Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study
Transféré par
Korina FranciscoDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Drug Study
Transféré par
Korina FranciscoDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
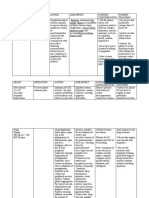
Drug name
Classification
Tramadol (TDL)
NSAIDS
Dose, Contraindications route and frequency Binds to mu50mg IV q Resp depression, opoid receptors. 8h especially in presence Inhibits reuptake of cyanosis and of serotonin and excessive bronchial norepinephrine secretion, and after op in the CNS. on biliary tract. Acute Therapeutic alcoholism, head effect: injuries, conditions in decreased pain which intracranial pressure is raised. Attack of bronchospasm. Heart failure secondary to chronic lung disease.
Mechanism of Action
Side effects
Nursing Responsibilities
Cefazolin (Stancef)
Antibiotics
Bind to bacterial cell wall membrane causing cell death. Therapeutic effect: bactericidal action against susceptible bacteria.
30 mg IV q 8h
History of shock by cefazolin.
Nausea, vomiting, fatigue, headache, constipation, drowsiness, confusion, skin reactions, dry mouth, facial flushing, sweating, vertigo, bradychardia, palpitation, orthostatic hypotension, hypothermia, restleness, changes in modod, miosis. Rarely, muscle weakness,appetite changes, difficulty in passing urine, biliary spasm Shock; hypersensitivity reactions; hematologic eg granulocytopenia, eosinophilia or thrombocytopenia; hepatic, renal impairment; GIT disease eg colitis; CNS signs including convulsions; alteration in bacterial flora; vit
1. assess type, location and intensity of pain before 2-3 hr after administration. 2. assess BP and RR. Respi depression has not occurred with recommended doses. 3. advise patient to change position slowly to minimize orthostatic hypotension. 4. do not confuse tramadol from toradol.
1. Give the medication around the clock at evenly spaced times and to finish the medication completely at directed, even if feeling better. 2. Check for signs of super infection (vaginal itching/ discharges) and allergy.
deficiencies & others eg headache, dizziness or malaise Ketorolac Tromethamine Brand Name: Toradol Anti Pyretic NSAIDS Antiinflammatory and analgesic activity; inhibits prostaglandins and leukotriene synthesis 30 mg IV q 8 Contraindicated with significant renal impairment, aspirin allergy, recent GI bleed or perforation Use cautiously with impaired hearing; allergies; hepatic conditions CNS: headache, dizziness, somnolence, insomnia, fatigue, dizziness tinnitus, ophthalmologic effects
1. Renal impairment, Impaired hearing, allergies, hepatic, 2. Skin color and lesions, orientation, reflexes, peripheral sensation, clotting times, CBC, adventitious sounds 3. Be aware that patient may be at risk for CV events, GI bleeding, renal toxicity, monitor accordingly 4. Keep emergency equipment readily available at time of initial dose, in case of severe hypersensitivity reaction 5. Protect drug vials from light. 6. Administer every 6 hrs to maintain serum levels and control pain.
Paracetamol
Anti pyretic
Decreases fever 300mg IV by inhibiting the q 4 PRN effects of t:37.8C pyrogens on the hypothalamic heat regulating center and by a hypothalamic action leading to sweating and vasodilation. Relieves pain by inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis at the CNS but does not have antiinflammatory action because of its minimal effect of peripheral prostaglandin synthesis.
Hypersensitivity: Intolerance to tartrazine (yellow dye #5) alcohol, table sugar, saccharin
Stimulation, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, hepatoxicity, hepatic seizure, renal failure, leucopenia, neutropenia, hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia, rash, urticaria, hypersensitivity, cyanosis, anemia, jaundice, pancytopenia, CNS stimulation, delirium, followed by vascular collapse, convulsion, coma, death
1. tell patient to read label on other OTC drugs. Advice patient to avoid taking more than one product containing paracetamol at one time; as this may cause toxicity if taken concurrently. 2. advise patient to avoid alcohol; acute poisoning with liver might occur 3. teach patients sign of chronic overdose; bleeding, bruising malaise, fever, sore throat.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Meloxicam drug study overviewDocument5 pagesMeloxicam drug study overviewABARAJPas encore d'évaluation
- TrazodoneDocument20 pagesTrazodoneAjay MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- ARCOXIADocument22 pagesARCOXIATeresa JunioPas encore d'évaluation
- HIV Case Study: Priority Nursing Diagnoses and CareDocument3 pagesHIV Case Study: Priority Nursing Diagnoses and CarechoobiPas encore d'évaluation
- Levemir Product Insert PDFDocument11 pagesLevemir Product Insert PDFDegee O. GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- DRUGSDocument5 pagesDRUGSDanica EspejoPas encore d'évaluation
- OMEPRAZOLEDocument2 pagesOMEPRAZOLEJenny Pearl PasalPas encore d'évaluation
- NURSING CARE PLAN ASSESSMENT FOR CONFUSED PATIENT ON HEMODIALYSISDocument3 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN ASSESSMENT FOR CONFUSED PATIENT ON HEMODIALYSISgagandipkS100% (1)
- Co DiovanDocument2 pagesCo DiovanianecunarPas encore d'évaluation
- HNBBDocument3 pagesHNBBManelle SingzonPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument20 pagesDrug StudydjanindPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study: Mechanis M OF ActionDocument9 pagesDrug Study: Mechanis M OF ActionLovely San SebastianPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Reasoning Questions - Lupus and Blood DonationDocument4 pagesClinical Reasoning Questions - Lupus and Blood DonationMohammad OmarPas encore d'évaluation
- ActemraDocument7 pagesActemraLinda KvastadPas encore d'évaluation
- Chromium Picolinate Drug StudyDocument1 pageChromium Picolinate Drug StudyjoellaPas encore d'évaluation
- AcknowledgementDocument9 pagesAcknowledgementjhzenPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP HemorrhoidsDocument2 pagesNCP Hemorrhoidsnurse_yramenaj0% (1)
- MotiliumDocument5 pagesMotiliumAkram KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- EndocrinedisorderDocument3 pagesEndocrinedisorderDyan LazoPas encore d'évaluation
- Myocardial Infarction Concept MapDocument7 pagesMyocardial Infarction Concept Mapkarelclarke629280% (5)
- Impaired Tissue Perfusion Related To The Weakening / Decreased Blood Flow To The Area of Gangrene Due To Obstruction of Blood VesselsDocument3 pagesImpaired Tissue Perfusion Related To The Weakening / Decreased Blood Flow To The Area of Gangrene Due To Obstruction of Blood VesselsKat AlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study EditedDocument5 pagesDrug Study EditedfabtaciousVeelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Side Effects:: AtropineDocument7 pagesSide Effects:: AtropinekletadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Brand NameDocument5 pagesBrand NameJunrey AbarcaPas encore d'évaluation
- DrugStudy - CamaristaColeenMaeC (BSN III-G) (Prednisone)Document2 pagesDrugStudy - CamaristaColeenMaeC (BSN III-G) (Prednisone)Coleen Mae CamaristaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pradaxa Patient Teaching for Atrial Fibrillation and Stroke RiskDocument2 pagesPradaxa Patient Teaching for Atrial Fibrillation and Stroke RiskBenPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study Domperidone CompressDocument1 pageDrug Study Domperidone CompressAngelica TolledoPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study Form TJDocument4 pagesDrug Study Form TJJasmin Santiago CarrilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Sa Sinus Tachycardia FinalDocument13 pagesNCP Sa Sinus Tachycardia FinalMYKRISTIE JHO MENDEZPas encore d'évaluation
- General ObjectivesDocument1 pageGeneral ObjectivesErwin DegraciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument40 pagesDrug StudyLyka Milo AvilaPas encore d'évaluation
- LortabDocument1 pageLortabSheri490Pas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJohn Ronald P. RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP For Impaired Oral Mucous MembraneDocument11 pagesNCP For Impaired Oral Mucous MembraneRYAN SAPLADPas encore d'évaluation
- EXPLANATION OF GOALS AND NURSING INTERVENTION RATIONALE FOR ACUTE PAIN RELATED TO INFLAMMATORY PROCESS SECONDARY TO GOUTY ARTHRITISDocument4 pagesEXPLANATION OF GOALS AND NURSING INTERVENTION RATIONALE FOR ACUTE PAIN RELATED TO INFLAMMATORY PROCESS SECONDARY TO GOUTY ARTHRITISimnasPas encore d'évaluation
- Myonal, Eperisone DrugDocument4 pagesMyonal, Eperisone DrugDhaneswara Adhyatama100% (1)
- Alendronate SodiumDocument3 pagesAlendronate SodiumGLen Caniedo100% (1)
- Cefoxitin and Ketorolac Edited!!Document3 pagesCefoxitin and Ketorolac Edited!!Bryan Cruz VisarraPas encore d'évaluation
- LevofloxacinDocument15 pagesLevofloxacinsonal aranhaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP PainDocument1 pageNCP PaindwightciderPas encore d'évaluation
- Cholecystitis NCPDocument6 pagesCholecystitis NCPDaud NasirPas encore d'évaluation
- Vit B1 ReportDocument19 pagesVit B1 ReportNatasha Faye UntalanPas encore d'évaluation
- Captopril Drug StudyDocument7 pagesCaptopril Drug StudyKimzie Joy Basco100% (1)
- Vitamin K (Phytomenadione) 2016: Indication Action Drug Type Trade Name Presentation Dosage / IntervalDocument3 pagesVitamin K (Phytomenadione) 2016: Indication Action Drug Type Trade Name Presentation Dosage / IntervalDeni Yuda Adi SaputraPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug MetronidazoleDocument1 pageDrug MetronidazoleSrkocherPas encore d'évaluation
- Hypertensive UrgencyDocument8 pagesHypertensive UrgencyTony A.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument1 pageDrug StudyMaui LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- Endocrine System DiabetesDocument1 pageEndocrine System Diabetessivakamasundari pichaipillaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyBien EstrellaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Total Hip ReplacementDocument11 pagesNCP Total Hip ReplacementDoneva Lyn MedinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) InhibitorsDocument4 pagesAngiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) InhibitorsPutri Mulia HasibuanPas encore d'évaluation
- SAS - Session-24-Research 1Document5 pagesSAS - Session-24-Research 1ella retizaPas encore d'évaluation
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideD'EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuidePas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing Considerations Ketorolac TromethamineDocument8 pagesDrug Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing Considerations Ketorolac TromethamineAiryn CanonPas encore d'évaluation
- Ketorolac (Drug Study)Document2 pagesKetorolac (Drug Study)Cassandra Grace Labial Paynter89% (18)
- Ketorolac Drug StudyDocument2 pagesKetorolac Drug StudyRic VelascoPas encore d'évaluation
- Abilify Drug Study: Therapeutic Effects, Indications, Contraindications and Adverse ReactionsDocument6 pagesAbilify Drug Study: Therapeutic Effects, Indications, Contraindications and Adverse ReactionsLuige AvilaPas encore d'évaluation
- COX-2 inhibitor relieves arthritis painDocument5 pagesCOX-2 inhibitor relieves arthritis painDiolan Novero BagorioPas encore d'évaluation
- HaldolDocument6 pagesHaldolJon ChuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study Poker Hands1Document28 pagesCase Study Poker Hands1api-238169773Pas encore d'évaluation
- DrugStudyFormatDocument2 pagesDrugStudyFormatSheryl Ann Barit PedinesPas encore d'évaluation
- Full Mouth Rehabilitation: A Smooth Pathway For Complex JourneyDocument8 pagesFull Mouth Rehabilitation: A Smooth Pathway For Complex JourneySkAliHassanPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Development and BEDocument19 pagesDrug Development and BEJoseph KamaleshPas encore d'évaluation
- LTCW Breast Write UpDocument21 pagesLTCW Breast Write Upapi-632682404Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chron's Disease 2Document3 pagesChron's Disease 2TarantadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Biperiden (Drug Study)Document3 pagesBiperiden (Drug Study)Mae Ann Bueno CastillonPas encore d'évaluation
- RN Fundamentals of Nursing PDFDocument325 pagesRN Fundamentals of Nursing PDFDonnabell DayudayPas encore d'évaluation
- A Systematic Review of The Effectiveness of Exercise, Manual Therapy, Electrotherapy, Relaxation Training, and Biofeedback in The Management of Temporomandibular DisorderDocument21 pagesA Systematic Review of The Effectiveness of Exercise, Manual Therapy, Electrotherapy, Relaxation Training, and Biofeedback in The Management of Temporomandibular DisorderJohnnatasMikaelLopesPas encore d'évaluation
- Adjuvant Analgesics (2015) PDFDocument177 pagesAdjuvant Analgesics (2015) PDFsatriomega100% (1)
- Case Study Class ActivityDocument3 pagesCase Study Class ActivityptanahinPas encore d'évaluation
- Melatonina e EndometrioseDocument8 pagesMelatonina e EndometrioseFatima VieiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Flopamfo 4490Document15 pagesFlopamfo 4490sabapahty chettiyarPas encore d'évaluation
- Threshold Reiki Reiki Ryoho HikkeiDocument27 pagesThreshold Reiki Reiki Ryoho HikkeiHarrison KoehliPas encore d'évaluation
- Bmet 262 Outline 2022 2023Document12 pagesBmet 262 Outline 2022 2023Emmanuel PrahPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan AutismDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Autismangeliejoy_110976% (29)
- Pope Keith Spiegel 2008Document16 pagesPope Keith Spiegel 2008Alina RotaruPas encore d'évaluation
- Unstable Angina Case ReportDocument24 pagesUnstable Angina Case ReportaybatariPas encore d'évaluation
- Asa Physical Status Classification System: By: Dr. Ali Anwar SutisnaDocument8 pagesAsa Physical Status Classification System: By: Dr. Ali Anwar Sutisnawan rennyPas encore d'évaluation
- Antidepressants For The Treatment of Depression in People With Cáncer 2018Document78 pagesAntidepressants For The Treatment of Depression in People With Cáncer 2018José Luis Rivera Z.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Psychotherapeutic Traditions HandoutDocument5 pagesPsychotherapeutic Traditions HandoutTina Malabanan CobarrubiasPas encore d'évaluation
- Background: Pediatric Chickenpox Next Section: PathophysiologyDocument12 pagesBackground: Pediatric Chickenpox Next Section: PathophysiologyRachel Johann Aquinto100% (1)
- Sepsis: Signs and SymptomsDocument5 pagesSepsis: Signs and SymptomssujithasPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Past Papers With Common MCQS: MedicineDocument17 pagesFinal Past Papers With Common MCQS: MedicineKasun PereraPas encore d'évaluation
- La Indications, Contraindications&Armamentarium - ppt2Document25 pagesLa Indications, Contraindications&Armamentarium - ppt2Nagendra Srinivas ChunduriPas encore d'évaluation
- Presented By: Bhawna Joshi Msc. Nursing 1 YearDocument52 pagesPresented By: Bhawna Joshi Msc. Nursing 1 YearBhawna JoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- HemorrhageDocument15 pagesHemorrhageMariegreat Piscos BisnarPas encore d'évaluation
- Ocluzia Dentara Ionita PetreDocument546 pagesOcluzia Dentara Ionita PetreTeodorPolitanschi100% (1)
- Emily Morgan - ResumeDocument2 pagesEmily Morgan - Resumeapi-283578734Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1000 Days Ni Baby PDFDocument31 pages1000 Days Ni Baby PDFppantollanaPas encore d'évaluation