Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Category: Physics Formulas
Transféré par
Kalpana ShankarDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Category: Physics Formulas
Transféré par
Kalpana ShankarDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Category
HOME | MD/MS | MDS | MCA | AIEEE | MBA | BANK PO | SSCE | NDA |
Advertise on PLANET E TUTORS
hysics All India Engineering Entrance Exams AIEEE FORMULAS
hemistry
Maths
Sponsored Institu
nglish
Math formulas for Class XI, Class XII and under graduates. Chemistry formulas for Class XI, Class XII and under graduates. Physics formulas for Class XI, Class XII and under graduates.
eneral Knowledge
ample Papers
ourse and Fees
pplication Form
PHYSICS FORMULAS
est Series Login ligibility
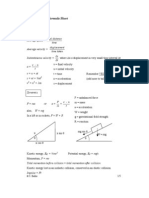
Density is mass per unit volume Density = mass / volume Force = rate of change of momentum Power is rate of work done Power = work / time Unit of power is watt Potential energy (P) PE = m.g.h m = mass g = acceleration due to gravity (9.81m/s2) h = height Acceleration due to gravity at a depth 'd' from earth surface is : velocity = displacement / time Momentum = mass . velocity Kinetic energy (P) P = (1/2).m.v2 m = mass v = velocity
eed Back
EMO TEST
r Channel Links
cussion Forum A Friend e Newsletter nts & Updates m Alerts mit Articles b Services s eer cles /Classified
st Series Demo S /MS BS
d gd = g(1R )
EEE O CE A A
Gravity (Force due to gravity) Fg : Force of attraction G : Gravitational constant M1 : Mass of first object M2 : Mass of second object
G M1 M2 Fg = r2
Escape velocity Escape velocity from a body of mass M and radius r is
Acceleration due to gravity at height 'h' from earth surface is : h is very much smaller than R
2h gh = g(1R )
For example if you want to calculate the escape verlocity of sa object from earth then, M is dmass of earth r is radius of earth
OPTICS Index of refraction n = c/v n - index of refraction c - velocity of light in a vacuum v - velocity of light in the given material
Under constant acceleration linear motion v = final velocity u = intitial velocity a = acceleration t = time taken to reach velocity v from u s = displacement v = u + a t s = ut + (1/2)a t 2 s = vt - (1/2)a t 2
v2 = u2 + 2 a s Friction force (kinetic friction) When the object is moving then Friction is defined as : Ff = Fn where Ff = Friction force, = cofficient of friction Fn = Normal force Linear Momentum Momentum = mass x velocity
Simple Capillary action motion The height to which the liquid can be lifted is given Simple by: motion by: d2x/dt2 2cos
harmonic harmonic is defined = - k x
h= gr
: liquid-air surface tension(T)(T=energy/area) : contact angle : density of liquid g: acceleration due to gravity r: is radius of tube Time period of pendulum Waves
1 f= T 2 = T
v = f . where
= Angular frequency, T=Time period, v = Speed of wave, =wavelength
Doppler effect Relationship between observed frequency f and emitted frequency f0:
Resonance of a strin g
nv v f = f0( v + vs
where, v=velocity of wave vs=velocity of source. It is positive if source of wave is moving away from observer. It is negative if source of wave is moving towards observer. Resonance of a open tube of air( appr oxim ate) where, L: length of the string n = 1, 2, 3...
frequency = f = ) 2L
Resonance of a open tube of air(accurate)
nv frequency = f = 2(L+0.8D)
nv Approximate frequency = f = 2L
where, L: length of the cylinder n = 1, 2, 3... v = speed of sound
where, L: length of the cylinder n: 1, 2, 3... v: speed of sound d:diameter of the resonance tube Resonance of a closed tube of air(accurate)
frequency = f =
nv
Resonance of a closed tube of air(approximate)
4(L+0.8D)
nv Approximate frequency = f = 4L
where, L: length of the cylinder n = 1, 2, 3... v = speed of sound where, L: length of the cylinder n: 1, 2, 3... v: speed of sound d:diameter of the resonance tube Bragg's law n = 2d sin where n = integer (based upon order) = wavelength d = distance between the planes = angle between the surface and the ray
int ens Sound Power ity intensity of sound = of area sou nd
I intensity of sound in decibel= 10log10 I0
I dB = 10log10 I0
where I=intensity of interest in Wm-2 I0=intensity of interest in 10-12Wm-2 Relation between energy and frequency
de Broglie equation
h = p
h mv
E = h where E = Energy h = Planck's constant = frequency
where p = momentum = wavelength h = Planck's constant v = velocity Davisson and Germer experiment Centripetal Force (F)
h F=
m v2 = m 2 r r
where e = charge of electron m = mass of electron V = potential difference between the plates thru which the electron pass = wavelength Circular motion formula v = r Torque (it measures how the force acting on the object can rotate the object) Torque is cross product of radius and Force Torque = (Force) X (Moment arm) X sin T = F L sin whete = angle between force and moment arm Stefan-Boltzmann Law The energy radiated by a blackbody
v2 Centripetal acceleration (a) = r
Forces of gravitation F = G (m1.m2)/r2 where G is constant. G = 6.67E - 11 N m2 / kg2
radiator per second = P P = AT4 where, = StefanBoltzmann constant = 5.6703 108 watt/m2K4 Efficiency of Carnot cycle Ideal gas law P V = n R T P = Pressure (Pa i.e. Pascal) V = Volume (m3) n = number of of gas (in moles) R = gas constant ( 8.314472 .m3.Pa.K1 mol-1] ) T = Temperatue ( in Kelvin [K]) Charles law (for ideal gas)
= 1-
Tc Th
Boyles law (for ideal gas) P1 V1 = P2V2 T (temperature is constant)
V1 V2 = T1 T2
P (pressure is constant) Translational kinetic energy K per gas molecule (average molecular kinetic energy:) Internal energy of monoatomic gas
3 3 K= kT 2
n = number of of gas (in moles) R = gas constant ( 8.314472 .m3.Pa.K1 mol-1] )
K= nRT 2
k = 1.38066 x 10-23 J/K Boltzmanns constant
Root mean square speed of gas
Ratio of specific heat ()
3kT V
2 rms
Cp = Cv
= m
k = 1.38066 x 10-23 J/K Boltzmanns constant m = mass of gas
Cp = specific heat capacity of the gas in a constant pressure process Cv = specific heat capacity of the gas in a constant volume process
Internal entergy of ideal gas In Adiabatic process no heat is Internal entergy of ideal gas gained or lost by the system. (U) = cv nRT Under adiabetic condition PV = Constant TV-1 = Constant where is ratio of specific heat.
Cp = Cv
Boltzmann constant (k) Speed of the sound in gas
R k= Na
R = gas constant(8.314 J/mol K) T = the absolute temperature M = the molecular weight of the gas (kg/mol)
R = gas constant Na = Avogadro's number.
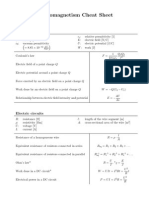
= adiabatic constant = cp/cv Capillary action Resistance of a wire The height to which the liquid can be lifted is given L by R= h=height of the liquid A lifted T=surface tension r=radius of capillary tube
2T h= rg
= rsistivity L = length of the wire A = cross-sectional area of the wire
Ohm's law V = I . R V = voltage applied R = Resistance I = current
Resistor combination If resistors are in series then equivalent resistance will be Electric power (P) = (voltage Req = R1 + R2 + R3 + applied) x (current) . . . . . . + Rn If resistors are in P = V . I = I2 . R parallel then V = voltage applied equivalent R = Resistance resistance will be I = current 1/Req = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3 + . . . . . . + 1/Rn In AC circuit average power is : Pavg = VrmsIrms cos where, Pavg = Average Power Vrms = rms value of voltage Irms = rms value of current In AC circuit Instantaneous power is : PInstantaneous = VmIm sint sin(t) where, PInstantaneous = Instantaneous Power Vm = Instantaneous voltage Im = Instantaneous current Total capacitance (Ceq) for PARALLEL Capacitor
Capacitors Q = C.V where
Q = charge on the capacitor C = capacitance of the capacitor V = voltage applied to the capacitor
Combinations: Ceq = C1 + C2 + C3 + . . . . . . + Cn Total capacitance (Ceq) for SERIES Capacitor Combinations: 1/Ceq = 1/C1 + 1/C2 + 1/C3 + . . . . . . + 1/Cn Cylindrical Capacitor
Parallel Plate Capacitor
A C = 0 d
where C = [Farad (F)] = dielectric constant A = Area of plate d = distance between the plate 0 = permittivity of free space (8.85 X 10-12C2/N m2)
L C = 2 0 ln (b/a)
where C = [Farad (F)] = dielectric constant L = length of cylinder [m] a = outer radius of conductor [m] b = inner radius of conductor [m] 0 = permittivity of free space (8.85 X 10-12 C2/N m2)
Spherical Capacitor
Magnetic force acting on a charge q moving with ab velocity v C = 4 0 F = q v B sin where b-a F = force acting on charge q (Newton) where q = charge (C) C = [Farad (F)] v = velocity = dielectric constant (m/sec2) a = outer radius of conductor B = magnetic field [m] = angle between V b = inner radius of conductor (velocity) and B [m] (magnetic field) 0 = permittivity of free space (8.85 X 10-12C2/N m2)
Force on a wire in magnetic field (B) F = B I l sin
where F = force acting on wire (Newton) I = Current (Ampere) l = length of wire (m) B = magnetic field = angle between I (current) and B (magnetic field)
In an RL circuit (Resistorinductor ), the time constant (in seconds) is: = L/R R = Resistance in C = Inductance in henries
In an RC circuit (ResistorCapacitor), the time constant (in seconds) is: = RC R = Resistance in C = Capacitance in in farads.
Self inductance of a solenoid = L = n2LA n = number of turns per unit length L = length of the solenoid.
Mutual inductance of two Energy stored in solenoid two long thin capacitor solenoids, one wound on top of the other 1 M = 0N1N2LA E= CV2 N1 = total number of turns per unit length for first 2 solenoid N2 = number of turns per unit length for second solenoid A = cross-sectional area L = length of the solenoid. Coulomb's Law Like charges repel, unlike charges attract. F = k (q1 . q2)/r2 where k is constant. k = 1/(4 0) 9 x 109N.m2/C2 q1 = charge on one body q2 = charge on the other body r = distance between them
Calculator based upon Coulomb's Law
Ohm's law V = IR where V = voltage I = current R = Resistence
Electric Field around a point charge (q) E = k ( q/r2 ) where k is constant. k = 1/(4 0) 9 x 109N.m2/C2 q = point charge r = distance from point charge (q)
Electric field due to thin infinite sheet
E= 2 0
where E = Electric field (N/C) = charge per unit area C/m2 0 = 8.85 X 1012 C2/N m2
Electric field due to thick infinite sheet
E= 0
Magnetic Field around a wire (B) when r is greater than the radius of the wire.
0 I B= 2r
where E = Electric field (N/C) = charge per unit area C/m2 0 = 8.85 X 10-12 C2/N m2
where I = current r = distance from wire and r Radius of the wire Magnetic Field At the center of an arc
Magnetic Field around a wire (B) when r is less than the radius of the wire.
0 I r B= 2 R2 B=
0 I 4r
where I = current R = radius of wire
where I = current r = radius from the
r = distance from wire and r Radius of the wire (R) Bohr's model
center of the wire
nh L= 2
Emitting Photons(Rydberg Formula)
1 Ephoton = E0( -
1 )
n12 n22
where L = angular momentum n = principal quantum number = 1,2,3,...n h = Planck's constant. Half life of radioactive element
where n1 < n2 E0 = 13.6 eV Average life of radioactive element
ln(2) t1/2 =
Syllabus Concepts & Formula Sheet Tips and Tricks
Solved Papers Model Paper Question Bank
Archives Tips to Attempt AIEEE Books For AIEEE About AIEEE Exam
CBSE Class XI Maths Sample paper Class XI Physics Sample paper Class XI Chemistry Sample paper Class XII Maths Sample paper Class XII Physics Sample paper Class XII Chemistry Sample paper
Business Associate | Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy | Contact Us | FAQ | About Us Copyright 2012 . All Rights Reserved
Category hysics
HOME | MD/MS | MDS | MCA | AIEEE | MBA | BANK PO | SSCE | NDA |
Advertise on PLANET E TUTORS
hemistry
Maths
All India Engineering Entrance Exams AIEEE FORMULAS
nglish
Math formulas for Class XI, Class XII and under graduates. Chemistry formulas for Class XI, Class XII and under graduates. Physics formulas forClass XI, Class XII and under graduates.
eneral Knowledge
ample Papers
ourse and Fees
pplication Form
MATHS FORMULAS
est Series Login
In an x-y Cartesian coordinate system, equation of the circle is: (x-a)2 + (y-b)2 = r2 cos 0 = 1 sin 30 = 1/2 tan 30 = 1/(3) cos 45 = 1/(2) sin 60 = (3)/2 tan 60 = 3 cos 90 = 0 sin = 1/cosec tan = 1/cot sin2 + cos2 = 1 1 + cot2 = cosec2 sin 0 = 0
ligibility
eed Back
EMO TEST
Our Channel Links
tan 0 = 0 cos 30 = (3)/2 sin 45 = 1/(2) tan 45 = 1 cos 60 = 1/2 sin 90 = 1 tan 90 = cos = 1/sec sin/cos = tan 1 + tan2 = sec2 sin( 90 - ) = cos
cussion Forum A Friend e Newsletter nts & Updates m Alerts mit Articles b Services s eer cles /Classified
st Series Demo S /MS BS
EE O CE A A
cos( 90 - ) = sin sin( 90 + ) = cos tan( 90 + ) = - cot cos( 180 - ) = - cos sin( 180 + ) = - sin tan( 180 + ) = tan
tan( 90 - ) = cot cos( 90 + ) = - sin sin( 180 - ) = sin tan( 180 - ) = tan cos( 180 + ) = cos Pythagorean Theorem: The square of the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of the legs a 2 = b2 + c 2 a,b - two sides of the triangle connected by the right angle c - hypotenuse of the triangle Area of Triangle Area of Triangle = (1/2) . b . h where, h = height of triangle b = the length of the base of triangle Area of circle Area of circle = . r 2 where, = PI = 22/7 r = radius of circle Area of Ellipse Area of Ellipse = . r 1 . r2 where, r1 = major radius r2 = minor radius Area of Cone (surface area) Area of Cone (surface area) = . r . l where, r = radius of cone l = length of side of the cone
circumference of a circle circumference of a circle = 2 . . r where, = PI = 22/7 r = radius of circle Area of rectangle Area of rectangle = l . b where, l = length of rectangle b = width of rectangle Area of trapezoid Area of trapezoid = (1/2) . (height). (base one + base two)
Area of Cylinder (surface area) Area of Cylinder (surface area) = 2 . . r . h where, r = radius of cylinder h = length of cylinder
Volume of cylinder Volume of cylinder = . r 2 . h where, = PI = 22/7 r = radius of cylinder h = length of cylinder Volume of Cone Volume of Cone = (1/3) . . r 2 . h where, = PI = 22/7 r = radius of Cone h = height of cone cosec(-x) = -cosec(x) sec(-x) = sec(x) cot(-x) = -cot(x) sin( - ) = sin cos cos sin cos( - ) = cos cos + sin sin
Volume of sphere Volume of sphere = (4/3) . . r 3 where, = PI = 22/7 r = radius of sphere sin(-x) = -sin(x)
cos(-x) = cos(x) tan(-x) = -tan(x) sin( + ) = sin cos + cos sin cos( + ) = cos cos - sin sin
(tan + tan) tan( + ) = (1 - tan tan) sin2 = 2 sin cos
(tan - tan) tan( - ) = (1 + tan tan) cos2 = cos2 - sin2 = 2cos2 - 1 = 1 - 2sin2 tan2 = (1 - tan2) sin3 = 3sin - 4sin3 For any triangle ABC with side lengths a,b,c Law of Cosines c2 = a2 + b2 - 2 a b cos C b2 = c2 + a2 - 2 c a cos B a2 = b2 + c2 - 2 b c cos A Law of Sines sinA/a = sinB/b = sinC/c cos3 = 4cos3 - 3cos
(2 tan)
cos( - ) + cos( + ) cos cos = 2
cos( - ) - cos( + ) sin sin = 2 sin cos =
sin( + ) + sin( - )
3sin - sin 3 sin = 4
3
3cos + cos 3 cos = 4
3
3sin 2 - sin 6 sin . cos = 32
3 3
3 - 4 cos 2 + cos 4 sin = 8
4
3 + 4 cos 2 + cos 4 cos = 8
4
3 - 4 cos 4 + cos 8 sin . cos = 128
4 4
10 sin - 5 sin 3 + sin 5 sin = 16
5
10 cos + 5 cos 3 + cos 5 cos = 16
5
Quadratic Equation For the equation: 10 sin 2 - 5 sin 6 + sin 10 a x 2 + b x + c = 0 sin5 . cos5 = 512 the value of x will be - b (b2 - 4 a c) x= 2a (a + b)2 = a2 + 2 a b + b2 (a - b)2 = a2 - 2 a b + b2
(a + b) . (a - b) = (a2 - b2)
Arithmetic progression: Arithmetic progression is a sequence of numbers such that the difference of any two successive members of the sequence is a constant. For example: Suppose a1, a2, a3, a4, ...... , an-1, an are in sequence of arithmetic progression Then the first term of an arithmetic series is a1 and assume that the common difference of successive members is d, then the nth term of the sequence is: an = a1 + (n - 1).d The sum of all the components of an arithmetic series is: S n = a1 + a 2 + a3 + ....... + an-1 + an i.e. Sn = (n).(a1 + an)/2 Logarithms: logb 1 = 0 logb b = 1 logb(X . Y) = logbX + logbY logb(X / Y) = logbX logbY logb(Xn) = n . logbX logmn . lognm = 1
Geometric progression: geometric progression OR geometric series is a sequence of numbers such that the quotient of any two successive members of the sequence is a constant. The ratio of two successive number is called common ratio. The constant ratio must not be equal to 0. Example of geometric series : ar1, ar2, ar3, . ....... ., arn-1, arn The nth term of the geometric series can be defined as: an = a r(n - 1) r is called common ratio and n must be greater than 0:
dC =0 dx
d(Cu)
du =C
dx
dx
d(u + v) du dv = dx + dx dx
d(u . v) =u dx
dv +v dx
du
dx
d u
v (du/dx) - u (dv/dx)
d ( u )= n u
n n-1
du
( )= dx v v2
dx
dx
d ( x )= n x dx
n n-1
d ( C )= C ln(C) dx
u u
du
dx
d ( e )= e dx
u u
du
d( ln(u)) 1du =
dx
dx
udx
d( sin(u)) = cos(u) dx
du
d( cos(u)) = - sin(u)
du
dx
dx
dx
d( tan(u)) = sec2(u) dx
du
d( cosec(u)) = - cosec(u) . cot(u)
du
dx
dx
dx
d( sec(u)) = sec(u) . tan(u) dx
du
d( cot(u)) = - cosec2(u)
du
dx
dx
dx
d(sin-1u) = dx
du
d(cos-1u) =
-1
du
dx
dx
dx
d(tan-1u) = dx
1 du
d(cot-1u) =
- 1 du
1 + u2dx
dx
1 + u2dx
d(sec-1u) = dx |u|
du
d(cosec-1u) =
-1
du
dx
dx
|u|
dx
Syllabus Concepts & Formula Sheet Tips and Tricks
Solved Papers Model Paper Question Bank
Archives Tips to Attempt AIEEE Books For AIEEE About AIEEE Exam
CBSE Class XI Maths Sample paper Class XI Physics Sample paper Class XI Chemistry Sample paper Class XII Maths Sample paper Class XII Physics Sample paper Class XII Chemistry Sample paper
Business Associate | Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy | Contact Us | FAQ | About Us Copyright 2012 . All Rights Reserved
Category hysics
HOME | MD/MS | MDS | MCA | AIEEE | MBA | BANK PO | SSCE | NDA |
Advertise on PLANET E TUTORS
hemistry
Maths
All India Engineering Entrance Exams AIEEE FORMULAS
nglish
Math formulas for Class XI, Class XII and under graduates. Chemistry formulas for Class XI, Class XII and under graduates. Physics formulas for Class XI, Class XII and under graduates.
eneral Knowledge
ample Papers
ourse and Fees
pplication Form
est Series Login
Chemistry formulas
Ideal Gas law PV = nRT n = number of moles R = universal gas constant = 8.3145 J/mol K Boyle's law P1V1 = P2V2 Combined Gas law
ligibility P1V1 = T1 T2
Charles law
eed Back
EMO TEST
Our Channel Links
P2V2
cussion Forum A Friend e Newsletter nts & Updates m Alerts mit Articles b Services s eer cles /Classified
V1 = T1
Gay-Lussac law
V2 T2
P1 = T1
P2 T2
Diffusion: Rate at which two gases mix Graham's law of diffusion The rate of diffusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of their density or the molar mass of the gas.
st Series Demo S /MS BS
EE O CE A A
Effusion: Rate at which a gas escapes thru pin hole Graham's law of effusion The rate of effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of either the density or the molar mass of the gas.
Solution: Solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances. Solute is a substance that is dissolved in the solution. Solvent is the substance that dissolves the solute. Solvent is present in greater amount.
Concentration is the ratio of solute and solvent. Concentration can be measured using molarity, molality and mole fraction.
Unit of Molarity (M) : mol/L : moles per litre Unit of Molality (M) : mol/kg : moles per kg
moles of solute Molarity (M) = liters of solution
moles of solute Molality (m) = kg of solution
Mole fraction: Mole fraction of a component in solution is the number of moles of that component divided by the total number of moles of all components in the solution.
molesa Mole-fraction (Xa)= molesa + molesb ....
Dilution: Siluting a solution means adding more solvent in solution without the addition of more solute. MiVi = MfVf Mi: Molarity of solution before diluting. Vi: Volume of solution before diluting. Mf: Molarity of solution after diluting. Vf: Volume of solution after
diluting.
Mole: Mole is the amount of substance that contains same number of particles as there are atoms in Carbon-12. One mole of substance is Avogadro's number (i.e. 6.023 x 1023). Relation between moles and grams 1 mole = molecular weight of substance in grams.
One mole of gas has volume of 22.4 liter at STP.
Ionization Enthalpy: It is the energy needed to remove an electron from an atom or molecule (i.e from low state to n=). It is always endothermic (i.e. positive). OR Ionization energy: energy needed to remove an electron from an atom
Henderson-Hasselbalch teacherone.com equation :
[A-]
pH = pKa + log10 [HA]
where [A-]: Concentration of conjugate base [HA]: concentration of the acid OR
[Conjugate Base] pH = pKa + log10 [Acid]
Syllabus Concepts & Formula Sheet
Solved Papers Model Paper
Tips and Tricks
Question Bank
Archives Tips to Attempt AIEEE Books For AIEEE About AIEEE Exam
CBSE Class XI Maths Sample paper Class XI Physics Sample paper Class XI Chemistry Sample paper Class XII Maths Sample paper Class XII Physics Sample paper Class XII Chemistry Sample paper
Business Associate | Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy | Contact Us | FAQ | About Us Copyright 2012 . All Rights Reserved
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Physics Formulas: G G (1-d) RDocument6 pagesPhysics Formulas: G G (1-d) Ronewing949Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Class 9 FormulasDocument13 pagesPhysics Class 9 FormulasJatin Gupta73% (63)
- Physics Class 9 FormulasDocument13 pagesPhysics Class 9 FormulasEKLABAY SONIPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Formulas: G G (1-d) RDocument6 pagesPhysics Formulas: G G (1-d) RAitazaz AhsanPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Formulas & SI UnitDocument14 pagesPhysics Formulas & SI Unitönemsiz biriPas encore d'évaluation
- O' Level Physics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesO' Level Physics Formula SheetYee Kai TanPas encore d'évaluation
- Higher Physics Formula Sheet: S. BakkeDocument5 pagesHigher Physics Formula Sheet: S. BakkeAbid RedwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics EquationsDocument5 pagesPhysics EquationsMichael CollinsPas encore d'évaluation
- Formula SheetDocument3 pagesFormula SheetMax MartinPas encore d'évaluation
- Compendium Book For IIT - MainsDocument28 pagesCompendium Book For IIT - MainsApex InstitutePas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Formula SheetDocument10 pagesEngineering Formula SheetAdarsh Kumar AngPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Unit One Formulas and MotionDocument32 pagesPhysics Unit One Formulas and MotionAHKEEL LESTER JONESPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics A and B Formula SheetDocument14 pagesPhysics A and B Formula SheetEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- CLASSICAL MECHANICS AND ELECTROMAGNETISMDocument13 pagesCLASSICAL MECHANICS AND ELECTROMAGNETISMmhasan13Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electromag Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesElectromag Cheat SheetAlex Muresan0% (1)
- Things To Know For The Physics GRE: Daniel Beller October 28, 2009Document20 pagesThings To Know For The Physics GRE: Daniel Beller October 28, 2009Arif SolmazPas encore d'évaluation
- Formula Sheet For PhysicsDocument6 pagesFormula Sheet For PhysicsAsim ButtPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanics Mekaniks: English Swedish Symbol Units Units-Name ValueDocument10 pagesMechanics Mekaniks: English Swedish Symbol Units Units-Name ValueEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- MPP 2Document3 pagesMPP 2Lian ChiPas encore d'évaluation
- The Following List of Data, Formulae and Relationships Will Be Provided in The Question Papers For Candidates' ReferenceDocument3 pagesThe Following List of Data, Formulae and Relationships Will Be Provided in The Question Papers For Candidates' ReferenceLian ChiPas encore d'évaluation
- POE Formula Sheet Rev 3-24-12Document6 pagesPOE Formula Sheet Rev 3-24-12poignantPas encore d'évaluation
- PhysicsDocument6 pagesPhysicsharryp3542Pas encore d'évaluation
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsD'EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsPas encore d'évaluation
- PhysicsDocument4 pagesPhysicsbells tharayilPas encore d'évaluation
- Radio and Light Radiations From A Moving Charged Particle Are Different 2016Document12 pagesRadio and Light Radiations From A Moving Charged Particle Are Different 20161357531Pas encore d'évaluation
- Formula Sheet: Electricity and MagnetismDocument3 pagesFormula Sheet: Electricity and MagnetismThivagar RajasekaranPas encore d'évaluation
- HKDSE Physics Formulae List (English Version)Document5 pagesHKDSE Physics Formulae List (English Version)flowerinsnowPas encore d'évaluation
- Wegner F., Classical Electrodynamics (Lecture Notes, Heidelberg SDocument137 pagesWegner F., Classical Electrodynamics (Lecture Notes, Heidelberg SAyman ElAshmawyPas encore d'évaluation
- Pocket PhysicsDocument10 pagesPocket PhysicsFaraz KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- RES9 Phys Flash CardsDocument5 pagesRES9 Phys Flash CardsnoobharvestorPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Physics: U NKTDocument6 pagesThermal Physics: U NKTzzyingPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 A.C. E.E Prof Dr MoenesDocument47 pagesChapter 4 A.C. E.E Prof Dr Moenesmahmoudaliabdelaziz11Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Final Notes on Travelling Waves, Superposition, Optics, Electricity and MagnetismDocument7 pagesPhysics Final Notes on Travelling Waves, Superposition, Optics, Electricity and MagnetismMichael BlairPas encore d'évaluation
- KVL Oscillations and WavesDocument21 pagesKVL Oscillations and WavesAkshay SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- PC1144 Summary (Chapter 37-39)Document1 pagePC1144 Summary (Chapter 37-39)Khor Shi-JiePas encore d'évaluation
- (S A) (S B) (S C) (S D)Document36 pages(S A) (S B) (S C) (S D)Lea BeberinoPas encore d'évaluation
- AP Physics B Equation Reference SheetDocument7 pagesAP Physics B Equation Reference SheetKevin JiempreechaPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Formula Sheet-By Er Rammohan MudgalDocument8 pagesPhysics Formula Sheet-By Er Rammohan MudgalRammohan Mudgal0% (1)
- Important Equation in Physics2Document5 pagesImportant Equation in Physics2Ghazi DallyPas encore d'évaluation
- (Continued) : The Laws of Electromagnetism Maxwell's Equations Displacement CurrentDocument21 pages(Continued) : The Laws of Electromagnetism Maxwell's Equations Displacement CurrentJai ChangPas encore d'évaluation
- Wave Optics Part IDocument62 pagesWave Optics Part IAt TanwiPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper 4 Tips A LevelsDocument7 pagesPaper 4 Tips A LevelsKumail MustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- HFE0611 BennettDocument4 pagesHFE0611 Bennettarunkr1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cat 1 - Answer Key - Engineering Physics - Set 2Document11 pagesCat 1 - Answer Key - Engineering Physics - Set 220 A Arshath AhamedPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Noise BackgroundDocument8 pagesThermal Noise BackgroundngvanduysnPas encore d'évaluation
- O-Level Formula List - OriginalDocument4 pagesO-Level Formula List - Originalbloober blooberPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics HandbookDocument10 pagesPhysics HandbookNational Physical Laboratory100% (1)
- Resistors in Series:: Resistor CombinationsDocument7 pagesResistors in Series:: Resistor CombinationsKeith E SproatPas encore d'évaluation
- CAP EXAMDocument4 pagesCAP EXAMmooseyannihilatorPas encore d'évaluation
- Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesCheat SheetPeter KoszoPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics 1 Honors Formula SheetDocument11 pagesPhysics 1 Honors Formula SheetCody JohnsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics PhlashcardsDocument8 pagesPhysics PhlashcardsAsha ElsberryPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1D'EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Advances in Structure Research by Diffraction Methods: Fortschritte der Strukturforschung mit BeugungsmethodenD'EverandAdvances in Structure Research by Diffraction Methods: Fortschritte der Strukturforschung mit BeugungsmethodenR. BrillPas encore d'évaluation
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterD'EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterPas encore d'évaluation
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsD'EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3D'EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3Évaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (2)
- The Basics of Hacking and Pen TestingDocument30 pagesThe Basics of Hacking and Pen TestingAnonPas encore d'évaluation
- A Method For Identifying Human Factors Concerns During The HAZOP Process - Dennis AttwoodDocument5 pagesA Method For Identifying Human Factors Concerns During The HAZOP Process - Dennis AttwoodAlvaro Andres Blanco GomezPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 4 Petrophysics - Part 4Document32 pagesTopic 4 Petrophysics - Part 4Aneesch PreethaPas encore d'évaluation
- Es E100091 Pi PDFDocument1 pageEs E100091 Pi PDFCarlos Humbeto Portillo MendezPas encore d'évaluation
- Finger Relaxation Technique Reduces Post-Appendectomy PainDocument13 pagesFinger Relaxation Technique Reduces Post-Appendectomy PainIan ClaxPas encore d'évaluation
- 3D Holographic Projection Technology SeminarDocument28 pages3D Holographic Projection Technology Seminarniteshnks1993Pas encore d'évaluation
- © Call Centre Helper: 171 Factorial #VALUE! This Will Cause Errors in Your CalculationsDocument19 pages© Call Centre Helper: 171 Factorial #VALUE! This Will Cause Errors in Your CalculationswircexdjPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Prepare Squash Specimen Samples For Microscopic ObservationDocument3 pagesHow To Prepare Squash Specimen Samples For Microscopic ObservationSAMMYPas encore d'évaluation
- TheMindReader TeaserA WhatDocument7 pagesTheMindReader TeaserA WhatnakulshenoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Antiepilepticdg09gdg 121231093314 Phpapp01Document145 pagesAntiepilepticdg09gdg 121231093314 Phpapp01Vaidya NurPas encore d'évaluation
- Bluehill BrochureDocument24 pagesBluehill BrochureGeorge SingerPas encore d'évaluation
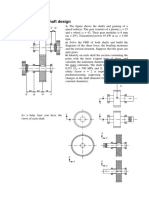
- Shaft design exercisesDocument8 pagesShaft design exercisesIvanRosellAgustíPas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet 9-2 - Math 7Document2 pagesWorksheet 9-2 - Math 7bfbrfvlfrerPas encore d'évaluation
- MC145031 Encoder Manchester PDFDocument10 pagesMC145031 Encoder Manchester PDFson_gotenPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 - Basic Logical Concepts - For Students PDFDocument65 pagesChapter 3 - Basic Logical Concepts - For Students PDFTiên Nguyễn100% (1)
- Charny - Mathematical Models of Bioheat TransferDocument137 pagesCharny - Mathematical Models of Bioheat TransferMadalena PanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ice Cream: Uses and Method of ManufactureDocument6 pagesIce Cream: Uses and Method of ManufactureMari LizPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity Design ScoutingDocument10 pagesActivity Design ScoutingHoneyjo Nette100% (9)
- STAR Worksheet Interviewing SkillsDocument1 pageSTAR Worksheet Interviewing SkillsCharity WacekePas encore d'évaluation
- Capitalism Communism Socialism DebateDocument28 pagesCapitalism Communism Socialism DebateMr. Graham Long100% (1)
- LMA Guide to London Market ProcessingDocument65 pagesLMA Guide to London Market ProcessingNanthawat Babybeb100% (1)
- Stereotype Threat Widens Achievement GapDocument2 pagesStereotype Threat Widens Achievement GapJoePas encore d'évaluation
- Neptune Sign House AspectDocument80 pagesNeptune Sign House Aspectmesagirl94% (53)
- Evidence My Favorite PlayerDocument2 pagesEvidence My Favorite PlayerReynel Soir0% (1)
- 1-7 Least-Square RegressionDocument23 pages1-7 Least-Square RegressionRawash Omar100% (1)
- Literary Text Analysis WorksheetDocument1 pageLiterary Text Analysis Worksheetapi-403444340Pas encore d'évaluation
- Finance Process Optimization - Mapping The Journey To High PerformanceDocument3 pagesFinance Process Optimization - Mapping The Journey To High PerformanceStephen G. LynchPas encore d'évaluation
- Growing Up Psychic by Chip Coffey - ExcerptDocument48 pagesGrowing Up Psychic by Chip Coffey - ExcerptCrown Publishing Group100% (1)
- MBA Study On Organisational Culture and Its Impact On Employees Behaviour - 237652089Document64 pagesMBA Study On Organisational Culture and Its Impact On Employees Behaviour - 237652089sunitha kada55% (20)
- D5435 PDFDocument6 pagesD5435 PDFZamir Danilo Morera ForeroPas encore d'évaluation