive Glycoproteins - attachment of bone cells and collagen fibers osteonectin - glue collagen and hydroxyapatite crystals sialoproteins osteopontin - cells to bone matrix sialoprotein I and II - mediate cell attachment - initiate calcium phosphate formation
c.3. Bone-specific, vitamin K-dependent proteins osteocalcin - capture Ca from circulation - attract & stimulate ostoeclasts protein S - removal of apoptotic cells matrix gla-protein (MGP) - devt of vascular calcifications c.4. Growth factors & cytokines - regulatory proteins: IGFs, TNF-, TGF-, PDGF, BMPs, IL-1, IL-6 BMPs are the most unique; induce differentiation of mesenchymal cells into osteoblasts * Bones are the organs of the skeletal system * Bone tissue - structural component of bones Bone tissue classification COMPACT SPONGY Substantia compacta Substantia spongiosa Dense layer Spicules, trabeculae Ouside of bone Interior of bone Seen with aid of Interconnecting cavities microscope Bone classification: shape: a. long bones - longer in one dimension ex. Tibia, metacarpals b. short bones - equal in length and diameter ex. Carpals of hand c. flat bones - thin and platelike ex. Calvaria, sternum d. irregular bones ex. Vertebra, etmoid bone (spaces)
Long Bone - page 220, figure 8.2 diaphysis shaft epiphysis expanded ends metaphysis flared portion marrow medullary cavity periosteum fibrous CT capsule * Shaft: compact > spongy * Ends: spongy > compact Outer Surface of Bones Periosteum - dense fibrous CT - outer covering of bone * actively growing bone - outer layer: dense CT - inner layer: osteoprogenitor cells * bone not in progress - in&out fibrous layer (dense CT) Periosteal cells - may undergo division (become osteoblasts) under appropriate stimulus Sharpeys fibers - collagen fibers of the ECM of bone tissue - perforating fibers - outer fibrous layer of periosteum Bone Cavities Endosteum - lining tissue - one cell layer thick - osteoprogenitor cells = endosteal cells - can differentiate into osteoblasts and bone-lining cells * in compact bone facing marrow cavity * in spongy bone trabeculae w/in cavity Red bone marrow - blood cells in different stages of devt * become yellow marrow in adults - found in: sternum, iliac crest
Mature Bone - lamellar bone - page 222, figure 8.3 Lacunae - spaces which contain the osteocyte Haversian systems - osteons - cylindrical units - concentric lamellae surrounding a central canal Osteonal (Haversian) canal - contain vascular and nerve supply Perforating (Volkmanns) canals - connect osteonal canals to one another - not surrounded by concentric lamellae Canaliculi - passage bet. osteocytes & blood vessels Interstitial lamellae - remnants of concentric lamellae Circumferential lamellae - entire inner and outer circumferences of the shaft of a long bone Cement lines - demarcates the limit between the Haversian and Interstitial system IMMATURE BONES Non-lamellar, bundle, woven Random cell arrangement (+) Ground substance Hematoxylin Not mineralized heavily Rapid formation Found in fetus In alveolar sockets of oral cavity, tendon-bone insertion In adults MATURE BONES Lamellar Same as lamellae Eosin Prolonged secondary mineralization
CELLS OF BONE TISSUE
OSTEOPROGENITOR CELLS Flattened or squamous cells OSTEOBLASTS Cuboidal or polygonal cells, single layer, apposition to forming bone Mature matrix: Acidophilic Bone-forming cells OSTEOCYTES Smaller cells, reduced perinuclear cytoplasm, in lacuna Slightly basophilic Maintain bone matrix. BONE-LINING CELLS Flat cells, attenuated cytoplasm OSTEOCLASTS Large, multinucleated
Slightly basophilic Osteoblast precursor cells
Slightly basophilic Maintenance & nutritional support of osteocytes From osteoblast
Acidophilic Bone resorption
From mesenchymal stem cells, Inner periosteum
Differentiated osteoprogenitor cell
Osteoblast surrounded by osteoid
From GMP (Granulocyte/ macrophage progenitor cells)
Osteoprogenitor Cells periosteal cells endosteal cells - line marrow cavities of Haversian canal Osteoblasts - flat or attenuated when inactive - secretes bone matrix Type I collagen 90% Osteoid BMPs - initial unmineralized bone * when surrounded by osteoid matrix, becomes an osteocyte Osteocytes Mechanotransduction - respond to mechanical forces death of osteocytes results in resorption by osteoclasts, followed by repair by osteoblasts. - communicate by: gap junctions signaling molecules - nitric oxide - glutamate transporters
Bone-Lining Cells periosteal cells - external bone surface enosteal cells - internal bone surface - regulate movement of Ca and PO4 into & out of the bone Osteoclasts Resorption bay - Howships lacuna - shallow bay under osteoclast * Needs to be activated to become bone-resorbing cell Three specialized regions of osteoclast of actively resorbing bone: a. ruffled border - direct contact with bone - finger-like projections - surface area for exocytosis b. clear zone - ringlike perimeter, actin filaments - demarcates the bone area being resorbed ECM adhesion molecules - tight seal between plasma c. basolateral region - exocytosis of digested material TRAP
BONE FORMATION Endochondral ossification Itramembranous ossification Endochondral ossification - cartilage model as bone precursor - bones of extremities, vertebrae * 2nd trimester of fetal life to early adulthood different zones in the epiphyseal cartilage zone of reserve cartilage - resting zone, no proliferation zone of proliferation - hyaline cartilage, chondrocyte columns - abundant matix between chondrocytes zone of hypertrophy - enlarged cartilage cells - metabolically active chondrocytes zone of calcified cartilage - hypertrophied cells begin to degenerate\ - calcification zone of resorption/ossification - nearest the diaphysis - in direct contact with CT of marrow cavity * secondary ossification center - cartilage undergoes hypertrophy and degenerates - only epiphyseal growth plate remains Epiphyseal growth plate * The thickness remains constant during growth * amount of new cartilage = amount of resorbed * resorbed cartilage is replaced by spongy bone * actual lengthening of the bone occurs when new cartilage matrix is produced at the epiphyseal plate * new cartilage pushes the epiphysis away from the diaphysis, elongating the bone * bone increases in width when aposistional growth of new bone occurs between the cortical lamellae and the periosteum
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM OF DEVELOPING BONE
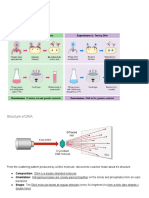
1. periosteal collar of bone forms around the diaphysis 2. bony collar calcifies 3. blood vessels and connective tissue cells invade the cartilage 4. primary center of ossification develops 5. periosteal bone is formed and perivascular cells invade the proximal epiphyseal cartilage 6. secondary ossification center is established in the proximal epiphysis 7. secondary (epiphyseal) ossification center forms at the distal end 8. epiphyseal cartilage is formed between each epiphysis and diaphysis. distal epiphyseal cartilage diasppears with continued growth 9. proximal epiphyseal cartilage disappears with growth cessation 10. metaphysis becomes continuous with epiphysis, epiphyseal lines remain Intramembranous ossification - simpler, no cartilage precursor - flat bones, clavicle - of mesenchymal cells into osteoblasts * 8th week of gestation in humans 1. mesenchymal cells (MC) migrate and aggregate in areas where bone is destined to form 2. MC differentiate into osteoprogenitor cells expressing Cbfa1 transcription for osteoblast diffrentiation 3. differentiated osteoblasts 4. osteoblasts secrete componets of bone matrix 5. woven obone or intramembranous bone is formed
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Chapter 6 Osseous Tissue and Skeletal StructureDocument70 pagesChapter 6 Osseous Tissue and Skeletal StructureStefanie Henry100% (1)
- MODULE 4 Skeletal SystemDocument16 pagesMODULE 4 Skeletal SystemKate Andrea PanizalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes 6Document11 pagesNotes 6lovj melPas encore d'évaluation
- Skeletal SystemDocument123 pagesSkeletal SystemZekiah MagsayoPas encore d'évaluation
- BONEDocument48 pagesBONEnivethaseshaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bone Tissue and The Skeletal SystemDocument10 pagesBone Tissue and The Skeletal SystemUloko ChristopherPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 Cartilage and BoneDocument5 pagesChapter 6 Cartilage and BoneSuperjunior8Pas encore d'évaluation
- BONE (Histology)Document65 pagesBONE (Histology)fhfebriiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cartilage & Bone '07Document44 pagesCartilage & Bone '07ade ayuningsih utamiPas encore d'évaluation
- Bone TissueDocument46 pagesBone TissueFiraol DiribaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bone & Jt. HoDocument10 pagesBone & Jt. Hojessa mae dugayPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture: Histology of Cartilage and BoneDocument49 pagesLecture: Histology of Cartilage and BonevictorPas encore d'évaluation
- Bone-06 11Document27 pagesBone-06 11api-19641337Pas encore d'évaluation
- Skeletal System: Bones and Bone TissueDocument49 pagesSkeletal System: Bones and Bone TissueSumit100% (1)
- Chapter 6 Bone Tissue 2304Document37 pagesChapter 6 Bone Tissue 2304Sav Oli100% (1)
- Alveolar BoneDocument81 pagesAlveolar BoneLavanya KalapalaPas encore d'évaluation
- CH8 Bone: Medullary CavitiesDocument9 pagesCH8 Bone: Medullary Cavitiesdanny olulanaPas encore d'évaluation
- DIT 104 LEC 1 - Classification & Types of BonesDocument27 pagesDIT 104 LEC 1 - Classification & Types of BonesRayan AndohPas encore d'évaluation
- Skeletal SystemDocument104 pagesSkeletal Systemsyafi zulPas encore d'évaluation
- BoneDocument33 pagesBoneNihal BilalPas encore d'évaluation
- (Manzanares) Skeletal System Study GuideDocument17 pages(Manzanares) Skeletal System Study GuideKyla ManzanaresPas encore d'évaluation
- Bone and CartilageDocument56 pagesBone and CartilageGodwin ZengeniPas encore d'évaluation
- Skeletal SystemDocument14 pagesSkeletal SystemCharlize PalmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Skeletal SystemDocument200 pagesSkeletal SystemJB AriasdcPas encore d'évaluation
- SKELETAL-SYSTEM-HANDOUT LongDocument40 pagesSKELETAL-SYSTEM-HANDOUT LongOtaku ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Point Presentation SKELETAL SYSTEMDocument75 pagesPower Point Presentation SKELETAL SYSTEMaprillianlozanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Relationship To Other Organ SystemsDocument11 pagesRelationship To Other Organ SystemsVern NuquiPas encore d'évaluation
- (BioSci Lec) Chapter 6Document13 pages(BioSci Lec) Chapter 6Jemille Anne Maranan MoroñaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bone Formation - Ossification 2 PDFDocument35 pagesBone Formation - Ossification 2 PDFalan100% (1)
- The Main Functions of BonesDocument9 pagesThe Main Functions of BonesabbaslafePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 Content Review Questions 1-8Document3 pagesChapter 6 Content Review Questions 1-8Rhonique MorganPas encore d'évaluation
- Osteomalacia, Bones Are Mineral-Deficient and Easily DeformedDocument16 pagesOsteomalacia, Bones Are Mineral-Deficient and Easily DeformedVarel JoanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture: Histology of Cartilage and BoneDocument49 pagesLecture: Histology of Cartilage and BoneStreet Fhigteer AgitatorPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification of Bones: Chapter 5: The Skeletal SystemDocument12 pagesClassification of Bones: Chapter 5: The Skeletal SystemJaica Mangurali TumulakPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 SkeletalDocument14 pages6 SkeletalprincessstephPas encore d'évaluation
- 511-525chapter 6-8 (1) An Introduction To The Skeletal SystemDocument6 pages511-525chapter 6-8 (1) An Introduction To The Skeletal Systemtomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayPas encore d'évaluation
- Skeletal System: CartilageDocument20 pagesSkeletal System: CartilageGrace PascualPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochemistry of Bone (Assignment)Document7 pagesBiochemistry of Bone (Assignment)haseeb ShafaatPas encore d'évaluation
- MAXILLA and MANDIBLE (Alveolar Process)Document35 pagesMAXILLA and MANDIBLE (Alveolar Process)ANVI SHARMAPas encore d'évaluation
- 09lect Bone Summary2017Document3 pages09lect Bone Summary2017Dan ChoiPas encore d'évaluation
- Histology 4 Cartilage and BoneDocument61 pagesHistology 4 Cartilage and BoneAbdul RahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Skeletal SystemDocument7 pagesThe Skeletal SystemKathleenJoyGalAlmasinPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 MariebDocument6 pagesChapter 6 Mariebmissy23papPas encore d'évaluation
- Cartilagebonembbsi 120126081822 Phpapp01Document28 pagesCartilagebonembbsi 120126081822 Phpapp01Muhammad AwaisPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Physiology Musculoskeletal System Chap 6 - 2401Document18 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Musculoskeletal System Chap 6 - 2401slyfoxkittyPas encore d'évaluation
- AnaPhy Unit 3 Notes ReviewerDocument12 pagesAnaPhy Unit 3 Notes Reviewer쥬얼이Pas encore d'évaluation
- Exam A-3Document11 pagesExam A-3yapues87Pas encore d'évaluation
- HANDOUTS Prelim CH 6Document40 pagesHANDOUTS Prelim CH 6Abia Annieson A. LorenzoPas encore d'évaluation
- 02 Skeletal SystemDocument32 pages02 Skeletal SystemHarshika KDGPas encore d'évaluation
- Table of ContentDocument52 pagesTable of ContentJasvir SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- 29 15okt TULANG RAWAN DAN TULANGDocument30 pages29 15okt TULANG RAWAN DAN TULANGelzhy 12Pas encore d'évaluation
- Anaphys SKELETAL SYSTEMDocument39 pagesAnaphys SKELETAL SYSTEMBEATRICE MAE MAGDALESPas encore d'évaluation
- Anaphy Prelims ReviewerDocument11 pagesAnaphy Prelims ReviewerMariz Elizabeth TaytayPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation OrthoDocument51 pagesPresentation OrthoPrateek ShivamPas encore d'évaluation
- Cartilage and BoneDocument54 pagesCartilage and BoneAGolosinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Skeletal 1Document196 pagesIntroduction To Skeletal 1Earl TrinidadPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Histology of BonesDocument32 pagesAnatomy and Histology of BonesAlan ThomasPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced farriery knowledge: A study guide and AWCF theory course companionD'EverandAdvanced farriery knowledge: A study guide and AWCF theory course companionPas encore d'évaluation
- Encyclopaedia Britannica, 11th Edition, Volume 15, Slice 5 "Joints" to "Justinian I."D'EverandEncyclopaedia Britannica, 11th Edition, Volume 15, Slice 5 "Joints" to "Justinian I."Pas encore d'évaluation
- Encyclopaedia Britannica, 11th Edition, Volume 15, Slice 5 "Joints" to "Justinian I."D'EverandEncyclopaedia Britannica, 11th Edition, Volume 15, Slice 5 "Joints" to "Justinian I."Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3.6 Proteins Exam Question: CH SHDocument3 pages3.6 Proteins Exam Question: CH SHShaePas encore d'évaluation
- Soalan Ulangkaji Bab 5 Tingkatan 4 PDFDocument22 pagesSoalan Ulangkaji Bab 5 Tingkatan 4 PDFIsmaliza Ishak0% (1)
- CB Catalog 4thedition B PDFDocument192 pagesCB Catalog 4thedition B PDFDifermoPas encore d'évaluation
- ImmunosuppressionDocument1 pageImmunosuppressionabc007200Pas encore d'évaluation
- Geriatric Nursing Theories of AgingDocument8 pagesGeriatric Nursing Theories of AgingAi RouPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Parts and Functions 2Document3 pagesCell Parts and Functions 2Arshelyn Donna NovenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell TheoryDocument31 pagesCell TheoryMarc Ian Young100% (1)
- InflammationDocument44 pagesInflammationramsiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQ PhysiologyDocument7 pagesMCQ Physiologydrng48Pas encore d'évaluation
- G Phase: Phase Describes A Cellular State Outside of The Replicative CellDocument9 pagesG Phase: Phase Describes A Cellular State Outside of The Replicative CellBlack WidowPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of Neurobiology 1st Edition Luo Test BankDocument15 pagesPrinciples of Neurobiology 1st Edition Luo Test BankOliviaHarrisonaxqyw100% (13)
- Hypertonic Stress Response: Natalia I. Dmitrieva, Maurice B. BurgDocument10 pagesHypertonic Stress Response: Natalia I. Dmitrieva, Maurice B. BurgKarina Pineda PérezPas encore d'évaluation
- Stem CellsDocument20 pagesStem CellsalibrownPas encore d'évaluation
- CONTOH RPHDocument4 pagesCONTOH RPHDara MoorePas encore d'évaluation
- Science 8 2nd Quarter ReviewerDocument5 pagesScience 8 2nd Quarter ReviewerMartin AlvinPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 7 Nucleic AcidsDocument8 pagesCH 7 Nucleic AcidsInes Ait Si SelmiPas encore d'évaluation
- 9796-Article Text-71626-2-10-20200824Document13 pages9796-Article Text-71626-2-10-20200824Yanet FrancoPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochemistry COURSE CODE: Ichem.3052 Group AssignmentDocument6 pagesBiochemistry COURSE CODE: Ichem.3052 Group AssignmentBizuayehu Ze GeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- Stem Cell Technology and Bioceramics: From Cell To Gene EngineeringDocument15 pagesStem Cell Technology and Bioceramics: From Cell To Gene Engineeringcobram1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Neuroscience Ch. 1 PowerPointDocument25 pagesNeuroscience Ch. 1 PowerPointKagiroPas encore d'évaluation
- Unicellular and Multicellular OrganisemsDocument54 pagesUnicellular and Multicellular Organisemsmenaga ilangkovanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 6 Cell The Unit of LifeDocument78 pagesLesson 6 Cell The Unit of LifeShriya RameshPas encore d'évaluation
- Botulinum Toxin in CancerDocument11 pagesBotulinum Toxin in CancerAlicia Ramirez HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- ArticleDocument16 pagesArticleDanielPas encore d'évaluation
- Sandra Central DogmaDocument82 pagesSandra Central Dogmakaren milloPas encore d'évaluation
- ANAT2341 Student 2015 Quiz QuestionsDocument12 pagesANAT2341 Student 2015 Quiz QuestionsHassan ContehPas encore d'évaluation
- Mcat Biochem VocabDocument12 pagesMcat Biochem VocabNataliePas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy of Nervous TissueDocument54 pagesAnatomy of Nervous TissueNand PrakashPas encore d'évaluation
- Folic Acid and FolatesDocument443 pagesFolic Acid and FolatesSuyog patilPas encore d'évaluation
- DNA Replication WorksheetDocument2 pagesDNA Replication WorksheetStrawberry RoPas encore d'évaluation