Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Bio SPM Intervensi m1
Transféré par
teahockTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Bio SPM Intervensi m1
Transféré par
teahockDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
LATIH TUBI BIOLOGI SPM JABATAN PELAJARAN KEDAH MODUL 1 TOPIC: CELL STRUCTURE AND CELL ORGANISATION SECTION
A: OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS Answer all the questions 1. The diagram shows the structure of a plant cell as seen under light microscope. Which of the parts A, B, C or D controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell?
2.
The diagram shows the structure of an animal cell. Which of the structures A, B, C or D has chromosomes in it?
3.
The diagram shows a plant cell. Which of the structures A, B, C or D is tonoplast?
4.
In which of the following is mitochondrion most abundantly found? A An ovum C A nerve cell B A sperm cell D A monocyte The diagram shows an organelle.
5.
What A B C D
is the function of the organelle? to generate energy to synthesise protein to control the activities of the cell to act as the site for photosynthesis
6.
Which of the following is correct about the cellular structure and its function? Cellular structure Ribosome Lysosome Cell wall Rough endoplasmic reticulum Function To synthesise lipids To produce energy To control the passage of materials in and out of the cells To transport proteins to the Golgi apparatus
A B C D
7.
Which substance acts as the medium for chemical reactions in the cell? A Water C Fatty acid B Glucose D Amino acid What is the purpose of adding iodine solution to the onion epidermis when observing it under the microscope? A To test for starch B To separate the cells C To kill the cells D To stain the cells Which of the following organelles are involved in protein synthesis? I Nucleus II Ribosomes III Golgi apparatus IV Rough endoplasmic reticulum A B C D I and II only I, III and IV only II, III and IV only I, II, III and IV apparatus is found in abundance in liver cells pancreatic cells interstitial cells in the testes goblet cells in the intestinal epithelium I and III only II and IV only I, II and III only II, III and IV only
8.
9.
10.
Golgi I II III IV A B C D
11.
Which of the following represents the heart? A Cell C Organ B Tissue D System Cell specialization is important in A Enabling the different type of cells to function efficiently B Enabling the different type of cells to function simultaneously C Enabling the organs to control their excretory products D Enabling the cells to divide at a faster rate
12.
13.
The diagram below shows an organ system.
What I II III IV A C 14.
are the functions of the organ system shown above? To transport oxygen to the body cells To defend the body against diseases To remove metabolic wastes To help regulate the volume and composition of blood I and II only B I and III only II and IV only D III and IV only IV Phloem
Which of the following are organs of plants? I Xylem II Roots III Leaves A I and II only B II and III only C I, II and III only D I, II, III and IV
15.
Which similarity between Amoeba sp. and Paramecium sp. listed below is true? A Both of them move in the same way B Both of them have the same shape C Both of them are unicellular organisms D Both of them feed in the same way. The diagram below shows a type of muscle tissue found in the human body. Where is the tissue found?
16.
A B 17.
Heart Pancreas
C D
Pancreas Small intestine
The diagram below shows the structure of a cell organelle.
Which cell does not possess the organelle shown in the diagram? A Guard cell B Epidermis cell C Spongy mesophyll cell
18.
D Palisade mesophyll cell Which substance acts as the medium for chemical reactions in the cell? A Water B Glucose C Fatty acid D Amino acid Which sequence correctly shows the involvement of organelles in protein synthesis? A mRNA, DNA, ribosome, rough endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus B DNA, mRNA, ribosome, Golgi apparatus, rough endoplasmic reticulum C mRNA, DNA, rough endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, ribosome D DNA, mRNA, ribosome, rough endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus The diagram shows the cell organelles involved in the synthesis of proteins.
19.
20.
Which of the following statements are true about the diagram? I Synthesis of protein occurs at Q II The synthesised protein are modified in R III Chromosomes in P carry the information for the synthesis of proteins IV The proteins travel through T without any change and is then released through S A I and III only B II and IV only C I, II and III only D I, II, III and IV SECTION B: STRUCTURED QUESTIONS Answer all questions in this section. 1. Diagram 1 shows two types of cells.
Diagram 1 (a) Suggest one difference between cell A and cell B.
[1 marks]
(b) (i)
For each of the following cells, state one way in which it is different from cell B in Diagram 1. How does this difference help the cell to function efficiently? Sperm cell:
(ii) Red blood cell:
[4 marks] ( c ) (i) Name the structures labelled K and L. K: . L: .. [2 marks] (ii) What are structures K and L made of? [2 marks] (iii) State the special features of structures K and L. [2 marks] (iv) Explain how the compound in structure L helps it to carry out its function. [2 marks] 2. Diagram 2 shows two types of organelles found in the cell.
Diagram 2
(a)(i)
Name organelles P and Q.
P: Q: . [1 mark]
(ii)
State the type of tissues where organelle P and Q can be found in large numbers.
[2 marks] (b) Both organelles are involved in physiological processes of living cells. Explain the importance of both organelles to the cells.
[2 marks] (c) What are the differences between the reactions which take place in organelle P in an oxygenrich condition and in an oxygen-deficient condition?
[3 marks] (d) Explain the role of structure X in helping organelle Q carries out its function.
[3 marks] 3. Diagram 3 shows the structure of a leaf cell as seen under a light microscope.
Diagram 3 (a) On Diagram 3, label the parts P, Q, R and S. [2 marks]
(b)(i) (ii)
On Diagram 3, use the letter T to label the part of the cell where food is made. [1 mark] State the part of the leaf where T is most abundantly found.
[1 mark] (iii) Explain how T is adapted for the making of food. [2 marks] (c) In making food, water is needed by the cell. Water enters the plant through the roots. The roots have cells called the root hair cells. (i) In the space below, draw and label hair cell as seen under a microscope.
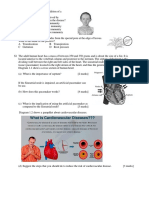
[2 marks] (ii) Give two differences between the root hair cell and the cell shown in Diagram 3. [2 marks] (d) Describe how water is absorbed by the root hair. [2 marks] SECTION C: ESSAY QUESTION 1. Diagram 4 shows five levels of cell organisation in man.
Diagram 4 (a) Describe the cell organisation in the formation of tissues, organs and systems based on the example of the digestive system of man shown in Diagram 4. [10 marks] (b)
MOST CELLS ARE SPECIALISED FOR THE FUNCTIONS THAT THEY PERFORM
Explain how the following cells are adapted for their functions: (i) (ii) Parenchyma cells Red blood cells [10 marks]
MARKING SCHEME MODUL 1 TOPIC: CELL STRUCTURE AND CELL ORGANISATION SECTION A: Objektive questions: 1B 11C 2D 12A 3C 13D 4B 14B 5D 15C 6D 16A 7A 17B 8D 18A 9D 19D 10B 20A
SECTION B: Structured Questions 1. (a) Cell A contain chloroplast, vacuoles and has a cell wall, all of which are not found in cell B. (b) (i) A sperm cell has a tail and a high density of mitochondria which allow it to swim towards an ovum. (ii) A red blood cell does not have a nucleus. This increases the total surface area to volume ratio for the rapid diffusion of gases (c) (i) K: Plasma membrane L: Cell wall (ii) K is made of proteins and phospholipids. L is made of cellulose. (iii) K is semi-permeable or selectively permeable. L is permeable to all substances. (iv) Cellulose fibre is tough and fairly rigid. It enables the cell wall to provide support, strength and shape to the plant cell. 2.(a)(i) P: Mitochondrion Q: Chloroplast (ii)P is found in large numbers in muscle tissues. Q is found in large numbers in palisade mesophyll tissues. (b) *P is important for cellular respiration. During cellular respiration, the oxidation of glucose produces energy (ATP) needed for the contraction of muscle tissues. *Q is important for photosynthesis. During photosynthesis, Q absorbs energy from the sun to synthesise glucose from carbon dioxide and water. (c) * In an oxygen-rich condition, glucose is completely broken down. * Conversely, in an oxygen-deficient condition, glucose is partially broken down. * Therefore, less energy is produced in an oxygen-deficient condition than in an oxygen-rich condition. 8
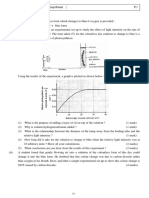
(d)
*X is grana. *Grana contain chlorophyll which captures light energy that excites the electrons of chlorophyll molecules to higher energy levels. *This light energy is also used to split water molecules into hydrogen ions and hydroxyl ions. Q: Cytoplasm R: Vacuole S: Nucleus
3. (a) P: Cell wall (b) (i)
(ii) (iii) (c) (i)
Palisade mesophyll Chloroplast contains chlorophyll for absorptionof light energy for Photosynthesis
(ii) * Root hair cell does not have chloroplast while the cell in Diagram 3 has chloroplast * Root hair cell has a protruding structure but the cell in Diagram 3 does not have a protruding structure (d) * Water is absorbed by the root hair through osmosis * Cell sap of the root hair has a higher solute concentration than the soil water. SECTION C: Essay Question 1 (a) * Tissues are groups of cells that have a common structure and function.[1m] * Epithelial tissue consists of one or a few layers of epithelial cell, and is found covering the outside of the body or lining organs and glands. [1m] * Epithelial tissue acts as a barrier or protection. It helps to protect organs from injury and fluid loss [1m] * It is found lining the oesophagus, stomach, intestines, villi and most parts of the digestive system.[1m] * The epithelial cells are adapted for absorption or secretion.[1m] * The wall of the upper part of the oesophagus (an organ) contain voluntary muscles.[1m] * Peristalsis is assisted by the circular muscles (smooth muscle tissue)[1m] * All the muscle tissues are formed from groups of muscle cells.[1m] * The wall of the stomach (an organ) has three layers of smooth muscle tissue.[1m] * There are connective tissues in the digestive system. The connective tissues include all the blood cells.[1m] * The digestive system is made up of several organs that work together as one unit. They are the stomach, liver, gall bladder, pancreas, small intestine, large intestine (colon) and rectum. [1m] ---------------------Maximum:10m --------------------(b)(i) *Parenchyma is gneric tissue [1m] 9
*It consists of living cells with thin walls containing cellulose[1m] *Parenchyma cells are rather large and there are prominent air spaces between them[1m] *There are the sites of physiological and biochemical processes of plant, including photosynthesis, starch storage and protein synthesis[1m] *Some parenchyma tissues assist in the support of herbaceous plants, roots and leaves[1m] *Some parenchyma cells become modified and specialised and are found in certain parts of plants, such as the epidermis, mesophyll cells of leaves, endodermis and pericycle of the root[1m] (ii) * Red blood cell are felxible, concave discs [1m] * This shape gives the rred blood cells a maximum surface area, facilitating the transfer of gases into and out of the cells[1m] *The flexibility of the cells enables them to move through the blood capillaries as they can be squeezed. (The blood capillaries are slightly larger than the red blood cells)[1m] *Red blood cells / erythrocytes deliver oxygen to the tissues and return carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs[1m] *Unlike most cells of the body, mature red blood cells do not have a nuclei.[1m] There are three reasons for this: -The main function of a red blood cells is to transport oxygen and carbon dioxide. The presence of a nucleus would decrease the amount of space available for the absorption of these gases.[1m] -The nucleus of a cell has a certain mass. Nucleated red blood cells would add significantly to the weight of the blood and increase the workload of the heart by about 20%.[1m] -Red blood cells are fully differentiated and do not require a nucleus to carry out the function of transporting oxygen and carbon dioxide[1m] --------------Maximum:10m ----------------
10
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Chapter 2: Cell Structur and Cell Organisation: Form 4Document5 pagesChapter 2: Cell Structur and Cell Organisation: Form 4Fazlun Haliza Mohd MaarofPas encore d'évaluation
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers HomeostasisD'EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers HomeostasisÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In PlantsD'EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In PlantsPas encore d'évaluation
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Reproduction In HumansD'EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Reproduction In HumansÉvaluation : 2 sur 5 étoiles2/5 (2)
- SCIENCE PMR Notes and ExperimentsDocument221 pagesSCIENCE PMR Notes and ExperimentsAzlina Ahmad100% (1)
- Scheme of Work BIOLOGY FORM 4, 2010Document28 pagesScheme of Work BIOLOGY FORM 4, 2010WanM.Syamim0% (1)
- Biology CH 7 Practice TestDocument6 pagesBiology CH 7 Practice Testvaleria100% (2)
- TSSM Unit 1 Exam 2018Document28 pagesTSSM Unit 1 Exam 2018nisulPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary Notes - Topic 2 Organisation of The Organism - CIE Biology IGCSEDocument4 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 2 Organisation of The Organism - CIE Biology IGCSECarola Bogezi100% (1)
- Cell Structure and OrganisationDocument26 pagesCell Structure and OrganisationNor Hafiza AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Inheritance (Multiple Choice) 1 QPDocument13 pagesInheritance (Multiple Choice) 1 QPOsvaldo Ola YaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Transport in PlantsDocument6 pagesTransport in PlantsFred H HalderPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise On Coordination and ResponseDocument8 pagesExercise On Coordination and ResponseNorliyana AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Biok 3Document22 pagesBiok 3Hazizi HanapiPas encore d'évaluation
- New Syllabus Questions Part OneDocument19 pagesNew Syllabus Questions Part OneKhaled Dabour100% (1)
- GCE A Level Biology Paper 2Document16 pagesGCE A Level Biology Paper 2Tamicka BonnickPas encore d'évaluation
- Myp Quiz 4 - PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesMyp Quiz 4 - Photosynthesisapi-257190713Pas encore d'évaluation
- Form 4 Biology Chapter 7 - RespirationDocument22 pagesForm 4 Biology Chapter 7 - RespirationChew Han Hoong0% (2)
- Paper 1 - Cell StructureDocument52 pagesPaper 1 - Cell StructureShubin Pokhrel100% (2)
- Biology SPM Forecast PapersDocument21 pagesBiology SPM Forecast PaperswhywhyqPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell - Structure, Function and OrganizationDocument1 pageCell - Structure, Function and Organization- adlina -100% (1)
- Chapter 7 Light Colour and Sight StudentDocument20 pagesChapter 7 Light Colour and Sight Studentwinniepeter1313Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of Paper 3 Biology SPMDocument20 pagesFundamentals of Paper 3 Biology SPMVei KeithPas encore d'évaluation
- O Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions EcologyD'EverandO Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions EcologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Notes PDFDocument79 pagesBiology Notes PDFSaket GudimellaPas encore d'évaluation
- (Spmsoalan) Soalan K1 Biology Tengah Tahun Kedah 2014Document33 pages(Spmsoalan) Soalan K1 Biology Tengah Tahun Kedah 2014SPM Soalan100% (2)
- Biology IGCSE GuideDocument20 pagesBiology IGCSE GuideJeremiah SinggihPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Chapter 2 Topical ExerciseDocument3 pagesBiology Chapter 2 Topical ExerciseAlan WangPas encore d'évaluation
- Latihan Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 4Document11 pagesLatihan Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 4李友志67% (3)
- Enzymes QuestionsDocument21 pagesEnzymes QuestionsJordan WanPas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER 2 - Textbook ExerciseDocument8 pagesCHAPTER 2 - Textbook ExercisenoorPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio ACE Form 4Document3 pagesBio ACE Form 4Myramel KlarisPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy and Respiration A2 NotesDocument15 pagesEnergy and Respiration A2 NotesMoe Chelsea100% (4)
- Science Form 1 Chapter 3Document25 pagesScience Form 1 Chapter 3Lai Swee HoPas encore d'évaluation
- Section 3.1 Solids, Liquids, and Gases: Reading StrategyDocument2 pagesSection 3.1 Solids, Liquids, and Gases: Reading StrategyensentisPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Topical Exercise Form 4 Chapter 2Document13 pagesBiology Topical Exercise Form 4 Chapter 2SanjeefKumrIIPas encore d'évaluation
- 0610 Topic QuestionsDocument302 pages0610 Topic QuestionsFor GamingPas encore d'évaluation
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Kelapa Sawit Form 4 Biology Yearly Lesson Plan SummaryDocument5 pagesSekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Kelapa Sawit Form 4 Biology Yearly Lesson Plan SummaryArvinth Guna SegaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio P1 SBP 2007Document23 pagesBio P1 SBP 2007Rozaini Othman100% (2)
- Classification NOTESDocument8 pagesClassification NOTESShahadMahmoud100% (1)
- CHAPTER 2 BiologyDocument10 pagesCHAPTER 2 BiologyMohamad ShukriPas encore d'évaluation
- Photosynthesis PastPaper QuestionsDocument24 pagesPhotosynthesis PastPaper QuestionsEva SugarPas encore d'évaluation
- MID-TERM EXAMINATION (Chapter 1 To Chapter 4)Document8 pagesMID-TERM EXAMINATION (Chapter 1 To Chapter 4)Shakilla HamzahPas encore d'évaluation
- GCSE BiologyDocument12 pagesGCSE BiologyTyler Hammond100% (1)
- KIFAYAT Tahisli Biology - First Edition V3Document135 pagesKIFAYAT Tahisli Biology - First Edition V3Ahmad Al FadelPas encore d'évaluation
- Cambridge Science Worksheet 8Document13 pagesCambridge Science Worksheet 8ozmanPas encore d'évaluation
- IGCSE Biology Revision Quiz Macromolecules and Movement Into and Out of CellsDocument2 pagesIGCSE Biology Revision Quiz Macromolecules and Movement Into and Out of CellsddddddffdfdfPas encore d'évaluation
- Living Organisms MapDocument1 pageLiving Organisms MapClayesmoreBiology100% (1)
- Biology 8B Worksheet No.6 PDFDocument10 pagesBiology 8B Worksheet No.6 PDFAli AshrafPas encore d'évaluation
- C 1 2 2025 Topic Test MsDocument4 pagesC 1 2 2025 Topic Test MsRawanMazen SharifPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical Paper 3 NotesDocument22 pagesPractical Paper 3 NotesSuperRuhalPas encore d'évaluation
- 0417 m17 QP 31Document8 pages0417 m17 QP 31Popi MastroianniPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology A Level OCR 2022Document6 pagesBiology A Level OCR 2022shPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Worksheets - XIIDocument188 pagesBiology Worksheets - XIIlatishabasilPas encore d'évaluation
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Coordination And ResponseD'EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Coordination And ResponsePas encore d'évaluation
- Practical Biology: For Advanced Level, Medical and Intermediate StudentsD'EverandPractical Biology: For Advanced Level, Medical and Intermediate StudentsPas encore d'évaluation
- Catatan 2Document1 pageCatatan 2teahockPas encore d'évaluation
- Respirasi Sel: PracticeDocument2 pagesRespirasi Sel: PracticeteahockPas encore d'évaluation
- Marks) : ConfidentialDocument3 pagesMarks) : ConfidentialteahockPas encore d'évaluation
- Variable Method To Handle The Variable Manipulated Variable Responding Variable Constant VariableDocument2 pagesVariable Method To Handle The Variable Manipulated Variable Responding Variable Constant VariableteahockPas encore d'évaluation
- Amistar Sygent A: Thiophanate - Methyl 70.0% Topsin MDocument2 pagesAmistar Sygent A: Thiophanate - Methyl 70.0% Topsin MteahockPas encore d'évaluation
- Development of PlacentaDocument1 pageDevelopment of PlacentateahockPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 Biological Molecules: Biology Term 1 STPMDocument1 pageChapter 1 Biological Molecules: Biology Term 1 STPMteahockPas encore d'évaluation
- GroupDocument5 pagesGroupteahockPas encore d'évaluation
- Catatan RefleksiDocument1 pageCatatan RefleksiteahockPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Handbook - GuidelineDocument16 pagesLab Handbook - GuidelineteahockPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Is Basic Unit of LiveDocument2 pagesCell Is Basic Unit of LiveteahockPas encore d'évaluation
- BioF5-4.1 Gamete FormationDocument21 pagesBioF5-4.1 Gamete FormationteahockPas encore d'évaluation
- Catatan RefleksiDocument1 pageCatatan RefleksiteahockPas encore d'évaluation
- 10th PeriodsDocument15 pages10th PeriodsteahockPas encore d'évaluation
- BioF5-4.4 Contribution of Science and Technology To Human ReproductionDocument24 pagesBioF5-4.4 Contribution of Science and Technology To Human ReproductionteahockPas encore d'évaluation
- BioF5C4 Revision 2017 SchoolDocument9 pagesBioF5C4 Revision 2017 SchoolteahockPas encore d'évaluation
- By A Transport Protein in The Pre-Synaptic Membrane. Describe How This Causes Depolarisation of The Post-Synaptic Membrane. (2 M)Document3 pagesBy A Transport Protein in The Pre-Synaptic Membrane. Describe How This Causes Depolarisation of The Post-Synaptic Membrane. (2 M)teahockPas encore d'évaluation
- BioF5-4.8 Primary and Secondary Growth in PlantsDocument14 pagesBioF5-4.8 Primary and Secondary Growth in PlantsteahockPas encore d'évaluation
- Biof5c5-Pattern of InheritanceDocument62 pagesBiof5c5-Pattern of InheritanceteahockPas encore d'évaluation
- BioF5Revision 2017 SchoolDocument5 pagesBioF5Revision 2017 SchoolteahockPas encore d'évaluation
- Kingdom FungiDocument5 pagesKingdom FungiteahockPas encore d'évaluation
- Byrophyta & FilicinophytaDocument9 pagesByrophyta & FilicinophytateahockPas encore d'évaluation
- Coniferophyta & AngiospermophytaDocument12 pagesConiferophyta & Angiospermophytateahock100% (1)
- BioF5C1 Revision 2017 SchoolDocument6 pagesBioF5C1 Revision 2017 SchoolteahockPas encore d'évaluation
- BioF5-4.7 The Growth CurveDocument16 pagesBioF5-4.7 The Growth CurveteahockPas encore d'évaluation
- Higher Order Thinking SkillsDocument177 pagesHigher Order Thinking SkillsRazak Kadir100% (6)
- BioF4C7 RespirationDocument29 pagesBioF4C7 RespirationteahockPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology-The Mistakes Did by The CandidatesDocument10 pagesBiology-The Mistakes Did by The CandidatesteahockPas encore d'évaluation
- Bank Soalan 2T2014Document19 pagesBank Soalan 2T2014teahockPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Mistakes-BiologyDocument8 pagesCommon Mistakes-BiologyteahockPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology NotesDocument6 pagesBiology NoteshelloPas encore d'évaluation
- Disclosure To Promote The Right To InformationDocument21 pagesDisclosure To Promote The Right To InformationBrijeshPas encore d'évaluation
- V6I109 3 February 2021Document9 pagesV6I109 3 February 2021Harrizul RivaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Journal No. 1 "The Gross Morphology and Structure of Leaves"Document12 pagesJournal No. 1 "The Gross Morphology and Structure of Leaves"Ej AgsaldaPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Merged PDFDocument210 pages3 Merged PDFthanPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 4 ReportDocument25 pagesExperiment 4 ReportFeroze Nizome67% (6)
- Bio School MCQ PaperDocument6 pagesBio School MCQ PaperRahul ChoudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Torres Et Al. 2018Document42 pagesTorres Et Al. 2018Andres TorresPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrient Disorders in Rice PosterDocument1 pageNutrient Disorders in Rice Posterhairuddin100% (1)
- DiMichele Et Al 2013Document24 pagesDiMichele Et Al 2013Ronaldo BarboniPas encore d'évaluation
- Carter2014 Sphenoclea Zeylanica (Sphenocleaceae) in North America-Dispersal, Ecology, and MorphologyDocument19 pagesCarter2014 Sphenoclea Zeylanica (Sphenocleaceae) in North America-Dispersal, Ecology, and MorphologyJamesPas encore d'évaluation
- Water-Soluble Phosphoric Acid (Ws-Pa)Document2 pagesWater-Soluble Phosphoric Acid (Ws-Pa)ronalit malintadPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology MCQDocument60 pagesBiology MCQpullaiPas encore d'évaluation
- CarbohydratessslDocument13 pagesCarbohydratessslCookie JarPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Transpiration Worksheet SolutionDocument24 pagesChapter Transpiration Worksheet SolutionZawad7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Corn Tastes Better On The Honor System - Robin Wall KimmererDocument53 pagesCorn Tastes Better On The Honor System - Robin Wall Kimmerertristram59100% (1)
- Dwnload Full Friendly Introduction To Number Theory 4th Edition Silverman Solutions Manual PDFDocument28 pagesDwnload Full Friendly Introduction To Number Theory 4th Edition Silverman Solutions Manual PDFjosephdcugward91% (11)
- Intermediate Accounting Volume 1 6th Edition Beechy Solutions ManualDocument38 pagesIntermediate Accounting Volume 1 6th Edition Beechy Solutions Manualumbarasanayab100% (13)
- B.SC - Botany - Pteridophytes, Anatomy and Embryology - II-Year - SPS PDFDocument160 pagesB.SC - Botany - Pteridophytes, Anatomy and Embryology - II-Year - SPS PDFAhmed KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9 - Plant Organization and Function - DoneDocument6 pagesChapter 9 - Plant Organization and Function - DoneApostolos KoutsaftisPas encore d'évaluation
- LESSON 2.5 - Plants Parts and Their FunctionsDocument16 pagesLESSON 2.5 - Plants Parts and Their FunctionsJen TaniecaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio 3.1 PhotosynthesisDocument7 pagesBio 3.1 PhotosynthesisSuzuko YukinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutritional Disorders in Chrysanthemums-Wageningen University and Research 427557Document39 pagesNutritional Disorders in Chrysanthemums-Wageningen University and Research 427557LAUM1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Disease Herbarium 3Document27 pagesDisease Herbarium 3Shahin Rahman 112700gmail.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Nezahat KandemirDocument18 pagesNezahat KandemirAriana ChimiPas encore d'évaluation
- Live Fence Posts in Costa Rica: A Compilation of The Farmer's Beliefs and TechnologiesDocument23 pagesLive Fence Posts in Costa Rica: A Compilation of The Farmer's Beliefs and TechnologiesRicardo RussoPas encore d'évaluation
- Beginner's Illustrated Guide To Gardening (2012)Document463 pagesBeginner's Illustrated Guide To Gardening (2012)SABA ALIPas encore d'évaluation
- Variations Among Coffee (Coffea Arabica L.) Genotypes For Sensitivity To Drought Induced by Soil Drying at Early Stages of Growth in EthiopiaDocument10 pagesVariations Among Coffee (Coffea Arabica L.) Genotypes For Sensitivity To Drought Induced by Soil Drying at Early Stages of Growth in EthiopiaPremier PublishersPas encore d'évaluation
- Dioscorea L. (PROSEA) - PlantUse English PDFDocument8 pagesDioscorea L. (PROSEA) - PlantUse English PDFfortuna_dPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 2.9 SL Photosynthesis QuestionsDocument14 pagesTopic 2.9 SL Photosynthesis QuestionsIzabella ReaPas encore d'évaluation