Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Regulations On M&A
Transféré par
Sudeshna Sahu0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
23 vues11 pagesMergers and Acquisitions are regulated by the Companies Act 1956 which lays down the procedures for valuation of shares and protection of the rights of investors. SEBI's take over code provides for transparent, economical and fast take over of listed companies apart from fl d f protecting the interest of minority shareholders. Mergers & acquisitions are also regulated by SEBI s take over regulations which provide for making of a tender offer to acquire shares from the shareholders of the target company.
Description originale:
Titre original
Regulations on M&A
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentMergers and Acquisitions are regulated by the Companies Act 1956 which lays down the procedures for valuation of shares and protection of the rights of investors. SEBI's take over code provides for transparent, economical and fast take over of listed companies apart from fl d f protecting the interest of minority shareholders. Mergers & acquisitions are also regulated by SEBI s take over regulations which provide for making of a tender offer to acquire shares from the shareholders of the target company.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
23 vues11 pagesRegulations On M&A
Transféré par
Sudeshna SahuMergers and Acquisitions are regulated by the Companies Act 1956 which lays down the procedures for valuation of shares and protection of the rights of investors. SEBI's take over code provides for transparent, economical and fast take over of listed companies apart from fl d f protecting the interest of minority shareholders. Mergers & acquisitions are also regulated by SEBI s take over regulations which provide for making of a tender offer to acquire shares from the shareholders of the target company.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 11
Mergers and Acquisitions: The Regulatory Perspectives
Conference on Mergers and Acquisitions, September 5, q , p , 2008
Why Mergers and Acquisitions?
Accelerate the companys growth company s Enhance profitability of the company through economies of scale, scale operating economies and synergy Facilitate di F ilit t diversification of risks of ifi ti f i k f the company Limits the severity of competition
Boom in M&A Activity
Boom in M and A Activity within the oo a d ct ty t t e country and across the borders In the recent past spurt in activity due to low valuations l l i Other major factors responsible for enhanced activity comprises buoyancy of economy, economy, additional available liquidity of corporate entities, dynamic attitude of Indian entrepreneurs and move towards globalization apart from favorable government policies
Regulation for Mergers and Acquisitions A i ii
Regulations aim at transparent deals and g p protecting the interest of all shareholders Mergers and Acquisitions are regulated by the Companies Act 1956 which lays down the procedures for valuation of shares and protection of the rights of investors SEBI has take over code which provides for transparent, economical and fast take over of listed companies apart from fl d f protecting interest of minority shareholders
Regulation for Mergers and Acquisitions A i ii
The Competition Act 2002 regulates various forms of business combinations through Competition Commission of India Foreign Exchange Management Act 1999 regulates mergers and acquisitions where cross border deals are involved
SEBI s SEBIs Take Over Code
SEBI Take over regulations provide for disclosure of acquisition/sale of shares beyond certain specified percentages SEBI Take over regulations provide for making of a tender offer to acquire shares from the shareholders of the target company when the acquisition exceeds certain specified limits
SEBI s SEBIs Take Over Code
The acquisition could be by an entity or a group q y y g p of entities acting in concert with one another, direct or indirect Mandatory requirement of acquisition specific disclosure cautions the existing management of an impending hostile bid by an acquirer The mandatory tender offer and the norms for determination of offer price provide for complimentary exit opportunity to the shareholders while enhances the value of shares held by them
SEBI s SEBIs Take Over Code
Exemptions from mandatory tender available for p y interse transfers among promoters, relatives, group companies, schemes of arrangement under India or Foreign law, take over panel etc. g , p Provides for limit on creeping acquisition of 5 per cent in a financial year in respect of acquirers holding more than 15 per cent and less than 55 per cent of shares or voting rights Clauses which make it difficult for acquirers to make frivolous offers and acquisitions
Dimensions of take over activity
During the period 1997 and 2000, 2000 3573 companies have undergone restructuring making use of the provisions of take over code Resultant open offers benefited large number of shareholders the benefit being of the order of Rs 82,000 crore 82 000
Some features of M&A Activity
Delays due to disputes e ays d sputes Disputes mainly on account of price adjustments for change in assumed fundamentals of business f d l fb i Risk potential is greatly enhanced in highly leveraged deals Companys appetite for risk is not often assessed correctly Merchant and Investment Bankers, major beneficiaries
Future of M &A Activity
Deals could become complex in futureea s cou d beco e co p e futureutu e environmental, legal and cultural complexities rampant Cross border activity could d C b d i i ld dampen temporarily due to not so encouraging world economic conditions Lower valuations may attract enhanced domestic activity during the days to come
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- PsuDocument165 pagesPsuSudeshna SahuPas encore d'évaluation
- Disinvestment in PsuDocument53 pagesDisinvestment in PsuSudeshna SahuPas encore d'évaluation
- Value AnalysisDocument32 pagesValue Analysisbrijkishor2017Pas encore d'évaluation
- F048 RecruitmentDocument7 pagesF048 RecruitmentNitesh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
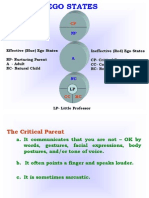
- Transacitional AnalysisDocument17 pagesTransacitional AnalysisSudeshna SahuPas encore d'évaluation
- Case AnalysisDocument15 pagesCase AnalysisSudeshna SahuPas encore d'évaluation
- Value Engineering Case StudyDocument7 pagesValue Engineering Case StudyYadhu JSPas encore d'évaluation
- HRM IntroDocument14 pagesHRM IntroSudeshna SahuPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer IntroDocument45 pagesComputer IntrosssritPas encore d'évaluation
- Aristotle's Model of Communication: By: Arunav Nayak Biswanath Chakravarty Jayjeet Dey Swagatika RathDocument10 pagesAristotle's Model of Communication: By: Arunav Nayak Biswanath Chakravarty Jayjeet Dey Swagatika RathSudeshna SahuPas encore d'évaluation
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Wits Appraisalnof Jaw Disharmony by JOHNSONDocument20 pagesWits Appraisalnof Jaw Disharmony by JOHNSONDrKamran MominPas encore d'évaluation
- Space Saving, Tight AccessibilityDocument4 pagesSpace Saving, Tight AccessibilityTran HuyPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit: 1: Newton's Laws of Motion & Principle of Transmissibility of ForceDocument5 pagesUnit: 1: Newton's Laws of Motion & Principle of Transmissibility of ForceKunal SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- El TontoDocument92 pagesEl TontoRobertPas encore d'évaluation
- T Rex PumpDocument4 pagesT Rex PumpWong DaPas encore d'évaluation
- Silapathikaram 3Document37 pagesSilapathikaram 3gavinilaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Performance Evaluation Report For Practicum TraineesDocument2 pagesPerformance Evaluation Report For Practicum TraineesJ.S100% (3)
- Portfolio AdityaDocument26 pagesPortfolio AdityaAditya DisPas encore d'évaluation
- Eu Clinical TrialDocument4 pagesEu Clinical TrialAquaPas encore d'évaluation
- FT FocusDocument19 pagesFT Focusobi1kenobyPas encore d'évaluation
- PDF Synopsis PDFDocument9 pagesPDF Synopsis PDFAllan D GrtPas encore d'évaluation
- Multi Core Architectures and ProgrammingDocument10 pagesMulti Core Architectures and ProgrammingRIYA GUPTAPas encore d'évaluation
- 5070 s17 QP 22 PDFDocument20 pages5070 s17 QP 22 PDFMustafa WaqarPas encore d'évaluation
- Hansen Aise Im Ch12Document66 pagesHansen Aise Im Ch12Rizki19maretPas encore d'évaluation
- Bankers ChoiceDocument18 pagesBankers ChoiceArchana ThirunagariPas encore d'évaluation
- A Vision System For Surface Roughness Characterization Using The Gray Level Co-Occurrence MatrixDocument12 pagesA Vision System For Surface Roughness Characterization Using The Gray Level Co-Occurrence MatrixPraveen KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Andromeda: Druid 3 Warborn06Document5 pagesAndromeda: Druid 3 Warborn06AlanPas encore d'évaluation
- BBO2020Document41 pagesBBO2020qiuPas encore d'évaluation
- ФО Англ.яз 3клDocument135 pagesФО Англ.яз 3клБакытгуль МендалиеваPas encore d'évaluation
- Name: Mercado, Kath DATE: 01/15 Score: Activity Answer The Following Items On A Separate Sheet of Paper. Show Your Computations. (4 Items X 5 Points)Document2 pagesName: Mercado, Kath DATE: 01/15 Score: Activity Answer The Following Items On A Separate Sheet of Paper. Show Your Computations. (4 Items X 5 Points)Kathleen MercadoPas encore d'évaluation
- ERBS UPDATE John Doe ProceedingDocument3 pagesERBS UPDATE John Doe ProceedingtpeppermanPas encore d'évaluation
- DescriptiveDocument1 pageDescriptiveRizqa Anisa FadhilahPas encore d'évaluation
- Catalogue Laboratory Products - Heraeus KulzerDocument288 pagesCatalogue Laboratory Products - Heraeus KulzerDentaDentPas encore d'évaluation
- Cutler Hammer Dry Type TransformerDocument220 pagesCutler Hammer Dry Type TransformernprajanPas encore d'évaluation
- M.T Nautica Batu Pahat: Clean Product Tanker 4,497 BHPDocument1 pageM.T Nautica Batu Pahat: Clean Product Tanker 4,497 BHPSuper 247Pas encore d'évaluation
- Wall Panel SystemsDocument57 pagesWall Panel SystemsChrisel DyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5 - Amino acids and Proteins: Trần Thị Minh ĐứcDocument59 pagesChapter 5 - Amino acids and Proteins: Trần Thị Minh ĐứcNguyễn SunPas encore d'évaluation
- Discover It For StudentsDocument1 pageDiscover It For StudentsVinod ChintalapudiPas encore d'évaluation
- Travelstart Ticket (ZA10477979) PDFDocument2 pagesTravelstart Ticket (ZA10477979) PDFMatthew PretoriusPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 4 How To Make Self-Rescue Evacuation Maps?Document85 pagesModule 4 How To Make Self-Rescue Evacuation Maps?RejiePas encore d'évaluation