Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
ISO 20k Checklist
Transféré par
maroli_yogeshCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
ISO 20k Checklist
Transféré par
maroli_yogeshDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
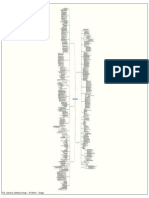
Process Administration ERP Factory Finance Human Resource IT Infrastructure Logistics Purchase Sales Software dev.
Warehousing Audit Date 6/2/2010 6/2/2010 6/3/2010 6/4/2010 6/7/2010 6/7/2010 6/8/2010 6/9/2010 6/10/2010 6/14/2010 6/15/2010
Auditees Rakesh Kumar Pankaj K, Neha G Dipesh S, Raja P Surendranath Ritesh R, Meena M Abhijeet p, Pankaj K Ganesh K, Yogesh B Shatrughna P, Shailesh S Ganapathi, Raj Sandeep, Nirmala R Raja P, Vairavel M, Dipesh S Process Human Resource Purchase Sales Administration ERP IT Infrastructure Logistics Finance Software dev. Warehousing Factory
Chandan M
Auditors Sudhir K
Yogesh M
Auditors
Auditees
3 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.3.1 3.3.2 3.3.3 4 4.1 4.1.1 4.1.2 4.1.3
4.1.4 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.4.1 4.4.2 5 5.1 5.2 6 6.1 6.1.1
6.1.2
6.1.3 6.1.4 6.2 6.2.1 6.2.2
6.2.3 6.3 6.3.1
6.3.2 6.3.3 6.3.4 6.4 6.4.1 6.4.2 6.4.3 6.4.4 6.5 6.6 6.6.1 6.6.2 6.6.3 6.6.4 6.6.5 6.6.6 6.6.7 7 7.1 7.2 7.2.1 7.2.2 7.2.3 7.3 7.3.1 7.3.2 7.3.3 7.3.4 7.3.5 7.3.6 8 8.1 8.1.1 8.1.2 8.2 8.2.1 8.2.2 8.3 8.3.1 8.3.2 8.3.3 8.3.4 8.3.5 8.3.6 8.3.7
8.3.8 8.3.9 8.3.10 9 9.1 9.1.1 9.1.2 9.1.3 9.1.4 9.1.5 9.2 9.2.1 9.2.2 9.2.3 9.2.4 10 10.1 10.1.1 10.1.2 10.1.3 10.1.4 10.1.5 10.1.6 10.1.7 10.1.8 10.1.9
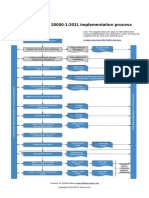
A management system with policies and framework to enable effective mngt. And implementation of services A Management representative supported by decision taking group with authority to define policies and enforce Policies, procedures, plans, processes and records should be documented and made avaialable for audit. These Competence, awareness andcompetence of the employee for the designated work. For this the mngt should define Management should ensure training competence for the role. Ensure that the personnel is aware of the criticality and importance of the position and how the position will contribute Identify the competency and skill level of the employee. Planning for training considering Professional development. to quality. existing requirements, future skill requirements and considering staff turnover.(Training can be courses, self study, mentoring and on job training). Individual professional and skill records should be maintained in chronological order An appropriate mix of short term and permanent recruits, with optimum mix of new with skilled staff. Also consider Plan Service management Plan implementation and delivery of service mngt Scope of the service management defined for org, location and the service rendered. A service management plan detailing implementation, delivery, changes, improvements and new services. Service management plan should be triggered by events such as service improvements, changes, standardizing infrastructure, regulatory & legislation changes, regulation resource, facilities and budgets necessary, framework of Contents of the plan. Scope, objectives and requirements, or deregulation of industry, mergers and acquisition. mngt responsibility and the process owners, interface bet'n processes. Approach to managing risks, resource allocation in terms of funds, skills and manpower. approach to change in plan, audit plans for quality control, processes and the tools to support the process. Implementing service management and providing services Monitor, measure and review the service management objectives and plans are achieved. For eg. Targets, resoure Continual improvement. Policy: Should drive the effort to make the services more effective and efficient. Awareness about the policy is a Planning for improvements: Initially define baseline for service quality and levels. With Data compare improvements Planning and implementing new or changed services Topics: Budgets, Manpower, existing service levels, SLAs / targets / service commitments, service mngt processes, Change management: Plans for recruitment, relocation, user training, communicating changes, changes in Service delivery process Service level management Service catalogue : Name of the service, targets, contact points, service hours / exceptions, on Customers business level agreements: Authorized by senior customer rep. SLA should be defined based security arrangements. needs and budget. SLAs should include appropriate subset of targets to focus attention. Min. content: Brief description, validity period / change control, authorization, communication including reporting, emergency team communication map, Service hours, scheduled and agreed interrruptions with notice details, customer responsibility, our liability and obligations, impact and priority, escalation and notification, complaints, service targets, workload limits, high level financial mngt, actionsthecase of service interruption, housekeeping procedures, glossary terms, Service level management: changes to in system due to growth, reorganization and mergers and changing customer requirements should be flexibly accomodated in the system. The process should manage and coordinate contributors of SLA i.e. agreement of service req. and workloads, service targets, measurement and reporting of service, reasons for targets not been achieved, Corrective actions and input for improving the service. Supporting service agreements : service dependency on delivered services should be documented and agreed with Servicerequirements for service reporting should bereliable,and recorded for customers and internal management. It Policy: reporting is done to produce agreed timely, agreed accurate reports for informed decision making and encompasses all measurable aspects of service, both current and historical analysis. These reports also apply to subcontractors and suppliers. Reports reports is tothe contract structure. Purpose and quality checks on service cascade on ensure timely, clear, reliable and concise reporting. Reports of both reactive as well as proactive nature shall be produced. Planned scheduled shall also be communicated in form of reports Service reports shall cover performance against Service level targets, Non-compliance, workload characteristics and volume information e.g incidents, problems, changes and tasks, classification, location, customer, seasonal trends, mix of priorities, number of requests for help. Performance reportingv following major events. Periodwise trend information. REporting on information from each process or functions. Reports to highlight future and scheduled Service continuity and available management helps to ensure agreed services continue to be provided in all Service continuity and availability requirements are assessed on the basis of customers business priorities, SLA and risk assessment. Sufficient Service capability needs to be maintianed with workable plans.
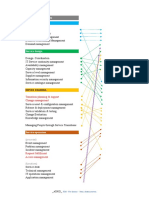
Service availability management should monitor and record avaialbility of service, maintain historical data, comparision with SLA to identify SLAs, and predict future avaialability and potential issues. Service continuity strategyplannedwith the customer on max permissible downtime, degraded and system shall be shared and tested for consistency, eg. Dependencies bet'n service service, RTO,RPO and components. Authority to invoke the plan. Backup of data, documenta and software, and any staff necessary for service restoration are quickly available following a major service failure or disaster. A minimal DR to be maintained. Budgeting and accounting for the cost of service provision Definition of what is chargeable and consideration cost types to be accounted, understood by the Service team and Fianancial management shal take in what is not should be clearly defined and breakups of overhead costs e.g. flat rate, fixed %age, based on size of the variable elements, divisions in the customer's business, rules governing the handling ofshould take into account variations, to service level management. Budgeting variances against budget and links planned changes exceeding budgeted funds. Also consider seasonal variations. Budget and cost tracking should support planning to operate and change the services sot ath SLA's are maintained throughout. Accounting process should be able to demonstrate over and under to meet the currentand understand cost of low Capacity management ensures that at all times, sufficient capacity spending/recovery and future agreed demands fo customer's business needs. A capacity plan documenting the actual performance of the infrastructure and the expected requirements should be produced at suitable frequencies. Information security management Information security is the result of a system of policies and procedures designed to identify, control and protect Asset classification security risk assessment risk to information assets. security and availability of information Controls and their application shall be managed by a personnel trained in the information security aspect. Documents and records shall be maintained relating to information security management system. Relationship Processes General Business relationship management Service reviews Service compliants Customer satisfaction measurements Supplier management Introduction Contract Management Service definition Managing mutiple suppliers Contractual disputes management Contract end Resolution processes Background Setting priorities workarounds incident management general Major incidents Problem management Scope of problem management Initiation of problem management Known errors Problem resolution Communication Tracking and escalation Incident and problem record closure
Problem reviews Topics of reviews Problem prevention Control processes Configuration management Configuration management planning and implementation Configuration identification configuration control Configuration status accounting and reporting Configuration verification and audit Change management Planning and implmentation Closing and reviewing the change request Emergency changes Change management reporting, analysis and actions Release process Release management process General Release policy Release and rollout planning Developing or acquiring software Design, build and configure release Release verification and acceptance Documentation Rollout, distribution and installation Post release and rollout
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- CheckList ISO 20000 1Document2 pagesCheckList ISO 20000 1Teresa SerraoPas encore d'évaluation
- ITIL Service DeliveryDocument1 pageITIL Service DeliverygringoricanPas encore d'évaluation
- Itil and The CMDBDocument5 pagesItil and The CMDBPaul James BirchallPas encore d'évaluation
- It Service Management: Improvement Plan: BY Uday Mishra, Global It Service Operation ManagerDocument31 pagesIt Service Management: Improvement Plan: BY Uday Mishra, Global It Service Operation Managerrajesh.j162763Pas encore d'évaluation
- Iso20000 2Document4 pagesIso20000 2Karloz PsyPas encore d'évaluation
- Iso 20000 2011.SMDocument36 pagesIso 20000 2011.SMiso20000docsPas encore d'évaluation
- ITIL v3 Overview AssessmentDocument13 pagesITIL v3 Overview AssessmentMohammad Faisal AbdulRabPas encore d'évaluation
- AvailabilityDocument9 pagesAvailabilityJyothi_B_PillaiPas encore d'évaluation
- ITIL - Service Validation and TestingDocument17 pagesITIL - Service Validation and TestingFederico MarzulloPas encore d'évaluation
- A Self-Assessment Tool For Estimation of IT MaturityDocument1 pageA Self-Assessment Tool For Estimation of IT MaturityVanessa García PinedaPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes ITIL4 Session 4-ITIL PDocument7 pagesNotes ITIL4 Session 4-ITIL PSean HunterPas encore d'évaluation
- QAF GuideDocument12 pagesQAF GuideShubham GoyalPas encore d'évaluation
- Iso Iec 20000Document16 pagesIso Iec 20000Aswini Srinath100% (1)
- Service Asset and Configuration ManagementDocument3 pagesService Asset and Configuration ManagementLauraCarvajalPas encore d'évaluation
- Service Level Management Leveraging Your Network InvestmentsDocument16 pagesService Level Management Leveraging Your Network InvestmentsΟλυμπίδης ΙωάννηςPas encore d'évaluation
- ISO 20000 2011 Vs ISO 9001 2015 Matrix EN PDFDocument21 pagesISO 20000 2011 Vs ISO 9001 2015 Matrix EN PDFIndu DevPas encore d'évaluation
- ITSM Training BrochureDocument55 pagesITSM Training Brochurevijayalakshmis76Pas encore d'évaluation
- ISO 20000 Implementation Diagram - ENDocument1 pageISO 20000 Implementation Diagram - ENNeymar Moura CarvalhoPas encore d'évaluation
- Process To PraticesDocument3 pagesProcess To PraticesAndrea GiulianiPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To ITIL V3Document62 pagesIntroduction To ITIL V3asheeshPas encore d'évaluation
- ITIL v.3 Processes & FunctionsDocument5 pagesITIL v.3 Processes & FunctionsAndrea GiulianiPas encore d'évaluation
- ITIL - ITIL Practitioner and Business Relationship ManagementDocument11 pagesITIL - ITIL Practitioner and Business Relationship ManagementgroenselboerPas encore d'évaluation
- ITIL, COBIT and EFQM - Can They Work Together PDFDocument12 pagesITIL, COBIT and EFQM - Can They Work Together PDFNiicolâs AndresPas encore d'évaluation
- A Survey of Information Technology GoverDocument27 pagesA Survey of Information Technology GoverLeo CerenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Service Desk: Process FactsheetDocument3 pagesService Desk: Process FactsheetPaul James BirchallPas encore d'évaluation
- 06 Continual Service ImprovementDocument19 pages06 Continual Service ImprovementIchwan HabibiePas encore d'évaluation
- IT Service Management: Using Process To Optimize Technology Resources and Delight CustomersDocument48 pagesIT Service Management: Using Process To Optimize Technology Resources and Delight CustomersJulius Villacruz100% (1)
- Continual Service Improvement (ITIL CSI) v3 - Process EvaluationDocument1 pageContinual Service Improvement (ITIL CSI) v3 - Process EvaluationAndrea GiulianiPas encore d'évaluation
- ETOM - AssuranceDocument32 pagesETOM - Assurancejaklaudiusz100% (1)
- Network Engineer Job Description PDFDocument2 pagesNetwork Engineer Job Description PDFPrasad KshirsagarPas encore d'évaluation
- It Asset ManagementDocument6 pagesIt Asset ManagementSwaminathan NatarajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Audit ChecklistDocument14 pagesAudit ChecklistARRY WIDODOPas encore d'évaluation
- GAP Analysis ChecklistDocument10 pagesGAP Analysis ChecklistKalpana SupePas encore d'évaluation
- Edition: Ning Itil V3 F Oundation E-Lear NingDocument2 pagesEdition: Ning Itil V3 F Oundation E-Lear NingAlejandro BoteroPas encore d'évaluation
- Capacity and PerformanceDocument358 pagesCapacity and PerformanceEric 'robo' Baafi100% (1)
- KnowYourBroadband AIRTELDocument15 pagesKnowYourBroadband AIRTELRohit AgarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Logging and Monitoring Policy-XX VersionDocument14 pagesLogging and Monitoring Policy-XX VersionRacs IndiaPas encore d'évaluation
- ITIL Service Operation Ver-1.2Document43 pagesITIL Service Operation Ver-1.2InvensislearningPas encore d'évaluation
- Iso 20000Document2 pagesIso 20000Wahid IqbalPas encore d'évaluation
- FIN Mindmap v4Document1 pageFIN Mindmap v4Paul James BirchallPas encore d'évaluation
- Four Dimension of Service ManagementDocument43 pagesFour Dimension of Service ManagementTiofenny AngelinaPas encore d'évaluation
- ISO 20000 Master List of DocumentsDocument1 pageISO 20000 Master List of DocumentsAditya YerunkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 10 - Managing Relationship With SupplierDocument25 pagesChapter 10 - Managing Relationship With SupplierChew hui qiPas encore d'évaluation
- PinkSCAN Change MGMTDocument8 pagesPinkSCAN Change MGMTMartin LeckPas encore d'évaluation
- ISACA-Mapping-Tool Res Eng 0117PDFDocument7 pagesISACA-Mapping-Tool Res Eng 0117PDFKhedidja OuhebPas encore d'évaluation
- BMC Remedy IT Service Management SuiteDocument4 pagesBMC Remedy IT Service Management SuiteAlexandru SteleaPas encore d'évaluation
- AVM Mindmap v4Document1 pageAVM Mindmap v4Paul James BirchallPas encore d'évaluation
- Valerie Arraj, Managing Director, Compliance Process Partners, LLCDocument5 pagesValerie Arraj, Managing Director, Compliance Process Partners, LLCmikeolmonPas encore d'évaluation
- ITSM Assessment Artifacts-1Document1 pageITSM Assessment Artifacts-1Murali PvPas encore d'évaluation
- 06100-FO8-Audit-Report 27001 27017 v2.0Document59 pages06100-FO8-Audit-Report 27001 27017 v2.0komal sablePas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study 4 Defra UnITyDocument46 pagesCase Study 4 Defra UnITyRohitPas encore d'évaluation
- Process Improvement Calculations ToolsDocument65 pagesProcess Improvement Calculations ToolsNevets Nonnac100% (1)
- Business Continuity Planning Final Internal Audit Report - Appendix 2 PDFDocument13 pagesBusiness Continuity Planning Final Internal Audit Report - Appendix 2 PDFkumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Management ProcessDocument15 pagesProblem Management ProcessVincenzo BasilePas encore d'évaluation
- NICF - Advanced - Network - Project - Presentation - Muhammad SalihinDocument11 pagesNICF - Advanced - Network - Project - Presentation - Muhammad Salihinمحمد صالحين بن سنينPas encore d'évaluation
- ISO 20000 Implementation Diagram - ENDocument1 pageISO 20000 Implementation Diagram - ENAyahnyaAzkaAzmiPas encore d'évaluation
- BMC Service Level Management 7.6.03 - Configuration GuideDocument124 pagesBMC Service Level Management 7.6.03 - Configuration GuidepisofPas encore d'évaluation
- SAP - QM ModuleDocument5 pagesSAP - QM Modulemaroli_yogeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Three GunasDocument10 pagesThree Gunasmaroli_yogeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Applicability of "5S" What Is "5S": Key To Succeed "5S" in AGSDocument20 pagesApplicability of "5S" What Is "5S": Key To Succeed "5S" in AGSmaroli_yogeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Degree To Which A Set of Inherent Characteristics Fulfills Requirements. (Stated, Implied or Obligatory)Document22 pagesDegree To Which A Set of Inherent Characteristics Fulfills Requirements. (Stated, Implied or Obligatory)maroli_yogeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Degree To Which A Set of Inherent Characteristics Fulfills Requirements. (Stated, Implied or Obligatory)Document22 pagesDegree To Which A Set of Inherent Characteristics Fulfills Requirements. (Stated, Implied or Obligatory)maroli_yogeshPas encore d'évaluation
- THREE COUNTS GA KM 10 25 2023 2Document15 pagesTHREE COUNTS GA KM 10 25 2023 2CannCon100% (4)
- Jurnal 5 PDFDocument8 pagesJurnal 5 PDFRatna Ayu KPas encore d'évaluation
- Strategic ProcurementDocument5 pagesStrategic ProcurementRick Spair100% (4)
- Pizza Hut and StarbucksDocument4 pagesPizza Hut and StarbucksHafizuddin ZaqiPas encore d'évaluation
- ITSM Excellence With Proven Training From The Industry LeaderDocument4 pagesITSM Excellence With Proven Training From The Industry LeadermeetacooldudePas encore d'évaluation
- Sia8 SoalDocument2 pagesSia8 SoalEsty Aisyah SarahPas encore d'évaluation
- Crocs Case StudyDocument2 pagesCrocs Case StudyJames WilliamsPas encore d'évaluation
- © Kumar NeerajDocument6 pages© Kumar NeerajsharmanmanuPas encore d'évaluation
- Hay Group Next Generation HR Research ReportDocument16 pagesHay Group Next Generation HR Research ReportbinubabuPas encore d'évaluation
- Schedule Assessment Guide - Best Practices For Project Schedules Dic15Document240 pagesSchedule Assessment Guide - Best Practices For Project Schedules Dic15José Nolasco100% (1)
- B327 Final TopicsDocument17 pagesB327 Final TopicsAbdullah SaleemPas encore d'évaluation
- BDSTIDocument5 pagesBDSTIPRANAV GOYALPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Resource Management: Decenzo and RobbinsDocument17 pagesHuman Resource Management: Decenzo and RobbinsMae FloresPas encore d'évaluation
- Electoral Reforms in India - Indian PolityDocument4 pagesElectoral Reforms in India - Indian PolityShweta Jain100% (1)
- Unisan, QuezonDocument2 pagesUnisan, QuezonSunStar Philippine NewsPas encore d'évaluation
- Sap PSDocument3 pagesSap PSSaif Ali MominPas encore d'évaluation
- Internal Audit StrategyDocument5 pagesInternal Audit StrategyAli CH0% (1)
- Kosh Patrika 2070 Nawa BarshaDocument124 pagesKosh Patrika 2070 Nawa Barshabinod_hada6975Pas encore d'évaluation
- Alabama 2020 Delegate Selection Plan FINAL v2Document51 pagesAlabama 2020 Delegate Selection Plan FINAL v2Ralph YoungPas encore d'évaluation
- Philippine Development Plan 2023 2028 - With - Link 351 450Document100 pagesPhilippine Development Plan 2023 2028 - With - Link 351 450Rocco ErarioPas encore d'évaluation
- Suffrage, Election, & Political PartiesDocument29 pagesSuffrage, Election, & Political PartiesDexter Balisi BacaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2: Analyzing The Business CaseDocument1 pageChapter 2: Analyzing The Business CaseteryPas encore d'évaluation
- PDF Isi CBR Trigonometri CompressDocument14 pagesPDF Isi CBR Trigonometri CompressAdam NurPas encore d'évaluation
- Domino's Pizza Inc Corporate Governance Principles For 2012Document6 pagesDomino's Pizza Inc Corporate Governance Principles For 2012Bhavya GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Supply Chain Management2977Document8 pagesSupply Chain Management2977andreea.gheorghescuPas encore d'évaluation
- Jack Welch Leading Organizational Change at GEDocument2 pagesJack Welch Leading Organizational Change at GEOmvirGautam100% (1)
- Explain Various Advantages of An SCM System For An OrganizationDocument2 pagesExplain Various Advantages of An SCM System For An Organizationpromi zahirPas encore d'évaluation
- Bahan SyllabusDocument2 pagesBahan SyllabusShantamPas encore d'évaluation
- Operations Management SeriesDocument4 pagesOperations Management SeriesErnest PaulPas encore d'évaluation
- Important Highlights of TLP 2021, Phase 1 ( 100 Days' Mains Answer Writing Program - Upsc 2021)Document4 pagesImportant Highlights of TLP 2021, Phase 1 ( 100 Days' Mains Answer Writing Program - Upsc 2021)HiamsjisbPas encore d'évaluation