Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Wills Bar Outline
Transféré par
John RisvoldCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Wills Bar Outline
Transféré par
John RisvoldDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
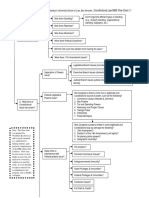
Wills I. Execution of wills A. Requirements for validly executed will 1.
Signed by testator (18) or proxy signature (at direction & in presence) 2. two attesting witnesses 3. each witness must sign in testators presence 4. Codicil must be executed with same formalities 5. Exact order of signing is not critical as long as contemporaneous transaction B. Signing in testators presence 1. UPC/Majority Rule: T does not to actually see witnesses just be near enough that he is conscious of what they are doing 2. IL Rule: Must be in interrupted scope of vision C. Attorney Liability for negligence in preparation of the will 1. Minority Rule: no privity with others so only client can sue 2. IL Rule: privity rejected as defense intended beneficiaries can sue D. Interested witness Statute beneficiary is attesting witness 1. Will can be admitted to probate but beneficiary-witness loses legacy a. Unless two disinterested witnesses or would take either way 2. executor not interested witness under majority rule (IL voids compensation) 3. Under IL law signing by spouse of interested witness voids legacy too 4. UPC states have abolished this rule E. Holographic wills 1. UPC/Majority Rule: recognize handwritten and signed but unwitnessed wills 2. IL Rule: do not recognize holographic wills because no witnesses a. foreign holographic wills can be admitted to probate Model Answer: In about 30 states, including Michigan, the instrument would be valid as a holographic will because it was entirely in Testators handwriting and signed by him. In Illinois, however, the instrument is not valid as will even though Testator may have intended it as such, because it was not witnessed by two witnesses. F. Conditional Wills 1. court may interpret apparent condition to be motive for creating will II. Revocation of Wills A. Valid Revocation mere intent is not enough 1. later testamentary instrument (appropriate formalities) 2. physical act on the will itself a. Proof of Lost Wills Statute i. proof of due execution ii. cause of wills nonproduction
iii. contents must be substantially proved B. Presumptions regarding revocation 1. not found at death, last seen in testators possession presume revoked by physical act 2. found mutilated at death, last seen in testators possession presume revoked by physical act 3. Neither of these applicable if last seen in someone elses possession 4. If more than one will: read together of possible inconsistencies revoked by implication C. Dependent Relative Revocation (DRR) 1. IL no revival of revoked wills unless formalities observed 2. DRR allows revocation to be set aside because of mistake of law or fact D. Changes of face of will after it has been executed 1. UPC/Majority Rule: change effective 2. IL: ineffective to change will unless reexecuted with proper formalities 3. Partial revocation by physical act is not valid III. Beneficiary dies during testators lifetime A. Anti-lapse statutes 1. IL: applies only when the predeceasing beneficiary was a child or other descendant of the testator 2. If anti-lapse does not apply, gift falls into residuary estate B. Lapse in residuary gift: surviving residuary beneficiaries rule 1. IL: If the residuary estate is devised to two or more persons and gift to on of them lapses, the surviving residuary beneficiaries take the entire residuary estate, in proportion to their interest in the residue 2. Anti-lapse statute trumps the surviving residuary beneficiaries rule if predeceasing beneficiary: a. was within the scope of the statute b. left descendants who survived the testator C. Class Gifts 1. where class member predeceases testator, other member succeed to his share (look for anti-lapse if descendant) 2. Rule of convenience class closes when some member is entitled to distribution (gestation of 280 days for fetuses) D. Deaths in Quick Succession 1. IL/Majority: Uniform Simultaneous Death Act: When title depends on order of deaths and there is no sufficient evidence that the person have died otherwise than simultaneously, the property of each passes as though he or she survived a. Wills: as though testator survived and beneficiary predeceased b. Intestacy: intestate survived and heir predeceased c. Insurance: though insured survived and beneficiary predeceased 2. Several states have adopted 120-hr rule need to live 120 hours to take
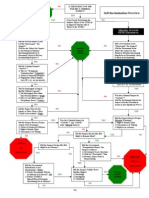
IV. Changes in Family after Wills Execution A. Testator Marries after will is executed 1. UPC: testator write will then marries, the pretermitted spouse takes an intestate share of the estate 2. IL (majority) no effect on will (no omitted spouse rule) a. spouse protected by elective share B. Testator is divorced after will is executed 1. IL (majority): Final decree of divorce or annulment revokes all gift and fiduciary appointments in favor of former spouse. Estate executed as if spouse predeceased the testator C. Testator has child after will executed pretermitted child 1. IL (majority): Rule only applies to after born children (incl. republ.) 2. take as if no will (intestate) unless it appears from will omission intentional V. Problems associated with testamentary gifts A. Abatement of Legacies not enough assets to satisfy gifts and creditors attack gifts, order: 1. intestate property 2. residuary assets 3. general legacies 4. specific bequests B. Specifically bequeathed property not in estate at death ademption 1. gift fails if asset not there (blackacre) 2. IL: if sales contract only partially performed devisee gets remaining 3. If incapacity after bequest, devisee can sue for value if traceable C. Bequests of stocks and other securities 1. generally seen as general legacies 2. unless uses my then specific and ademption applies 3. IL: includes everything but stock dividends D. Specific Gifts of Encumbered Property: Is lien exonerated 1. common law/ majority: absent contrary provision, liens are exonerated from residuary estate 2. IL/UPC: liens not exonerated take as testator had VI. Reference to Acts and events outside the will A. Incorporation by reference doctrine 1. Extrinsic document, not present when the will was executed can be incorporated if: a. document in existence when will executed b. will must refer to document being in existence c. will describes sufficient to permit identification 2. UPC exception - no disposition of money on tangible personal property
B. Acts of independent significance (nontestamentary acts) lifetime act with lifetime motive or purpose so even though it effects terms it is considered VII. Other Will Doctrines A. Mistake or Ambiguity in the Will 1. Plain meaning rule - extrinsic evidence inadmissible 2. latent ambiguity because of misdescription extrinsic evidence admissible (no declaration of intent) a. if evidence does not cure then gift fails 3. patent ambiguity mistake appears on face of will extrinsic evidence admissible B. Contracts Relation to Wills (Joint or Mutual Wills) 1. Under the UPC and by statute in several states, a will is never contractual unless the will expressly states that a contract does exist. In Illinois and a number of states, however, execution of a joint will be a husband and wife may be found contractual IF all or mist if the following factors are present: a. will labeled joint and mutual b. will leaves entire estate to surviving spouse c. will disposes of all of their property in a unified disposition d. there is a common dispositive scheme on the death of the survivor 2. If held contractual: a. apply will law b. apply contract law, breached will (constructive trust) 3. Reciprocal wills are never presumed to be contractual unless clear and convincing evidence C. Effect of Words of Disheritance in a Will 1. Under the UPCs negative bequest rule, a will can provide how property shall not be disposed of 2. IL applies common law (majority), if will does not make complete disposition of estate, words of inheritance are ineffective (passes intestate) D. Unlawful conditions 1. cannot induce divorce 2. can make partial restraint on marriage E. Thou shalt not kill 1. IL slayer statute: Killer forfeits interest in victims estate if he intentionally and unjustifiably causes the death of another 2. Applies to all forms of transfer F. Nonprobate assets 1. property passing by rights of survivorship 2. property passing by contract 3. property held by revocable trust
VIII. Intestate Succession (left no will, will denied probate, not complete disposition) A. Intestate Share of surviving spouse 1. if survived by descendants (family allowance regardless) 2. all if not survived by descendants B. Inheritance by Descendants (Issue) 1. strict per stirpes one share for each line of living descendants a. descendants of deceased children take by representation 2. cut at brother sister level if no kids C. Other intestate distribution rules 1. Majority Rule: testators estate inherited by parents if unmarried/no issues 2. IL Rule: parents and siblings split shares 3. parent disqualified if neglected, deserted, or failed to support child D. Adopted Children, Children Born out of Wedlock 1. Children adopted under 18 have full inheritance 2. unadopted stepchild cannot inherit 3. adopted child has no inheritance from natural kin 4. child adopted by spouse of natural parent has inheritance rights 5. adopted over 18 inherits from parent only 6. children born out of wedlock inherit from natural father if (PAP): a. Paternity suit b. Acknowledged paternity c. Probate proceedings E. Lifetime Gifts to Heir or Will Beneficiary 1. common law: lifetime gift is presumed advancement of childs intestate share 2. IL (majority): reverses the common law presumption and requires writing: A lifetime gift is not advancement unless a. declared as such in writing by the donor b. acknowledged as such in writing by the donee c. applies only to children 3. non-children must be explicit F. Disclaimer by heir or beneficiary 1. Able to disclaim at any time in IL (whole or part) 2. Treat as if predeceased 3. Done to avoid gift tax and creditors claims IX. Elective Share Statute Right of Renunciation A. Amount of Elective Share 1. 1/3 if survived by descendants 2. if not survived B. spouse must file notice of election to renounce will (IL 7 months) C. Election van be made by spouse or on incapacitated spouses behalf D. All beneficiaries contribute pro rata outright devises to spouse applied first E. Trusts
1. UPC/Majority: Elective share applies to the augmented estate, which includes lifetime transfers in which the grantor retained the power to revoke, or to invade consume or dispose of principal 2. IL: NO: Elective share means probate estate, does not apply to nonprobate transfers X. Will Contests only those who have economic interest can contest A. Lack of Testamentary Capacity: Did testator have sufficient capacity to: 1. understand the nature of the act he was doing 2. know the nature and approximate value of his property 3. know the natural objects of his bounty 4. understand the disposition he was making B. undue Influence contestants have burden to show: 1. existence and exertion of undue influence 2. effect of which has to overpower the mind and will of the testator 3. product is a will that would not be created but for influence 4. where a person is in a confidential or fiduciary relationship as active in procuring the will and that party will receive a substantial benefit under the will there is a presumption of undue influence which can be overcome with clear and convincing evidence C. No-contest clause 1. lawful in IL even if probable cause 2. lawful unless probable cause under UPC/majority XI. Powers of Appointment
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 101 Bar Exam Affirmations: Bar Exam Booklets, #1D'Everand101 Bar Exam Affirmations: Bar Exam Booklets, #1Évaluation : 2 sur 5 étoiles2/5 (4)
- Passing the Bar Exam: A Step-by-Step Guide for California Bar Re-TakersD'EverandPassing the Bar Exam: A Step-by-Step Guide for California Bar Re-TakersPas encore d'évaluation
- Business AssociationsDocument13 pagesBusiness AssociationsJeremiahgibsonPas encore d'évaluation
- MBE SM OutlineDocument8 pagesMBE SM OutlineMegan McCormackPas encore d'évaluation
- MBE Criminal Procedure SLIDESDocument50 pagesMBE Criminal Procedure SLIDESAlex McPettersonPas encore d'évaluation
- Bar Exam: Select Rule Statements - EvidenceDocument3 pagesBar Exam: Select Rule Statements - EvidenceMarlene MilgramPas encore d'évaluation
- Mbe Bar BriDocument24 pagesMbe Bar Briluckystar384Pas encore d'évaluation
- FlowchartDocument2 pagesFlowchartBre HitchPas encore d'évaluation
- 296060485-MBE-Memorization-Chart For Printing Feb. 22 Bar ExamDocument85 pages296060485-MBE-Memorization-Chart For Printing Feb. 22 Bar ExamRosely Torres50% (2)
- Con LawDocument2 pagesCon Lawchristell Casey50% (2)
- Wills LectureDocument6 pagesWills LectureBrenna Snow RahmlowPas encore d'évaluation
- Constitutional Law Outline Swartzwelder Standards of Review Intro Issue: RuleDocument37 pagesConstitutional Law Outline Swartzwelder Standards of Review Intro Issue: RuleKylee Colwell100% (2)
- Evidence Checklist ChillDocument1 pageEvidence Checklist Chillafisher-poguelawPas encore d'évaluation
- Crim Pro Essay OutlineDocument3 pagesCrim Pro Essay OutlineKeiara Pather100% (1)
- Intro: Legal Knowledge Skill Thoroughness PreparationDocument2 pagesIntro: Legal Knowledge Skill Thoroughness PreparationHaifaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mbe Evid Quiz 6-6Document16 pagesMbe Evid Quiz 6-6Kim BoSlicePas encore d'évaluation
- MBE Subject Matter OutlineDocument8 pagesMBE Subject Matter OutlineSalam TekbaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Partnership Law Attack SheetDocument1 pagePartnership Law Attack SheetKylee ColwellPas encore d'évaluation
- Really Good Prop OutlineDocument60 pagesReally Good Prop OutlineJustin Wilson100% (3)
- MBE Subject Matter Review ChecklistDocument3 pagesMBE Subject Matter Review Checklistbeebee83Pas encore d'évaluation
- MPT WorkshopDocument13 pagesMPT WorkshopStacy OliveiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Bar Quick-MBE MixedDocument1 pageBar Quick-MBE Mixedtreacherousasian657Pas encore d'évaluation
- BA - FreerDocument121 pagesBA - FreerEugene Yanul100% (1)
- Conlaw MBE OutlineDocument26 pagesConlaw MBE OutlineMarco FortadesPas encore d'évaluation
- Wills MnemonicsDocument6 pagesWills MnemonicsSemsudPas encore d'évaluation
- One Sheet - CriminalDocument2 pagesOne Sheet - Criminalchristell Casey100% (5)
- MBE Karlan CrimproDocument30 pagesMBE Karlan CrimproAlexandraMarie100% (1)
- Quick Attack SheetDocument2 pagesQuick Attack SheetBrianStefanovicPas encore d'évaluation
- Torts Weisberg 2018 OutlineDocument28 pagesTorts Weisberg 2018 OutlineLeopold bloomPas encore d'évaluation
- MPRE OutlineDocument14 pagesMPRE Outlineesquire1010Pas encore d'évaluation
- Realproperty OpeningpsDocument6 pagesRealproperty OpeningpsKellyMacDevittPas encore d'évaluation
- MBE-Evidence OutlineDocument20 pagesMBE-Evidence OutlineStacy Oliveira100% (1)
- MBE-Criminal Procedure OutlineDocument16 pagesMBE-Criminal Procedure OutlineYerinPas encore d'évaluation
- MBE-Con Law OutlineDocument31 pagesMBE-Con Law OutlineStacy Oliveira100% (3)
- Homicide Approach For The Bar ExamDocument1 pageHomicide Approach For The Bar Examsuperxl2009100% (1)
- 11 5th Amendment ChartDocument1 page11 5th Amendment ChartJose Gabriel CordovaPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 3: MC Practice Questions: Torts: To: de Cardenas, Gaston L.Document1 pageClass 3: MC Practice Questions: Torts: To: de Cardenas, Gaston L.Gaston Luis De Cardenas0% (1)
- Barbri Outline - MBE-NY (2005) - Constitutional LawDocument13 pagesBarbri Outline - MBE-NY (2005) - Constitutional Lawsab0714Pas encore d'évaluation
- Evicence Outline 1Document68 pagesEvicence Outline 1krys10938Pas encore d'évaluation
- Quicksheet - Property Law: Ownership of Real PropertyDocument15 pagesQuicksheet - Property Law: Ownership of Real PropertyTania AmentPas encore d'évaluation
- 2016 Evidence OutlineDocument6 pages2016 Evidence OutlineJanice Parmar100% (2)
- Const Law - Rule StatementsDocument4 pagesConst Law - Rule StatementsMarlene MilgramPas encore d'évaluation
- Professional Responsibility - Attack SheetDocument1 pageProfessional Responsibility - Attack SheetMissPardis100% (1)
- Themis - Corporation OutlineDocument7 pagesThemis - Corporation OutlineParker BushPas encore d'évaluation
- Pieper Bar ReviewDocument150 pagesPieper Bar ReviewJoanne Schioppi0% (1)
- Crimpro OutlineDocument9 pagesCrimpro OutlineAnonymous I5y6LT5100% (1)
- MBE Constitutional Law DrillsDocument18 pagesMBE Constitutional Law DrillsGabriela Maria Medina Marrero100% (1)
- MPRE Review - Professional ResponsibilitiesDocument10 pagesMPRE Review - Professional Responsibilitiesclairebear888Pas encore d'évaluation
- ABA Rules #ProfessionalresponsibilityDocument15 pagesABA Rules #ProfessionalresponsibilityRooter Cox100% (1)
- IL Corporations Bar OutlineDocument8 pagesIL Corporations Bar OutlineJulia NiebrzydowskiPas encore d'évaluation
- PR OutlineDocument20 pagesPR Outlineddavis105Pas encore d'évaluation
- Constitutional Law Essay GuideDocument2 pagesConstitutional Law Essay Guidesuperxl2009Pas encore d'évaluation
- MBE - Real Property OutlineDocument35 pagesMBE - Real Property OutlineStacy OliveiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Criminal Procedure-Final OutlineDocument37 pagesCriminal Procedure-Final Outlineeric berns100% (2)
- First Amendment 2011Document62 pagesFirst Amendment 2011DavidFriedmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Levels of Constitutional ScrutinyDocument22 pagesLevels of Constitutional ScrutinyFarah RahgozarPas encore d'évaluation
- Quicksheet - Evidence: General ProvisionsDocument14 pagesQuicksheet - Evidence: General ProvisionsTania Ament100% (1)
- Bar Prep - Outline - Con Law - ShortDocument16 pagesBar Prep - Outline - Con Law - ShortAnonymous Cbr8Vr2SX100% (6)
- MPRE Unpacked: Professional Responsibility Explained & Applied for Multistate Professional Responsibility ExamD'EverandMPRE Unpacked: Professional Responsibility Explained & Applied for Multistate Professional Responsibility ExamPas encore d'évaluation
- Torts OutlineDocument30 pagesTorts OutlineJohn RisvoldPas encore d'évaluation
- Trusts Bar OutlineDocument4 pagesTrusts Bar OutlineJohn RisvoldPas encore d'évaluation
- Secured Bar OutlineDocument3 pagesSecured Bar OutlineJohn RisvoldPas encore d'évaluation
- IL Civ Pro Bar OutlineDocument6 pagesIL Civ Pro Bar OutlineJohn RisvoldPas encore d'évaluation
- Suretyship Bar OutlineDocument2 pagesSuretyship Bar OutlineJohn RisvoldPas encore d'évaluation
- Family Law Bar OutlineDocument5 pagesFamily Law Bar OutlineJohn Risvold100% (1)
- Corporations Bar OutlineDocument4 pagesCorporations Bar OutlineJohn RisvoldPas encore d'évaluation
- Commercial Paper Bar OutlineDocument2 pagesCommercial Paper Bar OutlineJohn RisvoldPas encore d'évaluation
- Equity Bar OutlineDocument4 pagesEquity Bar OutlineJohn Risvold100% (1)
- Conflict of Laws Bar OutlineDocument4 pagesConflict of Laws Bar OutlineJohn Risvold50% (2)
- Travis Risvold Final OutlineDocument28 pagesTravis Risvold Final OutlineJohn Risvold0% (1)
- BOC 2014 - Civil Law ReviewerDocument481 pagesBOC 2014 - Civil Law ReviewerBayani KamporedondoPas encore d'évaluation
- Getting To Know The UCCDocument9 pagesGetting To Know The UCCBobby Souza100% (2)
- First Exam Obli (Undergrad)Document2 pagesFirst Exam Obli (Undergrad)geweePas encore d'évaluation
- Fernandez vs. Dela RosaDocument2 pagesFernandez vs. Dela RosaCeCe Em50% (4)
- PALE-CASE 41-NinanneDocument1 pagePALE-CASE 41-NinanneNiñanne Nicole Baring BalbuenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ja Anne GazaDocument8 pagesJa Anne GazaRhows BuergoPas encore d'évaluation
- JP 040215Document28 pagesJP 040215The AdvocatePas encore d'évaluation
- AgPart 925 - Memaid PartDocument10 pagesAgPart 925 - Memaid Partcezar delailaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes of CPC LatestDocument70 pagesNotes of CPC LatestAditya Singh ChouhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Transfer of Property Sale of Goods ActDocument16 pagesTransfer of Property Sale of Goods Actdikshit91vishalPas encore d'évaluation
- Form of TenderDocument6 pagesForm of TenderRoy TapizPas encore d'évaluation
- Delegated Legislation - Meaning, Advantages, Criticism Explained - MrunalDocument4 pagesDelegated Legislation - Meaning, Advantages, Criticism Explained - MrunalShirishJagtapPas encore d'évaluation
- Salil Dutta v. T.M. and M.C. (P) LTDDocument6 pagesSalil Dutta v. T.M. and M.C. (P) LTDAkshsPas encore d'évaluation
- Industrial Insurance V BondizzleDocument2 pagesIndustrial Insurance V BondizzleJet SiangPas encore d'évaluation
- Franklin LawsuitDocument24 pagesFranklin LawsuitMinnesota Public RadioPas encore d'évaluation
- Rules Flow ChartDocument6 pagesRules Flow Chartmrgoldsmith23100% (7)
- SEC Vs Subic Bay GoldDocument2 pagesSEC Vs Subic Bay GoldBrokenPas encore d'évaluation
- Motor Vehicle InsuranceDocument3 pagesMotor Vehicle InsuranceJoAizaD100% (1)
- Sy Chim v. Sy Siy Ho Sons Inc. 1Document3 pagesSy Chim v. Sy Siy Ho Sons Inc. 1Apol GimenezPas encore d'évaluation
- TalaqDocument27 pagesTalaqIqra MasudPas encore d'évaluation
- 2022LHC6894Document5 pages2022LHC6894Adeel AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Omni Innovations LLC v. Ascentive LLC Et Al - Document No. 63Document1 pageOmni Innovations LLC v. Ascentive LLC Et Al - Document No. 63Justia.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Penigar v. Douglas County Corrections Et Al - Document No. 7Document3 pagesPenigar v. Douglas County Corrections Et Al - Document No. 7Justia.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Elling O. Eide v. Sarasota County, A Political Subdivision of The State of Florida, 908 F.2d 716, 11th Cir. (1990)Document17 pagesElling O. Eide v. Sarasota County, A Political Subdivision of The State of Florida, 908 F.2d 716, 11th Cir. (1990)Scribd Government DocsPas encore d'évaluation
- Republic v. Vega G. R. No. 177790, Jan. 17, 2011Document15 pagesRepublic v. Vega G. R. No. 177790, Jan. 17, 2011Mp CasPas encore d'évaluation
- Scandal of Satyam ComputersDocument83 pagesScandal of Satyam ComputersShreshth BabbarPas encore d'évaluation
- 25.phil Bus Rabbit VS Phil American ForwardersDocument2 pages25.phil Bus Rabbit VS Phil American ForwardersKar EnPas encore d'évaluation
- 2011-10-13 Brook Field Properties LetterDocument2 pages2011-10-13 Brook Field Properties Letterjohnd7463Pas encore d'évaluation
- Crim 2 #12 Nostradamus Villanueva Petitioner, vs. Priscilla R. DomingoDocument2 pagesCrim 2 #12 Nostradamus Villanueva Petitioner, vs. Priscilla R. DomingoAmy Lou CabayaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Petitioners Vs Vs Respondents The Solicitor General Castillo Laman Tan Pantaleon & San JoseDocument18 pagesPetitioners Vs Vs Respondents The Solicitor General Castillo Laman Tan Pantaleon & San JoseMalen MalaluanPas encore d'évaluation