Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
00 - Grade 10 Optics Unit Outline
Transféré par
joseftrihandokoTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
00 - Grade 10 Optics Unit Outline
Transféré par
joseftrihandokoDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
SNC2D Optics
Grade 10 Optics Unit Outline 2009-2010 (draft)
(page numbers from Science Perspectives 10, Nelson)
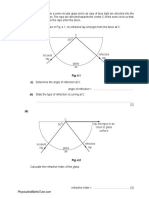
Lesson 1 Topic, Concepts Powerpoint: Introduction to Optics What is light and how is it produced? The Wave Model of Light Short video: Atomic spectra Activity: spectroscopes Powerpoint and demo: Sources of Light The Electromagnetic Spectrum, Math Review Solving equations and unit conversions Measurement, uncertainty, and significant digits Activity: measurement Quiz significant digits, solving equations, unit conversions, sources of light The Ray Model of Light Activity: Property of Light rectilinear propagation (i.e. light travels in straight lines) The Ray Model of Light image formation: camera obscura Camera obscura images (powerpoint) and examples Law of Reflection characteristics and position of images for plane mirrors: angle of incidence = angle of reflection Activity: Mirror Images, angle of incidence and reflection (ray boxes and plane mirrors) Question: how much mirror do you need to see your whole body? Characteristics and position of images for curved mirrors Activity: ray diagrams for mirror images Magnification equation Solar cookers and funhouse mirrors Demonstration: Gizmo/java applet Demonstration: floating pig Refraction of light light bends (speed changes) as it passes from 1 medium to another Demonstration straw bent in glass of water Definition of index of refraction, analogy to car traveling from one surface to another; java applet demo Lab: Refraction through prism or water-filled hemisphere (discovering Snells Law) Refraction II Snells Law: problems and examples Critical angle and total internal reflection demonstration: optical Pages 393-399 Handout questions
384-386 Handout questions Handout questions 479-481
3 4
481-482
420-425
434-439
441-443
SNC2D Optics
waveguides, water waveguide Refraction phenomena demos and powerpoint (disappearing coin demo, mirages, apparent depth, apparent sunset, diamonds) 9 Refraction and Lenses: Types of lenses Activity: ray boxes, convex and concave lenses Investigation: characteristics of images formed by converging lenses (metre stick optical table), magnification, object and image distance, focal length Characteristics and positions of images from the Thin Lens Equation (from the investigation), and ray diagrams; Gizmos or other applet demos Thin Lens Equation problems Properties of mirrors and lenses used in optical instruments (telescopes, microscopes, etc., photography depth of field, fish eye lenses, optical fibres for communications and for medicine); Activity design an optical device or a security system Human perception of light, parts of the eye Vision and colour Activity: vision tests; parts of the eye - how do we see things? Optical illusions Review 454-457, 482-489 448-454
10
11
12
468-477
13
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Physics Review Test - Optics - Grade 10Document11 pagesPhysics Review Test - Optics - Grade 10Arhant KarthikeyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Light and Optics Complete PDFDocument34 pagesLight and Optics Complete PDFJorge Montero Vallejo0% (2)
- Colleen Quinlan Unit Plan - Grade 12 Biology - Molecular GeneticsDocument7 pagesColleen Quinlan Unit Plan - Grade 12 Biology - Molecular Geneticsapi-209047436Pas encore d'évaluation
- Courage to More Money! Financial Freedom by Skills & Mindset: Achieve goals, get rich, negotiate & rise your salary, invest intelligently, learn risk management of the stock marketD'EverandCourage to More Money! Financial Freedom by Skills & Mindset: Achieve goals, get rich, negotiate & rise your salary, invest intelligently, learn risk management of the stock marketPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Mitosis in Plant and Animal CellsDocument4 pagesLab Mitosis in Plant and Animal Cellsc37619Pas encore d'évaluation
- Direct Real Estate Duration Risk, Total Risk and the Residential Mortgage Life Insurance (Rmli)D'EverandDirect Real Estate Duration Risk, Total Risk and the Residential Mortgage Life Insurance (Rmli)Pas encore d'évaluation
- 03 RefractionDocument18 pages03 RefractionHelenPas encore d'évaluation
- Cryptocurrency for Beginners: The Ultimate Digital Tokens Guide. Discover the Blockchain’s World and Start Making Money Using Profitable Trading Strategies.D'EverandCryptocurrency for Beginners: The Ultimate Digital Tokens Guide. Discover the Blockchain’s World and Start Making Money Using Profitable Trading Strategies.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Optics TestDocument2 pagesOptics Testiskenderbey100% (1)
- Course Outline French 5 1Document2 pagesCourse Outline French 5 1api-4757496450% (1)
- Egg Drop ChallengeDocument3 pagesEgg Drop Challengeapi-372546344Pas encore d'évaluation
- How to Make It When You're Cash Poor (Review and Analysis of Norton's Book)D'EverandHow to Make It When You're Cash Poor (Review and Analysis of Norton's Book)Pas encore d'évaluation
- French Core Grade 7Document1 pageFrench Core Grade 7api-296985446Pas encore d'évaluation
- How To LearnDocument43 pagesHow To LearnJoannaLinPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 8 - Science Unit PlanDocument2 pagesGrade 8 - Science Unit Planapi-349366941Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electron Microscopy: Fundamentals: Chemistry 445 Spring 2004Document31 pagesElectron Microscopy: Fundamentals: Chemistry 445 Spring 2004Simona TocaniePas encore d'évaluation
- OCD2 MetrologyDocument15 pagesOCD2 MetrologyGAURAV PANDEYPas encore d'évaluation
- MIT2 71S14 Lec2 NotesDocument16 pagesMIT2 71S14 Lec2 NotesPrasad AurangabadkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Reflection and Refraction of LightDocument44 pagesReflection and Refraction of LightArman Akram100% (1)
- S3 Physics 2015016 Light STUDENT 2015septDocument80 pagesS3 Physics 2015016 Light STUDENT 2015septMila VujovicPas encore d'évaluation
- IntroductiontoMicros PDFDocument74 pagesIntroductiontoMicros PDFFakhri KAPas encore d'évaluation
- Introductionto MicrosDocument74 pagesIntroductionto MicrosBrahim TamaaratPas encore d'évaluation
- Ncert 12 Physics 2Document254 pagesNcert 12 Physics 2shivaraj p86% (7)
- Light Microscopy: Basic Principles and Concepts: Carlo Bevilacqua Prevedel GroupDocument33 pagesLight Microscopy: Basic Principles and Concepts: Carlo Bevilacqua Prevedel Groupalvise30Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introductionto MicrosDocument74 pagesIntroductionto MicrosHuzaifa SyedPas encore d'évaluation
- MSN-518 SyllabusDocument2 pagesMSN-518 SyllabusTalha Masood KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan For SS2 Physics 3RD TermDocument13 pagesLesson Plan For SS2 Physics 3RD Termowei prosperPas encore d'évaluation
- Untitled DocumentDocument2 pagesUntitled DocumentprabhkangecommercePas encore d'évaluation
- SpectroscopyOfDeepSpaceObjectsUsingHomemadeDobsonianTelescope by ConleyDitsworthJr Fall2004Document20 pagesSpectroscopyOfDeepSpaceObjectsUsingHomemadeDobsonianTelescope by ConleyDitsworthJr Fall2004neurolordPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus For Optical Engg.Document16 pagesSyllabus For Optical Engg.ersumitkmrPas encore d'évaluation
- Compound Light MicroscopeDocument7 pagesCompound Light MicroscopeAila Janella ValdezPas encore d'évaluation
- (Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology) Robert Allen Meyers (Editor) - Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology - Optics-Academic Press (2001)Document344 pages(Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology) Robert Allen Meyers (Editor) - Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology - Optics-Academic Press (2001)Enzo Victorino Hernandez AgressottPas encore d'évaluation
- Karakterisasi Material 2Document52 pagesKarakterisasi Material 2George Amos BastianPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Geometrical Optics Fundamentals of PhotonicsDocument44 pagesBasic Geometrical Optics Fundamentals of PhotonicsYasser SabryPas encore d'évaluation
- NCERT Class 12 Physics Part 2 PDFDocument254 pagesNCERT Class 12 Physics Part 2 PDFprasadr67% (3)
- Foundations of Astronomy 13th Edition Seeds Solutions ManualDocument11 pagesFoundations of Astronomy 13th Edition Seeds Solutions Manualselenatanloj0xa100% (20)
- Introduction To Electron Microscopy and MicroanalysisDocument56 pagesIntroduction To Electron Microscopy and MicroanalysisPerlita2013100% (1)
- Chapter 1. Hieenr ViDocument60 pagesChapter 1. Hieenr ViTruong DucQuangPas encore d'évaluation
- Astronomical Telescope PhysicsDocument23 pagesAstronomical Telescope PhysicsRudra Pratap Patasani100% (1)
- Activity 1 Post-LabDocument44 pagesActivity 1 Post-LabAko Si Vern ÖPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 1Document53 pagesLecture 1Aalim KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- HPH103 - Waves and Optics 1 - Lecture # 10-1Document45 pagesHPH103 - Waves and Optics 1 - Lecture # 10-1Praise NehumambiPas encore d'évaluation
- Optical Mineralogy PropertiesDocument51 pagesOptical Mineralogy PropertiesAkqueza MendonçaPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment On Focal Length FinalDocument7 pagesExperiment On Focal Length Finallemigobena12Pas encore d'évaluation
- Art and Integrated Project Topic Telescope PhysicsDocument8 pagesArt and Integrated Project Topic Telescope PhysicsAditya SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Semester - IIIDocument6 pagesSemester - IIIWaaiz MohammedPas encore d'évaluation
- OpticsDocument2 pagesOpticsPrasanthPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Notes-1Document28 pages4 Notes-1SAJITH NFPas encore d'évaluation
- Intro To Astronomy - TelescopesDocument10 pagesIntro To Astronomy - TelescopessivuyisoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab ManualDocument21 pagesLab ManualMetal deptPas encore d'évaluation
- Refraction of Light and Lenses 1Document23 pagesRefraction of Light and Lenses 1dmykd9j9jrPas encore d'évaluation
- Subject Board For Physics: Course SyllabiDocument38 pagesSubject Board For Physics: Course SyllabiAbhishek UpadhyayPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.1 Optical Telescopes (UV, Visible, IR)Document68 pages3.1 Optical Telescopes (UV, Visible, IR)dkbradleyPas encore d'évaluation
- Psphystestju 04Document8 pagesPsphystestju 04joseftrihandokoPas encore d'évaluation
- Psphysicstestju 03Document8 pagesPsphysicstestju 03joseftrihandokoPas encore d'évaluation
- 9th Grade - Exercise On Dynamic ElectricityDocument1 page9th Grade - Exercise On Dynamic ElectricityjoseftrihandokoPas encore d'évaluation
- Blank Lesson Planning Template (UbD) With Calendar GridDocument1 pageBlank Lesson Planning Template (UbD) With Calendar GridjoseftrihandokoPas encore d'évaluation
- Psphystestju 02Document8 pagesPsphystestju 02joseftrihandokoPas encore d'évaluation
- PSP 108Document8 pagesPSP 108joseftrihandokoPas encore d'évaluation
- Psphystestau 02Document6 pagesPsphystestau 02joseftrihandokoPas encore d'évaluation
- Psphysics Exam Ja04Document8 pagesPsphysics Exam Ja04joseftrihandokoPas encore d'évaluation
- Psphystestja 03Document9 pagesPsphystestja 03joseftrihandokoPas encore d'évaluation
- PSP 606Document8 pagesPSP 606joseftrihandokoPas encore d'évaluation
- PSP 106Document10 pagesPSP 106joseftrihandokoPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Exam 608Document9 pagesPhysics Exam 608joseftrihandokoPas encore d'évaluation
- PSP 605Document7 pagesPSP 605joseftrihandokoPas encore d'évaluation
- Phytestjan 02Document17 pagesPhytestjan 02joseftrihandokoPas encore d'évaluation
- Phystestju 01Document19 pagesPhystestju 01joseftrihandokoPas encore d'évaluation
- PSP 607Document7 pagesPSP 607joseftrihandokoPas encore d'évaluation
- PSP 107Document10 pagesPSP 107joseftrihandokoPas encore d'évaluation
- Physicssamp 1Document15 pagesPhysicssamp 1joseftrihandokoPas encore d'évaluation
- Phystestja 05Document8 pagesPhystestja 05joseftrihandokoPas encore d'évaluation
- Phys 697Document19 pagesPhys 697joseftrihandokoPas encore d'évaluation
- Phys 698Document21 pagesPhys 698joseftrihandokoPas encore d'évaluation
- Phys 699Document25 pagesPhys 699joseftrihandokoPas encore d'évaluation
- Phys 0600Document21 pagesPhys 0600joseftrihandokoPas encore d'évaluation
- Phys 0101Document17 pagesPhys 0101joseftrihandokoPas encore d'évaluation
- PB 1999Document8 pagesPB 1999joseftrihandokoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pbowl 00Document9 pagesPbowl 00joseftrihandokoPas encore d'évaluation
- PB 1996Document10 pagesPB 1996joseftrihandokoPas encore d'évaluation
- PB 1998Document8 pagesPB 1998joseftrihandokoPas encore d'évaluation
- PB 1997Document9 pagesPB 1997joseftrihandokoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ray Optics - DPP 10 (Of Lecture 23)Document3 pagesRay Optics - DPP 10 (Of Lecture 23)Anmol KaushikPas encore d'évaluation
- Ray OpticsDocument31 pagesRay OpticsAnonymous a2kZINkPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics II Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSPas encore d'évaluation
- 77 Topper 21 101 2 4 62 Light Reflection and Refraction Up201807101458 1531214913 5575 PDFDocument10 pages77 Topper 21 101 2 4 62 Light Reflection and Refraction Up201807101458 1531214913 5575 PDFsudhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Amity International School Noida CLASS X (2021-22) Ch. Light-Reflection & Refraction MLP Worksheet-2Document2 pagesAmity International School Noida CLASS X (2021-22) Ch. Light-Reflection & Refraction MLP Worksheet-2Anushka TripathiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 8 Light and OpticsDocument2 pagesChapter 8 Light and OpticsMei Yun LiewPas encore d'évaluation
- 2021 - Rivision Unit 2 Part 4Document30 pages2021 - Rivision Unit 2 Part 4Sanvidu RathnayakePas encore d'évaluation
- 3rd Prep ScienceDocument16 pages3rd Prep ScienceAboahmed AliPas encore d'évaluation
- HKDSE PHY Ch3Document9 pagesHKDSE PHY Ch3Chloe ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Light Form 4 (Phsics)Document24 pagesLight Form 4 (Phsics)saffiya imanPas encore d'évaluation
- Pages From 0625 - s15 - QP - 31-01Document1 pagePages From 0625 - s15 - QP - 31-01lelon81Pas encore d'évaluation
- Coeficiente Roce MaterialesDocument7 pagesCoeficiente Roce MaterialesjomirosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Refraction Worksheet 1Document2 pagesRefraction Worksheet 1tharanga100% (1)
- Worksheet - Ray OpticsDocument2 pagesWorksheet - Ray OpticsAnubhav SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Light 4 QPDocument9 pagesLight 4 QPahmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Reflection, Refraction, and DiffractionDocument18 pagesReflection, Refraction, and Diffractionjaymart villartaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.9 Interference FiguresDocument33 pages1.9 Interference FigureswessilissaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cbse Test Paper-01 Class - Xii Physics (Ray Optics) : T D R When R T D R RDocument4 pagesCbse Test Paper-01 Class - Xii Physics (Ray Optics) : T D R When R T D R RrahulPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan: Mohdruza@uitm - Edu.myDocument3 pagesLesson Plan: Mohdruza@uitm - Edu.myEronecca Benidict100% (1)
- Physics Experiment Report (V) Basic Physics "Total Internal Reflection"Document9 pagesPhysics Experiment Report (V) Basic Physics "Total Internal Reflection"JeclinPas encore d'évaluation
- Prism Experiment PhysicsDocument16 pagesPrism Experiment PhysicsSakshi GodaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Image Formation in Lenses.Document5 pagesImage Formation in Lenses.Syed AkramPas encore d'évaluation
- Geometrical Optics - LensDocument10 pagesGeometrical Optics - LensMannyCesPas encore d'évaluation
- Phy BK Ans 3aDocument24 pagesPhy BK Ans 3aapi-253498969Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ray Optics Worksheet 1Document2 pagesRay Optics Worksheet 1Karthika UmashankarPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument17 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectTapash SunjunuPas encore d'évaluation
- MetamterialsDocument3 pagesMetamterialsdhruba88Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rayoptics CasebasedDocument12 pagesRayoptics CasebasedDisha RawatPas encore d'évaluation
- E3877 Optics FormulasDocument6 pagesE3877 Optics FormulasKaran DoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Bicknell, Apeiron, Apeiros Aer, PeriexonDocument23 pagesBicknell, Apeiron, Apeiros Aer, Periexonchr_maxmannPas encore d'évaluation