Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
RPT MT THN4
Transféré par
hafidie83Description originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
RPT MT THN4
Transféré par
hafidie83Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
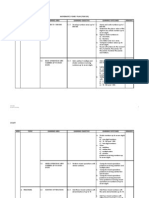
YEAR 4 FIRST SEMESTER
WEEK
TOPIC 1. WHOLE NUMBER S
LEARNING AREA 1. NUMBERS TO 100 000
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Pupils will be tought to : 1. Develop number sense up to100 000
LEARNING OUTCOMES Pupils will be able to : i. Name and write numbers up to 100 000 ii. Determine the place value of the digits in any whole number up to 100 000 iii. Compare value of numbers to 100 000 iv. Round of numbers to the nearest ten, hundred and thousand. i. Add any two to four numbers to 100 000 ii. Solve addition problems. i. Subtract one or two numbers from a bigger number less than 100 000
1 2/14/1/13
1. WHOLE NUMBER S 2 7/111/1/13 1. WHOLE NUMBER S
2. ADDITION WITH THE HIGHEST TOTAL OF 100 000 3. SUBTRACTION WITHIN THE RANGE OF 100 000 4.MULTIPLICATION WITH THE HIGHEST PRODUCT OF 100 000
1. Add numbers to the total of 100 000
1. Subtract numbers from a number less than 100 000
ii. Solve subtraction problems 1. Multiply any two number with the highest product of 100 000 i. Multiply four-digit numbers with a) one-digit numbers, b) 10, c) two-digit numbers.
1. WHOLE NUMBER S
ii. Multiply three-digit numbers with a) 100, b) two-digit numbers, iii. Multiply two-digit number with 1000 iv. Solve multiplication problems.
1. WHOLE 3 NUMBE 14/1RS 18/1/13
5. DIVISION WITH THE HIGHEST DIVIDEND OF 100 000
1. Divide a number less than 100 000 by a two-digit Number
i.
Divide five-digit numbers by a) one-digit numbers, b) 10, 100 and 1000, c) two-digit numbers.
ii. Divide four-digit numbers by a) one-digit numbers, b) 10, 100 and 1000, c) two-digit numbers. iii. Solve division problems. 1. WHOLE 4 NUMBER 21/1S 25/1/13 24/1Maulid -ur Rasul 6. MIXED OPERATION 1. Perform mixed operation involving addition and subtraction. i. Perform mixed operations involving addition and subtraction with numbers less than a) 100, b) 1000, c) 10 000.
ii. Solve mixed operation problems.
WEEK 4 21/125/1/13
TOPIC 2. FRACTION
LEARNING AREA 1. PROPER FRACTION
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Pupils will be tought to : 1. Name and write proper fractions with denominators up to 10
LEARNING OUTCOMES Pupils will be able to : i. Name and write proper fractions with denominators up to 10. ii. Compare the value of two proper fractions with a) The same denominators, b) The numerator of 1 and different Denominators up to 10.
2. FRACTION
2. EQUIVALENT FRACTIONS
1. Express equivalent fractions for proper fractions.
i. Express and write equivalent fractions for proper fractions. ii. Express equivalent fractions to its simplest form. iii. Recognise fractions as equal shares of a whole set with denominator up to 10.
5 29/11/2/13 28/1-Cuti Ganti Hari Thaipusam
2. FRACTION
3. ADDITION OF PROPER FRACTIONS
1. Add two proper fractions with denominators up to 10
i.
Add two proper fractions with the same denominator up to 10 to its simplest form a) With 1 as the numerator for both fractions, b) With different numerators.
ii. Add two proper fractions with different denominators up to 10 to its simplest form a) With 1 as the numerator for both fractions, c) With different numerators. iii. Solve problems involving addition of proper fractions.
6 4/2-8/2/13
2. FRACTION
4. SUBTRACTION OF PROPER FRACTIONS
1. Subtract proper fractions with denominators up to 10
i. Subtract two proper fractions with the same denominator up to 10 to its simplest form d) With 1 as the numerator for both fractions, e) With different numerators. ii. Subtract two proper fractions with different denominators up to 10 to its simplest form a) With 1 as the numerator for both fractions, c) With different numerators. iii. Solve problems involving subtraction of proper fractions.
WEEK 7 13/215/2/13 11/212/2/13Cuti Tahun Baru Cina
TOPIC 3. DECIMALS
LEARNING AREA 1. INTRODUCTION TO DECIMAL NUMBER
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Pupils will be tought to : 1. Understand and use the vocabulary related to decimals i.
LEARNING OUTCOMES Pupils will be able to : Name and write decimals with a) one decimal place b) two decimal place Recognise the place value of a) tenths, b) hundredths, c) tenths and hundredths.
ii.
iii. Convert fraction to decimals of a) tenths, b) hundredths, c) tenths and hundredths and vice versa
8 19/221/2/13
UPTP1/UP1
9 25/21/3/13
3. DECIMALS
2. ADDITION OF DECIMAL NUMBER
1. Add decimals up to two decimal place.
i.
Add any two to four decimals of one decimal place involving a) decimals only, b) whole number and decimals, c) mixed decimals.
ii. Add any two to four decimals of two decimal place involving a) decimals only, b) whole number and decimals, a) mixed decimals. ii. Solve problems involving addition of decimal number
10 4/38/3/13
3. DECIMALS
3. SUBTRACTION OF DECIMAL NUMBER
1. Subtract decimals up to two decimal place.
i.
Subtract one to two decimals from a decimal of one decimal place involving a) decimals only, b) mixed decimals, c) whole numbers and decimals (mixed decimals) ii. Subtract one to two decimals of one or two decimal place iii. Solve problems involving subtraction of decimals
WEEK 11 11/315/3/13
TOPIC 3. DECIMALS
LEARNING AREA 4.MULTIPLICATION OF DECIMAL NUMBER
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Pupils will be tought to : 1. Multiply decimals up to two decimal places with a whole number i.
LEARNING OUTCOMES Pupils will be able to : Multiply any decimal of one decimal place with a) a one-digit number b) 10, 100 and 1000
ii. Multiply any decimal of two decimal place with a) a one-digit number b) 10, 100 and 1000 iii. Solve problems involving multiplication of decimals 12 18/322/3/13 3. DECIMALS 5. DIVISION OF DECIMAL NUMBER 1. Divide decimals up to two decimal places by a whole number. i. Divide decimals of one decimal place by a) a one-digit whole number, b) 10.
ii. Divide decimals of two decimal place by one-digit whole number. iii. Divide decimals by a whole number with the dividend value of up to two decimal place. iv. Solve problems involving division of decimals 13 25/329/3/13 14 1/45/4/13 4. MONEY CUTI SEKOLAH PERTENGAHAN PENGGAL 1
5. MONEY TO RM 10 000
1. Understand and use the vocabulary related to money 2. Use and apply knowledge of money in real life.
i.
Read and write the value of money up to RM 10 000.
4. MONEY
i.
Add money up to RM 10 000
ii. Subtract money from up to RM 10 000 iii. Multiply money to the highest product of RM 10 000 iv. Divide money with dividend not more than RM 10 000
15 8/412/4/13
4. MONEY
5. MONEY TO RM 10 000
2. Use and apply knowledge of money in real life.
v. Perform mixed operation involving addition and subtraction involving money up to RM 10 000 vi. Round of money to the nearest ringgit. vii. Solve problems involving money of up to RM 10 000
WEEK 16 15/419/4/13 16/4-17/4Sukantara
TOPIC 5. TIME
LEARNING AREA 1. READING AND WRITING TIME
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Pupils will be tought to : 1. Understand, read and write time in hours and minutes.
LEARNING OUTCOMES Pupils will be able to : i. Read time in hours and minutes according to the 12-hour system. ii. Write time in hours and minutes according to the 12-hours system.
5. TIME
2. TIME SCHEDULE 2. TIME SCHEDULE
1. Construct a simple schedule. 2. Read a calendar
i. Construct, read and extract information from a simple schedule. i. Extract information from a calendar ii. Solve simple real life problems involving reading the calendar.
5. TIME
17 22/426/4/13
5. TIME
3. RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN UNITSOF TIME
3. Understand the relationship between units of time
i. State the relationship between units of time:a) 1 day = 24 hours, b) 1 year= 365/366 days, c) 1 decade= 10 years. ii. Convert:a) years to days, and vice versa b) decade to years, and vice versa c) Years to months, and vice versa d) Hours to days, and vice versa. iii. Convert time from:a) hours to minutes, and vice versa b) hours and minutes to minutes and vice versa, c) minutes to hours and minutes, and vice versa
18 30/43/5/13
5. TIME
4. BASIC OPERATIONS INVOLVING TIME
1. Add, subtract, multiply and divide units of time.
i.
29/4-Cuti Peristiwa Hari Sukan
Add time involving conversion of units with answers in compound units of:a) hours and minutes, b) years and months, c) decades and years. ii. of Subtract time involving conversion units with answers in compound units of:a) hours and minutes, b) years and months, c) decades and years.
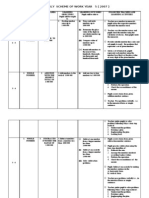
YEAR 4 SECOND SEMESTER
WEEK 19 6/510/5/13 TOPIC 5. TIME LEARNING AREA 4. BASIC OPERATIONS INVOLVING TIME LEARNING OBJECTIVES Pupils will be thought to : 1. Add, subtract, multiply and divide units of time LEARNING OUTCOMES Pupils will be able to : iii. Multiply time involving conversion of units with answers in compound units of:a) hours and minutes, b) years and months, c) decades and years. iv. Divide time involving conversion of units with answers in compound units of:a) hours and minutes, b) years and months, c) decades and years. v. Solve problems involving basic operations of time :a) hours and minutes, b) years and months, c) decades and years. Read and state the start and the end of an event from a schedule,
20 13/517/5/13 17/5Sambutan Hari Guru P.Sek 21 20/524/5/13 22&23 24 10/614/6/13
5. TIME
5. TIME DURATION
1. Use and apply knowledge of time to find the duration
i.
ii. Calculate the duration of an event from a schedule in a) minutes, b) hours, c) hours and minutes within a day and two consecutive live days.
UPTP2/PKSR1 CUTI PENGGAL 1 5. TIME 5. TIME DURATION 1. Use and apply knowledge of time to find the duration iii. Calculate the start or the end of an event from a given duration of time and read the start or end of an event.
25 17/621/6/13
6. LENGTH
1. MEASURING LENGTH
1. Measure lengths using standard units.
i. ii.
Read measurement of length using units of milimetre.
Write measurement of length to the nearest scales of length division for :a) centimetre, b) metre. iii. Measure and record lengths of object using units of:a) milimetre, b) centimeter and milimetre, c) metre and centimeter. iv. Estimate the lengths of objects in :a) milimetre, b) metre and milimetre, centimeter and milimetre.
WEEK 26 24/626/6/13 27/628/6/13Raptai HAC & HAC
TOPIC 6. LENGTH
LEARNING AREA 2.RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN UNITS OF LENGTH
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Pupils will be thought to : 1. Understand the relationship between units of length. i. ii.
LEARNING OUTCOMES Pupils will be able to : State the relationship between centimeter and milimetre. Convert units of length from; a) milimetres to centimeters and vice versa, b) compound units to a unit.
iii. Solve problems involving conversion of units of length.
27 1/75/7/13 1/7/13Cuti peristiwa HAC
6. LENGTH
3. BASIC OPERATIONS INVOLVING LENGTH
1. Add and subtract length.
i. Add units of length, involving conversion of units in; a) milimetre, b) metre and centimetre, c) centimeter and milimetre. ii. Subtract units of length, involving conversion of units in; a) milimetre, b) metre and centimetre, c) centimeter and milimetre. d) i. Multiply units of length, involving conversion of units by; a) one-digit number, b) 10, 100 and 1000 ii. Divide units of length, involving conversion of units by; a) one-digit number, b) 10, 100 and 1000 iii. Solve problems involving basic operation on length. i. ii. and grams. iii. Estimate the masses of objects using kilograms and grams. Measure of masses using in units of kilogram and gram Read measurement of masses to the nearest scales division of kilograms
28 8/712/7/13
6. LENGTH
3. BASIC OPERATIONS INVOLVING LENGTH
2. Multiply and divide length.
29 15/719/7/13
7. MASS
1 . MEASURING MASS
1. Measure mass using standard units.
WEEK
TOPIC 7. MASS
LEARNING AREA 2. RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN UNITS OF MASS 3. BASIC OPERATIONS INVOLVING MASS
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Pupils will be tought to : 1. Understand the relationship between units of mass. i.
LEARNING OUTCOMES Pupils will be able to : Convert units of mass from a) Kilograms to grams, b) Kilograms and grams to grams, c) Kilograms and grams to kilograms
30 22/7-26/7/13
7. MASS
1. Add and subtract involving units of mass
i. Add mass involving units of mass in; a) kilograms, b) grams, c) kilograms and grams. ii. Subtract mass involving units of mass in; a) kilograms, b) grams, c) kilograms and grams.
10
31 29/7-2/8/13
7. MASS
3. BASIC OPERATIONS INVOLVING MASS
2. Multiply and divide units of mass.
i. of
Multiply mass involving conversion units, with a) one-digit number, b) 10, 100 and 1000.
ii.
Divide mass involving conversion of units; a) one-digit number, b) 10, 100 and 1000
iii. Solve problems involving basic operation with mass. 32 5/8-6/8/13 7/8-9/8/13Cuti Pertengahan Penggal 2 8. VOLUME OF LIQUID 1. MEASURING VOLUME OF LIQUID 1. Measure and compare volume of liquid using standard units. i. Read measurement of volume of liquid in litres and mililitres. ii. Write measurement of volume of liquid to the nearest scales of tenth division for a) litre, b) mililitre. iii. Measure and record the volume of liquid in litres and mililitres. iv. Estimate the volume of liquid in litres and mililitres. 33 CUTI PERTENGAHAN PENGGAL 2
WEEK 34 19/823/8/13
TOPIC 8. VOLUME OF LIQUID
LEARNING AREA 2. RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN UNITS OF VOLUME OF LIQUID
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Pupils will be tought to : 1. Understand the relationship between units of volume of liquid. i.
LEARNING OUTCOMES Pupils will be able to : Convert unit of volume from a) litres to mililitres, b) mililitres to litres, c) litres and mililitres to litres, d) litres and mililitres to mililitres.
11
35 26/830/8/13
8. VOLUME OF LIQUID
3. BASIC OPERATIONS INVOLVING VOLUME OF LIQUID
1. Add and subtract involving units of volume
i. Add volume of liquid involving conversion of units in; a) litre, b) mililitre, c) litre and mililitre ii. Subtract volume of liquid involving conversion of units in; a) litre, b) mililitre, c) litre and mililitre. Subtract volume of liquid involving conversion of units by; a) one-digit number b) 10, 100 and 1000.
36 2/96/9/13
8. VOLUME OF LIQUID
3. BASIC OPERATIONS INVOLVING VOLUME OF LIQUID 3. BASIC OPERATIONS INVOLVING VOLUME OF LIQUID
2. Multiply and divide involving units of volume
i.
37 9/913/9/13
8. VOLUME OF LIQUID
2. Multiply and divide involving units of volume
ii.
Divide volume of liquid involving conversion of units by; a) one-digit number b) 10, 100 and 1000. iii. Solve problems involving volume of liquids. i. Identify the sides of a; a) square, b) rectangle, c) triangle. Measure and record the perimeter of a) square, b) rectangle, c) triangle. d)
38 16/920/9/13 16/9Cuti Hari Malaysia
9. SHAPE ANDSPAC E
1. TWO DIMENSIONAL SHAPES
1. Understand the figure related to perimeter
ii. a
39 23/927/9/13
9. SHAPE AND SPACE
1. TWO DIMENSIONAL SHAPES
2. Understand the figure related to area.
i.
Identify the dimensions of a a) square, b) rectangle. Compare squares with a unit square; a) rectangle, b) Square.
ii.
12
WEEK 40 30/94/10/13
TOPIC 9. SHAPE AND SPACE
LEARNING AREA 1. TWO DIMENSIONAL SHAPES
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Pupils will be tought to : 3. Record and calculate the area and perimeter 2-D shapes. i. of ii.
LEARNING OUTCOMES Pupils will be able to : Measure and record the dimensions squares and rectangles. Calculate the area of squares and rectangles.
iii. Solve problems involving perimeter and area of 2-D shapes. 41 7/1011/10/13 9. SHAPE AND SPACE 2. THREE DIMENSIONAL SHAPES 1. Understand the volume of cubes and cuboids. i. ii. of Identify the dimensions of cubes and cuboids. Measure and record the dimensions
cubes and cuboids. iii. Compare with a cube unit; a) cuboid, b) cube. 9. SHAPE AND SPACE 2. THREE DIMENSIONAL SHAPES 2. Find the volume for cubes and cuboids. i. Calculate the volume of cubes and cuboids. ii. Solve problems involving volume of cubes and cuboids.
42 43 21/1025/10/13 10. DATA HANDLIN G 1. PICTOGRAPH
PKSR 2 1. Recognise and draw pictograph i. Recognise a pictograph that represents; a) one unit; b) more than one unit. ii. Draw pictograph. iii. Represent data by a pictograph.
44 28/1031/10/13
1. BAR GRAPHS
1. Recognise, read and draw bar graphs.
i.
Recognise:a) horizontal bar graphs, b) vertical bar graphs.
ii.
Express the difference between a horizontal and a vertical bar graphs based on the axis. iii. Tabulate data from data sources. iv. Build:a) horizontal bar graphs, b) vertical bar graphs. v. Interpret data from the bar graphs.
13
14
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Mathematics: Analysis and Approaches Higher Level Paper 3: Instructions To CandidatesDocument3 pagesMathematics: Analysis and Approaches Higher Level Paper 3: Instructions To CandidatesMADANPas encore d'évaluation
- Civil Service Riviewer 2019 PDFDocument160 pagesCivil Service Riviewer 2019 PDFJanelito OlorPas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Plan Math Year 5 2013Document11 pagesYearly Plan Math Year 5 2013rdmasrinPas encore d'évaluation
- RPT & Plan-J Math Year 4Document27 pagesRPT & Plan-J Math Year 4Syafiah EppiePas encore d'évaluation
- Topic Learning Area Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes: Yearly Plan Mathematics Year 5Document19 pagesTopic Learning Area Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes: Yearly Plan Mathematics Year 5ranj19869Pas encore d'évaluation
- RPT & Plan-J Math Year 5 2012Document26 pagesRPT & Plan-J Math Year 5 2012sapuanazianPas encore d'évaluation
- RPT & Plan-J Math Year 5 2010Document20 pagesRPT & Plan-J Math Year 5 2010Zoe KooPas encore d'évaluation
- RPT Mathematics Year 4Document9 pagesRPT Mathematics Year 4YoNz AliaTiPas encore d'évaluation
- RPT: Mathematics Year 5Document20 pagesRPT: Mathematics Year 5man_zero1984Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rancangan Tahunan Matematik Tahun 5 - 2012Document8 pagesRancangan Tahunan Matematik Tahun 5 - 2012mrdan100% (1)
- Yearly Plan MathsDocument8 pagesYearly Plan MathsTasaratha Rajan AnamalaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Rpt&Plan-j Math Year 4Document27 pagesRpt&Plan-j Math Year 4Kee SekKhaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Plan Mathematic Year 6Document8 pagesYearly Plan Mathematic Year 6Rosni OthmanPas encore d'évaluation
- RPT MT THN4Document17 pagesRPT MT THN4Yakin DayyanPas encore d'évaluation
- RPT MT THN4Document14 pagesRPT MT THN4Malcom X MalcomPas encore d'évaluation
- Week Topic / Learning Area Learning Objective / Learning Outcomes Suggested Activities 1 Whole NumbersDocument11 pagesWeek Topic / Learning Area Learning Objective / Learning Outcomes Suggested Activities 1 Whole NumbersGane GanesanPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics Year 3 2012Document12 pagesMathematics Year 3 2012Izyan IsmailPas encore d'évaluation
- RPT Math Tahun 4 2013Document11 pagesRPT Math Tahun 4 2013Preloved BoutiqeuPas encore d'évaluation
- RPT MT THN4Document14 pagesRPT MT THN4Sk Saujana Impian DuaPas encore d'évaluation
- RPT MT THN4Document14 pagesRPT MT THN4startecerPas encore d'évaluation
- Rancangan Tahunan Matematik Tahun 5 2013Document8 pagesRancangan Tahunan Matematik Tahun 5 2013Nurulnaim OmarPas encore d'évaluation
- Rancangan Tahunan Matematik Tahun 6 - 2012Document6 pagesRancangan Tahunan Matematik Tahun 6 - 2012mrdanPas encore d'évaluation
- Rancangan Tahunan Math Tahun 5 2012 MS Excell Shared by AzyDocument13 pagesRancangan Tahunan Math Tahun 5 2012 MS Excell Shared by AzyTravis MonroePas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics Yearly Plan (Year 6) Sk. Kem Terendak 1 Encik Ramli Bin BabaDocument4 pagesMathematics Yearly Plan (Year 6) Sk. Kem Terendak 1 Encik Ramli Bin BabaFaridah Binti KamaludinPas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Plan Year 3Document8 pagesYearly Plan Year 3Shima OmarPas encore d'évaluation
- MT Yearly Plan Year 1 6Document6 pagesMT Yearly Plan Year 1 6abusufian80Pas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Scheme of Work Year 4: Norahazleenda Hairuman SK Trolak SelatanDocument16 pagesYearly Scheme of Work Year 4: Norahazleenda Hairuman SK Trolak SelatanSalwa HanimPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics Yearly Plan (Year 5) 2010: WE EK Topic / Learning Areas Learning Objectives / Learning Outcome RemarksDocument10 pagesMathematics Yearly Plan (Year 5) 2010: WE EK Topic / Learning Areas Learning Objectives / Learning Outcome RemarksMoorsyidee MokhtaruddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics Yearly Plan (Year 4)Document9 pagesMathematics Yearly Plan (Year 4)Mhreal PetronasPas encore d'évaluation
- RPT Matematik Tahun 4Document11 pagesRPT Matematik Tahun 4mees-samaPas encore d'évaluation
- Year3 Mat HSPDocument6 pagesYear3 Mat HSPnorzunita1973Pas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Plan Y4 2012Document13 pagesYearly Plan Y4 2012Fauzia AngelPas encore d'évaluation
- Curriculum Specifications Mathematics For Year 3 Yearly Plan 2005Document8 pagesCurriculum Specifications Mathematics For Year 3 Yearly Plan 2005Muhamad IrhamPas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Scheme of Work Year 4 2013Document15 pagesYearly Scheme of Work Year 4 2013muhdmudzakkirPas encore d'évaluation
- Rancangan Tahunan Math Tahun 6 2013 BiDocument10 pagesRancangan Tahunan Math Tahun 6 2013 BiNajwa NurPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics Yearly Plan 2014 Year 5 Week Topic / Learning Area Learning Objectives / Learning OutcomesDocument8 pagesMathematics Yearly Plan 2014 Year 5 Week Topic / Learning Area Learning Objectives / Learning OutcomesMohd ZahariPas encore d'évaluation
- Rancangan Tahunan Math Tahun 6 - 2013 - BiDocument10 pagesRancangan Tahunan Math Tahun 6 - 2013 - BimrdanPas encore d'évaluation
- Rancangan Tahunan Math Tahun 6 2013 BiDocument10 pagesRancangan Tahunan Math Tahun 6 2013 Binaim8889Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics Yearly Plan (Year Six) : 1. Whole NumbersDocument3 pagesMathematics Yearly Plan (Year Six) : 1. Whole NumbersAdemizan AhadPas encore d'évaluation
- RPT MT THN 6Document11 pagesRPT MT THN 6Denny PetrusPas encore d'évaluation
- RPT MT THN 6Document11 pagesRPT MT THN 6Mohd AsrafPas encore d'évaluation
- Year3 Mat HSPDocument8 pagesYear3 Mat HSPShazwani HamzahPas encore d'évaluation
- Math Yearly Plan Year 3 RPHDocument16 pagesMath Yearly Plan Year 3 RPHnorizan bt awang100% (1)
- Matematik Tahun 2Document6 pagesMatematik Tahun 2Azmin OsmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Rancangan Tahunan MatematikDocument19 pagesRancangan Tahunan MatematikHailmi OthmanPas encore d'évaluation
- RPT MT THN2Document9 pagesRPT MT THN2Hasnawati BachoPas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematic YEAR 5Document17 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Mathematic YEAR 5SanjukuttyPas encore d'évaluation
- Year3 Mat HSPDocument8 pagesYear3 Mat HSPyuslinaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Year3 Mat HSP SGT BagusDocument9 pagesYear3 Mat HSP SGT BagusMaryah Yahya AzlimdnorPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics Yearly Plan (Year 5) : Week Topic / Learning Areas Learning Objectives / Learning Outcome RemarksDocument8 pagesMathematics Yearly Plan (Year 5) : Week Topic / Learning Areas Learning Objectives / Learning Outcome RemarksMhreal PetronasPas encore d'évaluation
- Curriculum Specifications Mathematics For Year 3 Yearly Plan 2005Document8 pagesCurriculum Specifications Mathematics For Year 3 Yearly Plan 2005Khaulah Al-HumayyraPas encore d'évaluation
- 2010 Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form Two SMK Raja Mahadi KlangDocument12 pages2010 Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form Two SMK Raja Mahadi KlangLooyee ChenPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics Yearly Plan (Year Six) : 1. Whole NumbersDocument3 pagesMathematics Yearly Plan (Year Six) : 1. Whole NumbersRamziah BongsuPas encore d'évaluation
- RPT MT THN2Document9 pagesRPT MT THN2Muhammad Fadzli HamzahPas encore d'évaluation
- Whole NumbersDocument4 pagesWhole Numbersmr.itfreakPas encore d'évaluation
- MT Yearly Plan Year 1 - 6Document40 pagesMT Yearly Plan Year 1 - 6Ibnu YusoffPas encore d'évaluation
- RT Mat T3Document8 pagesRT Mat T3Candace ClayPas encore d'évaluation
- RPT MT Y4Document10 pagesRPT MT Y4Noraini MohamadPas encore d'évaluation
- Curriculum Specifications Mathematics Year 3: Week Topic Learning Area Learning Objectives Learning OutcomesDocument23 pagesCurriculum Specifications Mathematics Year 3: Week Topic Learning Area Learning Objectives Learning Outcomesmuhammad syafiq bin arifinPas encore d'évaluation
- Let's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 5D'EverandLet's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 5Pas encore d'évaluation
- Math Fluency Activities for K–2 Teachers: Fun Classroom Games That Teach Basic Math Facts, Promote Number Sense, and Create Engaging and Meaningful PracticeD'EverandMath Fluency Activities for K–2 Teachers: Fun Classroom Games That Teach Basic Math Facts, Promote Number Sense, and Create Engaging and Meaningful PracticeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Republic of The Philippines: Set - ADocument3 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Set - AJeana Rick GallanoPas encore d'évaluation
- MODULE 3-Circle Area and PerimeterDocument14 pagesMODULE 3-Circle Area and PerimetersyarelPas encore d'évaluation
- Algorithms & FolwchartsDocument6 pagesAlgorithms & FolwchartsNaveen ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- 2014 MTAP 5 ReviewerDocument6 pages2014 MTAP 5 ReviewerRodel AgcaoiliPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 9 Asset QB MathematicsDocument14 pagesGrade 9 Asset QB Mathematicsmayo muyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Algebra Coaching 1 PDFDocument21 pagesAlgebra Coaching 1 PDFlouie n. gustoPas encore d'évaluation
- Plane ShapesDocument21 pagesPlane Shapeswelearnplayandgrow SamuelPas encore d'évaluation
- Test For AdmissionDocument8 pagesTest For AdmissionarsalanPas encore d'évaluation
- New Update Paper C Q PDFDocument94 pagesNew Update Paper C Q PDFBui Lan Huong100% (1)
- Fundamental MathDocument417 pagesFundamental Mathjaffa jaffaPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 7 Mensuration Perimeter Area VolumeDocument2 pagesGrade 7 Mensuration Perimeter Area VolumeDaniel Trencheski100% (1)
- Maths PDFDocument8 pagesMaths PDFRajalaxmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Selina Concise Mathematics Class 7 ICSE Solutions For Chapter 11 - Fundamental ConceptsDocument146 pagesSelina Concise Mathematics Class 7 ICSE Solutions For Chapter 11 - Fundamental Conceptsutsav kakkadPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQ 7th STD Math Decimal and FractionDocument17 pagesMCQ 7th STD Math Decimal and FractionTimPas encore d'évaluation
- MC S2 B IH8 Irfm VCG XMOy VDocument14 pagesMC S2 B IH8 Irfm VCG XMOy VyugiPas encore d'évaluation
- Area of Regular PolygonsDocument4 pagesArea of Regular Polygonsapi-237271221Pas encore d'évaluation
- Activity2 HandshakeDocument3 pagesActivity2 HandshakehypatiaphdPas encore d'évaluation
- AISSEE Sainik Schools Syllabus 2021 For Class 6 PDF - Exam Pattern - SainikSchoolGuide - inDocument5 pagesAISSEE Sainik Schools Syllabus 2021 For Class 6 PDF - Exam Pattern - SainikSchoolGuide - inLandon MitchellPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics Curriculum Guide Grade 4Document92 pagesMathematics Curriculum Guide Grade 4Vic garciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Year 10 Higher SOW: Overview: Securing Grade 5, 6 & 7, Extending To Grades 8 & 9Document43 pagesYear 10 Higher SOW: Overview: Securing Grade 5, 6 & 7, Extending To Grades 8 & 9Mansoor Aaqib MalikPas encore d'évaluation
- GRE Math QuestionsDocument23 pagesGRE Math QuestionsratnaPas encore d'évaluation
- N A C P FinalDocument26 pagesN A C P Finalrahul__dahekar@yahoo.co.inPas encore d'évaluation
- Mid Term Class 6 Maths PaperDocument4 pagesMid Term Class 6 Maths PaperArvind KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Homework PracticeDocument85 pagesHomework PracticeJason GarnerPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics Class Viii PDFDocument13 pagesMathematics Class Viii PDFKhushi GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
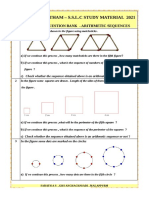
- FOCUS AREA ARITHMETIC SEQUENCES Sample Questions by Sarath Sir Part II EM PDFDocument28 pagesFOCUS AREA ARITHMETIC SEQUENCES Sample Questions by Sarath Sir Part II EM PDFSachinPas encore d'évaluation
- Perimeter of Polygons PDFDocument4 pagesPerimeter of Polygons PDFJohn Carl SarePas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 8 Mathematics June 2021Document5 pagesGrade 8 Mathematics June 2021jeff477000Pas encore d'évaluation