Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Voltage & Reactive Power Control Problems With Solutions
Transféré par
devcharuTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Voltage & Reactive Power Control Problems With Solutions
Transféré par
devcharuDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
CHAPTER 15 Voltage & Reactive Power Control Problems with Solutions
Prob. No: 15.1 15.2 15.3 15.4
e.mail address: Indulkar@ieee.org
Topic Cost of power factor improvement Reactive power required to re-establish the fall in voltage due to load. Load angle for a given load across an interconnector with the ends maintained at different voltages Two generating stations connected by an interconnector- voltage adjustments required to equalise the loads at the two stations
WEBSITE
takes you to the start page after you have read this Chapter. Start page has links to other Chapters.
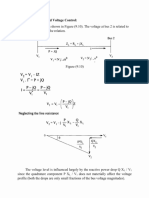
Prob.15.1 Cost of power factor improvement A consumer's load of 250 kw has power factor of 0.78 lagging. The power supply charges are 50 cents per kVa of maximum demand per month plus 0.5 cents per kW -hr. The cost of power factor improving apparatus is US dollar 10 per kVA, and the rate of interest & depreciation is 10 %. To what extent the power factor should be improved so that the amount saved is a maximum?. Calculate also the kVA capacity of the power factor improving apparatus. Solution: O f1 f2 P kW A
New kVA Old kVA C kVAr capacity of power factor improving apparatus B
cos f1 pf1 0.78 lag pf2 most economical pf, cos f 2 P 250 kW kVAr capacity of power factor improving apparatus =P * (tan f1- tan f2) U cost of power supply 0.5 USD/kVa E cost of energy 0.05 USD/kW-hr A cost of apparatus 10 USD I Interest & depreciation 10 % Annual charge for power factor improving apparatus = A*(I/100)*P*(tan f1 -tan f2 ) B D Saving by improving the pf is = U*((P/ pf1)-(P/pf2))= Consumer's gross saving
S Consumer's net saving = D-B To maximize S, (dS/d f2) =0= (dD/d f2 )-(dB/d f 2) =-U*Ptan (f 2) * sec( f2)+ A*(I/100)*Psec f2*sec f2 or sin f2 = A*(1/100)/U Cos f2 0.2 0.979796 lag Answer
Capacity of power factor improving apparatus =P * (tan f1- tan f2) 127.6231 kVAr Top of Page
Answer
Prob.15.2 Reactive power required to re-establish the fall in voltage due to load. Three supply points A,B and C are connected to a common busbar M. Supply point A is maintain at a nominal 66 kV and is connected to M through a 66/33 kV transformer (0.1 pu reactance) an a 33 kV line of reactance 20 ohms. Supply point B is nominally at 33 kV and is connected to M by a 66/33kV transformer (0.1 pu reactance0 and a 33 kV line of 20 ohms reactance. If at a particular system load , the line voltage at M falls by 5 kV, calculate the magnitude of the reactive volt-ampere injection required at M to re-establish the original voltage. The pu values a re based on a 100 MVA base. Solution: A 66/33 kV 66 kV 20 ohms 20 ohms 33 kV .1 pu 20 ohms M B
.1pu
66/33 kV
MVAb Xb Xl Xlpu
in 33 kV circuit Line reactance
66 kV 100 10.89 20 1.836547
C ohms ohms pu
j.1 A
j1.836
j1.836 M j1.836 j.1 B
C N Xt Transformer reactance Xa Reactance M to A Xd Reactance M to C Parallel combination of Xa & Xd Xc Reactance M to B Equivalent reactance M to N 0.1 1.936547 1.936547 0.968274 1.836547 0.634009 pu pu pu pu pu pu
Fault MVA at M = MVAb/equivalent reactance= 157.7266 MVA Fault current = Fault MVA*1000/(1.73205*33)= 2759.501 A d Qm/ d Vm =1.73205*fault current= 4779.594 Vars/Volt 4.779594 MVAr /kV Drop in voltage at M(l-L) 5 kV Reactive power required 23.89797 MVAr Top of Page
at 0 power factor lagging
Answer
Prob.15.3 Load angle for a given load across an interconnector with the ends maintained at different voltages Two units of generators maintain 66 kV (L-L) and 60 kV (L-L) at the ends of an interconnection of inductive reactance per phase of 23.094 ohms and with negligible resistance and shunt capacitance. A load of 12 MW is to be transferred from the 66 kV unit to the other end. Calculate the load angle across the interconnector, and the power factor of the current transmitted. Solution: jX Vs d Vr I
= Vs d - Vr o jX Complex power
= Vs Cos d + jVs Sind -Vr jX = Vr *I conjugate = VrVs Sin d -jVr (Vr-Vs Cosd ) X
P P Vs Vr X Sin d d Cos d tan f cos f
Real power
Vr.VsSin d/X 12 MW 66 kV 60 kV 23.04 ohms =PX/Vr*Vs 0.069818 4.003535 deg Answer 0.99756 =(-Vs cos d+ Vr)/Vs Sin d -1.26778 0.61931 lag Answer Top of Page
Prob.15.4 Two generating stations connected by an interconnector- voltage adjustments required to equalize the loads at the two stations Two generating stations A and B are linked by a line and two transformers of total 20 ohms referred to 132 kV and negligible resistance. A load of 100 MW .9 pf lagging is by the busbars of A and 200 MW ,.85 pf lagging from B. Determine the phase angles between the busbars of A and b, and the voltage adjustment required to equalize the load on each station. Initially both stations have busbar voltages of 11 kV which are in phase Solution: A X= 20 ohms VA P1=100 MW,.9 pf Phasor diagram: VB P2=200MW, .85 pf PA P, Q, I PB B
VA dV d VB I DV MW lag MVAr MW lag MVAr MW MW MVAr jX.I
P1 100 pf1 0.9 Q1 =P1*tan (ACOS(pf1)) 48.43221 P2 200 pf2 0.85 Q2 =P2*tan (ACOS(pf2)) 123.9489 To equalize the load on each station, PA = PB = 150 P =PA-P1 50 QA = QB = =(Q1+Q2)/2 86.19054
Q =QA-Q1 37.75833 MVAr From the phasor diagram, dV =X*Pph/VB X 20 ohms VB per phase 76.21027 kV Pph per phase 16.66667 MW dV 4.373864 kV From the phasor diagram, Sin d =dV/VA=dV/VB= 0.057392 d 3.291799 deg Hence busbar A is 3.29 deg in advance of busbar B. DV Qph VA DV = XQph/VAph per phase = XQph/VAph 12.58611 76.21027 3.302996 5.720954
,ignoring Qloss = I*IX in line
Answer
MVAr kV kV per ph kV(L-L) Answer
5.75 kV increase on 132 side of A Top of Page
dress: Indulkar@ieee.org
d at different
tan f1 -tan f2 )
6.904353 144.8362 23.89797
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Per Unit SystemDocument18 pagesPer Unit SystemAmrMashhourPas encore d'évaluation
- Power System Analysis Lab1-LEYBOLD EQUIPMENT INSPECTION & TRANSIENT MEASUREMENTDocument15 pagesPower System Analysis Lab1-LEYBOLD EQUIPMENT INSPECTION & TRANSIENT MEASUREMENTMalith DeemanthaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cooling Tower Handbook - FINAL PDFDocument33 pagesCooling Tower Handbook - FINAL PDFOscarJimenez19870% (1)
- Data MiningDocument721 pagesData MiningAuly Natijatul AinPas encore d'évaluation
- Cap15 Voltage & Reactive Power Control PDFDocument10 pagesCap15 Voltage & Reactive Power Control PDFIsidro SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- ExamenDocument8 pagesExamenJosué Him ZuraPas encore d'évaluation
- Ejercicios Resueltos de Máquinas TérmicasDocument11 pagesEjercicios Resueltos de Máquinas TérmicasJosepBravoDávilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Short - Circuit Problems With SolutionsDocument22 pagesShort - Circuit Problems With Solutionsgsantosh06Pas encore d'évaluation
- Per Unit CalculationsDocument7 pagesPer Unit Calculationsanbuelectrical100% (1)
- 03 EM3 Sample QA 3-Phase TransformersDocument8 pages03 EM3 Sample QA 3-Phase TransformerskhuzaimPas encore d'évaluation
- Appendix 1 Per-Unit Notation: Al.L TransformersDocument23 pagesAppendix 1 Per-Unit Notation: Al.L TransformersJay KuizonPas encore d'évaluation
- Power System Mcqs PDFDocument5 pagesPower System Mcqs PDFHarith NawfelPas encore d'évaluation
- Capacitor Banks in Power System Part OneDocument6 pagesCapacitor Banks in Power System Part OneTigrilloPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.per Unit System PDFDocument10 pages1.per Unit System PDFlaxman100% (1)
- Per UnitDocument18 pagesPer UnitPeter CalvoPas encore d'évaluation
- March 2009Document10 pagesMarch 2009Myles RangirisPas encore d'évaluation
- Schneider - Power Factor Correction and Harmonic Filtering (B - 954 - 503 - 439)Document82 pagesSchneider - Power Factor Correction and Harmonic Filtering (B - 954 - 503 - 439)Ieremeiov Vladimir100% (1)
- Tutorial 6 Solution - 21955Document9 pagesTutorial 6 Solution - 21955Sahil GalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Objective Questions On Electrical Transmission - 2 - Electrical Study App by SARU TECHDocument9 pagesObjective Questions On Electrical Transmission - 2 - Electrical Study App by SARU TECHGanesh RadharamPas encore d'évaluation
- Excel First Review and Training Center, Inc.: Cebu: Davao: Manila: BaguioDocument3 pagesExcel First Review and Training Center, Inc.: Cebu: Davao: Manila: Baguiojomark ampoloquioPas encore d'évaluation
- Control Loops 2Document22 pagesControl Loops 2Muntadher AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- Catalogue Sisvar en V4Document82 pagesCatalogue Sisvar en V4Saša MiloševićPas encore d'évaluation
- Cap02 Maquinas SincronicasDocument43 pagesCap02 Maquinas SincronicasJulio Begazo PeñaPas encore d'évaluation
- Transformer Ratings: Dumaguin, Mike Dexter GDocument7 pagesTransformer Ratings: Dumaguin, Mike Dexter GMike DumaguinPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 25961 628Document9 pages5 25961 628Belayneh TadessePas encore d'évaluation
- 03 EM3 Sample QA 3-Phase TransformersDocument8 pages03 EM3 Sample QA 3-Phase Transformersbinu_10Pas encore d'évaluation
- MCQ PS IiiDocument9 pagesMCQ PS IiiAkash Koley18-2089Pas encore d'évaluation
- Advance Electrical MachinesDocument26 pagesAdvance Electrical MachinesSammar AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- Capacitor Banks in Power System PDFDocument6 pagesCapacitor Banks in Power System PDFmanichePas encore d'évaluation
- TU2 TransformerDocument3 pagesTU2 TransformerLove Nepal Is BackPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial Sheet EEC2110 - Electrical Machines-I Unit - I and II (Transformers)Document2 pagesTutorial Sheet EEC2110 - Electrical Machines-I Unit - I and II (Transformers)SunilkumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Power System Analysis: Transformers, Per UnitDocument43 pagesPower System Analysis: Transformers, Per UnitMamta MrjnPas encore d'évaluation
- Capacitor Banks in Power System Part OneDocument4 pagesCapacitor Banks in Power System Part OneJack SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- Transformer BixDocument2 pagesTransformer BixUmer HassanPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Calculate Voltage Regulation of Distribution Line - EEPDocument8 pagesHow To Calculate Voltage Regulation of Distribution Line - EEPelectworldPas encore d'évaluation
- Question 1 (Problem 2-5 in The Text)Document5 pagesQuestion 1 (Problem 2-5 in The Text)Racheal KirbyPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment-4: V S Akshit 19BEE0435 L39+L40 1 September 2020Document10 pagesExperiment-4: V S Akshit 19BEE0435 L39+L40 1 September 2020Akshit VSPas encore d'évaluation
- Capaciters in PsDocument20 pagesCapaciters in PsVasudev AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- EE 109 System ProtectionDocument4 pagesEE 109 System ProtectionIan Acuzar PunzalanPas encore d'évaluation
- Report On Workshop: Submitted byDocument54 pagesReport On Workshop: Submitted byrajimuruganPas encore d'évaluation
- T3 TugasDocument15 pagesT3 TugasSri rahayuPas encore d'évaluation
- Synchronous Machine Problems With SolutionsDocument34 pagesSynchronous Machine Problems With Solutionsgsantosh06Pas encore d'évaluation
- Question BankDocument17 pagesQuestion BankNisarg PanchalPas encore d'évaluation
- AlepDocument10 pagesAlepMiz AelyfhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Web For Power Systems II B.tech 6th SemDocument16 pagesWeb For Power Systems II B.tech 6th Semskyline1122Pas encore d'évaluation
- !7374656d5f26736f6c7574696f6e73 PDFDocument12 pages!7374656d5f26736f6c7574696f6e73 PDFluckyPas encore d'évaluation
- Where Do You Need This?: 1.maintenance Engineer 2.energy Management System 3.energy ManagerDocument31 pagesWhere Do You Need This?: 1.maintenance Engineer 2.energy Management System 3.energy Managerconference RequirementsPas encore d'évaluation
- K. Arputharaju, Assistant Executive Engineer / Operation, Basin Bridge Gas Turbine Power Station, TANGEDCO, TNEB LTD., Chennai - 600 012Document20 pagesK. Arputharaju, Assistant Executive Engineer / Operation, Basin Bridge Gas Turbine Power Station, TANGEDCO, TNEB LTD., Chennai - 600 012navi_0403Pas encore d'évaluation
- Capacitor Banks in Power System (Part-1) - EEPDocument5 pagesCapacitor Banks in Power System (Part-1) - EEPMuhammad JunaidPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial Pse - 2012-2013Document23 pagesTutorial Pse - 2012-2013Mahesh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- TransformerDocument2 pagesTransformerBsal SokoPas encore d'évaluation
- D.C.Machine Problems With Solutions: Date Modified-30 Jun.1999Document16 pagesD.C.Machine Problems With Solutions: Date Modified-30 Jun.1999Sandunga SalsotecaPas encore d'évaluation
- Figure 1.8 Map of National Grid, Malaysia and South-East AsiaDocument10 pagesFigure 1.8 Map of National Grid, Malaysia and South-East AsiaDa Harlequin GalPas encore d'évaluation
- Generator Capability CurveDocument20 pagesGenerator Capability Curvearputharaju_k78% (9)
- Pse Problems Group AssignmentDocument14 pagesPse Problems Group AssignmentSajid KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Reactive Power ManagementDocument45 pagesReactive Power ManagementSudhakar YsPas encore d'évaluation
- TransformerDocument4 pagesTransformerSalu ShigriPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre-Board Exam in EeDocument4 pagesPre-Board Exam in EeJohn Eduard Felix Betuin100% (1)
- How Capacitors Improve The Power Factor and How To Calculate ThemDocument6 pagesHow Capacitors Improve The Power Factor and How To Calculate ThemmarbyPas encore d'évaluation
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)D'EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- DC ComponentDocument5 pagesDC ComponentjosePas encore d'évaluation
- SafeStartingOfMotors 0514Document4 pagesSafeStartingOfMotors 0514Enrique Javier González HenríquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Indian DIN &BS Fuse Link & Base - Technical Catalog - 23-04-15 PDFDocument26 pagesIndian DIN &BS Fuse Link & Base - Technical Catalog - 23-04-15 PDFdevcharuPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Carbon Brush Technical Guide Mersen - 07Document40 pages5 Carbon Brush Technical Guide Mersen - 07Dhanraj PatilPas encore d'évaluation
- Marland 2014Document154 pagesMarland 2014devcharuPas encore d'évaluation
- RCFA TablesOfContents PDFDocument26 pagesRCFA TablesOfContents PDFasrinivasareddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Power TransformerMaintenance ScheduleDocument3 pagesPower TransformerMaintenance Scheduledh24992499Pas encore d'évaluation
- Predicting Transformer Temperature Rise and Loss oDocument10 pagesPredicting Transformer Temperature Rise and Loss odevcharuPas encore d'évaluation
- ABB - Technical Guide No.7 - REVCDocument40 pagesABB - Technical Guide No.7 - REVCgafscottPas encore d'évaluation
- Distribution Transformer Main Handbook PDFDocument84 pagesDistribution Transformer Main Handbook PDFdevcharuPas encore d'évaluation
- 32083-Guidance Notes For Generators - Submission of Grid Code DataDocument39 pages32083-Guidance Notes For Generators - Submission of Grid Code DataJuan AntonioPas encore d'évaluation
- 6668 LossEffective DD 20150318 WebDocument9 pages6668 LossEffective DD 20150318 WebChristos ApostolopoulosPas encore d'évaluation
- Resumo Diogo Silva 73583Document11 pagesResumo Diogo Silva 73583devcharuPas encore d'évaluation
- TransformerDocument204 pagesTransformerdevcharu75% (4)
- 11 Chap3Document28 pages11 Chap3tutywaodePas encore d'évaluation
- ML12334A508Document22 pagesML12334A508devcharuPas encore d'évaluation
- Condition Monitoring of Transformers SAILDocument17 pagesCondition Monitoring of Transformers SAILavadiraja100% (1)
- White Paper The Value of A Maintenance AuditDocument5 pagesWhite Paper The Value of A Maintenance AuditdevcharuPas encore d'évaluation
- Signal Conditioning Circuits1Document16 pagesSignal Conditioning Circuits1Karthik SriramakavachamPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Maintenance Best PracticesDocument22 pages12 Maintenance Best Practicespepenapao1217Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cement Plant Emission ManualDocument71 pagesCement Plant Emission Manualtsrinivasan5083Pas encore d'évaluation
- Recip or Screw - The Customers Choice PDFDocument2 pagesRecip or Screw - The Customers Choice PDFdevcharuPas encore d'évaluation
- V35s1a11 PDFDocument9 pagesV35s1a11 PDFdevcharuPas encore d'évaluation
- TealBookDocument2 pagesTealBookdevcharuPas encore d'évaluation
- Transformer Insulation Life ExtensionDocument31 pagesTransformer Insulation Life ExtensiondevcharuPas encore d'évaluation
- Workshop Transformer Residual Life EnhancementDocument4 pagesWorkshop Transformer Residual Life EnhancementdevcharuPas encore d'évaluation
- Distribution System Redesign EPRIDocument210 pagesDistribution System Redesign EPRIhafezasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Transformer Age AssessmentDocument7 pagesTransformer Age AssessmentEngr Irfan AkhtarPas encore d'évaluation
- Distribution System Redesign EPRIDocument210 pagesDistribution System Redesign EPRIhafezasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Civpro RevDocument102 pagesCivpro RevJocelyn Baliwag-Alicmas Banganan BayubayPas encore d'évaluation
- Grant Miller Resume-ColliersDocument3 pagesGrant Miller Resume-ColliersDeven GriffinPas encore d'évaluation
- PCU CalculationDocument2 pagesPCU CalculationMidhun Joseph0% (1)
- Basic Details: Government Eprocurement SystemDocument4 pagesBasic Details: Government Eprocurement SystemNhai VijayawadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 03 Investments in Debt SecuritiesDocument4 pagesAssignment 03 Investments in Debt SecuritiesJella Mae YcalinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Application Letters To Apply For A Job - OdtDocument2 pagesApplication Letters To Apply For A Job - OdtRita NourPas encore d'évaluation
- cv20672778 Prashanth - Sadak Operations-ManagerDocument4 pagescv20672778 Prashanth - Sadak Operations-ManagerBhasker NiftyPas encore d'évaluation
- 671 - BP Well Control Tool Kit 2002Document19 pages671 - BP Well Control Tool Kit 2002Ibama MirillaPas encore d'évaluation
- PRI SSC TutorialDocument44 pagesPRI SSC TutorialSantosh NarayanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ibm v3700 Storeage PDFDocument694 pagesIbm v3700 Storeage PDFJanakackvPas encore d'évaluation
- Scientific American - Febuary 2016Document84 pagesScientific American - Febuary 2016Vu NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Innova M3 New: 3. InstallationDocument8 pagesInnova M3 New: 3. InstallationAndreea DanielaPas encore d'évaluation
- PraxiarDocument8 pagesPraxiara_roy003Pas encore d'évaluation
- DBR KochiDocument22 pagesDBR Kochipmali2Pas encore d'évaluation
- NGOs in Satkhira PresentationDocument17 pagesNGOs in Satkhira PresentationRubayet KhundokerPas encore d'évaluation
- LaMOT Rupture DiscsDocument20 pagesLaMOT Rupture Discshlrich99Pas encore d'évaluation
- IMO Special Areas Under MARPOLDocument2 pagesIMO Special Areas Under MARPOLRavi Viknesh100% (1)
- Pavement Design - (Rigid Flexible) DPWHDocument25 pagesPavement Design - (Rigid Flexible) DPWHrekcah ehtPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1: Exercise 1: Match The Words With The Pictures. Use The Words in The BoxDocument9 pagesUnit 1: Exercise 1: Match The Words With The Pictures. Use The Words in The BoxĐoàn Văn TiếnPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 3 Revision Worksheet 2 Class 6 CSDocument1 pageCH 3 Revision Worksheet 2 Class 6 CSShreyank SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise Guide - Broad Crested WeirDocument18 pagesExercise Guide - Broad Crested Weirvipul anandPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Title: G.R. No.: Date: Venue: Ponente: Subject: TopicDocument3 pagesCase Title: G.R. No.: Date: Venue: Ponente: Subject: TopicninaPas encore d'évaluation
- CDCS Self-Study Guide 2011Document21 pagesCDCS Self-Study Guide 2011armamut100% (2)
- West Bengal Joint Entrance Examinations Board: Provisional Admission LetterDocument2 pagesWest Bengal Joint Entrance Examinations Board: Provisional Admission Lettertapas chakrabortyPas encore d'évaluation
- A-Panel Dual Polarization Half-Power Beam Width Adjust. Electr. DowntiltDocument2 pagesA-Panel Dual Polarization Half-Power Beam Width Adjust. Electr. DowntiltUzair AkbarPas encore d'évaluation
- Aug 2020 Builders Line Tamil MonthlyDocument48 pagesAug 2020 Builders Line Tamil MonthlyBuildersLineMonthlyPas encore d'évaluation
- Vacuum Dehydrator & Oil Purification System: A Filter Focus Technical Publication D1-14Document1 pageVacuum Dehydrator & Oil Purification System: A Filter Focus Technical Publication D1-14Drew LeibbrandtPas encore d'évaluation
- Sustainable Livelihood Program SWPPSDocument21 pagesSustainable Livelihood Program SWPPSHanabusa Kawaii IdouPas encore d'évaluation
- Agile Marketing Reference CardDocument2 pagesAgile Marketing Reference CardDavid BriggsPas encore d'évaluation