Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
73 Year Old Male
Transféré par
Nick Arngel CorporalDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
73 Year Old Male
Transféré par
Nick Arngel CorporalDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Introduction
This is a blog devoted completely to the discussion of pneumothorax. Here you will find an actual case study of a patient who experienced a pneumothorax, as well as pictures, external links, and a short quiz comprised of NCLEX like questions. Please, look around and let me know if you have any questions.
The Patient
73 Year Old Male 145 lbs. NKA Full Code Admitted for: 1. Right-sided pain of the thorax and upper arm 2. Four centimeter scalp laceration
History of Present Condition
Patient sustained a 10 foot fall Diagnosed as having: 1. Right-sided pneumothorax 2. Right sided fractured ribs 3. Right-sided sternoclavicular joint dislocation 4. Four centimeter scalp laceration. Immediate Course of Action: Day #1 Patient came in to the ED following a fall. He was subject to chest x-rays, CT scan (head, chest, abdomen, pelvis, and cervical spine), as well as an MRI (lumbar, thoracic, and cervical spine). As
stated above he was diagnosed as having a right-sided pneumothorax, multiple rib fractures, and
a sternoclavicular joint dislocation.
To treat the pneumothorax he had a chest tube inserted with 20cm dry suction water-seal drainage ordered. The patient endured no complications as a result of this procedure. To treat the dislocated joint he had his arm placed in a sling to stabilize the sternoclavicular joint. The scalp laceration was closed with staples. For his pain the patient had a thoracic epidural placed (10mgDilaudid, 2mL q4min). Course of Action: Day #2 Patient received another chest x-ray to monitor the s
tatus of the chest tube placement andpneumothorax. Results showed that the right lung hadreexpanded. Patient also went in to atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response. He was placed on a Cardizem drip to maintain a HR of greater than 120 and SBP greater than 90. Course of Action: Day #3 Patient received another chest x-ray to monitor the status of the chest tube placement and pneumothorax.Results showed that the right lung remained fully expanded. He also converted back to normal sinus rhythm at 2200. Course of Action: Day #4 Patient received another chest x-ray to monitor the status of the chest tube placement and pneumothorax.Results showed that the right lung remained fully expanded,
however there was increased opacity of the LLL suggestive of pneumonia. Patient was placed
on Levaquin (750mg every 24 hours x 5 days). Course of Action: Day #5-10 Patient'slung remains reexpanded. Copious amounts of drainage collected in water-seal system. He also completed his round of IV antibiotics for the pneumonia. Course of Action: Day #11 Patient's chest tube removed as well as the staples from his scalp laceration. Course of Action: Day #12 Patient was dismissed home. Went home with sling for his arm to stabilize the sternoclavicular joint.
Pathophysiology
A pneumothorax occurs when air enters the pleural space between the visceral pleura and parietal pleura causing partial or complete lung collapse. Signs & Symptoms: Mediastinal shifting usuallyoccurring with distant to absent breath sounds on the affected side. Sudden onset of acute pleuritic chest pain on the affected side usually occurs with labored breathing and dyspnea. Other problems that may occur include uneven chest wall movement, tachycardia, respiratory distress (severe tachyapnea).
Past Medical History
- Hypothyroidism - History of duodenal stricture - No history of smoking or drinking
Assessment Findings
0800: VS- 97.7/100/16, BP 128/76 in left arm, O2 sat 93%. Pt. alert, oriented x3. Skin pale, warm to cool, dry, intact. Eccymosis diffuse over right lateral thorax. MM moist, pink, intact. Nail beds pale pink, <3 seconds. Radial pulse 2+ bilat., PP 2+ bilat. Lung sounds clear bilat. ant/post. Abdomen soft, flat, bowel sounds present x4. IV in right forearm, occluded. Pt. c/o pain of 7/10 in right shoulder area radiating down to his right side ribs. Oxycodone (10 mg) administered. 0900: Pt. rates pain at 1-2/10, and is more comfortable now. Pt. taught cough and deep breathing and encouraged performing this every hour. 1200: Right forearm IV dcd, catheter intact. 1300: C/o pain 5/10 Lortab (1 tablet) given. 1345: Pt. rates pain on 0/10 and is more comfortable. VS: 99.2/84/16, BP 126/58, O2 sat 93%. All other assessments remain unchanged.
Relevant Labs
WBC = 12.8 (5.0-10.0)- Related to trauma, inflammation Free T3 = 1.88 (2.77-5.27)- Related to hypothyroid state Free T4 = .32 (0.78-2.19)- Related to hypothyroid state TSH= NA (0.5-5.0)
Diagnostic Tests
On Admission: Day #1 Chest X-ray: for suspected pneumothorax Large right pneumothorax Multiple right rib fractures CT scan: routine for falls/trauma Head = subgaleal hematoma Chest = right pneumothorax Cervical spine = wedging of T1 vertebral body (compression fracture) MRI: for pain post-trauma Lumbar = negative Thoracic = Mild fracture of T1, small right pleural effusion Cervical = Mild fracture of T1 Day #2 Chest X-ray: for status of pneumothorax and chest tube position
Right pneumothorax re-expanded following, chest tube in good position Day #3 Chest X-ray: for status of pneumothorax and chest tube position Right lung remains fully expanded, chest tube in good position Day #4 Chest X-ray: for status of pneumothorax and chest tube position Right lung remains fully expanded, chest time in good position, increased opacity of LLL suggestive of pneumonia.
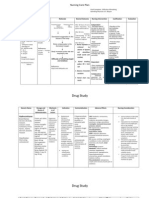
Relevant Medications
Hydromorphone (Dilaudid) 10mg (2mL q4min) Epidural Reason: To control severe pain r/t rib fracture, etc. Classification: Opiate agonist Actions: Structurally similar to morphine but with 8-10 times more potent analgesic effect. Side Effects: Hypotension, bradycardia, respiratory depression, blurred vision. Morphine 2mg Q4h IV Administration: Dilute 210 mg in at least 5 mL of sterile water for injection. Give a single dose over 45 min. Avoid rapid administration. Reason: To control severe pain r/t rib fracture, etc. Classification: Opiate agonist Actions: Natural opium alkaloid with agonist activity by binding with the same receptors as endogenous opioid peptides Side effects: Respiratory depression, flush of face, neck, and upper thorax, oliguria, pulmonary edema **Narcan is antidote for overdose! Naloxone (Narcan) 40mL/h PRN IV Administration: Dilute 2 mg in 500 mL of D5W or NS to yield 4 mcg/mL (0.004 mg/mL). Give 0.4 mg or fraction thereof over 1015 sec. Reason: Opiate overdose antidote Classification: Opiate antagonist Actions: Reverses the effects of opiates, including respiratory depression, sedation, and hypotension. Side effects: Reversal of analgesia, increased BP, HR, and tachycardia. Oxycodone (Oxycontin) 5-10mg BID PO Reason: Treatment of moderate to severe pain (dislocation, simple fractures) Classification: Opiate analgesic
Actions: Binds with stereo-specific receptors in various sites of CNS to alter both the perception of pain and emotional response to pain. Side effects: Respiratory depression, pruritus, bradycardia, urinary retnetion or urinary frequency Cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril) 10mg TID PO Reason: Relief of muscle spasm associated with acute musculoskeletal conditions Classification: Skeletal muscle relaxant Actions: Acts primarily within CNS at brain stem; some action at spinal cord level is also probable. Depresses tonic somatic motor activity. Side effects: Edema of tongue and face, tachycardia, postural hypotension, flatulence, tremor, impotence. Levofloxacin (Levaquin) 750mg Q24h x 5 days IV Administration: Normal (750mg Q24 hours X 5 days). Diluted with D5W, NS, D5/NS, D5/RL from 500mg (25mg/mL) to produce 5mg/mL. Intermittent- adm over >60min, do not bolus or infuse too rapidly Reason: Community-acquired pneumonia Classification: Broad-spectrum fluoroquinolone antibiotic Actions: Inhibits bacterial DNA replication, transcription, repair, and recombination. Side effects: Decreased vision, foreign body sensation, transient ocular burning, ocular pain, photophobia, chest or back pain, phlebitis. Levalbuterol (Xopenex) 1.25mg TID IH Administration: Nebulizer treatment Reason: Reversal of bronchospasm with reversible obstructive airway disease. Increases vital capacity. Actions: Acts on the beta2 receptors of the smooth muscles of the bronchial tree, thus resulting in bronchodilation. Classification: Beta-adrenergic agonist Side effects: Migraine, tachycardia, increased serum glucose, dyspepsia, increased HR, insomnia. Diltiazem (Cardizem) 240mg Daily PO Administration: Do NOT crush, withhold if SBP <90, class="blsp-spelling-error" id="SPELLING_ERROR_14">subthreshold levels insufficient to stimulate cell excitation and contraction. Side effects: Syncope, arrhythmias, flushing, hypotension, weight increase.Liothyronine (Cytomel) 25mcg Daily PO Administration: In morning, after breakfast Reason: Hypothyroidism treatment (replace decreased amounts of T4) Classification: Thyroid hormone substitute, with more rapid action and disappearance. Actions: Replacement therapy for diminished/absent thyroid function resulting from primary or
secondary atrophy of gland. Increase in the metabolic rate of all body tissues. Side effects: Irritability, nervousness, HA, tremor, sweating, weight loss
Anatomy
The inner surface of the thoracic cage (parietal pleura) is contiguous with the outer surface of the lung (visceral pleura); this space contains a small amount of lubricating fluid and is normally under negative pressure compared to the alveoli. Determinants of pleural pressure are the opposing recoil forces of the lung and chest wall.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Essential Oil ExtractionDocument159 pagesEssential Oil ExtractionAubrey Hernandez100% (4)
- Cardiovascular Medicine:Question 1Document101 pagesCardiovascular Medicine:Question 1abdullahmushlihPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiac Case StudyDocument12 pagesCardiac Case StudyEdwin Delos Reyes Abu100% (1)
- 2) Vital SignsDocument7 pages2) Vital SignsJudy JalbunaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Case Study Based On Actual PatientDocument6 pagesSample Case Study Based On Actual PatientRamalingam ChandrasekharanPas encore d'évaluation
- Deep Vein ThrombosisDocument38 pagesDeep Vein ThrombosisvincentthedyPas encore d'évaluation
- Amenzade Yu.a. - Theory of Elasticity-Mir (1979)Document284 pagesAmenzade Yu.a. - Theory of Elasticity-Mir (1979)Javier100% (1)
- Case Study PneumothoraxDocument9 pagesCase Study PneumothoraxLee_Cabral_693967% (3)
- Test Taking Tips For The Nursing Board ExamDocument3 pagesTest Taking Tips For The Nursing Board ExamNick Arngel CorporalPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Taking Tips For The Nursing Board ExamDocument3 pagesTest Taking Tips For The Nursing Board ExamNick Arngel CorporalPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Practice of Anesthesiology FinalDocument70 pagesBasic Practice of Anesthesiology FinalAfiqah So JasmiPas encore d'évaluation
- SN3308 Installation Manual Rev J PDFDocument132 pagesSN3308 Installation Manual Rev J PDFsav33Pas encore d'évaluation
- Emergency Room: Case Scenario (Group 1)Document40 pagesEmergency Room: Case Scenario (Group 1)Victoria Castillo TamayoPas encore d'évaluation
- Anna Kingsford, Edward Maitland - The Perfect Way, or The Finding of Christ (1909)Document484 pagesAnna Kingsford, Edward Maitland - The Perfect Way, or The Finding of Christ (1909)Momir Miric100% (1)
- Chest Pain: Sumit Bose, MD PGY-3Document55 pagesChest Pain: Sumit Bose, MD PGY-3Irfan100% (1)
- Post Anesthesia Care UnitDocument19 pagesPost Anesthesia Care UnitRizqidio LarisoPas encore d'évaluation
- Severe Acute Respiratory SyndromeDocument11 pagesSevere Acute Respiratory SyndromeNick Arngel CorporalPas encore d'évaluation
- Truss Design GuidDocument3 pagesTruss Design GuidRafi HasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Arab-Board ExamDocument104 pagesArab-Board Examahmed.farag.ali2020Pas encore d'évaluation
- MKSAP13-Cardiovascular MedicineDocument102 pagesMKSAP13-Cardiovascular MedicineManisha DesaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Alum Rosin SizingDocument9 pagesAlum Rosin SizingAnkit JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Sedation in Critically IllDocument32 pagesSedation in Critically IllSamantha Deshapriya100% (1)
- Emergency and Disaster NursingDocument101 pagesEmergency and Disaster NursingJnll SbPas encore d'évaluation
- LP 1st ObservationDocument6 pagesLP 1st ObservationMichael AnoraPas encore d'évaluation
- ANSWER KEY-RESPIRATORY Assessment and ReasoningDocument9 pagesANSWER KEY-RESPIRATORY Assessment and ReasoningMaryAnn Tiburcio CuevasPas encore d'évaluation
- Plab 2 MaterialDocument24 pagesPlab 2 MaterialradugaPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study HypertensionDocument7 pagesCase Study Hypertensionsanthyakunjumon67% (3)
- 'Batangas Medical Center Case Report by PGI Carlos H. AcuñaDocument7 pages'Batangas Medical Center Case Report by PGI Carlos H. AcuñaCarlos H. AcuñaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anesthesia For Emergency SurgeryDocument85 pagesAnesthesia For Emergency Surgeryansuh22100% (11)
- Alert Medical Series: Emergency Medicine Alert I, II, IIID'EverandAlert Medical Series: Emergency Medicine Alert I, II, IIIPas encore d'évaluation
- Colonoscopy ProcedureDocument2 pagesColonoscopy ProcedureNick Arngel CorporalPas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatric EmergencyDocument98 pagesPediatric Emergencyian ismail100% (5)
- Emergency Drugs (LEAD)Document8 pagesEmergency Drugs (LEAD)RayePrudentePas encore d'évaluation
- Ochure02 03Document2 pagesOchure02 03Nick Arngel CorporalPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan: Epidural Hematoma Post CraniotomyDocument14 pagesNursing Care Plan: Epidural Hematoma Post CraniotomyTepperoni78% (23)
- Respiratory Distress Syndrome (HMD) MODocument77 pagesRespiratory Distress Syndrome (HMD) MOikhsan_drPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute PneumoniaDocument6 pagesAcute PneumoniaMa Clara MolinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study TpapnDocument7 pagesCase Study TpapnAnjali NaudiyalPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study: Cough and A Bad Headache: Entia Non Sunt Multiplicanda Praeter NecessitatemDocument32 pagesCase Study: Cough and A Bad Headache: Entia Non Sunt Multiplicanda Praeter NecessitatemLoren SangalangPas encore d'évaluation
- Case 1 - Pneumonia (Final)Document4 pagesCase 1 - Pneumonia (Final)Joegie ArioPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study Amlodipine & HydrocortisoneDocument4 pagesDrug Study Amlodipine & HydrocortisoneJohn Kristoffer JisonPas encore d'évaluation
- Clerk GCPDocument19 pagesClerk GCPNikki DiocampoPas encore d'évaluation
- HHD 9 Accident EmergencyDocument6 pagesHHD 9 Accident Emergencymusy9999Pas encore d'évaluation
- Potts Disease Case AnalysisDocument5 pagesPotts Disease Case AnalysisAdrian MallarPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 1: Cardiac Arrest I Understand The Ethics of Starting/stopping Resuscitation Withholding CPRDocument79 pagesWeek 1: Cardiac Arrest I Understand The Ethics of Starting/stopping Resuscitation Withholding CPRTessPas encore d'évaluation
- Prehospitalresearch - Eu-Case Study 5 Antero-Lateral STEMIDocument8 pagesPrehospitalresearch - Eu-Case Study 5 Antero-Lateral STEMIsultan almehmmadiPas encore d'évaluation
- "Don't Take My Breath Away" A Case Presentation On Pneumocystis PneumoniaDocument20 pages"Don't Take My Breath Away" A Case Presentation On Pneumocystis PneumoniaNikki DiocampoPas encore d'évaluation
- Criem2015 868519Document4 pagesCriem2015 868519m.fahimsharifiPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study For Cardiorespiratory PhysiotherapyDocument3 pagesCase Study For Cardiorespiratory Physiotherapypp ssPas encore d'évaluation
- CardioDocument9 pagesCardioVirgilio Reyes ManuelPas encore d'évaluation
- BCM 229 General Consideration in AnesthesiaDocument11 pagesBCM 229 General Consideration in AnesthesiaTechnovePas encore d'évaluation
- Cast Study 1Document4 pagesCast Study 1Thelda Mae Arteche SablanPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam in IccuDocument15 pagesExam in IccuDewi AmeliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Emergency Red Flags: DR - Magdy Khames AlyDocument58 pagesEmergency Red Flags: DR - Magdy Khames AlyJerry AblePas encore d'évaluation
- Case Infeksi TetanusDocument36 pagesCase Infeksi TetanusIndri Ayu PratiwiPas encore d'évaluation
- Case ReportDocument16 pagesCase ReportFarah ZahidaPas encore d'évaluation
- CHF DrugDocument50 pagesCHF DrugMhOt AmAdPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Standardized Oral Exam Questions: Session 1 - 35 MinutesDocument4 pagesSample Standardized Oral Exam Questions: Session 1 - 35 MinutesManuela CormioPas encore d'évaluation
- Brinna Anindita Novira WidajantiDocument32 pagesBrinna Anindita Novira WidajantiBrinna Anindita SatriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Documentation in Your 3 Year and Beyond: Summer Quarter 2010Document32 pagesDocumentation in Your 3 Year and Beyond: Summer Quarter 2010Roberto ParedesPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study 2Document27 pagesCase Study 2Hal00mPas encore d'évaluation
- Rapid Sequence Ion EditedDocument52 pagesRapid Sequence Ion EditedSurgicalgownPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study in Competency Appraisal II - ABC and EDNDocument5 pagesCase Study in Competency Appraisal II - ABC and EDNRogelio Saupan Jr100% (1)
- Case Study Jim SandersonDocument6 pagesCase Study Jim SandersonJessica McAlexanderPas encore d'évaluation
- Cristobal, Rocelyn P. MS Lec Post Task Triage FinalDocument10 pagesCristobal, Rocelyn P. MS Lec Post Task Triage FinalRocelyn CristobalPas encore d'évaluation
- USMLE CompilationDocument101 pagesUSMLE CompilationRendi RafsanjaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Advance Cardiac SuppDocument32 pagesAdvance Cardiac SuppVijith.V.kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiogenic ShockDocument3 pagesCardiogenic Shockmerin sunilPas encore d'évaluation
- PTB Pneumonia Chronic Kidney Disease Gout Nephropathy Heart Failure Copd Hypertension CVA Hepatic EncephalopathyDocument1 pagePTB Pneumonia Chronic Kidney Disease Gout Nephropathy Heart Failure Copd Hypertension CVA Hepatic EncephalopathyNick Arngel CorporalPas encore d'évaluation
- Research Paper: Ateneo de Naga University College of NursingDocument5 pagesResearch Paper: Ateneo de Naga University College of NursingNick Arngel CorporalPas encore d'évaluation
- ENA: Weigh Pediatric Patients Only in Kilograms: Monday August 20, 2012Document1 pageENA: Weigh Pediatric Patients Only in Kilograms: Monday August 20, 2012Nick Arngel CorporalPas encore d'évaluation
- EducationDocument1 pageEducationNick Arngel CorporalPas encore d'évaluation
- Untitled 1Document1 pageUntitled 1Nick Arngel CorporalPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 - Physical Properties of Liquid PDFDocument43 pagesChapter 1 - Physical Properties of Liquid PDFrohit sharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- 002-679e-08.19 v1.6.x KLDocument523 pages002-679e-08.19 v1.6.x KLChanon OnramoonPas encore d'évaluation
- 14 Parabola Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument9 pages14 Parabola Formula Sheets QuizrrChandanPas encore d'évaluation
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science Grade 10Document9 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science Grade 10christian josh magtarayoPas encore d'évaluation
- MariaDB Onboarding Databases To Sonar Reference Guide 11-8-2023Document12 pagesMariaDB Onboarding Databases To Sonar Reference Guide 11-8-2023Jateen SoniPas encore d'évaluation
- DEMU COUP - Leviat - 17 1 EDocument28 pagesDEMU COUP - Leviat - 17 1 EJianhua WuPas encore d'évaluation
- Bhsa Inggris'Document5 pagesBhsa Inggris'Dwi NovianaPas encore d'évaluation
- MHR PreCal 12 Textbook CH 1 SolutionsDocument57 pagesMHR PreCal 12 Textbook CH 1 SolutionsBryan LowPas encore d'évaluation
- NSC Solution F2 enDocument8 pagesNSC Solution F2 ensaeidPas encore d'évaluation
- Crop Prot 2 Final Edited (Checked)Document108 pagesCrop Prot 2 Final Edited (Checked)Cortez ReztyPas encore d'évaluation
- Faculty Profile: Dr. Injam Siva ParvathiDocument9 pagesFaculty Profile: Dr. Injam Siva ParvathiMr. Y. RajeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Criteria For Decorative Cosmetics PDFDocument3 pagesCriteria For Decorative Cosmetics PDFsamudra540Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pid 14 MT23 160412Document20 pagesPid 14 MT23 160412Amol ChavanPas encore d'évaluation
- List of Japanese Company in IndiaDocument2 pagesList of Japanese Company in Indiakaushalshinde317Pas encore d'évaluation
- Workbook No. 2 by Jimena SosaDocument125 pagesWorkbook No. 2 by Jimena SosaLourdes de Fatima Pacheco VasquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercises PDFDocument39 pagesExercises PDF910220Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Bath DepositionDocument6 pagesChemical Bath DepositionJune AlapaPas encore d'évaluation
- Aeration PaperDocument11 pagesAeration PapersehonoPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 2 1 1 5b Equipmend Data Sheets CommDocument40 pages2 2 1 1 5b Equipmend Data Sheets CommMilic MilicevicPas encore d'évaluation
- Hostel B Menu From 16 March To 31 March'2024Document4 pagesHostel B Menu From 16 March To 31 March'2024govindkauPas encore d'évaluation
- Design Analysis and Comparison Between The Conventional Materialswith Composite Material of The Leaf Springs Fmoa 1000127Document20 pagesDesign Analysis and Comparison Between The Conventional Materialswith Composite Material of The Leaf Springs Fmoa 1000127Anonymous oTrMzaPas encore d'évaluation
- CERN Courier - Digital EditionDocument33 pagesCERN Courier - Digital EditionFeriferi FerencPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculus II: Prepared By: Cathleen HoboDocument19 pagesCalculus II: Prepared By: Cathleen HoboEspinosa Teves FernanPas encore d'évaluation