Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Different Types of Wave1
Transféré par
Patrick Joshua ZacariasDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Different Types of Wave1
Transféré par
Patrick Joshua ZacariasDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Different Types of Waves
Waves can be classified into three types:
1. Mechanical waves 2. Electromagnetic waves 3. Matter waves. Mechanical Waves act as the propagation of a disturbance through a material medium due to the repeated periodic motion of the particles of the medium about their mean positions, the disturbance being handed over from one particle to the next. Electromagnetic Waves are the disturbance, which does not require any material medium for its propagation and can travel even through vacuum. They are caused due to varying electric and magnetic fields. Matter Waves are the waves produced in electrons and particles.
Mechanical Waves
The existence of medium is essential for propagation. The Method of energy propagation in which disturbance propagates with definite velocity without changing its form is called Mechanical Wave. Energy and momentum propagates by motion of particles of medium. But medium remains at previous position. The mass transfer does not take possible here. The Propagation is possible due to property of medium like elasticity and inertia. Examples: vibration of string, vibration of string, the surface wave produced on the surface of solid and liquid, sound waves, tsunami waves, earthquake P-waves, ultra sounds, vibrations in gas, and oscillations in spring, internal water waves, and waves in slink etc. Mechanical waves are of two types: 1. Transverse Wave 2. Longitudinal Wave.
Transverse Waves
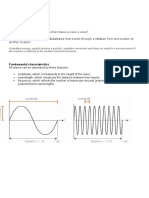
The medium has particles that vibrate in a direction perpendicular to the direction of the propagation of wave. This Kind of wave produced is called Transverse Wave.
Here the formation of crust and trough takes place. For example: vibration of string. Here the direction of propagation of energy is perpendicular to the direction of oscillations. There are always two directions that are independent of each other that can be used as the direction of wave.
Longitudinal Waves
Consider a wave moving. if the vibration of the particles of the medium are in the direction of wave propagation. We call it as Longitudinal Waves.
A Longitudinal wave proceeds in the form of compression and rarefaction which is the stretched rubber band. For a longitudinal wave at places of compression the pressure and density tends to be maximum, while at places where rarefaction takes place, the pressure and density are minimum. Longitudinal waves are known as Compression waves. Examples of longitudinal waves: Sound waves, tsunami waves, earthquake P - waves, ultra sounds, vibrations in gas, and oscillations in spring, internal water waves, and waves in slink etc. In gases only longitudinal waves propagate.
Electromagnetic Waves
The existence of medium is not essential for propagation. The Periodic changes takes place in electric and magnetic fields hence it is called Electromagnetic Wave. Properties: 1. In vacuum E.M waves travel with light velocity. 2. E.M waves can be polarized. 3. E.M waves are transverse in nature. 4. Medium is not required for propagating the E.M waves. 5. E.M waves have momentum. Example: Radio waves, light waves, thermal radiation, X ray etc.
Matter Waves
These are also called De Broglie waves. They show or depict the wave nature or wave like nature of all matter, everything that makes up our body, the atoms etc. Considering the quantum physics we have a proof that the wavelength of matter waves is very small. There are various equations called the De Broglie equations which basically suggest the dual nature of matter. The frequency of these waves is directly depends on their kinetic energy,
Momentum is not directly proportional to the wavelength of the particle and not inversely proportional.
Surface Waves
These waves can have mechanical nature. They can have an electromagnetic nature. Example is a ground wave propagating close to the earths surface. It can propagate between two fluids with different densities. For example a diving sea creature can create a surface wave. They are also calledRayleigh waves.
Elastic Waves
The body which is elastic in nature produces this Elastic wave.The elastic body is responsible for setting the vibratory motion of particles. This vibratory motion basically causes the Elastic wave. For an elastic wave the particles always tend to come back to their original positions when set in wave motion. This leads to the formation of the wave. Thus Elastic Wave is a type of mechanical wave. Restoring force is provided causing the wave motion. It also propagates in the visco-elastic medium. The study of the elastic waves is called Elastodynamics. Example: When gas which when compressed tend to come to its original position. When sound is transmitted through the gas then it is transmitted as an elastic wave.
Sound Waves
For sound waves the existence of material medium is very necessary for the propagation of the waves. The propagation of waves taking place in solid, liquid and gases which makes us hear the sound is called Sound wave. Properties:
1. Sound waves are longitudinal in nature. 2. Material medium is necessary for the propagation of the sound waves. 3. The Speed of sound in air at N.T. P is 332 m/s. 4. The Sound is audible only between 20 Hz to 20 KHz.
Standing Waves
When a wave remains in a constant position it is called Standing wave. This is possible due to 2 reasons: 1. When the medium moves in a direction opposite to the direction of propagation of wave it is possible. 2. When the phenomenon of interference takes place between the two waves traveling in an opposite direction then it is possible. When two waves having equal frequency and amplitude overlap each other then we get a standing wave. This is possible due to the obstruction of the wave by some boundary and hence the reflection of it back in the same medium.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Different Types of WavesDocument4 pagesDifferent Types of Waveselladionisio01Pas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Class 11 Physics Chapter 15 Waves Revision Notes - PDFDocument53 pagesCBSE Class 11 Physics Chapter 15 Waves Revision Notes - PDFrazi sharifPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 1 IntroductionDocument13 pagesLecture 1 IntroductionRocking Himanshu21Pas encore d'évaluation
- " Wave Motion": Ma. Clarissa Cantos - G6 Innah Denyse Almarez - G2 IV - St. Stephen Mrs. Viola AbratiqueDocument12 pages" Wave Motion": Ma. Clarissa Cantos - G6 Innah Denyse Almarez - G2 IV - St. Stephen Mrs. Viola AbratiqueMaria ClarissaPas encore d'évaluation
- Vakev Physics Term 2 L5 Els&sodDocument21 pagesVakev Physics Term 2 L5 Els&sodvigiraneza0Pas encore d'évaluation
- An Introduction To WaveDocument9 pagesAn Introduction To WaveOyeladun IdrisPas encore d'évaluation
- WavesDocument21 pagesWavesTintinententen Christine TintinPas encore d'évaluation
- Wave HandoutDocument2 pagesWave HandoutBridget CumlatPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics II - WavesDocument15 pagesPhysics II - WavesVicky Waran RajPas encore d'évaluation
- WaveDocument10 pagesWaverosalynPas encore d'évaluation
- Pintuan Joshua MoisesDocument7 pagesPintuan Joshua MoisesKate Winslet Love Galan FazonPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Half-Yearly Notes by Dillon Halder The World CommunicatesDocument5 pagesPhysics Half-Yearly Notes by Dillon Halder The World Communicatesuhhwot100% (1)
- How Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksD'EverandHow Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation On WavesDocument7 pagesPresentation On Wavesmaqsood ahmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1 LESSON 1 2Document8 pagesUnit 1 LESSON 1 2kachechiekurosakiPas encore d'évaluation
- Wave Motion PDFDocument23 pagesWave Motion PDFFRANCES VISAYA100% (1)
- Propagation of WaveDocument18 pagesPropagation of WaveVipul KhandelwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Year 10 Revision RSG 2015 - WavesDocument5 pagesYear 10 Revision RSG 2015 - Waves이다은Pas encore d'évaluation
- Factsheet No WaveDocument6 pagesFactsheet No WaveJohn Van Dave TaturoPas encore d'évaluation
- Wave Properties Name: Valeria OchoaDocument2 pagesWave Properties Name: Valeria OchoaValeria OchoaPas encore d'évaluation
- Properties of WavesDocument8 pagesProperties of Wavesjames paulo abandoPas encore d'évaluation
- BuDocument15 pagesBubreycariganPas encore d'évaluation
- Oscillation of Energy: An Oscillation That Travels Through A MediumDocument2 pagesOscillation of Energy: An Oscillation That Travels Through A MediumApril Joy Gelilang PulgaPas encore d'évaluation
- A Wave Is A Disturbance in A Medium That Carries Energy Without A Net Movement of ParticlesDocument5 pagesA Wave Is A Disturbance in A Medium That Carries Energy Without A Net Movement of ParticlesMercy PaduaPas encore d'évaluation
- Waves and The Wave Motion How Are Waves Produced?Document4 pagesWaves and The Wave Motion How Are Waves Produced?Kevin Felipe Carrillo EspinosaPas encore d'évaluation
- WaveDocument17 pagesWaveJevanthe Miguel ObusanPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning Activity Sheet: WavesDocument7 pagesLearning Activity Sheet: WavesKyera LovesPas encore d'évaluation
- C12 Electromagnetic WavesDocument80 pagesC12 Electromagnetic WavesmarianrosecardanioPas encore d'évaluation
- IN Physics 1: Caballero, Joel Timothy C. MTS1A1 Mrs. EnriquezDocument4 pagesIN Physics 1: Caballero, Joel Timothy C. MTS1A1 Mrs. EnriquezJoseph CaballeroPas encore d'évaluation
- PSC 9Document17 pagesPSC 9AryannaPas encore d'évaluation
- WavesDocument41 pagesWavesMimi CiervaPas encore d'évaluation
- About Experiment ..: Wave VelocityDocument2 pagesAbout Experiment ..: Wave VelocityRajeev GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Waves: Physics Departement Mathematics and Science Faculty Padang State University 2011Document13 pagesWaves: Physics Departement Mathematics and Science Faculty Padang State University 2011Yuli AriyadiPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.2 Travelling WavesDocument5 pages4.2 Travelling WavesEesha SajidPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanicalvselectromagneticwaves 121211033256 Phpapp01Document29 pagesMechanicalvselectromagneticwaves 121211033256 Phpapp01almira villarealPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 1 Biophysics IIDocument9 pagesLecture 1 Biophysics IIMohamed AshmawyPas encore d'évaluation
- General Physics 2 Module 3 My AnswersDocument3 pagesGeneral Physics 2 Module 3 My AnswersMatth N. ErejerPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics - Unit 01 SHMDocument7 pagesPhysics - Unit 01 SHMAleena kazmiPas encore d'évaluation
- 03+G7 WavesDocument26 pages03+G7 WavesRose Ann YamcoPas encore d'évaluation
- Wa0001.Document15 pagesWa0001.Ishan KhadkaPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 Physics Cbse WavesDocument9 pages11 Physics Cbse Wavesvickyvicky0022okPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes On Interference N Diffraction of WavesDocument10 pagesNotes On Interference N Diffraction of WavesHubbak KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Q3Document7 pagesScience Q3Jaycel StudiesPas encore d'évaluation
- WaveDocument14 pagesWaveLitiaMikoPas encore d'évaluation
- Waves: General ViewDocument3 pagesWaves: General ViewAdri PrawiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Laser and Optics ExitDocument49 pagesLaser and Optics Exitdavididosa40Pas encore d'évaluation
- Wave MotionDocument23 pagesWave Motionanubh50Pas encore d'évaluation
- Wave and Oscillatory MotionDocument9 pagesWave and Oscillatory MotionnishantPas encore d'évaluation
- Two Types Waves: Transverse Waves Longitudinal Waves Transverse WaveDocument2 pagesTwo Types Waves: Transverse Waves Longitudinal Waves Transverse WaveSamuel NigatuPas encore d'évaluation
- Wave Motion: You Know That Motion Is An Example of Periodic MotionDocument10 pagesWave Motion: You Know That Motion Is An Example of Periodic MotionIncognito UntraceablePas encore d'évaluation
- EM WAVE PPT OriginalDocument39 pagesEM WAVE PPT Originalsujithrasuji773Pas encore d'évaluation
- Waves: Lecture 1 (2 Week) Prepared By: Muhammad Saiful Badri MansorDocument18 pagesWaves: Lecture 1 (2 Week) Prepared By: Muhammad Saiful Badri MansorNor HusnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Complete General Science For NSEJS NTSE KVPY IAS Physics Chemistry Biology Sifox Publication Praveen Kumar PDFDocument550 pagesComplete General Science For NSEJS NTSE KVPY IAS Physics Chemistry Biology Sifox Publication Praveen Kumar PDFtanisha pianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Waves:: Wave Disturbance Medium or Space Accompanied by A Transfer of EnergyDocument4 pagesWaves:: Wave Disturbance Medium or Space Accompanied by A Transfer of EnergyAriyan Abrar SaifPas encore d'évaluation
- MODELO - PROYECTO Caf 3Document5 pagesMODELO - PROYECTO Caf 3fabian marcelo urteaga ramirezPas encore d'évaluation
- Waves Homework From The Book:: MechanicalDocument11 pagesWaves Homework From The Book:: MechanicalMaha Letchumy BalakeristananPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics 4 PDFDocument122 pagesPhysics 4 PDFBABU JOHNPas encore d'évaluation
- Universe of Light: Solving the Biggest Mysteries in PhysicsD'EverandUniverse of Light: Solving the Biggest Mysteries in PhysicsPas encore d'évaluation
- Quantum Mechanics 2: Reality, Uncertainty, & Schrödinger’s CatD'EverandQuantum Mechanics 2: Reality, Uncertainty, & Schrödinger’s CatÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (4)
- Order Form: Item Code Category Qty - Sold On-Hand Order Group BDocument9 pagesOrder Form: Item Code Category Qty - Sold On-Hand Order Group BAlleine TupazPas encore d'évaluation
- Spall Velocity of Blast Loaded ConcreteDocument5 pagesSpall Velocity of Blast Loaded Concretefoush bashaPas encore d'évaluation
- Foundations of The New Physics, Harald KautzDocument77 pagesFoundations of The New Physics, Harald KautzAniko Gergely-VargaPas encore d'évaluation
- Use of X-Ray Fluorescence Analysis For TheDocument17 pagesUse of X-Ray Fluorescence Analysis For TheGaryPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Study Materials - Wave OpticsDocument7 pagesPhysics Study Materials - Wave OpticschashmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Waveguides S NotesDocument84 pagesWaveguides S NotesjuniPas encore d'évaluation
- RiprocDocument1 pageRiprocChemGuyPas encore d'évaluation
- Brochure Zeiss Hunting Catalogue enDocument69 pagesBrochure Zeiss Hunting Catalogue enDawn GatePas encore d'évaluation
- Molecular SpectrosDocument68 pagesMolecular SpectrosGaganpreetSinghPas encore d'évaluation
- 12.penawaran SHIMADZU BandungDocument2 pages12.penawaran SHIMADZU BandungHarry MukhrivanPas encore d'évaluation
- Bien Tan Invt Chf100aDocument156 pagesBien Tan Invt Chf100aHữu Tấn Nguyễn100% (1)
- Experiment 3 Thermal RadiationDocument7 pagesExperiment 3 Thermal RadiationSheila Roselley100% (2)
- G482 Mod 5 2.5.4 Energy Levels in AtomsDocument5 pagesG482 Mod 5 2.5.4 Energy Levels in AtomsAmberPas encore d'évaluation
- Schmidt Bender Catalog 2019 en US 2Document52 pagesSchmidt Bender Catalog 2019 en US 2Francisco Deny SAPUTROPas encore d'évaluation
- Ex Er Cise-02 MCQ (One or More Choice Correct)Document3 pagesEx Er Cise-02 MCQ (One or More Choice Correct)Abhishek jainPas encore d'évaluation
- Evidence With ImageDocument193 pagesEvidence With ImageLawrence Jones100% (1)
- Industrial Borescope: Operating ManualDocument16 pagesIndustrial Borescope: Operating ManualFAISHAH ISAHAKPas encore d'évaluation
- Team 400 Problem A: "Journey To Proxima B"Document9 pagesTeam 400 Problem A: "Journey To Proxima B"Swarnali SarkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Laser and Its ApplicationsDocument147 pagesLaser and Its Applicationsviji nanduPas encore d'évaluation
- 7 Review of Fundamentals - Heat and Mass TransferDocument20 pages7 Review of Fundamentals - Heat and Mass TransferPRASAD326100% (2)
- Tamron Lens CatalogueDocument15 pagesTamron Lens CatalogueLoh Jian ChengPas encore d'évaluation
- Optical Satellite Communications DocumentationDocument23 pagesOptical Satellite Communications Documentationఉమామహేశ్వర్ పబ్బతి100% (2)
- 2nd Exam ScienceDocument3 pages2nd Exam ScienceItsMe SirMJPas encore d'évaluation
- Surigao State College of Technology: Republic of The Philippines Del Carmen Campus Del Carmen, Surigao Del NorteDocument3 pagesSurigao State College of Technology: Republic of The Philippines Del Carmen Campus Del Carmen, Surigao Del NorteEDMAR POLVOROZAPas encore d'évaluation
- "Plasma Antenna Technology": Presentation On Technical Seminar Report of 8 Semester B.E. ONDocument20 pages"Plasma Antenna Technology": Presentation On Technical Seminar Report of 8 Semester B.E. ONNagaveniPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Communication SystemsDocument16 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Communication SystemsMelz WiggiePas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic RadiationDocument5 pagesElectromagnetic RadiationrendakianPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 22 - Physics - Coordinated Science - IGCSE CambridgeDocument154 pagesChapter 22 - Physics - Coordinated Science - IGCSE CambridgeAlvin DuanePas encore d'évaluation
- Photoshop Post-Processing Master 3D Renders - TutorialDocument13 pagesPhotoshop Post-Processing Master 3D Renders - TutorialWilliam Sosa de León100% (1)
- Essilor - Price List With BarcodeDocument58 pagesEssilor - Price List With BarcodeeyesdealeyewearudhnaPas encore d'évaluation