Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Network Fundamentals - CCNA Exploration Companion Guide - Chapter 6 Notes
Transféré par
snowwolfyDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Network Fundamentals - CCNA Exploration Companion Guide - Chapter 6 Notes
Transféré par
snowwolfyDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Base 10, base 16, base 2 Base 16 is IPv6 Base 2 is IPv6 /26 is 32 /27 is 8 There are groups in 8 binary
(0-255) 255.255.2555.0 Subnet 192.168.1.25 # ALU multiplies subnet by the # All 0s =digital lter Mask * #=Network 1st # in any group is network # last number is the broadcast Class A 1-126 /8 Class B 128-191 /16 Class C 192-223/24 (256 addresses) Class D 224-239 Multicast Class E 240-255 exp 127 is a loop 169.254.x.x= DHCP is ofine, and ip was attained automatically. Loopback is 127.0.0..1-127.255.255.254 Untrackable IPs are 10.x.x.x or 172.(16-31).x.x Broadcast 255.255.255.255 Test route 192.0.2.0/24 Default route 0.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 192.168.1.21-200 DHCP pool is for workstations and voip 192.168.1.0-20 is for devices Layer 3 header has the destination IP Interface card cannot have a network number ip /26 /27 /25 /27 /23=512-2 255.255.254.0 /24=256-2 255.255.255.0
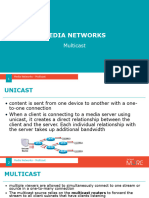
/25=128-2 255.255.255.128 /26=64-2 255.255.255.192 /27=32-2 255.255.255.224 /28=16-2 255.255.255.240 /29=8-2 255.255.255.248 /30=4-2 255.255.255.252 IPv4 has three common communication addressing: Unicast- Sending packet from one host to another host (Most common) Broadcast- Sending a packet from host to all in a network Multicast- Sending packet from host to a select group of hosts Broadcast: Layer 4 sending packet from host to all hosts Broadcast address- special address that allows communication, allows all receiving hosts to accept a packet (used by broadcast and multicast) Used for : Mapping upper-layer addresses to lower-layer addresses, requesting an address, exchanging routing info by routing protocols Not forwarded by a router (usually) Two types of Broadcasts: Directed broadcast, limited broadcast Directed Broadcast: Sent to all hosts on a network Used for sending broadcasts to all hosts on a nonlocal network Uses IPv4 destination with the highest address in a network Can be congured to be forwarded by a router Limited Broadcast: Limited to all hosts on the local network Can not be congured to be forwarded by a router A IPv4 network is better known as a broadcast domain Routers: Form boundary for a broadcast domain Multicast: Designed to conserve the bandwidth of a IPv4 Network Reduces trafc (allows a host to send a single packet to a certain set of hosts) Multicast groups: Hosts that want to receive multicast data are clients. When subscribed to the client joins a multicast group Represented by a single multicast address, but packets are also addressed to a unicast address for the client Multicast Used For: Video and audio broadcasts, routing (exchanging) information by some routing protocols, Distribution of software, News feeds
Multicast IPv4: Range:
Start Possible 224.0.0.0 End 239.255.255.255 Packets sent to these addresses are always transmitted with a Time To Live value of 1 Extra info
Reserved (for link-local addresses) 224.0.0.0
224.0.0.255
Multicast addresses are subdivided into: Reserved link-local addresses, globally scoped
addresses, and administratively scoped addresses (limited-scope addresses) See http://tools.ietf.org/pdf/rfc919.pdf for more info
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Ip Addressing The IP (Internet Protocol)Document5 pagesIp Addressing The IP (Internet Protocol)Novelyn RabinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ccna Notes KitDocument81 pagesCcna Notes KitMukesh BhakarPas encore d'évaluation
- MikroTik Lesson-02Document29 pagesMikroTik Lesson-02Tanvir AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Internet ProtocolDocument4 pagesInternet ProtocolMark Lester PicazoPas encore d'évaluation
- IPv6 UpdateDocument48 pagesIPv6 UpdateSivagnanam ThanusiganPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Network - Pertemuan 6 Dan 7Document26 pagesComputer Network - Pertemuan 6 Dan 7BantuinAku KakPas encore d'évaluation
- Internet Protocol MulticastDocument19 pagesInternet Protocol MulticastAbhijit ThakurPas encore d'évaluation
- Sub Netting ConceptsDocument29 pagesSub Netting Conceptsvijayd_gowdaPas encore d'évaluation
- Shortnote LabDocument22 pagesShortnote LabSamiPas encore d'évaluation
- Internet Protocol MulticastDocument17 pagesInternet Protocol MulticastPatricio QueglesPas encore d'évaluation
- IPv4 ReportDocument34 pagesIPv4 ReportGWYNETH DIOGRACIASPas encore d'évaluation
- Network LayerDocument22 pagesNetwork LayerRashed SobujPas encore d'évaluation
- 14.1 Manage Red Hat Enterprise Linux NetworkingDocument9 pages14.1 Manage Red Hat Enterprise Linux Networkingamit_post2000Pas encore d'évaluation
- IPV4Document25 pagesIPV4Shajjad Hossain ShisherPas encore d'évaluation
- Wiki Internet Protocol MulticastDocument19 pagesWiki Internet Protocol MulticastErmenegildo ZegnaPas encore d'évaluation
- 98-366 MVA Slides Lesson 4Document31 pages98-366 MVA Slides Lesson 4cvigaPas encore d'évaluation
- Internet Protocol: Ahsan WajahatDocument34 pagesInternet Protocol: Ahsan WajahatSajjad UmraniPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 6 Logical AddressingDocument26 pagesLecture 6 Logical Addressingmucers.influencerPas encore d'évaluation
- IP-Basics 04-21-2014Document23 pagesIP-Basics 04-21-2014Ridzky AryaPas encore d'évaluation
- CCN Lectures CLO-02Document148 pagesCCN Lectures CLO-02BaleniagencyPas encore d'évaluation
- F5 101 - Application Delivery Fundamentals: Part 1: Networking BasicsDocument26 pagesF5 101 - Application Delivery Fundamentals: Part 1: Networking BasicsAgus HerdiyanaPas encore d'évaluation
- IPV4 and IPV6: Presented by Ye Kyaw Thein M.SC (Physics), M.I.ScDocument41 pagesIPV4 and IPV6: Presented by Ye Kyaw Thein M.SC (Physics), M.I.ScMie NgePas encore d'évaluation
- Day 3Document14 pagesDay 3charan charanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch02 Network AdministerationsDocument56 pagesCh02 Network Administerationsadaneasefa969Pas encore d'évaluation
- IP Subnet MaskDocument10 pagesIP Subnet MaskCemee Faith Muleta EscarillaPas encore d'évaluation
- ELE3214-Handout10-CCNGuest-Network LayerV2Document80 pagesELE3214-Handout10-CCNGuest-Network LayerV2Ambrose OnapaPas encore d'évaluation
- IPv 4Document17 pagesIPv 4YahiaKhoujaPas encore d'évaluation
- Arellano, Kristine C. BSIT 4-1NDocument5 pagesArellano, Kristine C. BSIT 4-1NtinmacabrePas encore d'évaluation
- Ipx 4Document4 pagesIpx 4Tecnology WpnPas encore d'évaluation
- Midterm Revision Section FCDS AUDocument39 pagesMidterm Revision Section FCDS AUmanarsabry08Pas encore d'évaluation
- Clase 6. Direccionamiento IPv4Document66 pagesClase 6. Direccionamiento IPv4javierPas encore d'évaluation
- Addressing & SubnettingDocument80 pagesAddressing & SubnettingboybkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Networking Concepts and HardwareDocument28 pagesNetworking Concepts and HardwareSelvam ManiPas encore d'évaluation
- Networking Essential Chapter 8Document14 pagesNetworking Essential Chapter 8Hari KarkiPas encore d'évaluation
- Multicast Address: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 pagesMulticast Address: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaNishant MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- CSVTU Syllabus Unit 3 Routing Protocols (INTRODUCTION)Document19 pagesCSVTU Syllabus Unit 3 Routing Protocols (INTRODUCTION)Eshita ShuklaPas encore d'évaluation
- Networking Protocols Explained: TCP/IP, IPv4, IPv6, Ports & MoreDocument33 pagesNetworking Protocols Explained: TCP/IP, IPv4, IPv6, Ports & MoreSean DickersonPas encore d'évaluation
- InternetDocument60 pagesInternetoureducation.inPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Comm Part 2.ppt NewDocument48 pagesData Comm Part 2.ppt Newmuhabamohamed21Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tema 7. Multicast-IDocument54 pagesTema 7. Multicast-IluiscolchagPas encore d'évaluation
- IP Addresses and Classes ExplainedDocument13 pagesIP Addresses and Classes ExplainedRitwik UphalePas encore d'évaluation
- Nplab Viva QuestionsDocument4 pagesNplab Viva QuestionsShabin MuhammedPas encore d'évaluation
- Networking Finals ReviewerDocument32 pagesNetworking Finals Reviewererror55Pas encore d'évaluation
- Inter-Networking Session I: IP and Networking BasicsDocument82 pagesInter-Networking Session I: IP and Networking BasicskevotooPas encore d'évaluation
- Media Networks - MulticastDocument53 pagesMedia Networks - MulticastAdrian HuitPas encore d'évaluation
- Network Subnetting 4 PDFDocument6 pagesNetwork Subnetting 4 PDFEdison Jr. GaudicosPas encore d'évaluation
- Ipv 6Document39 pagesIpv 6DEEPALI BAGULPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Network - Lecturer3Document32 pagesDigital Network - Lecturer3sammydtechPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 IpDocument94 pages8 IpSaras PantulwarPas encore d'évaluation
- Internet Protocol and ApplicationsDocument86 pagesInternet Protocol and ApplicationsHamis RamadhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- BSCI30S08 IPv6Document73 pagesBSCI30S08 IPv6Amine TellibiPas encore d'évaluation
- Tcp/Ip and Ipv4 - Address ClassesDocument33 pagesTcp/Ip and Ipv4 - Address ClassesjayshreePas encore d'évaluation
- IP Addressing and Subnets ExplainedDocument37 pagesIP Addressing and Subnets ExplainedVi RusPas encore d'évaluation
- Ipv6 Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesIpv6 Cheat SheetDaNnYtYpEs100% (1)
- chapter3-IP AddressingDocument47 pageschapter3-IP AddressingmulugetaPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Communication and Networking IP Addressing Sub NetworksDocument4 pagesData Communication and Networking IP Addressing Sub NetworksNelumPas encore d'évaluation
- 00 NAT IntroductionDocument27 pages00 NAT IntroductiontestoffsurfPas encore d'évaluation
- IPV4 and IPV6: Understanding Internet Protocol Versions and AddressesDocument24 pagesIPV4 and IPV6: Understanding Internet Protocol Versions and Addressesvishnu neupanePas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 7Document31 pagesLecture 7karemt52Pas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Info Security OverviewDocument36 pagesBasic Info Security OverviewsnowwolfyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4Document1 pageChapter 4snowwolfyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7Document1 pageChapter 7snowwolfyPas encore d'évaluation
- Redundancy STP ExplainedDocument2 pagesRedundancy STP ExplainedsnowwolfyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 Part 1Document2 pagesChapter 2 Part 1snowwolfyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 0-1Document2 pagesChapter 0-1snowwolfyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1Document2 pagesChapter 1snowwolfyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1Document4 pagesChapter 1snowwolfyPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethernet Architecture: Section 4Document4 pagesEthernet Architecture: Section 4snowwolfyPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethernet Architecture: Josh M-H CIS 185 Section 4Document4 pagesEthernet Architecture: Josh M-H CIS 185 Section 4snowwolfyPas encore d'évaluation
- Perceptions On Licensure ExaminationsDocument69 pagesPerceptions On Licensure ExaminationsMaria Paz CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- Precast Segmental Bridge Construction: John E. Kristensen PE., PLS., PMPDocument38 pagesPrecast Segmental Bridge Construction: John E. Kristensen PE., PLS., PMPकुँवर विभा पुत्रPas encore d'évaluation
- zt350t Euro V 2022Document115 pageszt350t Euro V 2022Kunji ManiPas encore d'évaluation
- Scotsman ENUDocument114 pagesScotsman ENUMario PitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Panel Rymsa TUU-AT15-250Document1 pagePanel Rymsa TUU-AT15-250Hector CardosoPas encore d'évaluation
- C172 EmergencyDocument2 pagesC172 Emergencyjgills240100% (2)
- Ford Focus 2007 Real-Time Data and Fault CodesDocument3 pagesFord Focus 2007 Real-Time Data and Fault CodesAndrei CiobanasuPas encore d'évaluation
- Application Answers:: Dual-Gradient DrillingDocument4 pagesApplication Answers:: Dual-Gradient Drillinglich_tran01Pas encore d'évaluation
- Water ChemistryDocument14 pagesWater ChemistryJosé Luis Nava RebollarPas encore d'évaluation
- REX Relay Board2Document1 pageREX Relay Board2Abdalhakeem AlturkyPas encore d'évaluation
- Datasheet Powerpack2-5 AllDocument2 pagesDatasheet Powerpack2-5 AllLorenzo67% (3)
- Yahoo Finance stock data snapshotDocument9 pagesYahoo Finance stock data snapshotsandip_exlPas encore d'évaluation
- Bosch P-Pump Fuel Injection - Diesel Tech - Diesel Power MagazineDocument2 pagesBosch P-Pump Fuel Injection - Diesel Tech - Diesel Power Magazinerxhughes100% (3)
- Evaluation and Application of Characteristic Values Based On Eurocode 7 Design MethodologyDocument5 pagesEvaluation and Application of Characteristic Values Based On Eurocode 7 Design MethodologySeng SiongPas encore d'évaluation
- Kelayakan Investasi Instalasi Sea Water Reverse Osmosis (Swro) Di Kawasan Wisata Pantai Kenjeran SurabayaDocument9 pagesKelayakan Investasi Instalasi Sea Water Reverse Osmosis (Swro) Di Kawasan Wisata Pantai Kenjeran SurabayaKang SudikPas encore d'évaluation
- Bushes: Hosefloat Bush Set-Up InstructionsDocument1 pageBushes: Hosefloat Bush Set-Up InstructionsJasmi Noor SahudinPas encore d'évaluation
- MS - Electrical Second FixDocument9 pagesMS - Electrical Second Fixirfan vpPas encore d'évaluation
- Pin-Fuse Joint FinalDocument10 pagesPin-Fuse Joint FinalShubham BeraPas encore d'évaluation
- Performance ParametersDocument18 pagesPerformance ParametersChikePas encore d'évaluation
- Isc BU103A: Isc Silicon NPN Power TransistorDocument2 pagesIsc BU103A: Isc Silicon NPN Power TransistorAnca SterianPas encore d'évaluation
- 09931372A Clarus 590 User's GuideDocument284 pages09931372A Clarus 590 User's GuideLuz Idalia Ibarra RodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- 12000btu - Google SearchDocument4 pages12000btu - Google SearchahmedcoPas encore d'évaluation
- Bored Cast In-Situ Pile Method StatementDocument10 pagesBored Cast In-Situ Pile Method StatementVijay JamadarPas encore d'évaluation
- Quantity SurveyDocument6 pagesQuantity Surveypmm05479Pas encore d'évaluation
- Section MN: FL WL SK CL FL WL SK CL FL WL SK CLDocument1 pageSection MN: FL WL SK CL FL WL SK CL FL WL SK CLS Amit RaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Method Statement For Installation of Chillers Rev 1 - AFUDocument12 pagesMethod Statement For Installation of Chillers Rev 1 - AFUAzwan SunlinePas encore d'évaluation
- Catalog 201506 PDFDocument75 pagesCatalog 201506 PDFDairo OvallePas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 1 - Unit Pressure PDFDocument60 pagesLesson 1 - Unit Pressure PDFJenuine LimonPas encore d'évaluation
- DmesgDocument71 pagesDmesgAnonymous d1kyvAsPas encore d'évaluation