Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Ang Guryon
Transféré par
Ge AlenainDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Ang Guryon
Transféré par
Ge AlenainDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
"Ang Guryon" ni Ildefonso Santos Tanggapin mo, anak, itong munting guryon na yari sa patpat at papel de Hapon; magandang
laruang pula, puti, asul, na may pangalan mong sa gitna naroon. Ang hiling ko lamang, bago paliparin ang guryon mong ito ay pakatimbangin; ang solo't paulo'y sukating magaling nang hindi mag-ikit o kaya'y magkiling. Saka pag sumimoy ang hangin , ilabas at sa papawiri'y bayaang lumipad; datapwa't ang pisi'y tibayan mo, anak,
at baka lagutin ng hanging malakas. Ibigin mo't hindi, balang araw ikaw ay mapapabuyong makipagdagitan; makipaglaban ka, subali't tandaan na ang nagwawagi'y ang pusong marangal. At kung ang guryon mo'y sakaling madaig, matangay ng iba o kaya'y mapatid; kung saka-sakaling di na mapabalik, maawaing kamay nawa ang magkamit! Ang buhay ay guryon: marupok, malikot, dagiti't dumagit, saanman sumuot... O, paliparin mo't ihalik sa Diyos, bago pa tuluyang sa lupa'y sumubsob!
1.Skimming is reading by the sign posts or clues in the selection. It is fast reading in which the reader reads headings and topic sentences and spot-reads parts of paragraphs. It gives the reader an overview of the material. 2.Scanning is glancing through a page to locate a particular kind of information. It requires the reader first to identify key words or phrases related to the information sought and then focus attention on just those words as he glances over a page. 3.Idea reading is rapid reading of the main idea. The eyes catch large phrases at each glance and register in the brain only the most significant words in those phrases. Idea reading means making quick decisions, as to the importance of the different clues and rapidly associating them with ideas assimilated in previous experiences. 4.Explorative reading is done when one aims to get a fairly accurate picture of a whole presentation of ideas. It requires more concentration. 5. Study reading is characterize as the learner gets maximum understanding of the main idea and their relationships.
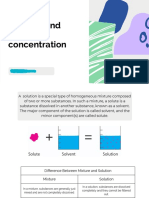
6.Critical reading is the reader stops to consider the facts carefully. It is not necessary to read fast because rapid reading of the main idea might lead to false conclusions. 7.Analytical reading is the type that demands careful attention to each word and its relative importance in relation to other words in the sentence or paragraph. In chemistry, a solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of only one phase. In such a mixture, a solute is a substance dissolved in another substance, known as a solvent. The solvent does the dissolving. The solution more or less takes on the characteristics of the solvent including its phase, and the solvent is commonly the major fraction of the mixture. The concentration of a solute in a solution is a measure of how much of that solute is dissolved in the solvent. the 2 parts of a solution are the solute and the solvent. The solute is what is being dissolved and the solvent is what is dissolving the solute. for example when you mix sugar and water the water is the solvent because the sugar gets dissolved by the water and the sugar is the solute because it is being dissolved. 1. gaseous solution- includes gases or vapors dissolved in one another.two or more gases can form a solution. Air is an example of a gaseous solution. When dry is made up of oxygen gas dissolved in nitrogen gas. 2. liquid solution-contain a liquid solvent in which gas, liquid, or solid is dissolved. Water is the most common liquid solution. Many things can be dissolved in it. Table salt is an example of a solid dissolved in a liquid. A liquid and a gas can also be dissolved in a liquid solution. 3. A solid solution-is a mixture of solids spread equally throughout one another. Metal is an example of a solid solution at room temperature.
1. Effect of Temperature For some substances to dissolve in a given solvent, heat is absorbed. The reaction is endothermic. In this case, an increase in temperature increases solubility. For some substances, heat is released when they dissolve in a given solvent. The reaction is called exothermic. In this case, an increase in temperature decreases solubility. Generally, an increase in temperature in the solubility of solids in liquids increases solubility. But for solubility of gas in liquids, an increase in temperature decreases solubility because gas evaporates as temperature increases. . 2. Effect of Pressure Pressure unlike temperature has little effect on solutions unless the solute is a gas. An increase in pressure causes greater interaction between particles of the gas and the liquid, thus, increasing solubility.
3. Nature of solute and solvent Nature of both the solute and the solvent affect the solubility. Substances with similar intermolecular attractive forces tend to be soluble in one another. This generalization is stated as "like dissolves like." Nonpolar solutes are soluble in non-polar solvents; polar or ionic solutes are soluble in polar solvents Liquids that are attracted by charged objects are composed of polar molecules; those that are not attracted by a charged body are non-polar
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Solubility in Inorganic ChemistryDocument17 pagesSolubility in Inorganic ChemistryGessa GelocaPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 4 in Physical ScienceDocument10 pagesModule 4 in Physical ScienceDarlyn MontillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Differentiating Solutes and Solvents in SolutionsDocument24 pagesDifferentiating Solutes and Solvents in Solutionscharis m. alejoPas encore d'évaluation
- SolutionsDocument6 pagesSolutionsKathryne May JinonPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity On SolutionsDocument7 pagesActivity On SolutionsPequiro, Dielle Ana ZilphaPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2 SolutionDocument2 pagesModule 2 SolutionLJ Valdez100% (1)
- The Big Chemistry Book on Solutions - Chemistry for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksD'EverandThe Big Chemistry Book on Solutions - Chemistry for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksPas encore d'évaluation
- Properties of solutionsDocument2 pagesProperties of solutionspratikPas encore d'évaluation
- Science: Quarter 1 - Module 1 Lesson 3: Factors Affecting SolubilityDocument4 pagesScience: Quarter 1 - Module 1 Lesson 3: Factors Affecting SolubilityAJ ALMODAPas encore d'évaluation
- Solutions Unit 4Document4 pagesSolutions Unit 4Toh YangPas encore d'évaluation
- Solutions: Solutions Are Homogeneous Mixtures. The Major Component Is Called Solvent, and TheDocument3 pagesSolutions: Solutions Are Homogeneous Mixtures. The Major Component Is Called Solvent, and TheAijeleth Shahar Gunay AwacayPas encore d'évaluation
- Qué Es Una Disolución Mapa ConceptualDocument3 pagesQué Es Una Disolución Mapa ConceptualYELITZAPas encore d'évaluation
- LP 5 Inorganic Chemistry With TemplateDocument11 pagesLP 5 Inorganic Chemistry With TemplateJOHNERROL CARCELLARPas encore d'évaluation
- Solutions and SolubilityDocument9 pagesSolutions and SolubilityDarrell W. GarwayPas encore d'évaluation
- Dr. Saidane Lecture Notes Properties of Solutions: Chem 200Document10 pagesDr. Saidane Lecture Notes Properties of Solutions: Chem 200Marko QuebralPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Properties of SolutionDocument3 pagesPhysical Properties of SolutionRhye Tabaday LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment NoDocument9 pagesExperiment NoJoselle Antonio BautistaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap 1 ChemistryDocument31 pagesChap 1 ChemistryLina AnberPas encore d'évaluation
- Melting and Boiling Points vs PolarityDocument14 pagesMelting and Boiling Points vs PolarityMALOU ELEVERAPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 6 Quarter 1 - Module 1 Lesson 3: Factors Affecting SolubilityDocument32 pagesScience 6 Quarter 1 - Module 1 Lesson 3: Factors Affecting Solubilitycharis m. alejoPas encore d'évaluation
- Edexcel IGCSE Chemistry States of Matter NotesDocument3 pagesEdexcel IGCSE Chemistry States of Matter NotesRS123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Substances Lesson 2 PropertiesDocument95 pagesChapter Introduction Lesson 1 Substances Lesson 2 PropertiesDavid Berl100% (1)
- растворы и концентрация 1Document21 pagesрастворы и концентрация 1Dorama AikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Las Piñas City National Science High School Module on Types of SolutionsDocument3 pagesLas Piñas City National Science High School Module on Types of SolutionsAvirel Reynante PodadorPas encore d'évaluation
- Essay SampleDocument7 pagesEssay SamplehanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 7 Reviewer ModulesDocument3 pagesScience 7 Reviewer ModulesArgie Mabag100% (2)
- Chapter 4 SolutionDocument22 pagesChapter 4 SolutionFiraol MamoPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 7 - Module 6 - Q1Document8 pagesScience 7 - Module 6 - Q1Benedick Conrad R. Glifunia67% (3)
- Solution, Suspension, ColloidsDocument149 pagesSolution, Suspension, ColloidsApril Eballena100% (1)
- Grade 6: Unit 2: MixtureDocument43 pagesGrade 6: Unit 2: MixtureEmylie Alvarez LantoriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Dissolution Explained: Solute Breaks Down Into SolventDocument1 pageDissolution Explained: Solute Breaks Down Into SolventAlma De GuzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of ChemistryDocument14 pagesPrinciples of ChemistrydinuPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 - SolutionsDocument6 pages8 - SolutionsDeng FajardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Solubility and Concentration of SolutionsDocument74 pagesSolubility and Concentration of SolutionstabilinPas encore d'évaluation
- HandoutsDocument4 pagesHandoutsMaria Sahara FregilPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution: Types of SolutionsDocument7 pagesSolution: Types of SolutionsJoanne SarzonaPas encore d'évaluation
- 12stem B - Week7Document3 pages12stem B - Week7Franz SorianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Physically CombinedDocument82 pagesPhysically CombinedRonalyn CariñoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch8 NotesDocument14 pagesCh8 NotesTriet NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Biology 8Document9 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Biology 8haniePas encore d'évaluation
- Solubility Factors and Solution TypesDocument10 pagesSolubility Factors and Solution TypesJohn Wilkins ToraynoPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.solutions FDocument33 pages2.solutions Fshrutianand8915Pas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Mixtures: Solutions, Colloids, and SuspensionsDocument1 pageTypes of Mixtures: Solutions, Colloids, and SuspensionsgabrielPas encore d'évaluation
- Mixtures and Solutions ExplainedDocument14 pagesMixtures and Solutions ExplainedSneham PalangdarPas encore d'évaluation
- Factors Affecting SolubilityDocument3 pagesFactors Affecting SolubilitySaphia W. DibarosanPas encore d'évaluation
- Solutions Properties and TypesDocument12 pagesSolutions Properties and TypesNikunj BatraPas encore d'évaluation
- Properties of Solutions - Students HandoutDocument2 pagesProperties of Solutions - Students HandoutOrlando Hepulan BandolesPas encore d'évaluation
- Study of Diffusion of Solids in LiquidsDocument15 pagesStudy of Diffusion of Solids in LiquidsAbhijithjb Jb88% (17)
- Lectuer 3-FOEDocument27 pagesLectuer 3-FOEamr.120230006Pas encore d'évaluation
- R. Marsh (Lab 1) - CorrectedDocument3 pagesR. Marsh (Lab 1) - CorrectedRavaughn MarshPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 3 - SOLUTION AND SOLUBILITYDocument4 pagesModule 3 - SOLUTION AND SOLUBILITYGabo AlfonsoPas encore d'évaluation
- MatterDocument4 pagesMatterJacinta MartinPas encore d'évaluation
- 0 - CH 6 - SolutionsDocument59 pages0 - CH 6 - SolutionsHazel OrionPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of Solutions: A Guide to Solvents, Solutes, Concentration and Factors Affecting SolubilityDocument24 pagesParts of Solutions: A Guide to Solvents, Solutes, Concentration and Factors Affecting SolubilityAlice RiveraPas encore d'évaluation
- Solubility: Physical PharmacyDocument14 pagesSolubility: Physical Pharmacyيوسف نوري عبدالله لايذPas encore d'évaluation
- Stem 006 Day 10Document8 pagesStem 006 Day 10Jayzl Lastrella CastanedaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5: Water and SolutionDocument10 pagesChapter 5: Water and SolutionYvonne LingPas encore d'évaluation
- 1bchemical MixturesDocument5 pages1bchemical MixturesCarlene Ashley AcebesPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of SolutionsDocument3 pagesTypes of SolutionsLinda VergesePas encore d'évaluation
- The Extraordinary Properties of Ordinary Solutions Fialkov MIRDocument110 pagesThe Extraordinary Properties of Ordinary Solutions Fialkov MIRstreetba100% (1)
- How To Write Chapter 5Document26 pagesHow To Write Chapter 5Ge Alenain100% (1)
- Context CluesDocument18 pagesContext CluesGe AlenainPas encore d'évaluation
- The Ten CommandmentsDocument1 pageThe Ten CommandmentsGe AlenainPas encore d'évaluation
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Quiz 1 - MacromoleculesDocument3 pagesQuiz 1 - MacromoleculesMariano Valiente Jr.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 4 Corrosion Rate - Tafel Plot Nurul HusnaDocument6 pagesExperiment 4 Corrosion Rate - Tafel Plot Nurul HusnaNurul Husna100% (1)
- Calcium Octoate MSDSDocument4 pagesCalcium Octoate MSDSFuture InnovationsPas encore d'évaluation
- tempPDF1288224222725463939 PDFDocument4 pagestempPDF1288224222725463939 PDFdeepanmb007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Stoichiometry Handout 6.1Document5 pagesStoichiometry Handout 6.1Vanesa DimasacupanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry - Test PrepDocument7 pagesChemistry - Test PrepMCHPas encore d'évaluation
- Study the Foaming Capacity of SoapDocument28 pagesStudy the Foaming Capacity of SoapAbhyudaya singh TanwarPas encore d'évaluation
- Semi Solid DosageDocument6 pagesSemi Solid Dosagekamini bahirPas encore d'évaluation
- The Cuprex Metal Extraction Process: Recovering Copper From Sulfide OresDocument6 pagesThe Cuprex Metal Extraction Process: Recovering Copper From Sulfide OresAwaken69Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cryogenic Piping Stress AnalysisDocument6 pagesCryogenic Piping Stress AnalysismasilamaniPas encore d'évaluation
- ESAB 308L, 316L & 309L Plus Stainless Steel ElectrodesDocument1 pageESAB 308L, 316L & 309L Plus Stainless Steel Electrodesanupmenon menonPas encore d'évaluation
- Cod and BodDocument7 pagesCod and BodTEDPas encore d'évaluation
- Nitrogen ChemistryDocument3 pagesNitrogen ChemistryjammyjammersPas encore d'évaluation
- Dust CleanerDocument2 pagesDust CleanercendraPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation Section 3 Pharmaceutical Form - enDocument12 pagesPresentation Section 3 Pharmaceutical Form - enalexPas encore d'évaluation
- Wk-Class 11 16-10-23 - 13102023 - 113902Document6 pagesWk-Class 11 16-10-23 - 13102023 - 113902Adithya PramodPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 18 - Pricelist of MedicinesDocument4 pagesLesson 18 - Pricelist of MedicinesGrace RepolloPas encore d'évaluation
- Explosion Proof ATEX LiftsDocument12 pagesExplosion Proof ATEX LiftshtpsharePas encore d'évaluation
- Castrol Iloform PN 49: DescriptionDocument2 pagesCastrol Iloform PN 49: DescriptionEmin MešićPas encore d'évaluation
- 10.1016@S0379 07380100484 4 PDFDocument8 pages10.1016@S0379 07380100484 4 PDFBrandon TimmPas encore d'évaluation
- Self-Smoothing Epoxy Cement for FloorsDocument2 pagesSelf-Smoothing Epoxy Cement for FloorsJohn vincent SalazarPas encore d'évaluation
- Return To TOC: Dowty Propellers Standard Practices ManualDocument11 pagesReturn To TOC: Dowty Propellers Standard Practices ManualNicolás PiratovaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemsheets GCSE 1093 (Reacting Mass Calculations 1) ANS 09351Document2 pagesChemsheets GCSE 1093 (Reacting Mass Calculations 1) ANS 09351J 6342100% (2)
- Submis 2Document14 pagesSubmis 2Cao Chen-RuiPas encore d'évaluation
- So2 AbsorptionDocument54 pagesSo2 AbsorptionWalamaniIbrahimPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Touch (RCC Do / Die Questions) Chapter: S-BlockDocument13 pagesFinal Touch (RCC Do / Die Questions) Chapter: S-Blockharita shindePas encore d'évaluation
- GALabsite - EXERCISE 4Document4 pagesGALabsite - EXERCISE 4EggPas encore d'évaluation
- APC Notes 2Document84 pagesAPC Notes 2srisuji14Pas encore d'évaluation
- D5819-05 (Reapproved 2016)Document11 pagesD5819-05 (Reapproved 2016)mithileshPas encore d'évaluation
- 0620 w15 Ms 63Document7 pages0620 w15 Ms 63Andrew HarrisonPas encore d'évaluation