Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
There Are Three Types of Rock
Transféré par
Jayson Jugan MangubatDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
There Are Three Types of Rock
Transféré par
Jayson Jugan MangubatDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
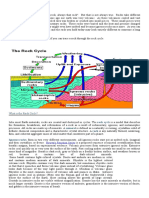
There are three types of rock. 1.
Igneous: these are rocks that solidified directly from molten silicates, which geologists call magma. Examples are: granite, basalt, pumice and flint (which is a form of quartz). 2. Sedimentary: these are formed when igneous rocks are eroded as a sediment under the sea. Fossils are often found in this layer. Examples are limestone, chalk, sandstone. 3. Metamorphic: these are made up of igneous and sedimentary rocks of all ages which have been subjected to intense pressure. Examples are: slate, marble, quartzite Weathering is the gradual destruction of rock under surface conditions. DEGRADATION the act of degrading or the state of being degraded. Gravity is a force that is exerted between to objects with mass. This force is also what keeps planets, asteroids, comets, and star in orbit. Erosion is the general name for the processes that break down rocks (weathering) and the processes that carry away the breakdown products (transportation). Sediments solid fragments of inorganic or organic material that come from the weathering of rock and are carried and deposited by wind, water, or ice. Compaction the process by which the porosity of a given form of sediment is decreased as a result of its mineral grains being squeezed together by the weight of overlying sediment or by mechanical means. Cementationthe process of heating a solid with a powdered material tomodify the properties of the solid, esp the heatin g of wroughtiron, surrounded with charcoal, to 750--900C to produce steel
Stages of Cognitive Development
Stage Sensori-motor (Birth-2 yrs) Characterised by Differentiates self from objects Recognises self as agent of action and begins to act intentionally: e.g. pulls a string to set mobile in motion or shakes a rattle to make a noise Achieves object permanence: realises that things continue to exist even when no longer present to the sense (pace Bishop Berkeley) Pre-operational (2-7 years) Learns to use language and to represent objects by images and words Thinking is still egocentric: has difficulty taking the viewpoint of others Classifies objects by a single feature: e.g. groups together all the red blocks regardless of shape or all the square blocks regardless of colour Concrete operational (7-11 years) Can think logically about objects and events Achieves conservation of number (age 6), mass (age 7), and weight (age 9) Classifies objects according to several features and can order them in series along a single dimension such as size. Formal operational (11 years and up) Can think logically about abstract propositions and test hypotheses systemtically Becomes concerned with the hypothetical, the future, and ideological problems
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Types of Rocks: Learning Activity Sheet in Earth and Life Sciences No. 4Document13 pagesTypes of Rocks: Learning Activity Sheet in Earth and Life Sciences No. 4Lopez AeraPas encore d'évaluation
- Module SCI101 EARTH SCI ROCKSDocument8 pagesModule SCI101 EARTH SCI ROCKSLarah Jane MaravilesPas encore d'évaluation
- Rock Cycle & Formation of Igneous, Sedimentary, Metamorphic RocksDocument8 pagesRock Cycle & Formation of Igneous, Sedimentary, Metamorphic RocksJamesBuensalidoDellavaPas encore d'évaluation
- ELS Q1 Module-2Document10 pagesELS Q1 Module-2Teacher Charlyn VlogPas encore d'évaluation
- Earth Science ReviewerDocument4 pagesEarth Science ReviewerMark Vincent Rei VillacruzPas encore d'évaluation
- 7 ExogenicDocument24 pages7 ExogenicLorena DizonPas encore d'évaluation
- Muli Abm 3 Lesson3 RocksDocument2 pagesMuli Abm 3 Lesson3 RocksKristine Joy MuliPas encore d'évaluation
- Rocks Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesRocks Lesson Planapi-241268840Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1st Quarter NotesDocument6 pages1st Quarter NotesCherry Pink VillanuevaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rocks and MineralsDocument5 pagesRocks and MineralsRachelle Monn OcsioPas encore d'évaluation
- Name: Atangen, Kezel Ann D. Schedule: WSAT / 3:30PM-6:10PMDocument3 pagesName: Atangen, Kezel Ann D. Schedule: WSAT / 3:30PM-6:10PMKezel AtangenPas encore d'évaluation
- Earth Science HandoutsDocument6 pagesEarth Science HandoutsPhia ViaPas encore d'évaluation
- Trimmed 19 Es q2 Week 2.3Document7 pagesTrimmed 19 Es q2 Week 2.3Nikha Mae BautistaPas encore d'évaluation
- 8I Science T3 Studypack 03 (7H Rocks)Document6 pages8I Science T3 Studypack 03 (7H Rocks)Mohammed AlmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Geology and Rock CycleDocument13 pagesGeology and Rock CycleMichael AkinolaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Rock CycleDocument3 pagesThe Rock CycleRODJHEN ANNE P. BARQUILLAPas encore d'évaluation
- Science ReviewerDocument6 pagesScience ReviewerPositive ReflectionPas encore d'évaluation
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument18 pagesEarth and Life Scienceamaeamee ameaimePas encore d'évaluation
- Reviewer in EARTH and LIFE SCIENCE 11Document4 pagesReviewer in EARTH and LIFE SCIENCE 11ashryn blaizePas encore d'évaluation
- SSC Petrology: Classification of Igneous, Sedimentary & Metamorphic RocksDocument11 pagesSSC Petrology: Classification of Igneous, Sedimentary & Metamorphic RocksArianne Mae De Vera GallonPas encore d'évaluation
- Rock Cycle 2Document21 pagesRock Cycle 2Shineey AllicerePas encore d'évaluation
- (2-3) ES Reviewer - 2Document5 pages(2-3) ES Reviewer - 2rudfrancoPas encore d'évaluation
- LP LP 1Document7 pagesLP LP 1gienald jane gargarPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Earth (Fifth Ed.) Chapter 4Document23 pagesUnderstanding Earth (Fifth Ed.) Chapter 4Patrece TogaPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 28 Earth and Life ScienceDocument6 pagesWeek 28 Earth and Life ScienceAntonette CastilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2 Earth and Life Science Sep.27Document19 pagesModule 2 Earth and Life Science Sep.27Denise CañaPas encore d'évaluation
- Melc 9 Stratification of RocksDocument26 pagesMelc 9 Stratification of Rockslost at seaPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Geography SyllabusDocument21 pagesPhysical Geography SyllabusAwais BakshyPas encore d'évaluation
- Els FinalsDocument8 pagesEls FinalsAlliah ManilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan For Demo TeachingDocument4 pagesLesson Plan For Demo TeachingJane TanamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Metamorphic, Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks : Sorting Them Out - Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksD'EverandMetamorphic, Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks : Sorting Them Out - Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksPas encore d'évaluation
- EarthSci Reviewer - Layers of Rocks and WeatheringDocument8 pagesEarthSci Reviewer - Layers of Rocks and WeatheringKipi KipsPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Rocks2Document4 pagesTypes of Rocks2Shahid BaigPas encore d'évaluation
- 11ELDocument12 pages11ELCutieclaire AcPas encore d'évaluation
- Cruz, Kyrene Kesia B. 11 STEM-HDocument5 pagesCruz, Kyrene Kesia B. 11 STEM-HKesia CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Eal Module 2Document7 pagesEal Module 2Angelina Jolai CentenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Exogenic Forceslong QuizDocument7 pagesExogenic Forceslong QuizMr Shn MrcdPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 3 EARTH MATERIALS AND PROCESSESDocument6 pagesLesson 3 EARTH MATERIALS AND PROCESSESAj ManalastasPas encore d'évaluation
- Local Media5988609580861488696Document9 pagesLocal Media5988609580861488696Dise WrightsPas encore d'évaluation
- Rock Cycle and Weathering ProcessesDocument9 pagesRock Cycle and Weathering ProcessesRiguel Jameson AllejePas encore d'évaluation
- WK 2 LasDocument5 pagesWK 2 LasRONALD ARTILLEROPas encore d'évaluation
- Rock Cycle and Weathering ProcessesDocument10 pagesRock Cycle and Weathering ProcessesNagum RhiannePas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Geology PDFDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Geology PDFAydan MustafayevaPas encore d'évaluation
- Evidence 2 - Lesson Plan 8 The Rock CycleDocument4 pagesEvidence 2 - Lesson Plan 8 The Rock Cycleapi-280103959Pas encore d'évaluation
- What Will You Learn?: The Rock CycleDocument6 pagesWhat Will You Learn?: The Rock CycleXylef Christiana Love YonsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Earth Life Science Week 2 Final 1Document17 pagesEarth Life Science Week 2 Final 1Ronald ArtilleroPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 2 Earth ScieDocument10 pagesLesson 2 Earth Sciecrizanne barsatanPas encore d'évaluation
- G11 Earth Science - Week 3Document16 pagesG11 Earth Science - Week 3mn KimPas encore d'évaluation
- Middle School Lesson Plan Totally TectonicDocument9 pagesMiddle School Lesson Plan Totally Tectonicapi-617919130Pas encore d'évaluation
- Video-Based Instruction in ELSDocument13 pagesVideo-Based Instruction in ELSJESSA SUMAYANGPas encore d'évaluation
- LAS EALS Final - Rock CycleDocument1 pageLAS EALS Final - Rock CycleBenito OmalPas encore d'évaluation
- Traditional Theories Genesis - Hebrew, Bible 6 Days of CreationDocument6 pagesTraditional Theories Genesis - Hebrew, Bible 6 Days of CreationRoniel Erni Bernarte100% (1)
- Rock and Extrusive Igneous RockDocument1 pageRock and Extrusive Igneous Rocklovely venia m jovenPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 5-HLAS (Stratified Rocks Formation)Document13 pagesWeek 5-HLAS (Stratified Rocks Formation)Cheena Francesca LucianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pertemuan 2 - MikropaleontologiDocument18 pagesPertemuan 2 - MikropaleontologiHairun AnwarPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 4: Classification of Rocks: ObjectivesDocument6 pagesLesson 4: Classification of Rocks: ObjectivesArabella Balasanos MorfePas encore d'évaluation
- Earth Science Module 12Q2 ReviewerDocument6 pagesEarth Science Module 12Q2 ReviewerJohn Aiddy VillahermosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Teaching Science in The Elementary GradesDocument9 pagesTeaching Science in The Elementary GradesJeffrey CabangonPas encore d'évaluation
- Rock Collecting for Kids: An Introduction to GeologyD'EverandRock Collecting for Kids: An Introduction to GeologyÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- E-Class Record Sheet SummaryDocument63 pagesE-Class Record Sheet SummaryMae MallaprePas encore d'évaluation
- First Periodical Test in Math IV-2022-23Document5 pagesFirst Periodical Test in Math IV-2022-23Jayson Jugan MangubatPas encore d'évaluation
- IPlan Scope & Sequence in Science VDocument1 pageIPlan Scope & Sequence in Science VJayson Jugan MangubatPas encore d'évaluation
- 20 Powerful Health Benefits of Guyabano Leaves TeaDocument8 pages20 Powerful Health Benefits of Guyabano Leaves TeaJayson Jugan Mangubat100% (4)
- MS EXCEL USER MANUAL COMMANDSDocument5 pagesMS EXCEL USER MANUAL COMMANDSNhil Cabillon QuietaPas encore d'évaluation
- Thinking Out Loud PDFDocument2 pagesThinking Out Loud PDFRonald SondakhPas encore d'évaluation
- Africa FlagDocument1 pageAfrica FlagJayson Jugan MangubatPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Electronics (Report)Document20 pagesBasic Electronics (Report)Jayson Jugan MangubatPas encore d'évaluation
- Closing PrayerDocument1 pageClosing PrayerJayson Jugan MangubatPas encore d'évaluation
- Scout YellsDocument2 pagesScout YellsThristan Dy Polintan83% (6)
- Grad MSG 13editDocument1 pageGrad MSG 13editJayson Jugan MangubatPas encore d'évaluation
- Edukasyong An at PangkabuhayanDocument122 pagesEdukasyong An at PangkabuhayanXylene Lariosa-Labayan100% (7)
- Chapter 6 Outline MemoryDocument9 pagesChapter 6 Outline MemoryJayson Jugan MangubatPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes Scout Songs 01Document6 pagesNotes Scout Songs 01marnf09Pas encore d'évaluation
- STEP Skills Home Economics Appliqué ContestDocument5 pagesSTEP Skills Home Economics Appliqué ContestJayson Jugan MangubatPas encore d'évaluation
- Prayer After ClassDocument2 pagesPrayer After ClassJayson Jugan MangubatPas encore d'évaluation
- 2276 Compound WordsDocument66 pages2276 Compound WordsMoonBunnyPas encore d'évaluation
- Word OrderDocument4 pagesWord OrderJayson Jugan MangubatPas encore d'évaluation
- Six Rules For Making Subjects and Verbs AgreeDocument2 pagesSix Rules For Making Subjects and Verbs AgreeJayson Jugan MangubatPas encore d'évaluation
- Structure of Sedimentary RockDocument62 pagesStructure of Sedimentary RockOmelPas encore d'évaluation
- Geology of North Machakos - Thika AreaDocument48 pagesGeology of North Machakos - Thika AreaBernard Kipng'enoPas encore d'évaluation
- Other Characteristics:: Name of Rock: Granite Type of Rock: IgneousDocument2 pagesOther Characteristics:: Name of Rock: Granite Type of Rock: IgneousKamal CEPas encore d'évaluation
- Las BambasDocument5 pagesLas BambasEduardo GamboaPas encore d'évaluation
- Geological Desciption (Simple Way To Describe) ..SpecialDocument8 pagesGeological Desciption (Simple Way To Describe) ..SpecialSyed ShaiqPas encore d'évaluation
- Tbi ScriptDocument2 pagesTbi ScriptMC Hanith ScdPas encore d'évaluation
- An Rs Final Mineral ReportDocument95 pagesAn Rs Final Mineral ReportYohannes Woldekidan100% (3)
- Sedimentology WikipediaDocument5 pagesSedimentology Wikipediaalpes27Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Executive Summary PT. BJE - PT. MJENDocument37 pages1 Executive Summary PT. BJE - PT. MJENSinatra LimPas encore d'évaluation
- Petrology 40 1241 - UnlockedDocument29 pagesPetrology 40 1241 - UnlockedMarco MinamiPas encore d'évaluation
- Geochronology in Myanmar (1964-2017)Document47 pagesGeochronology in Myanmar (1964-2017)Nay AungPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 7Document33 pagesModule 7Dan Philip De GuzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 1 - Module 9: Igneous Rocks: How Are They Formed?Document26 pagesEarth and Life Science: Quarter 1 - Module 9: Igneous Rocks: How Are They Formed?KJEN CALOSOR100% (5)
- Girish Part 4Document21 pagesGirish Part 4Girish GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 12: Understanding VolcanoesDocument47 pagesModule 12: Understanding VolcanoesBagas AryaPas encore d'évaluation
- Jairo Alonso Paredes-C., Luís Miguel Romero-R., Julián David de Bedout-O. & Carlos Mauricio Bernal-RDocument7 pagesJairo Alonso Paredes-C., Luís Miguel Romero-R., Julián David de Bedout-O. & Carlos Mauricio Bernal-RJhon barreraPas encore d'évaluation
- Inside Our EarthDocument3 pagesInside Our EarthAli Imran NaqviPas encore d'évaluation
- Sulfur isotope study reveals sources of elements in Macedonian metal depositsDocument4 pagesSulfur isotope study reveals sources of elements in Macedonian metal depositsgoranktasevPas encore d'évaluation
- Geoheritage of Labuan Island: Bulletin of The Geological Society of Malaysia December 2016Document14 pagesGeoheritage of Labuan Island: Bulletin of The Geological Society of Malaysia December 2016songkkPas encore d'évaluation
- Optimizing Mineral Resource Management in North BengkuluDocument11 pagesOptimizing Mineral Resource Management in North Bengkuluharman dwi rPas encore d'évaluation
- Stratified RocksDocument16 pagesStratified RocksJanuxie ParkPas encore d'évaluation
- Metamorphic RocksDocument33 pagesMetamorphic RocksTiisetso MokwanePas encore d'évaluation
- Science CanvaDocument2 pagesScience CanvaGraciella Abigail ConsolacionPas encore d'évaluation
- MetamorfDocument19 pagesMetamorfrandom personPas encore d'évaluation
- Philippine Volcanoes ModuleDocument39 pagesPhilippine Volcanoes ModuleAngeline Panaligan AnselaPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification of RocksDocument5 pagesClassification of RocksStephanie Nichole Ian CasemPas encore d'évaluation
- PreCm Geology of Finland - Lehtinen Et Al - 2005 - BOOK PDFDocument751 pagesPreCm Geology of Finland - Lehtinen Et Al - 2005 - BOOK PDFLubomira MachevaPas encore d'évaluation
- Earth Science: Quarter 1 - Module 3Document36 pagesEarth Science: Quarter 1 - Module 3Adrian Valdez100% (2)
- The Palaeozoic Sedimentary Rocks of Peninsular MalaysiaDocument19 pagesThe Palaeozoic Sedimentary Rocks of Peninsular MalaysiaMuhammadHaziqYussofPas encore d'évaluation
- IJETR022949Document5 pagesIJETR022949erpublicationPas encore d'évaluation