Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Topic: GDP, GNP, NNP, N.I, P.I, D.P.I : Fask Faculty of Administrative Sciences and Department of Business Administration
Transféré par
Ali AhmadDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Topic: GDP, GNP, NNP, N.I, P.I, D.P.I : Fask Faculty of Administrative Sciences and Department of Business Administration
Transféré par
Ali AhmadDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Topic: GDP, GNP, NNP, N.I, P.I, D.P.
I Subject: Introduction to Economics
Theory (Macro) Submitted to: Sir. Ali Asghar Ghayour Submitted by: Wajahat Ali Ghulam Class: Roll No. BBA-I (Morning) 2010-14 01
FASK FACULTY OF ADMINISTRATIVE SCIENCES AND DEPARTMENT OF BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION
1
UNIVERSITY OF AZAD JAMMU AND KASHMIR
In a beautiful and
aesthetic, but
subtle, way the Quran guides us toward acquisition of knowledge observing and studying the elements of nature regards as the signs of Allah, thinking, reflection and researching in his sign and eventually realizing coquets over the elements of nature for the service of mankind as well as for an upward spiritual movement. In this assignment I have discussed the company form of a business and I also have discussed the characteristics of company and its existence in the world of Business. I am also thankful to my Honorable Sir. Ali Asghar
Ghayour
Preliminary thanking, bow my head before Almighty Allah who given me wisdom and an opportunity to undertake this exploring work. Also to m y parents whose prayers always do a miracle for me. Infect I was not able to prepare this assignment individually; definitely there are many supports who have provided me information and encouraged to complete this assignment. I am also thankful to
Sir. Ali Asghar Ghayour that he
assigned this assignment; it is our training towards our upcoming life and future.
SR.N O
TOPIC
PAGE NO.
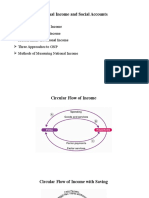
Net national product (NNP) Definition Net national product. Gross domestic product (GDP) Determining GDP Example: the expenditure method:
5
ii
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) GDP=(P*Q) GDP=C+I+G+(X-M) Gross National Product (GNP) GNP vs. GDP Concepts of National Income National Income (NI) NI=NNP + Subsidies-Interest Taxes Personal Income and Disposable Personal Income Personal Income (PI) Personal Income (PI) Disposable Income (DI) PCI=Total National Income/Total National Population References
iii
iv
8 9
Net national product (NNP) Definition Gross national product (GNP) less allowances for capital consumption Net National Product - NNP What Does Net National Product - NNP Mean? The monetary value of finished goods and services produced by a country's citizens, whether overseas or resident, in the time period being measured (i.e., the gross national product, or GNP) minus the amount of GNP required to purchase new goods to maintain existing stock (i.e., depreciation). Alternatively, net national product (NNP) can be calculated as total payroll compensation + net indirect tax on current production + operating surpluses. Net national product. (NNP) is the total market value of all final goods and services produced by residents in a country or other polity during a given period (gross national product or GNP) minus depreciation. The net domestic product (NDP) is the equivalent application of NNP within 4
macroeconomics, and NDP is equal to gross domestic product (GDP) minus depreciation: NDP = GDP - depreciation. Depreciation (also known as consumption of fixed capital) measures the amount of GNP that must be spent on new capital goods to maintain the existing physical capital stock. NNP is the amount of goods in a given year which can be consumed without reducing future consumption. Setting part of NNP aside for investment permits capital stock growth (see economic growth and capital formation), and greater future consumption. Gross domestic product (GDP) refers to the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period. It is often considered an indicator of a country's standard of living. Gross domestic product is related to national accounts, a subject in macroeconomics. Determining GDP GDP can be determined in three ways, all of which should, in principle, give the same result. They are the product (or output) approach, the income approach, and the expenditure approach. The most direct of the three is the product approach, which sums the outputs of every class of enterprise to arrive at the total. The expenditure approach works on the principle that all of the product must be bought by somebody, therefore the value of the total product must be equal to people's total expenditures in buying things. The income approach works on the principle that the incomes of the productive factors ("producers," colloquially) must be equal to the value of their product, and determines GDP by finding the sum of all producers' incomes. Example: the expenditure method: GDP = private consumption + gross investment + government spending + (exports imports), or
Note: "Gross" means that GDP measures production regardless of the various uses to which that production can be put. Production can be used for immediate consumption, for investment in new fixed assets or inventories, or for replacing depreciated fixed assets. "Domestic" means that GDP measures production that takes place within the country's borders. In the expenditure-method equation given above, the exports-minusimports term is necessary in order to null out expenditures on things not produced in the country (imports) and add in things produced but not sold in the country (exports). Gross Domestic Product (GDP) The most important concept of national income is Gross Domestic Product. Gross domestic product is the money value of all final goods and services produced within the domestic territory of a country during a year. Algebraic expression under product method is, GDP=(P*Q) where, 5
GDP=Gross Domestic Product P=Price of goods and service Q=Quantity of goods and service denotes the summation of all values. According to expenditure approach, GDP is the sum of consumption, investment, government expenditure, net foreign exports of a country during a year. Algebraic expression under expenditure approach is, GDP=C+I+G+(X-M) Where, C=Consumption I=Investment G=Government expenditure (X-M)=Export minus import GDP includes the following types of final goods and services. They are: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Consumer goods and services. Gross private domestic investment in capital goods. Government expenditure. Net exports (exports-imports). Net factor income from abroad. Exports and imports.
Gross National Product (GNP) is the market value of all products and services produced in one year by labor and property supplied by the residents of a country. Unlike Gross Domestic Product (GDP), which defines production based on the geographical location of production, GNP allocates production based on ownership. GNP does not distinguish between qualitative improvements in the state of the technical arts (e.g., increasing computer processing speeds), and quantitative increases in goods (e.g., number of computers produced), and considers both to be forms of "economic growth". GNP=GDP+NFIA (Net Factor Income from Abroad) or, GNP=C+I+G+(X-M) +NFIA GNP vs. GDP Gross National Product (GNP) is often contrasted with Gross Domestic Product (GDP). While GNP measures the output generated by a country's enterprises - whether physically located domestically or abroad - GDP measures the total output produced within a country's borders - whether produced by that country's own firms or not. When a country's capital or labor resources are employed outside its borders, or when a foreign firm is operating in its territory, GDP and GNP can produce different measures of total output. In 2009 for instance, the United States estimated its GDP at $14.119 trillion, and its GNP at $14.265 trillion.
Concepts of National Income There are various concepts of National Income. The main concepts of NI are: GDP, GNP, NNP, NI, PI, DI, and PCI. These different concepts explain about the phenomenon of economic activities of the various sectors of the various sectors of the economy. National Income (NI) National Income is also known as National Income at factor cost. National income at factor cost means the sum of all incomes earned by resources suppliers for their contribution of land, labor, capital and organizational ability which go into the years net production. Hence, the sum of the income received by factors of production in the form of rent, wages, interest and profit is called National Income. Symbolically, NI=NNP + Subsidies-Interest Taxes or, GNP Depreciation + Subsidies-Indirect Taxes or, NI=C+G+I+(X-M)+NFIA-Depreciation-Indirect Taxes + Subsidies Personal Income and Disposable Personal Income Personal Income (PI): This measures all of the income that is received by individuals, but not necessarily earned. Examples of this include social security benefits, unemployment compensation, welfare payments, benefits for veterans, and food stamps. Individuals also contribute income which they do not receive. This includes corporate profits that are undistributed, indirect business taxes, and the contribution of employers to Social Security. PI = NI + income received but not earned - income earned but not received Disposable Personal Income (DI): There are other personal taxes which are not considered when calculating personal income. In order to derive disposable personal income we must subtract these personal taxes from personal income. DI = PI - Personal Income Taxes Disposable personal income represents what people actually have that they can spend. It is also a result of consumer spending as well as private saving. Net national product. Personal Income (PI) Personal Income is s the total money income received by individuals and households of a country from all possible sources before direct taxes. Therefore, personal income can be expressed as follows: PI=NI-Corporate Income Taxes-Undistributed Corporate Profits-Social Security Contribution + Transfer Payments Disposable Income (DI) 7
The income left after the payment of direct taxes from personal income is called Disposable Income. Disposable income means actual income which can be spent on consumption by individuals and families. Thus, it can be expressed as: DI=PI - Direct Taxes From consumption approach, DI=Consumption Expenditure + Savings Per Capita Income (PCI) Per Capita Income of a country is derived by dividing the national income of the country by the total population of a country. Thus, PCI=Total National Income/Total National Population
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- National Income MeaurementDocument9 pagesNational Income MeaurementBKMEIN100% (1)
- Group 1 Measuring The National Income AccountDocument10 pagesGroup 1 Measuring The National Income AccountAmie Lyyn CabrerosPas encore d'évaluation
- National IncomeDocument13 pagesNational IncomeMuzammil MotoorPas encore d'évaluation
- Measures of National Income and OutputDocument6 pagesMeasures of National Income and OutputSatyabrat DehuryPas encore d'évaluation
- National IncomeDocument29 pagesNational Incomeshahidul0Pas encore d'évaluation
- Measuring The National Income AccountDocument19 pagesMeasuring The National Income AccountAmie Lyyn CabrerosPas encore d'évaluation
- National IncomeDocument21 pagesNational IncomeMurali Krishna Pavan PappuPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 Econ Devt PDFDocument29 pagesChapter 2 Econ Devt PDFHarvey AdanPas encore d'évaluation
- National Income-1Document5 pagesNational Income-1Qamar VirkPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Macroeconomics? Its OriginDocument30 pagesWhat Is Macroeconomics? Its Origintheanuuradha1993gmaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Gross Domestic Product What Is Gross Domestic Product? DefinitionDocument7 pagesGross Domestic Product What Is Gross Domestic Product? DefinitionArslan siddiquePas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment No: 01: Uzair Iftikhar (Fa19-Bba-091) Naveed Ahmed (Fa19-Bba-064Document8 pagesAssignment No: 01: Uzair Iftikhar (Fa19-Bba-091) Naveed Ahmed (Fa19-Bba-064Talha Iftekhar KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- National Income ConceptsDocument15 pagesNational Income Conceptsrinky_trivediPas encore d'évaluation
- Measures of National Income and OutputDocument6 pagesMeasures of National Income and OutputNii AdjeiPas encore d'évaluation
- FULL HOUSE - ReportDocument11 pagesFULL HOUSE - ReportAmie Lyyn CabrerosPas encore d'évaluation
- Gross Domestic ProductDocument18 pagesGross Domestic ProductTemy RosenfelPas encore d'évaluation
- Macroeconomics Assignment #1Document11 pagesMacroeconomics Assignment #1Qamar VirkPas encore d'évaluation
- National Income Account: Module CDocument8 pagesNational Income Account: Module CGolamSarwarPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Economics PPT-UNIT - IIDocument41 pagesEngineering Economics PPT-UNIT - IIShashi KUMARPas encore d'évaluation
- Module-Lecture 6-National Income AccountingDocument14 pagesModule-Lecture 6-National Income AccountingGela ValesPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 Introduction EconomicsDocument57 pagesChapter 6 Introduction Economicssinte beyuPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter VI Macroeconomics PartDocument44 pagesChapter VI Macroeconomics PartBereket MuniyePas encore d'évaluation
- Report On NATIONAL INCOMEDocument19 pagesReport On NATIONAL INCOMEanurag_20110% (1)
- Measures of National Income and OutputDocument10 pagesMeasures of National Income and OutputMohammed YunusPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Nationa WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesWhat Is Nationa WPS OfficeAmie Lyyn CabrerosPas encore d'évaluation
- National Income-Zunaira AhmedDocument31 pagesNational Income-Zunaira AhmedMuhammad AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- National Income Part-1Document10 pagesNational Income Part-1Ibrahim MondolPas encore d'évaluation
- CHap. 2Document36 pagesCHap. 2ZePas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 1 and Lesson 2Document21 pagesLesson 1 and Lesson 2Qui BuiPas encore d'évaluation
- National IncomeDocument9 pagesNational Incomeshahnawaz malikPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 1Document18 pagesGroup 1SouvikPas encore d'évaluation
- National IncomeDocument5 pagesNational IncomeAkshit Kumar100% (1)
- MODULE 9 MicroDocument7 pagesMODULE 9 MicroGladz De ChavezPas encore d'évaluation
- TOPIC 3 - National IncomeDocument11 pagesTOPIC 3 - National IncomeCharlesPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Six FundamentalDocument22 pagesChapter Six FundamentalBikila DessalegnPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT - IV, National Income Accounting: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) All Output Produced Within A NationDocument15 pagesUNIT - IV, National Income Accounting: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) All Output Produced Within A NationanushreePas encore d'évaluation
- Theory of National IncomeDocument72 pagesTheory of National IncomeAlex RockPas encore d'évaluation
- Macro Eco 3Document113 pagesMacro Eco 3br bhandariPas encore d'évaluation
- Concepts of Macroeconomics Lesson 1Document6 pagesConcepts of Macroeconomics Lesson 1Dj I amPas encore d'évaluation
- Definitions of National IncomeDocument14 pagesDefinitions of National IncomeabassalishahPas encore d'évaluation
- Measurement of Economic PerformanceDocument14 pagesMeasurement of Economic PerformanceGodfrey RushaburePas encore d'évaluation
- Explanation For Multi Sector or Four Sector Model (Add Diagram From PPP)Document9 pagesExplanation For Multi Sector or Four Sector Model (Add Diagram From PPP)PRANAV SUKUMARANPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is National Income?: AnswerDocument7 pagesWhat Is National Income?: AnswerredsalutePas encore d'évaluation
- National IncomeDocument20 pagesNational IncomeoggyPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 3Document10 pagesLecture 3Hitisha agrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 National Income Complete PDF-2Document67 pagesChapter 3 National Income Complete PDF-2shivam kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Macroeconomics: BY: Maria Deanna S. Salalima, Ed.DDocument7 pagesMacroeconomics: BY: Maria Deanna S. Salalima, Ed.DLerryPas encore d'évaluation
- MacroeconomicsDocument40 pagesMacroeconomicsLakshmi Harshitha YechuriPas encore d'évaluation
- The Total Net Value of All Goods and Services Produced Within A Nation Over A Specified Period of TimeDocument5 pagesThe Total Net Value of All Goods and Services Produced Within A Nation Over A Specified Period of Timekavitachordiya86Pas encore d'évaluation
- Concepts of National IncomeDocument25 pagesConcepts of National IncomePule JackobPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is 'Gross National Product - GNP': Personal Consumption Expenditures Investment Net ExportsDocument3 pagesWhat Is 'Gross National Product - GNP': Personal Consumption Expenditures Investment Net ExportsTerry SaguiguitPas encore d'évaluation
- Cha-2 Macroeconomics IDocument33 pagesCha-2 Macroeconomics Ilidya berhanemeskelPas encore d'évaluation
- Measuring of National Income: The Output ApproachDocument3 pagesMeasuring of National Income: The Output ApproachMohammad MasumPas encore d'évaluation
- Eco Part - 1Document8 pagesEco Part - 1Rajesh Mahesh BohraPas encore d'évaluation
- MODULE 6: The National Income Accounting: GDP and GNP: An OverviewDocument10 pagesMODULE 6: The National Income Accounting: GDP and GNP: An OverviewLeigh CabritoPas encore d'évaluation
- EconomicsDocument26 pagesEconomicsnarkour777Pas encore d'évaluation
- National Income2Document44 pagesNational Income2Faith100% (1)
- National Income PDFDocument12 pagesNational Income PDFReshma JainPas encore d'évaluation
- WEEK 8b - NATIONAL INCOME ANALYSIS & InflationDocument19 pagesWEEK 8b - NATIONAL INCOME ANALYSIS & Inflationndagarachel015Pas encore d'évaluation
- Summary Of "The Economic Aggregates" By Jorge Souto: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESD'EverandSummary Of "The Economic Aggregates" By Jorge Souto: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESPas encore d'évaluation
- Panama Leaks Case Verdict PDFDocument549 pagesPanama Leaks Case Verdict PDFAli AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Theories of MotivationDocument48 pagesTheories of MotivationAli AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- History of ComputerDocument23 pagesHistory of ComputerAli AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Poverty in PakistanDocument16 pagesPoverty in PakistanAli AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To PsychologyDocument16 pagesIntroduction To PsychologyAli AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Privatization Liberalization of Banking Sector in PakistanDocument23 pagesPrivatization Liberalization of Banking Sector in Pakistankhanayesha191Pas encore d'évaluation
- Resource PlanningDocument36 pagesResource PlanningAli AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Report BodyDocument46 pagesReport BodyAli AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Type of AdsDocument5 pagesType of AdsAli AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Strategic Management CH 05 PresDocument62 pagesStrategic Management CH 05 PresAli Ahmad100% (1)
- Who Is Most Merciful, Gracious: in The Name of Allah AlmightyDocument44 pagesWho Is Most Merciful, Gracious: in The Name of Allah AlmightyAli AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Write An Effective System ProposalDocument5 pagesHow To Write An Effective System ProposalAli AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Strategic AlliancesDocument15 pagesStrategic AlliancesAli AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Sole - Proprietorship & PartnershipDocument5 pagesSole - Proprietorship & PartnershipAli AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Communication Skills Assignment by WAJAHAT ALI GHULAMN CELL 03135592853, 03435693853Document16 pagesCommunication Skills Assignment by WAJAHAT ALI GHULAMN CELL 03135592853, 03435693853Ali AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Economics Second AssignmentDocument19 pagesEconomics Second AssignmentAli AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Business Communication Second AssignmentDocument13 pagesBusiness Communication Second AssignmentAli AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- First Aid Is The Provision of Initial Care For An Illness or InjuryDocument2 pagesFirst Aid Is The Provision of Initial Care For An Illness or InjuryBasaroden Dumarpa Ambor100% (2)
- Obsa Ahmed Research 2013Document55 pagesObsa Ahmed Research 2013Ebsa AdemePas encore d'évaluation
- DMDocument12 pagesDMDelfin Mundala JrPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis Essay of CPSDocument6 pagesAnalysis Essay of CPSJessica NicholsonPas encore d'évaluation
- NeoLiberalism and The Counter-EnlightenmentDocument26 pagesNeoLiberalism and The Counter-EnlightenmentvanathelPas encore d'évaluation
- Community-Based Health Planning Services: Topic OneDocument28 pagesCommunity-Based Health Planning Services: Topic OneHigh TechPas encore d'évaluation
- C.V ZeeshanDocument1 pageC.V ZeeshanZeeshan ArshadPas encore d'évaluation
- Atlas Engineering Early Australian Ship BuildingDocument8 pagesAtlas Engineering Early Australian Ship BuildingparkbenchbrucePas encore d'évaluation
- Bba - Fa Ii - Notes - Ii Sem PDFDocument40 pagesBba - Fa Ii - Notes - Ii Sem PDFPRABHUDEVAPas encore d'évaluation
- SLRC InstPage Paper IIIDocument5 pagesSLRC InstPage Paper IIIgoviPas encore d'évaluation
- Hon. William Ruto's Speech at The Jubilee Manifesto LaunchDocument10 pagesHon. William Ruto's Speech at The Jubilee Manifesto LaunchH.E. President Uhuru KenyattaPas encore d'évaluation
- Revelry in TorthDocument43 pagesRevelry in TorthArets Paeglis100% (2)
- Grupo NovEnergia, El Referente Internacional de Energía Renovable Dirigido Por Albert Mitjà Sarvisé - Dec2012Document23 pagesGrupo NovEnergia, El Referente Internacional de Energía Renovable Dirigido Por Albert Mitjà Sarvisé - Dec2012IsabelPas encore d'évaluation
- Income Tax CalculatorDocument11 pagesIncome Tax Calculatorsaty_76Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cosmetics & Toiletries Market Overviews 2015Document108 pagesCosmetics & Toiletries Market Overviews 2015babidqn100% (1)
- 02-Case Study ESSS - Milestone 01 Scope DefinitionDocument10 pages02-Case Study ESSS - Milestone 01 Scope Definition3LIX 311Pas encore d'évaluation
- BARD 2014 Product List S120082 Rev2Document118 pagesBARD 2014 Product List S120082 Rev2kamal AdhikariPas encore d'évaluation
- Bookkeeping BasicsDocument19 pagesBookkeeping BasicsAbeer ShennawyPas encore d'évaluation
- TriboSys 3203 3204Document1 pageTriboSys 3203 3204Hayden LeePas encore d'évaluation
- International Scientific Journal "Interpretation and Researches"Document5 pagesInternational Scientific Journal "Interpretation and Researches"wowedi333Pas encore d'évaluation
- Inclusive Approach For Business Sustainability: Fostering Sustainable Development GoalsDocument1 pageInclusive Approach For Business Sustainability: Fostering Sustainable Development Goalsaakash sharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Purging CostSavingsDocument2 pagesPurging CostSavingscanakyuzPas encore d'évaluation
- Internship ReportDocument44 pagesInternship ReportRAihan AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Company Loan PolicyDocument2 pagesCompany Loan PolicyKaleem60% (5)
- "Ako Ang Daigdig" by Alejandro Abadilla: An AnalysisDocument3 pages"Ako Ang Daigdig" by Alejandro Abadilla: An AnalysisJog YapPas encore d'évaluation
- Levi Strass and Co v. Papikan Enterprises Trademark MSJDocument12 pagesLevi Strass and Co v. Papikan Enterprises Trademark MSJNorthern District of California BlogPas encore d'évaluation
- Experience Certificate For English TeacherDocument2 pagesExperience Certificate For English TeacherShaher Alburaihy86% (7)
- WukolumDocument2 pagesWukolumHammed OkusiPas encore d'évaluation
- Complete ES1 2023 Vol1Document334 pagesComplete ES1 2023 Vol1Chandu SeekalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Business Requirement Document HR Portal 1.0Document16 pagesBusiness Requirement Document HR Portal 1.0Usman TariqPas encore d'évaluation