Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Technical Report
Transféré par
redheadgirl25Description originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Technical Report
Transféré par
redheadgirl25Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
RUNNING HEAD: ABORTION
Abortions Technical Report Lyndsay Paradise August 13, 2012 Brain Jean Stats 1510 Online
RUNNING HEAD: ABORTION Abstract Abortion is one of the most common medical procedures performed in the United States each year. More than 40% of all women will end a pregnancy by abortion. Of these unplanned pregnancies, about half end in abortion. Before the 19th century, most US states had no specific abortion laws. Women were able to end a pregnancy prior to viability with the assistance of medical personnel. The next 20 years saw the passing of a series of laws restricting abortion. Introduction
Most abortions are performed after your doctor or health care provider takes a medical report. The provider will ask whether you have a history of diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disease, anemia, bleeding disorders, or surgery. A brief physical examination is usually performed before an abortion also. The main goal is to figure out when your pregnancy began and whether you are healthy enough to go through the procedure.
Participants /Methods /Materials
Women living below the federal poverty line abort at a higher rate than women living above the poverty line (Guttmacher Institute. 2008, July. Facts on Induced Abortion in the United States. http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/fb_induced_abortion.html).
RUNNING HEAD: ABORTION
Providers of abortions are generally specialists in women's health such as obstetricians and gynecologists. However, many studies have shown the safety of allowing a variety of other health care providers (physicians, physician assistants, midwives, and nurse practitioners) to perform these procedures. According to the Guttmacher Institute abortion breaks down along racial/ethnic lines as follows:
White: 34%
Black: 37%
Hispanic: 22%
Other: 7%
Procedure
Some of the procedures done are as follows:
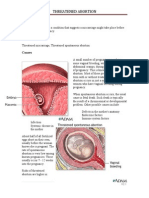
Dilation and Curettage (D&C) In a D&C (dilation and curettage) abortion, typically performed in the first trimester, a curette (a sharp looped knife) is inserted into the uterus to scrape its walls.
RUNNING HEAD: ABORTION The curette is then used to dismember the fetus and placenta (Willke, John, MD and Barbara Willke).
Dilation and Evacuation (D&E) A D&E (dilation and evacuation) abortion is typically performed in the first half of the second trimester (13-20 weeks), but can be used up to approximately 28 weeks. At this stage of pregnancy, the fetus tendons, muscles, and bones are more developed. In a D&E abortion, forceps are inserted into the uterus to forcibly dismember the fetus, and the pieces are removed one by one. Larger fetuses must also have their skulls crushed so the pieces can pass through the cervix. Typically, the cervix must be dilated for a period of one to three days prior to a D&E abortion. This is most often done by inserting laminaria (dried seaweed sticks) into the cervix. Therefore, a D&E abortion usually requires two visits to the abortion facility. (Willke, John, MD and Barbara Willke).
Dilation and Extraction (D&X or Partial-birth Abortion) A D&X (dilation and extraction) or partial-birth abortion is typically performed in the late second or third trimester. As with a D&E abortion (see above), the cervix must first be dilated, usually with laminaria (dried seaweed sticks). Forceps are then inserted into the uterus to grasp the fetus legs. The fetus is delivered breech while the head remains inside the birth canal. Using blunt-tipped surgical scissors, the base of the skull is pierced, and a suction catheter is inserted to extract the contents of the skull. This causes the skull to collapse, and the dead fetus is then fully delivered. Despite the fact that the United States Supreme Court upheld the federal Partial-Birth Abortion Ban Act in 2007, D&X abortions are still being performed. An abortionist can avoid violating the law by first injecting the fetus with a lethal intracardiac injection to ensure that the fetus will already be dead when it is partially delivered (Willke, John, MD and Barbara Willke).
RUNNING HEAD: ABORTION
Instillation (Saline) Abortion In a saline abortion, amniotic fluid is removed from the uterus and replaced with a saline solution, which the fetus swallows. The fetus is killed by salt poisoning, dehydration, brain hemorrhage and convulsions. Saline abortions, typically performed in the second and early third trimester, are rarely used today, due to the risk of particularly serious health complications to the woman.
Prostaglandin Abortion In a prostaglandin abortion, a dose of prostaglandin hormones is injected into the uterine muscle, which induces violent labor resulting in the death of the fetus. Prostaglandin abortions, typically performed in the second and early third trimester, are rarely used today, due to the relatively high chance that the fetus will survive the abortion and be born alive.
Results
Gestational Age Percentage Yearly total
< 9 weeks 61.8%
9-10 weeks 17.1%
11-12 weeks 9.1%
13-15 weeks 6.6%
16-20 weeks 3.8%
RUNNING HEAD: ABORTION 21+ weeks 1.5%
All abortions (100%) 1.2 million
This means that approximately 89% of abortions occur in the first trimester (first 12 weeks) of pregnancy.
The age breakdown of women having abortions, according to the Centers for Disease Control, is as follows:
Less than 15 years: < 0.5%
Age 15-19: 16.4%
Age 20-24: 32.6%
Age 25-29: 23.4%
Age 30-34: 14.5%
RUNNING HEAD: ABORTION Age 35-39: 8.7%
Age 40+: 3.2%
This means that half of all abortions are performed on women 24 years old or younger.
Discussion Laws address a variety of controversial questions including:
Should spouses be notified before a woman has an abortion? Should public funds be used for abortions? What regulations if any should apply to abortion providers? What provisions might be made against specific abortion techniques? Should emergency contraception be allowed? Should the rules be different in cases of sexual assault and rape?
RUNNING HEAD: ABORTION References Trupin, Suzanne R, MD. (6/20/2007). Abortion. http://www.emedicinehealth.com/abortion/article_em.htm
Willke, John, MD and Barbara Willke. 2003. Abortion: Questions & Answers. Cincinnati: Hayes Publishing Company. The Guttmacher Institute. http://www.whyprolife.com/abortion-facts/
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Complications of PregnancyDocument33 pagesComplications of PregnancyMilagros Maglasang100% (1)
- It's Not Just a Heavy Period; The Miscarriage HandbookD'EverandIt's Not Just a Heavy Period; The Miscarriage HandbookÉvaluation : 2 sur 5 étoiles2/5 (1)
- Medical Transcription Sample OBDocument8 pagesMedical Transcription Sample OBAngelo AlbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Abortion Is The Termination of Pregnancy by The Removal or Expulsion From The Uterus of ADocument7 pagesAbortion Is The Termination of Pregnancy by The Removal or Expulsion From The Uterus of ALauren YoungPas encore d'évaluation
- Evaluation of Fetal DeathDocument9 pagesEvaluation of Fetal DeathVinisia TakaraiPas encore d'évaluation
- Family BookDocument9 pagesFamily BookYakubu AliuPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study For OB Skills DocxDocument14 pagesCase Study For OB Skills DocxMaica QuilangPas encore d'évaluation
- Villena - Embryo Final AssignmentDocument4 pagesVillena - Embryo Final AssignmentKaelPas encore d'évaluation
- AbortionDocument4 pagesAbortionDr. Muha. Hasan Mahbub-Ur-RahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Brief DescriptionDocument7 pagesBrief DescriptionPrincess Pilove GawongnaPas encore d'évaluation
- MiscarriageDocument4 pagesMiscarriageJack BangcoyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pregnancy Uterus Fetus Embryo: Morbidity Selectively Reduce Multiple PregnancyDocument4 pagesPregnancy Uterus Fetus Embryo: Morbidity Selectively Reduce Multiple Pregnancynyzgirl17Pas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study MiscariageDocument14 pagesCase Study MiscariagesexiiimammaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 17Document21 pagesUnit 17Bhaiya KamalenduPas encore d'évaluation
- Abortion TypesDocument19 pagesAbortion TypesFany MaldoPas encore d'évaluation
- Rejina Raita Class - Xii Roll No-Mr. Ashutosh Subudhi: Abortion in IndiaDocument12 pagesRejina Raita Class - Xii Roll No-Mr. Ashutosh Subudhi: Abortion in IndiaCSC LanjipadarPas encore d'évaluation
- AbortionDocument19 pagesAbortionjeza_nolasco100% (2)
- Case Study #1: AbortionDocument42 pagesCase Study #1: AbortionJhoanne DelloroPas encore d'évaluation
- Abortion PaperbackDocument89 pagesAbortion PaperbackLarryPas encore d'évaluation
- AbortionDocument32 pagesAbortioncherubrockPas encore d'évaluation
- Antenatal AssessmentDocument40 pagesAntenatal AssessmentKailash NagarPas encore d'évaluation
- YULIYANTODocument5 pagesYULIYANTOadehendriePas encore d'évaluation
- Disorders of Female Reproductive SystemDocument6 pagesDisorders of Female Reproductive SystemjoannaPas encore d'évaluation
- MiscariageDocument17 pagesMiscariagemitchillPas encore d'évaluation
- ScriptDocument1 pageScriptCharlie M LozaritaPas encore d'évaluation
- StillbirthDocument4 pagesStillbirthTubagus Siswadi WijaksanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Abortion, What Is ItDocument3 pagesAbortion, What Is ItAssero EricPas encore d'évaluation
- Abortion Facts: Alan Guttmacher InstituteDocument4 pagesAbortion Facts: Alan Guttmacher InstituteDekwerizPas encore d'évaluation
- Abortion and The 21st CenturyDocument5 pagesAbortion and The 21st CenturyReiVanPas encore d'évaluation
- Atypical Ductal HyperplasiaDocument6 pagesAtypical Ductal HyperplasiapgalamilloPas encore d'évaluation
- AbortionDocument7 pagesAbortionDiego MontoyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Day 4 Placenta Previa Abruptio Placenta....Document51 pagesDay 4 Placenta Previa Abruptio Placenta....Marga WreathePas encore d'évaluation
- Threatened Abortion PDFDocument3 pagesThreatened Abortion PDFAizat KamalPas encore d'évaluation
- Research Paper For AbortionDocument10 pagesResearch Paper For AbortionMarevisha Vidfather75% (4)
- AbortionDocument18 pagesAbortionfadhli-bin-hj-ahmad-3390Pas encore d'évaluation
- Classification: Miscarriage or Spontaneous Abortion Is The Spontaneous End of A Pregnancy at ADocument9 pagesClassification: Miscarriage or Spontaneous Abortion Is The Spontaneous End of A Pregnancy at AAnn GelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Abortion SolenyDocument123 pagesAbortion SolenyAyalewPas encore d'évaluation
- Before Starting The Presentation, I Am Requesting You All To Get A HandkerchiefDocument35 pagesBefore Starting The Presentation, I Am Requesting You All To Get A HandkerchiefOng KarlPas encore d'évaluation
- Health Ethics & Bioetical IssuesDocument76 pagesHealth Ethics & Bioetical Issuesmers puno100% (3)
- Ectopic Pregnancy - CenitaDocument15 pagesEctopic Pregnancy - CenitaPrincess Huey GreyPas encore d'évaluation
- 14 Abortion Noted PDFDocument37 pages14 Abortion Noted PDFmohammed farajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Uterus: Signs and SymptomsDocument11 pagesUterus: Signs and SymptomsJoy Parallag - BautoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ectopic Pregnancy: Medlineplus TopicsDocument9 pagesEctopic Pregnancy: Medlineplus TopicsJonathan BendecioPas encore d'évaluation
- AbortionDocument57 pagesAbortionThanga Durai100% (1)
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument17 pagesEctopic PregnancyB.HemavarshiniPas encore d'évaluation
- AbortionDocument18 pagesAbortionLalit PacPas encore d'évaluation
- Abdominal Pain in The Pregnant Patient Ectopics MRI and MoreDocument22 pagesAbdominal Pain in The Pregnant Patient Ectopics MRI and Morequester1515Pas encore d'évaluation
- Abortion & Abnormalities of Early PregnancyDocument20 pagesAbortion & Abnormalities of Early PregnancyHasan DahamshehPas encore d'évaluation
- Bioethics-Abortion-And-Euthanasia 2Document3 pagesBioethics-Abortion-And-Euthanasia 2Alvin Josh CalingayanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 5-The Process of ReproductionDocument25 pagesLesson 5-The Process of ReproductionDiana HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- MCN - Individual Activity 3Document23 pagesMCN - Individual Activity 3AngelicaJaneA.SuanPas encore d'évaluation
- Fetal Dev, AbortionDocument128 pagesFetal Dev, AbortionAr JayPas encore d'évaluation
- Abortion: Abortion Is Defined As The Termination ofDocument14 pagesAbortion: Abortion Is Defined As The Termination oflemersonlPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 - Abortion or MiscarriageDocument43 pages5 - Abortion or Miscarriageasifdawar2011Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gestational AgeDocument34 pagesGestational AgeAaliyaan KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ectopic Pregnancy: MoreDocument18 pagesEctopic Pregnancy: Moreaaaaa_01Pas encore d'évaluation
- AbortionDocument35 pagesAbortionZahida Aida Ida Paramore100% (1)
- Hysterectomy A-Z: Why, When, How and What afterD'EverandHysterectomy A-Z: Why, When, How and What afterÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (2)
- Revised OB Handout Part 2 MAY 2023 PNLE RefresherDocument9 pagesRevised OB Handout Part 2 MAY 2023 PNLE RefresherMatelyn OargaPas encore d'évaluation
- BreechDocument2 pagesBreechBrel KirbyPas encore d'évaluation
- Obstructed Labor AND ITS CAUSE, CORD PROLAPS AND PRESENTATIONDocument59 pagesObstructed Labor AND ITS CAUSE, CORD PROLAPS AND PRESENTATIONmaezu100% (2)
- Induction of LaborDocument19 pagesInduction of LaborMomshie Felaih Binasoy Dela CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- ANTEPARTUM HEMORRHAGE - Afina RazibDocument11 pagesANTEPARTUM HEMORRHAGE - Afina Razibرفاعي آكرمPas encore d'évaluation
- Antepartum & Postpartum HemorrhageDocument68 pagesAntepartum & Postpartum HemorrhageZee YongPas encore d'évaluation
- Mal PresentationsDocument4 pagesMal Presentationsإسراء محمودPas encore d'évaluation
- CTG, PartogramDocument7 pagesCTG, PartogramEtana AdamPas encore d'évaluation
- OLIGOHYDRAMNIOSDocument27 pagesOLIGOHYDRAMNIOSSimi SaiPrasoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Abortion EssayDocument3 pagesAbortion EssayAndrew BennettPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 21: Nursing Care of A Family Experiencing A Sudden Pregnancy ComplicationDocument9 pagesChapter 21: Nursing Care of A Family Experiencing A Sudden Pregnancy ComplicationAlyssaGrandeMontimor100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of ChorioamnionitisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Chorioamnionitisjhobarry0% (1)
- Abnormalities of Placenta and CordDocument47 pagesAbnormalities of Placenta and CordShrooti Shah75% (4)
- Intern Roster September Part 1Document5 pagesIntern Roster September Part 1Ashim mondalPas encore d'évaluation
- Demographics Abortion PhilippinesDocument3 pagesDemographics Abortion PhilippinesspringdingPas encore d'évaluation
- Marcus Gordon, M.D.'S Massachusetts Physician License Applications Part 1Document31 pagesMarcus Gordon, M.D.'S Massachusetts Physician License Applications Part 1crush2482Pas encore d'évaluation
- Antenatal Class: Prof DR Jamil Mohd SharifDocument61 pagesAntenatal Class: Prof DR Jamil Mohd SharifNoor ShuhaadahPas encore d'évaluation
- Pregnancy (Y)Document64 pagesPregnancy (Y)Mohamed AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- Very Advanced Maternal Age, TOG-2021Document10 pagesVery Advanced Maternal Age, TOG-2021saeed hasan saeedPas encore d'évaluation
- Daftar Pustaka FixxxxDocument4 pagesDaftar Pustaka FixxxxRahmawati HamudiPas encore d'évaluation
- Coding BPJS KesehatanDocument3 pagesCoding BPJS Kesehatananang tri joe100% (1)
- Determining-Gravidity-And-Parity and How To Solve For AOG and EDDDocument15 pagesDetermining-Gravidity-And-Parity and How To Solve For AOG and EDDJoseph Hechanova AsenjoPas encore d'évaluation
- SDL Abruptio Placenta Vs Placenta PreviaDocument3 pagesSDL Abruptio Placenta Vs Placenta PreviaVannesa TarifaPas encore d'évaluation
- AbortionDocument24 pagesAbortionkashyap priyankaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mayzen Tita Loka - RMIK B1 - Praktikum 13 Lat 12 - KSGKDocument2 pagesMayzen Tita Loka - RMIK B1 - Praktikum 13 Lat 12 - KSGKTita LokaPas encore d'évaluation
- Common ManagementDocument7 pagesCommon ManagementaslanPas encore d'évaluation
- Abruptio Placenta B-1Document29 pagesAbruptio Placenta B-1drsachinhPas encore d'évaluation
- Abortus Spontaneous Incomplete With Previous Curettage InfectionDocument4 pagesAbortus Spontaneous Incomplete With Previous Curettage InfectionNofita AizzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Research ProposalDocument45 pagesResearch ProposalBoruuf If GammachuuPas encore d'évaluation
- Jurnal Ilmu Kedokteran Dan Kesehatan, Volume 7, Nomor 1, Januari 2020 393Document8 pagesJurnal Ilmu Kedokteran Dan Kesehatan, Volume 7, Nomor 1, Januari 2020 393Nurhalimah HarahapPas encore d'évaluation