Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Circle Theorems
Transféré par
Amir MohdDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Circle Theorems
Transféré par
Amir MohdDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
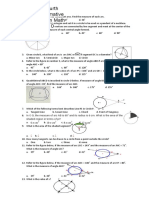
GCSE MATHEMATICS Higher Tier, topic sheet.
CIRCLE THEOREMS
1. In the diagram, O is the centre of the circle. Angle OAC = 12 and angle BOC = 80.
Calculate the size of the following angles, giving a geometrical reason for each of your answers. (a) (c) Angle OCA Angle ACB (b) (d) Angle AOC Angle ABC A
O C
B 2. The line PQR is a tangent to a circle with centre O. QS is a diameter of the circle. T is a point on the circumference of the circle such that POT is a straight line. The angle OPQ is 34. S
Not drawn accurately T
Calculate the size of angle TQR.
34 Q
3.
ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral and PA is a tangent to the circle at A. Angle BAP = 20 and angle ADC = 62. C
B P
20 62
Not to scale D
Find angles ABC and BAC.
A
B
4.
In the diagram, O is the centre of the circle. Angle COA = 100 Calculate
O
Not drawn accurately
(a) (b)
angle CBA,
100
angle CDA
C D
GCSE Topic sheets\Topic sheet Higher tier Circle theorems.doc
5.
A, B and C are points on the circumference of a circle centre O.
B P
D is a point on BC such that AOD is a straight line. PA is a tangent to the circle at A. Calculate angles x, y and z.
52
D O z A x 20 y
Not to scale
6.
In the diagram, O is the centre of the circle. SAT is a tangent to the circle at A. Angle BAC = 80 and angle SAB = angle TAC.
A
(a)
Calculate (i) angle BOC (iii) angle ABO
80
(ii) (iv)
angle OBC angle ACO.
B
O T
(b)
Explain why triangles OAB and OAC are congruent (identical).
C
7.
A, B, C and D are points on the circumference of a circle. BD is a diameter of the circle and PA is a tangent to the circle at A. Angle ADB = 25 and angle CDB = 18. (a) Write down the value of angle B (i) (b) BCD (ii) PAB. P Calculate angle ABC.
18 25
A
C
8.
AD is a diameter of a circle centre O. B and C are points on the circumference such that DC is parallel to OB. The angle OAC = 64. (a) (b) (c) (d) Calculate the size of angle ODC. Calculate the size of angle AOB.
D
64 O
Calculate the size of angle ACB. Calculate the size of angle OBC.
GCSE Topic sheets\Topic sheet Higher tier Circle theorems.doc
Answers. 1. (a) (b) (c)
(d) 2. 3. 62o.
OCA = OAC by isosceles triangles. 12o. Angles in a triangle add to 180o. 156o. 1 1 ACB = AOB = (156 80) = 38o. 2 2 1 (360 156) = 102o. 2
ABC = 180 62o = 118o. {ACB = 20o by the alternate segment theorem} BAC = 180 (118 + 20) = 42o.
(a) (b) 100 2 = 50o. 180 50 = 130o.
4.
5.
x = 52o by the alternate segment theorem. AOC = 2 52o = 104o. y = 180 104 = 76o. z = 58o.
(a) (b) (a) (b) (a) (b) (c) (d) (ii) 10o (iii) 40o (iv) 40o. (i) 160o Each triangle has 2 pairs of equal sides and all corresponding angles equal. (i) 90o o 137 . 26o. 26o. 13o. 77o. (ii) 25o.
6.
7.
8.
GCSE Topic sheets\Topic sheet Higher tier Circle theorems.doc
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Unit 10 (Circles) : Exercise 10.1: Multiple Choice Questions (MCQS)Document26 pagesUnit 10 (Circles) : Exercise 10.1: Multiple Choice Questions (MCQS)renu tomarPas encore d'évaluation
- Summative Test 2.4Document2 pagesSummative Test 2.4Jaymar SarvidaPas encore d'évaluation
- Circle Theorems Exam QuestionsDocument4 pagesCircle Theorems Exam QuestionsglennPas encore d'évaluation
- Circle Theorems Exam QuestionsDocument4 pagesCircle Theorems Exam Questionssanand1180% (5)
- Circle Theorems Worksheet: B A B ODocument1 pageCircle Theorems Worksheet: B A B Ogirlzrock2230% (1)
- Exam Style Trig With Bearings With AnswersDocument6 pagesExam Style Trig With Bearings With AnswersrishiPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT 4 Scientific Notation CSEC Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument2 pagesUNIT 4 Scientific Notation CSEC Multiple Choice QuestionsJagdeesh Gosine100% (1)
- Pythagorean Theorem: Score: NameDocument2 pagesPythagorean Theorem: Score: NamecharolesPas encore d'évaluation
- Circle Theorems 1Document2 pagesCircle Theorems 1Nurul NajwaPas encore d'évaluation
- Grey Kangaroo 2021 SolutionsDocument12 pagesGrey Kangaroo 2021 SolutionsAbu Huraira CheemaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 6 Practice Test Equations and InequalitiesDocument9 pagesUnit 6 Practice Test Equations and Inequalitiesapi-302040584100% (1)
- Similarity+criteria+worksheet pdf1Document5 pagesSimilarity+criteria+worksheet pdf1shihadnk0% (3)
- Geometry Chapter 12 Surface Area and VolumeDocument6 pagesGeometry Chapter 12 Surface Area and VolumeAlisaSivro0% (1)
- 7-Similar TrianglesDocument6 pages7-Similar Trianglesapi-2372712210% (1)
- Sin and Cos Rule Exam QuestionsDocument3 pagesSin and Cos Rule Exam QuestionsKavya KishorePas encore d'évaluation
- Math 10 - Post Test - TQ KA TOSDocument16 pagesMath 10 - Post Test - TQ KA TOSAmelita TupazPas encore d'évaluation
- Math 9 1stDocument10 pagesMath 9 1stWerty Gigz DurendezPas encore d'évaluation
- LInes and Angles MCQs Grade 9Document6 pagesLInes and Angles MCQs Grade 9zomer rowmahsPas encore d'évaluation
- Ws - Lines and AnglesDocument4 pagesWs - Lines and AnglesManya Elhance100% (1)
- Similarity Revision Test Mathematics Class XDocument3 pagesSimilarity Revision Test Mathematics Class XTalha SiddiquiPas encore d'évaluation
- Coordinate GeometryDocument5 pagesCoordinate Geometrynaisha kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- 2009 Metrobank-Mtap-Deped Math Challenge National Finals, Fourth-Year Level 4 April 2009 Questions, Answers, and SolutionsDocument9 pages2009 Metrobank-Mtap-Deped Math Challenge National Finals, Fourth-Year Level 4 April 2009 Questions, Answers, and SolutionsDanny Velarde0% (1)
- Summative Test Grade 10Document5 pagesSummative Test Grade 10Karen QuinioPas encore d'évaluation
- SS2 MCQDocument5 pagesSS2 MCQFranca OkechukwuPas encore d'évaluation
- Math 8 1st SummativeDocument2 pagesMath 8 1st SummativePano Mo NasabePas encore d'évaluation
- Math Preboards BangaloreDocument6 pagesMath Preboards Bangalorekarun.senthil.kumar.25Pas encore d'évaluation
- ReviewerDocument3 pagesReviewerGERRY MAKILANPas encore d'évaluation
- IB Math AI SL Questionbank - Hypothesis TestingDocument1 pageIB Math AI SL Questionbank - Hypothesis TestingCarolina CarlierPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Space QuestionsDocument2 pagesSample Space Questionsdela20% (1)
- Arithmetic Progression WorksheetDocument5 pagesArithmetic Progression Worksheetindian2011100% (2)
- Class 8 Math Worksheet 05-A Sequences (Turned In)Document3 pagesClass 8 Math Worksheet 05-A Sequences (Turned In)Arshad Bilal50% (2)
- CHAPTER 2 Polygons PDFDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 2 Polygons PDFherdiey_baikPas encore d'évaluation
- Diagnostic Exam in General MathematicsDocument2 pagesDiagnostic Exam in General MathematicsKaren PacabisPas encore d'évaluation
- Coordinate Geometry WorksheetDocument2 pagesCoordinate Geometry WorksheetsuperchellyPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Rules to Determine Congruent TrianglesDocument2 pages4 Rules to Determine Congruent TrianglesDenver O. Lelina100% (1)
- Grade 7: Lines and AnglesDocument4 pagesGrade 7: Lines and AnglesEduGain0% (1)
- Test 1 Discrete MathDocument3 pagesTest 1 Discrete MathMarcus McWile MorningstarPas encore d'évaluation
- Set Language & Notation WorksheetDocument5 pagesSet Language & Notation Worksheetphillochray5473Pas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Class 11 Mathematics Worksheet - Sequences and SeriesDocument1 pageCBSE Class 11 Mathematics Worksheet - Sequences and SeriesOmprakash BanshiwalPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 7. Trig and Radian MeasuresDocument15 pages6 7. Trig and Radian MeasuresMl SurakshaPas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Class 10 Mathematics Worksheet - Coordinate GeometryDocument2 pagesCBSE Class 10 Mathematics Worksheet - Coordinate GeometrySandya100% (1)
- Sine and Cosine Rule Exam QuestionsDocument2 pagesSine and Cosine Rule Exam QuestionsAPetulla5Pas encore d'évaluation
- Class 6-8 Maths and Science QuestionsDocument17 pagesClass 6-8 Maths and Science QuestionsRakesh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Exponent Laws I Review Grade 9Document6 pagesExponent Laws I Review Grade 9api-313311184Pas encore d'évaluation
- GCSE Entrance Exam MathsDocument6 pagesGCSE Entrance Exam MathsSun Htun KhinePas encore d'évaluation
- Name: - Date: - Score: - /95 Grade & Section: - Teacher: Ms. Joyce Anne T. YabutDocument2 pagesName: - Date: - Score: - /95 Grade & Section: - Teacher: Ms. Joyce Anne T. YabutJoyce Anne Tuala Yabut100% (1)
- Worksheet 1 - MatricesDocument10 pagesWorksheet 1 - MatricesShnia RodneyPas encore d'évaluation
- Imo Maths Olympiad Sample Question Paper 1 Class 5 (1) 2016Document20 pagesImo Maths Olympiad Sample Question Paper 1 Class 5 (1) 2016nitinguptachdPas encore d'évaluation
- Statistics Concepts Explained: Mean, Median, Mode, Range, Graphs & ExamplesDocument10 pagesStatistics Concepts Explained: Mean, Median, Mode, Range, Graphs & ExamplesZonish BakshPas encore d'évaluation
- Without Answers Circle GeoDocument5 pagesWithout Answers Circle GeoSWISH IncPas encore d'évaluation
- Nsejs Geometry Sa7Document8 pagesNsejs Geometry Sa7gobinda prasad barmanPas encore d'évaluation
- 1st and 2nd July-Geometry-Day17&18Document6 pages1st and 2nd July-Geometry-Day17&18Pradeep PanwarPas encore d'évaluation
- Geometry Practice Questions For SSC CGLDocument7 pagesGeometry Practice Questions For SSC CGLrajshrichormare21Pas encore d'évaluation
- LP 140317 Y11 Circle Thms 1Document4 pagesLP 140317 Y11 Circle Thms 1Redzuan SaidiPas encore d'évaluation
- Maths Class Ix Chapter 10 Circles Practice Paper 11 AnswersDocument10 pagesMaths Class Ix Chapter 10 Circles Practice Paper 11 Answersyash upasaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Circle 1Document2 pagesCircle 1Kritika DixitPas encore d'évaluation
- Geometry 123Document3 pagesGeometry 123vinayhedaoo28Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sine and Cosine Rule Problems (SL)Document22 pagesSine and Cosine Rule Problems (SL)Rudi Berlian100% (2)
- Properties of CirclesDocument14 pagesProperties of CirclesKhizar SaysPas encore d'évaluation
- FRACTIONS INSTRUCTION SHEET GUIDEDocument11 pagesFRACTIONS INSTRUCTION SHEET GUIDEfocuc98Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematicians: Mr. Clutter Villegas Middle School 2006-2007Document10 pagesMathematicians: Mr. Clutter Villegas Middle School 2006-2007Amir MohdPas encore d'évaluation
- What Are DecimalsDocument13 pagesWhat Are DecimalsAmir MohdPas encore d'évaluation
- Bodmas RuleDocument7 pagesBodmas RuleAmir MohdPas encore d'évaluation
- Golden Principles of Raising ChildrenDocument19 pagesGolden Principles of Raising ChildrenAmir MohdPas encore d'évaluation
- Asean Psychology in Context - Elizabeth NairDocument36 pagesAsean Psychology in Context - Elizabeth NairBram HarunPas encore d'évaluation
- Stat InferDocument114 pagesStat InferAmir MohdPas encore d'évaluation
- Compare Fractions and DecimalsDocument19 pagesCompare Fractions and DecimalsAmir MohdPas encore d'évaluation
- Teachers' Guide to MS Office ToolsDocument5 pagesTeachers' Guide to MS Office ToolsAmir MohdPas encore d'évaluation
- Circles Revision: Transformations Intercepts Using The Discriminant ChordsDocument11 pagesCircles Revision: Transformations Intercepts Using The Discriminant ChordsAmir MohdPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics and Civilizations: A Glimpse of The History of MathematicsDocument35 pagesMathematics and Civilizations: A Glimpse of The History of MathematicsPathik PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Guidance for Candidates Exam TipsDocument1 pageGuidance for Candidates Exam TipsAmir MohdPas encore d'évaluation
- Sets NotebookDocument26 pagesSets NotebookAmir MohdPas encore d'évaluation
- Trigonometric Functions Transformations and GraphingDocument12 pagesTrigonometric Functions Transformations and GraphingAmir MohdPas encore d'évaluation
- Great MathematiciansDocument17 pagesGreat MathematiciansSANDEEP SAXENA100% (14)
- Gaga Hand Dodgeball UnitDocument11 pagesGaga Hand Dodgeball Unitapi-488087636Pas encore d'évaluation
- Resume - CarlyDocument1 pageResume - Carlyapi-317491156Pas encore d'évaluation
- Multiplication Tables From 1 To 50Document51 pagesMultiplication Tables From 1 To 50Sairaj RajputPas encore d'évaluation
- Ib Psychology Course Syllabus 2014-15Document6 pagesIb Psychology Course Syllabus 2014-15api-255249178Pas encore d'évaluation
- Andrew Burton Resume1Document2 pagesAndrew Burton Resume1api-113889454Pas encore d'évaluation
- Synthika DocumentsDocument74 pagesSynthika Documentsje82929408Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pre Midterm Exam in NSTP 211Document3 pagesPre Midterm Exam in NSTP 211Daeniel PerladoPas encore d'évaluation
- Operations Management Managing Global Supply Chains 1st Edition Venkataraman Solutions ManualDocument32 pagesOperations Management Managing Global Supply Chains 1st Edition Venkataraman Solutions Manualburgee.dreinbwsyva100% (45)
- Savitribai Phule Pune University, Online Result PDFDocument1 pageSavitribai Phule Pune University, Online Result PDFshreyashPas encore d'évaluation
- Mark Scheme (Results) : November 2017Document20 pagesMark Scheme (Results) : November 2017BigPas encore d'évaluation
- Capitol University Medical Center PoliciesDocument5 pagesCapitol University Medical Center PoliciesCharles CagaananPas encore d'évaluation
- Eapp Q2 W3 FinalDocument9 pagesEapp Q2 W3 FinalMarven SindayPas encore d'évaluation
- Tragic Eikonografy A Conceptual History PDFDocument553 pagesTragic Eikonografy A Conceptual History PDFCristian TeodorPas encore d'évaluation
- Cpts 440 / 540 Artificial IntelligenceDocument65 pagesCpts 440 / 540 Artificial IntelligenceDuc Minh LePas encore d'évaluation
- Cultural Centre SynopsisDocument12 pagesCultural Centre SynopsisAr Manpreet Prince50% (2)
- Press Release - Beyond The HijabDocument2 pagesPress Release - Beyond The Hijabapi-307832929Pas encore d'évaluation
- Iliad Commentary Janko 13-16Document482 pagesIliad Commentary Janko 13-16crux95100% (10)
- The Hen in A Pen TBDocument5 pagesThe Hen in A Pen TBmauroPas encore d'évaluation
- Accounting Modular LearningDocument21 pagesAccounting Modular LearningClarissa Rivera VillalobosPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Two: Entrepreneurial Background, Trait and Motivation 2.1 The Entrepreneurial BackgroundDocument13 pagesChapter Two: Entrepreneurial Background, Trait and Motivation 2.1 The Entrepreneurial Backgroundsami damtewPas encore d'évaluation
- 3f48a028-bc42-4aa4-8a05-6cf92f32955aDocument15 pages3f48a028-bc42-4aa4-8a05-6cf92f32955ahoyiPas encore d'évaluation
- 2020-2021 Instructional Assistant ExpectationsDocument37 pages2020-2021 Instructional Assistant Expectationsapi-470333647Pas encore d'évaluation
- Student Interest SurveyDocument7 pagesStudent Interest Surveymatt1234aPas encore d'évaluation
- Racism in The ClassroomDocument30 pagesRacism in The ClassroomStephenPortsmouth100% (1)
- 1 Practical ResearchhhhhhhhhhDocument9 pages1 Practical ResearchhhhhhhhhhKarley GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- PR1 Sample Research MethodologyDocument25 pagesPR1 Sample Research MethodologyAliyah Wayne SunPas encore d'évaluation
- The Syndetic Paradigm: Robert AzizDocument334 pagesThe Syndetic Paradigm: Robert AzizBrian S. Danzyger100% (1)
- Daily Lesson Plan/Learning Guide For 2/9/17: The Diary of Anne FrankDocument2 pagesDaily Lesson Plan/Learning Guide For 2/9/17: The Diary of Anne Frankapi-341242820Pas encore d'évaluation
- OMSC Learning Module on the Contemporary WorldDocument105 pagesOMSC Learning Module on the Contemporary WorldVanessa EdaniolPas encore d'évaluation
- TLE CHS q3 Mod8 Basic Concepts of Electricity (Part III)Document15 pagesTLE CHS q3 Mod8 Basic Concepts of Electricity (Part III)Alona Acot100% (1)