Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Bonding Lab Rport
Transféré par
MarlynCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Bonding Lab Rport
Transféré par
MarlynDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Marlyn Rodriguez 11/9/12 Period 4 Ionic vs.
Covalent Bonding Lab Investigation Introduction: Most atoms are never found by themselves; instead they are bonded to other atoms in ionic or covalent bonds. This is because the atoms are not stable. Atoms electrons are not held with great force to the nucleus and, therefore, are easily lost to other atoms in ionic bonding or shared with other atoms in covalent bonding. Combining the atoms in bondings will make the atoms stable and satisfied with a full octet. Ionic bonds are made up of metals and non-metals and conduct electricity when dissolved in water, since the electrons are in motion in the metal part of the bond. The valence electrons in ionic bonds are transferred, causing them to lose electrons to other atoms to give each atom a full octet. Covalent compounds are two non-metals bonded together, the bonds share valence electrons in order for them to have a full shell as well. Covalent compounds do not conduct electricity since its electrons are not in motion. The purpose of this lab is to find which compounds form ionic or covalent bonds. Hypotheses: Table 1: The expected results of testing five different chemicals Chemical Hypothesis 1: Hypothesis 2: High Hypothesis 3: Will Compounds to Formula it conduct be Tested Ionic or or Low melting Covalent? point? electricity? Distilled (pure) H2 O Covalent Low No water Sodium NaCl Ionic High Yes, when Chloride dissolved in water Sucrose (sugar) C12H22O11 Covalent Low No Dextrose C6H12O6 Covalent Low No Sodium Sulfate NaSO4 Ionic Medium Yes, when dissolved in water
Procedures: Part I. Melting Point and Strength of Bonds 1
1. Aluminum foil was shaped to neatly fit the ring-stand. A small sample of each different compound was placed on the square of the aluminum foil. 2. The tray was placed on the ring stand and heated with the Bunsen burner for no longer than 1-2 minutes. 3. The observations were recorded, in detail, while keeping track of the order in which the samples melted or didnt melt. 4. The foil was washed into the sink after the square of foil cooled off. Part II. Electrical Conductivity 1. Each compound was placed into different wells on a well plate 2. The dry compounds were tested for conductivity with the tester and the observations were recorded. 3. Distilled water was added to the well to dissolve in the compounds. 4. The compounds were tested for conductivity with the tester. The observations were recorded and the tester was washed with distilled water after every use. 5. The steps were repeated for all the samples. Results: Table 2: The final results of testing five different chemicals. Name/Chemical Part I: Melting Point Part II: Conducted FINAL Formula: (1-5; High, Med. or Electricity? (Yes/No) CONCLUSION: Low?) Ionic or Covalent Dry Dissolved Bonds? 1. Distilled (pure) Water/ H2O 2. Sodium Chloride/ NaCl 3. Sucrose (sugar) / C12H22O11 4. Dextrose/ C6H12O6 5. Sodium Sulfate/ NaSO4 Conclusion: After this laboratory, it was concluded that sodium chloride and sodium sulfate were ionic compounds, while; water, sucrose, and dextrose were covalent compounds. All of the 2 1=lowest: (already melted) 5=High 1=Low 1=Low 3=Medium N/A No No No No No Yes No No Yes Covalent Ionic Covalent Covalent Ionic
initial hypotheses were correct. From the results, the ionic compounds were those that conducted electricity in water and had high melting points (strong bonds). However, the covalent compounds did not conduct electricity in water and had high melting points (weak bond). Covalent compounds are formed from metal cations (+) and non-metal anions (-) so when the compounds dissolve in water, electricity (moving charge) can flow through the solution. Additionally, ionic compounds are very strong since the electrons are held together by electrostatic attraction. Ionic compounds have both a high electronegativity, since the electrons are further away from the nucleus, and low ionization energy, since the electrons are easier to remove because of electronegativity, causing the bonds to be strong and transfer the needed electrons to one another. Ionic compounds conduct electricity only when the compounds are in water because electrons are in motion in half of the ionic bond since ionic bonds are part metal. Covalent bonds do not conduct electricity since the compounds have high electronegativity, the higher the atoms electronegativity is, the farther away the last electron shell is from the nucleus. This causes the bond to be weak and share its electrons with other compounds.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Ionic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab Investigation: Carefully On The Square FoilDocument3 pagesIonic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab Investigation: Carefully On The Square FoilLesliePas encore d'évaluation
- Ionic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationDocument3 pagesIonic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationItaloPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Italo Calderon Lab ReportDocument3 pages4 Italo Calderon Lab ReportLesliePas encore d'évaluation
- Ionic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationDocument4 pagesIonic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationAngelicaPas encore d'évaluation
- Christian Lara Lab ReportDocument3 pagesChristian Lara Lab ReportLesliePas encore d'évaluation
- Ionic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab Investigation: HypothesesDocument3 pagesIonic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab Investigation: HypothesesLesliePas encore d'évaluation
- Ionic v. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationDocument3 pagesIonic v. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationJackelinePas encore d'évaluation
- Ionic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationDocument3 pagesIonic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationLesliePas encore d'évaluation
- Larkin Lab ReportDocument3 pagesLarkin Lab ReportChristopherAguilar33% (3)
- Ionic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationDocument3 pagesIonic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationLesliePas encore d'évaluation
- Ionic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationDocument3 pagesIonic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationLesliePas encore d'évaluation
- Hypothesis:: Compounds To Be Tested Ionic or Covalent High or Low Melting Point? Electricity?Document3 pagesHypothesis:: Compounds To Be Tested Ionic or Covalent High or Low Melting Point? Electricity?LesliePas encore d'évaluation
- Matthew McClain Lab Report Period 4Document4 pagesMatthew McClain Lab Report Period 4mmcclain2014Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ionic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationDocument3 pagesIonic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationIngridPas encore d'évaluation
- Ionic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationDocument3 pagesIonic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationMarcoluisPas encore d'évaluation
- Katia Medina Larkin 2Document3 pagesKatia Medina Larkin 2kmedina2014Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ionic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationDocument4 pagesIonic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationLesliePas encore d'évaluation
- Jose Camacho Chem LABDocument3 pagesJose Camacho Chem LABLesliePas encore d'évaluation
- Larkin's Lab ReportDocument3 pagesLarkin's Lab ReportRicardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ionic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationDocument3 pagesIonic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationitzelPas encore d'évaluation
- Ionic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationDocument3 pagesIonic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationLesliePas encore d'évaluation
- GCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsD'EverandGCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (3)
- Ionic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab ReportDocument3 pagesIonic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab ReportLesliePas encore d'évaluation
- 8 Thhourlab 9 BakerbrunatikallalkaneoberlanderDocument5 pages8 Thhourlab 9 Bakerbrunatikallalkaneoberlanderapi-297169088Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5 Chemical BondDocument8 pagesChapter 5 Chemical Bondمسنيزواتي محمد نورPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry: Inestigatory ProjectDocument16 pagesChemistry: Inestigatory ProjectAnshulPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 5Document8 pagesChemistry Form 4 Chapter 5ManiArasiChandranPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrolyte and NonDocument7 pagesElectrolyte and NonSuwahono, M.PdPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Bond Notes by TouhidDocument23 pagesChemical Bond Notes by Touhidnabilnakib0077Pas encore d'évaluation
- Investigation of The Chemical and Physical Properties of Ionic and Covalent BondingDocument7 pagesInvestigation of The Chemical and Physical Properties of Ionic and Covalent Bondingapi-238781118100% (1)
- Chemistry Lab 3Document2 pagesChemistry Lab 3Sherida GibbsPas encore d'évaluation
- REVISION 1Document69 pagesREVISION 1Biology BảoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Lab PresentationDocument5 pagesChemistry Lab PresentationIhfaz NoorPas encore d'évaluation
- Ionic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationDocument3 pagesIonic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationLesliePas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Study Notes Igcse EdexcelDocument34 pagesChemistry Study Notes Igcse EdexcelAhmed KhalilPas encore d'évaluation
- IMFA and Chemical BondingDocument137 pagesIMFA and Chemical BondingEnna SertPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT-2 Chem Bonding-2Document13 pagesUNIT-2 Chem Bonding-2KARTIKAY LADDHAPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrolysis of Water Study Guide: MaterialsDocument2 pagesElectrolysis of Water Study Guide: Materialsagbajelola idrisPas encore d'évaluation
- ChemistryDocument15 pagesChemistryTGC NINJAPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparing Covalent and Ionic Lattices S4Document3 pagesComparing Covalent and Ionic Lattices S4Fatima Ahmed-VeriterPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Curriculum by Aaron KellerDocument7 pagesScience Curriculum by Aaron KellerResta THawPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 5 Dissimilarity Between Ionic and Covalent CompoundsDocument5 pagesExperiment 5 Dissimilarity Between Ionic and Covalent CompoundsNurasyilah YakubPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade-9-Science Q2 Wk3 GLAKDocument16 pagesGrade-9-Science Q2 Wk3 GLAKMorana TuPas encore d'évaluation
- Rajkumar Chemistry 2-1Document13 pagesRajkumar Chemistry 2-1Gopala krishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Acknowledgment: Electrochemical CellDocument12 pagesAcknowledgment: Electrochemical CellMSD PrajwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Thank You for Helping Me Complete My Project ReportDocument12 pagesThank You for Helping Me Complete My Project ReportMSD PrajwalPas encore d'évaluation
- High Tech High North County, San Marcos, CA: Solution Conductivity Experiment Lab ReportDocument4 pagesHigh Tech High North County, San Marcos, CA: Solution Conductivity Experiment Lab Reportapi-271065755Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chem 2Document15 pagesChem 2CR7STUDIO 70% (1)
- Experiment 5 Properties of Ionic and Covalent CompoundsDocument5 pagesExperiment 5 Properties of Ionic and Covalent CompoundsAbdul Rahman Abdul Najib100% (1)
- Ionic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab Investigation: PART I. Melting Point and Strength of BondsDocument3 pagesIonic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab Investigation: PART I. Melting Point and Strength of BondsLesliePas encore d'évaluation
- DHRITIDocument13 pagesDHRITIrekha raniPas encore d'évaluation
- CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR GEOMETRYDocument4 pagesCHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR GEOMETRYRen ManalotoPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.1 The Organization of Matter: Elements and AtomsDocument6 pages2.1 The Organization of Matter: Elements and Atomsspencer_jordan_2Pas encore d'évaluation
- 02 CHEM X ICSE SUMMARY Chemical BondingDocument9 pages02 CHEM X ICSE SUMMARY Chemical BondingNatasha DalalPas encore d'évaluation
- Inquiry Into Bonding Lab - Intro TestDocument5 pagesInquiry Into Bonding Lab - Intro Testapi-491531529Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Times School Ix-Chemistry Reasoning Questions and Their AnswersDocument4 pagesThe Times School Ix-Chemistry Reasoning Questions and Their AnswersHina RabbaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical BondingD'EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical BondingÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (3)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical Bonding with AnswersD'EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical Bonding with AnswersÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsD'EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5)
- The Romance of War Inventions: A Description of Warships, Guns, Tanks, Rifles, Bombs, and Other Instruments and Munitions of Warfare, How They Were Invented & How They Are EmployedD'EverandThe Romance of War Inventions: A Description of Warships, Guns, Tanks, Rifles, Bombs, and Other Instruments and Munitions of Warfare, How They Were Invented & How They Are EmployedPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 2 Chapter 2Document2 pagesTutorial 2 Chapter 2Marko IrwinPas encore d'évaluation
- Conductance ManualDocument12 pagesConductance ManualhannibalmrPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Transmission (Winter)Document20 pagesThermal Transmission (Winter)Robin Charles SamuelPas encore d'évaluation
- Maglev Wind Mill ReportDocument24 pagesMaglev Wind Mill ReportBalu MahendarPas encore d'évaluation
- smts-2 Theory of Structures by B.C. Punmia Text PDFDocument497 pagessmts-2 Theory of Structures by B.C. Punmia Text PDFAman Dubey100% (1)
- Mini Project-PCHES Project OVER VIEW OF THE 120MW SWITCHYARDDocument54 pagesMini Project-PCHES Project OVER VIEW OF THE 120MW SWITCHYARDManasa VeenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Operation Sandstone. Nuclear Explosions 1948, Scientific Director's Report of Atomic Weapon TestsDocument341 pagesOperation Sandstone. Nuclear Explosions 1948, Scientific Director's Report of Atomic Weapon TestsMikeF88Pas encore d'évaluation
- Delhi Transco Limited Training ReportDocument61 pagesDelhi Transco Limited Training ReportDevashish Kumar33% (3)
- Transformers and Tapchangers Version EDocument81 pagesTransformers and Tapchangers Version Emartinez_josel100% (1)
- Measuring Pressure and Weight Using LVDTDocument20 pagesMeasuring Pressure and Weight Using LVDTsindhu100% (1)
- 2019 Summer Question Paper (Msbte Study Resources)Document5 pages2019 Summer Question Paper (Msbte Study Resources)Ashish patharePas encore d'évaluation
- Fluent ExerciseDocument44 pagesFluent ExerciseDesign guruPas encore d'évaluation
- DSCE ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS-I AND PHYSICS SYLLABUSDocument119 pagesDSCE ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS-I AND PHYSICS SYLLABUSNandan MaheshPas encore d'évaluation
- Rectilinear and rotational kinematics problemsDocument5 pagesRectilinear and rotational kinematics problemsAljay Dungao40% (5)
- CFD Analysis of Flow in After BurnerDocument10 pagesCFD Analysis of Flow in After BurnermortezaastroPas encore d'évaluation
- Ic Engines Quiz - 1Document1 pageIc Engines Quiz - 1ratchagarajaPas encore d'évaluation
- fle, Tii,:v,' Jy ' TR Ijf, Q D, 4cto'r:.,ma, Ri:al' :1j::"""Document4 pagesfle, Tii,:v,' Jy ' TR Ijf, Q D, 4cto'r:.,ma, Ri:al' :1j::"""Ovidijus RučinskasPas encore d'évaluation
- MIT Arts, Design and Technology University, Rajbaug, Pune - Ordinary Differential Equations and Advanced Calculus Question BankDocument8 pagesMIT Arts, Design and Technology University, Rajbaug, Pune - Ordinary Differential Equations and Advanced Calculus Question BankJohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Penurunan Persamaan BETDocument7 pagesPenurunan Persamaan BETDyah Ayu Pramoda WardaniPas encore d'évaluation
- States of Matter PDFDocument42 pagesStates of Matter PDFSarthak GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Theory of PlasticityDocument110 pagesTheory of Plasticitytayyeb803Pas encore d'évaluation
- Shock and Vibration PDFDocument211 pagesShock and Vibration PDFEnrique Lopez De ArroyabePas encore d'évaluation
- 3.A - The First Law of Thermodynamics (Answer) - Physics LibreTextsDocument5 pages3.A - The First Law of Thermodynamics (Answer) - Physics LibreTextsFASIKAW GASHAWPas encore d'évaluation
- Vessel seismic design calculationDocument11 pagesVessel seismic design calculationinnovativekarthiPas encore d'évaluation
- 4PH0 1P Rms 20120823 PDFDocument24 pages4PH0 1P Rms 20120823 PDFwalyatPas encore d'évaluation
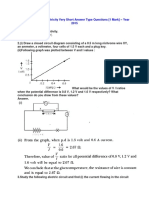
- Electricity Chapter Wise Important Questions Class 10 Science - Learn CBSEDocument39 pagesElectricity Chapter Wise Important Questions Class 10 Science - Learn CBSEAmitChopraPas encore d'évaluation
- Universe - WikipediaDocument19 pagesUniverse - WikipediaTejasPas encore d'évaluation
- Long-Term Stability of Rubber Hardness Reference Blocks: Anton Tibler, Konrad Herrmann, Zoran U TeriDocument6 pagesLong-Term Stability of Rubber Hardness Reference Blocks: Anton Tibler, Konrad Herrmann, Zoran U TeriVinod KrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Circuits & Resistors: Conductors & InsulatorsDocument10 pagesCircuits & Resistors: Conductors & InsulatorsH Aries OñaPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction 2Document30 pagesIntroduction 2niteshPas encore d'évaluation