Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 4: Basic CAD Drawing Techniques: Section 1: Setting Display Format and Precision (UNITS and DDUNITS)
Transféré par
MukeshwaranDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Unit 4: Basic CAD Drawing Techniques: Section 1: Setting Display Format and Precision (UNITS and DDUNITS)
Transféré par
MukeshwaranDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Unit 4: Basic CAD Drawing Techniques
Overview
Most architectural drawings use architectural units. You will rst learn how to set architectural units and precision of units commonly used in architectural CAD drawings. Then you will set up a template drawing. This template drawing will be used in later units to speed up and standardize the drawing process.
Objectives
Set the architectural display format and precision. Create template drawings for C and D size paper. Begin a new drawing by using the template drawing. Create geometry for a architectural drawing using the coordinate system of data entry.
Introduction
Most architectural drawings use the architectural type of scale displaying measurements in feet and inches, such as 16-2. Even though you will set your units to architectural, AutoCAD allows you to use any type of units in your drawing. If it is more convenient to enter information in decimal, for example, you can change your units at any time. Changing units or entering units in a different format will not affect any other objects in the drawing. A template drawing normally contains values for limits, grid, and snap. After setting the correct units, you will create a template drawing containing the values for limits, grid, and snap commonly used in a D size architectural drawing.
Section 1: Setting Display Format and Precision (UNITS and DDUNITS)
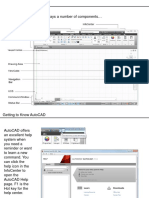
To set the units, access the Units Control dialog box. This can be accomplished by:: Choose the Format/Units pull-down menu. Enter ddunits at the Command: prompt.
Although AutoCAD has ve different measurement report formats, architectural units are generally used in architectural drafting, as recommended by the American Institute of Architects. AutoCAD can display a maximum of 1/256. Since decimal is the default type of unit in AutoCAD, you will have to change the units to architectural using the Units Control dialog box.
36
After setting the measurement report format to architectural units, the next step is to set the display precision. AutoCAD rounds the value of the display to the nearest fraction of an inch. For example, if you set the precision at 1/2 and your actual measurement was set to 3/8, the display will read 1/2. Regardless of what you set the display precision at, AutoCAD is accurate to 14 decimal places. For architectural drawings, 1/2, 1/4, 1/8, and 1/16 precision are normally used, depending on the type of drawing.
Angular Measurement
Angular measurement is also set in the Units Control dialog box. AutoCAD has ve different angular measurement options. Decimal degrees are generally used in architectural drafting, and so decimal degrees is the default type of angular measurement in AutoCAD. Decimal degrees displays angular measurement as real numbers with up to eight decimal places, such as 42.500. One-place decimal degrees are normally used for architectural drawings.
Tutorial 4.1: Setting Units and Angular Measurement
In this tutorial you will set the units and angular measurement for a architectural drawing. 1. From the Standard toolbar, select New. If prompted with the Save Changes dialog box, select No. In the Create New Drawing dialog box, enter the proper path, name the drawing DPROTO, then select OK. 2. Choose Format/Units. Set the units to Architectural, 01-0 1/2 for Precision. Set the angles to Decimal Degrees, Precision 0 (AutoCAD default). Your Units Control dialog box should look like gure 4.1. 3. Choose OK to close the Units Control dialog box. The next tutorial will continue from here. Figure 4.1 The units and angular measurement for an architectural drawing.
37
Section 2: Working with Template Drawings
A template drawing may be dened as any drawing le that you want to use as the basis for the new drawing you are creating. Proper use of a template drawing can save a lot of work. When you begin a new drawing you normally set different variables, such as the limits, snap increment, and grid spacing. The advantage of using a template drawing is that it frees you from having to change these settings every time you start a new drawing.
Tutorial 4.2: Creating an Architectural Template for a D Size Drawing
In this tutorial you will create an architectural template drawing. You will set the limits, grid, and snap to values commonly used in a D size drawing. When entering values, AutoCAD automatically assumes that you are entering a value in feet, unless you specify inches after the number. 1. Continue from the previous tutorial. Choose Format/Drawing Limits. 3. At the [ON/OFF]<0-0,0-0>: prompt, press Enter. 4. At the <1-0,0-9>: prompt, type 136,88 and press Enter. To show the entire limits within the view window, choose the ZOOM ALL option: 1. From the Standard toolbar, choose the Zoom All icon. After the limits are established, set the grid to 4 and the snap to 2. 2. Choose Tools/Drafting Setting to access the Drafting Settings dialog box. Enter 4 for the grid X and Y spacing. Enter 2 for the snap X and Y spacing. 3. Check the Snap On and Grid On check boxes. Your dialog box should appear as shown in gure 4.2. 4. The DPROTO template le is now ready to be saved. To save the drawing, click the SAVE icon on the Standard toolbar. In the Save as Type box make sure you change the le extension to DWT and make sure you are in the correct subdirectory.
38
Figure 4.2 Setting the grid to 4 and the snap to 2 for an architectural drawing.
Section 3: Coordinate System Basics
Even though you may have set grid and snap modes in your template drawing, any coordinate entered through the keyboard overrides these settings. This is true even if the desired point location does not fall on the grid or cannot be snapped to, or if the To point: location is at an angle to the previous location with Polar Tracking turned on. Remember you can switch the coordinate entry method at any time during a command sequence. The rst coordinate may be absolute, followed by a relative move and an absolute polar coordinate, and then you use the pointing device. You can also change the type of units at any time during the drawing. For example, even though your units are set to architectural, you can enter values in decimal format if it is more convenient. Changing the coordinate entry method will not affect any other objects previously created in your drawing.
39
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Basic Autocad Start UpDocument22 pagesBasic Autocad Start UpuntoniPas encore d'évaluation
- Cadcam Lab ManualDocument48 pagesCadcam Lab ManualashutoshfandePas encore d'évaluation
- Auto Cad For Electrical Eng StudentDocument59 pagesAuto Cad For Electrical Eng StudentSabikan Sulaiman100% (4)
- A Training Manual ON AutocadDocument85 pagesA Training Manual ON AutocadAdeniran JoshuaPas encore d'évaluation
- AutoCAD 2010 Drawing SetupDocument17 pagesAutoCAD 2010 Drawing SetuppoetmbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning Objectives: After Completing This Chapter, You Will Be Able ToDocument38 pagesLearning Objectives: After Completing This Chapter, You Will Be Able ToJonas hernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Autocad 5Document7 pagesAutocad 5seventhhemanthPas encore d'évaluation
- Drawing Setup LTDocument17 pagesDrawing Setup LTMary MarasiganPas encore d'évaluation
- Eagle Point Manual (2012 - 10 - 17 08 - 24 - 43 UTC)Document64 pagesEagle Point Manual (2012 - 10 - 17 08 - 24 - 43 UTC)saddshish94% (18)
- 2.drawing Setup LTDocument17 pages2.drawing Setup LTmariasuperqPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 2: Drawing Setup in Autocad 2011Document17 pagesTutorial 2: Drawing Setup in Autocad 2011Roi JacquesPas encore d'évaluation
- TutorialcadDocument15 pagesTutorialcadraoram769959Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Report 01Document10 pagesLab Report 01Muhammad TalhaPas encore d'évaluation
- AutoCAD Lab ManualDocument37 pagesAutoCAD Lab ManualTommyVercettiPas encore d'évaluation
- Autocadd Notes - WordfileDocument7 pagesAutocadd Notes - WordfileroopathakurPas encore d'évaluation
- LESSON 1 Introduction To The AUTOCAD User InterfaceDocument7 pagesLESSON 1 Introduction To The AUTOCAD User InterfaceNeriz Deomampo100% (1)
- AutoCad Manual - Layout, Paper Space and Model SpaceDocument4 pagesAutoCad Manual - Layout, Paper Space and Model SpaceLarry9302Pas encore d'évaluation
- AutoCad Tutorial LayoutsDocument6 pagesAutoCad Tutorial LayoutsLarry9302Pas encore d'évaluation
- GUIDE TO AUTOCAD BASICS: Basics, Viewing, Geometry, and PrecisionDocument16 pagesGUIDE TO AUTOCAD BASICS: Basics, Viewing, Geometry, and Precisionjomarie apolinarioPas encore d'évaluation
- Auto CadDocument50 pagesAuto CadGanesh DongrePas encore d'évaluation
- The Hitchhiker AutocadDocument87 pagesThe Hitchhiker Autocadnur hasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 3 - Creating Engineering Drawings in I-DeASDocument8 pagesLesson 3 - Creating Engineering Drawings in I-DeASpapipapiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ect 111 Autocad ModulDocument70 pagesEct 111 Autocad ModulRegarz Arrow100% (1)
- Introduction To Autocad: Auto CadDocument44 pagesIntroduction To Autocad: Auto CadSHANKY CHADDAPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Computer Aided DesignDocument45 pagesIntroduction To Computer Aided DesignMizs Cla Abdul RaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Cad Cam Lab Manual FinalDocument54 pagesCad Cam Lab Manual FinalRadha KrishnaPas encore d'évaluation
- AutoCAD BeginnersDocument26 pagesAutoCAD Beginnerssquirticus100% (2)
- The Hitchhiker Guide To Autocad BassicsDocument57 pagesThe Hitchhiker Guide To Autocad Bassicsgordolobo67Pas encore d'évaluation
- Auto CADDocument6 pagesAuto CADsurvesangPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Notes - Session 1Document14 pagesBasic Notes - Session 1AmalBazilah Isa100% (1)
- AutoCAD Tutorial 2D & 3DDocument63 pagesAutoCAD Tutorial 2D & 3DRon Harold IglePas encore d'évaluation
- AutoCAD BasicsDocument66 pagesAutoCAD BasicsketipakketipungPas encore d'évaluation
- BSC Information TechnologyDocument9 pagesBSC Information TechnologyLukasi DeonePas encore d'évaluation
- Revit Archi 2012Document33 pagesRevit Archi 2012Khin Chan MyaePas encore d'évaluation
- GUIDE TO AUTOCAD BASICS: Layouts, Notes and Labels, Dimensions, PrintingDocument12 pagesGUIDE TO AUTOCAD BASICS: Layouts, Notes and Labels, Dimensions, Printingjomarie apolinarioPas encore d'évaluation
- Dimensions Lesson - 1 - PDFDocument19 pagesDimensions Lesson - 1 - PDFRadovanPas encore d'évaluation
- Rajkiya Engineering College, Mainpuri: Presentation On AutocadDocument32 pagesRajkiya Engineering College, Mainpuri: Presentation On AutocadKshitij MallPas encore d'évaluation
- Basics Study For AUTOCADDocument6 pagesBasics Study For AUTOCADJoy BersabePas encore d'évaluation
- Guide To AutoCAD BasicsDocument72 pagesGuide To AutoCAD BasicsTemitope OsadarePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter - 1: AutocadDocument30 pagesChapter - 1: AutocadRaghava VPas encore d'évaluation
- CAD Module-4Document30 pagesCAD Module-4Mark JosephPas encore d'évaluation
- Map Tools-A Transformative ExperienceDocument8 pagesMap Tools-A Transformative ExperienceTshepiso NthitePas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 4 Extrusions: ObjectivesDocument28 pagesLesson 4 Extrusions: ObjectivesGuru PrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- MAE 477/577 - Spring 2016 CAD Applications: CategoryDocument22 pagesMAE 477/577 - Spring 2016 CAD Applications: CategoryZurina MAPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Aided Design: What Is CAD?Document19 pagesComputer Aided Design: What Is CAD?Auto VeteranPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Aided Design: What Is CAD?Document19 pagesComputer Aided Design: What Is CAD?Auto VeteranPas encore d'évaluation
- Internship Report ON Autocad' Submitted To I.T.S Engineering College, Greater NoidaDocument32 pagesInternship Report ON Autocad' Submitted To I.T.S Engineering College, Greater Noidanitendra kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- AutoCAD Tutorials Level 2Document26 pagesAutoCAD Tutorials Level 2Hadeel FayezPas encore d'évaluation
- Autocad Summer Training ReportDocument52 pagesAutocad Summer Training ReportPawan mehta58% (74)
- SolidWorks 2016 Learn by doing 2016 - Part 3D'EverandSolidWorks 2016 Learn by doing 2016 - Part 3Évaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (3)
- SolidWorks 2015 Learn by doing-Part 3 (DimXpert and Rendering)D'EverandSolidWorks 2015 Learn by doing-Part 3 (DimXpert and Rendering)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (5)
- Solidworks 2018 Learn by Doing - Part 3: DimXpert and RenderingD'EverandSolidworks 2018 Learn by Doing - Part 3: DimXpert and RenderingPas encore d'évaluation
- ITE Election Eport: Solar Resource Mapping in The MaldivesDocument36 pagesITE Election Eport: Solar Resource Mapping in The MaldivesMukeshwaranPas encore d'évaluation
- GRIHA Rating ProcessDocument3 pagesGRIHA Rating ProcessMukeshwaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Effect of Sludge Cell Disruption On Compactibility of Biological SludgesDocument8 pagesEffect of Sludge Cell Disruption On Compactibility of Biological SludgesMukeshwaranPas encore d'évaluation
- IITM Summer Fellowship Programme 2010Document4 pagesIITM Summer Fellowship Programme 2010MukeshwaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Regional Office Bangladesh, India, Nepal, Sri Lanka: Degree: Work Experience: Age LimitDocument4 pagesRegional Office Bangladesh, India, Nepal, Sri Lanka: Degree: Work Experience: Age LimitMukeshwaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Indian Institute of Chemical Biology: Summer Training 2010Document4 pagesIndian Institute of Chemical Biology: Summer Training 2010MukeshwaranPas encore d'évaluation
- M. Arch Digital ArchitectureDocument12 pagesM. Arch Digital ArchitectureMukesh WaranPas encore d'évaluation
- 12V140 Seris Engine Shop ManualDocument471 pages12V140 Seris Engine Shop ManualRaed Mahyoub100% (4)
- Consumer Behaviour ProjectDocument43 pagesConsumer Behaviour ProjectMuhammad UsmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Microwave Project ReportDocument30 pagesMicrowave Project ReportMd RakibPas encore d'évaluation
- Lifestyle Mentor. Sally & SusieDocument2 pagesLifestyle Mentor. Sally & SusieLIYAN SHENPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment #3 Venturi Meter: Home Unquantized ProjectsDocument7 pagesExperiment #3 Venturi Meter: Home Unquantized ProjectsEddy KimathiPas encore d'évaluation
- GS Ep Tec 260 enDocument61 pagesGS Ep Tec 260 enCesarPas encore d'évaluation
- KaranDocument4 pagesKarancristioronaldo90Pas encore d'évaluation
- Data Structures and Algorithms AssignmentDocument25 pagesData Structures and Algorithms Assignmentعلی احمد100% (1)
- Vernacular in Andhra PradeshDocument1 pageVernacular in Andhra PradeshNandyala Rajarajeswari DeviPas encore d'évaluation
- L5CoachMentorReflectiveLog TemplateDocument9 pagesL5CoachMentorReflectiveLog TemplateHadusssPas encore d'évaluation
- CV LeTranNguyen enDocument4 pagesCV LeTranNguyen enLe Tran NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- FMDS0102Document69 pagesFMDS0102hhPas encore d'évaluation
- May 2021 Examination Diet School of Mathematics & Statistics ID5059Document6 pagesMay 2021 Examination Diet School of Mathematics & Statistics ID5059Tev WallacePas encore d'évaluation
- Case Analysis, Case 1Document2 pagesCase Analysis, Case 1Aakarsha MaharjanPas encore d'évaluation
- Investigation: Present By:Shivam Ranabhat Project Title: Esport Players Recruit SystemDocument18 pagesInvestigation: Present By:Shivam Ranabhat Project Title: Esport Players Recruit Systemjames chhetriPas encore d'évaluation
- MoveInSync Native Android Mobile AppDocument12 pagesMoveInSync Native Android Mobile AppRismaPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis and Design of Cantilever Slab Analysis and Design of Cantilever SlabDocument3 pagesAnalysis and Design of Cantilever Slab Analysis and Design of Cantilever SlabMesfinPas encore d'évaluation
- Waste Heat BoilerDocument7 pagesWaste Heat Boilerabdul karimPas encore d'évaluation
- Product-Oriented Learning Competencies: (Beginner)Document4 pagesProduct-Oriented Learning Competencies: (Beginner)Kri S ELPas encore d'évaluation
- Normal DistributionDocument23 pagesNormal Distributionlemuel sardualPas encore d'évaluation
- Symptoms and DiseasesDocument8 pagesSymptoms and Diseaseschristy maePas encore d'évaluation
- Piramal Revanta - Tower 3Document13 pagesPiramal Revanta - Tower 3bennymahaloPas encore d'évaluation
- Vishay Load Cell Calibration System - ENDocument3 pagesVishay Load Cell Calibration System - ENSarhan NazarovPas encore d'évaluation
- DOPE Personality TestDocument8 pagesDOPE Personality TestMohammed Hisham100% (1)
- Neal Peres Da CostaDocument507 pagesNeal Peres Da CostaNoMoPoMo576100% (1)
- Metascope An/Pas-6 (5855-790-6197) : Technical ManualDocument38 pagesMetascope An/Pas-6 (5855-790-6197) : Technical ManualDens VillaPas encore d'évaluation
- JMPGuitars 18 Watt Tremolo TMB Reverb LayoutDocument1 pageJMPGuitars 18 Watt Tremolo TMB Reverb LayoutRenan Franzon GoettenPas encore d'évaluation
- Gravitational Fields 1Document18 pagesGravitational Fields 1Smart linkPas encore d'évaluation
- Guide For H Nmr-60 MHZ Anasazi Analysis: Preparation of SampleDocument7 pagesGuide For H Nmr-60 MHZ Anasazi Analysis: Preparation of Sampleconker4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tridium Europe DatasheetDocument2 pagesTridium Europe DatasheetHoàngTrầnPas encore d'évaluation