Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Pathophysiology of DM
Transféré par
Nicole Louise N. VillanuevaDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Pathophysiology of DM
Transféré par
Nicole Louise N. VillanuevaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
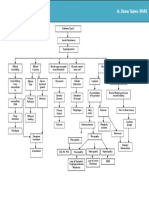
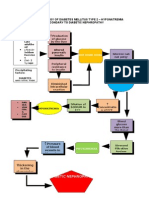
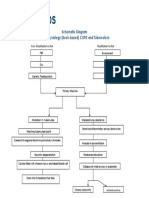
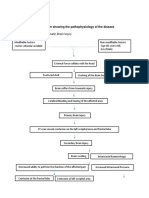
Obesity: BMI of 33
Cholesterol: 280 mg/dL, Triglycerides: 180, LDL 180, HDL 25 Bruises and puncture wound in the left ankle caused my misplaced wire
Increased Insulin Resistance
Decreased amount of insulin (Hypoinsulinemia)
Little breakdown of fat in cells (lipolysis)
Breakdown of glycogen into glucose
Decreased peripheral use of glucose
Protein breakdown
Activation of immune system and inflammatory response against infection WBC: 28 x 109/L with bandemia Temp: 39C UA - Pus cells: over 100/hpf UA - RBC: 20/hpf (+) Proteinuria Release of epinephrine, glucagon, growth hormone, and cortisol
Some free fatty acids are transported to the liver
Formation of new glucose from proteolysis HYPERGLYCEMIA FBS: 180 mg/dL HYPEROSMOLARITY
Increased serum creatinine: 8.9 mg/dL
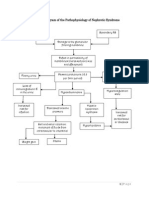
Oxidized LDL Little or (-) ketone bodies Oxidative Stress
Stimulation of inflammatory cytokines
Endothelial Dysfunction Kidneys will normally excrete extra glucose and fluid from the body through the urine (Osmotic diuresis)
Expression of adhesion molecules from the endothelium Adhesion and subendothelial migration of macrophages
Extracellular dehydration
Accumulation of Foam Cells in the endothelium
Smooth muscle cell migration and proliferation Extracellular matrix production
Renal Insufficiency BP: 210/100; Crea: 8.9mg/dL; (+) glucosuria and proteinuria
Severe hyperosmolality and hemoconcentration (Hgb: 110 and Hct: 28)
Potassium shifts from the ICF to the ECF. (Hypokalemia : 2.7 mg/dL) Water retention is low because of low sodium levels in the ECF. (Hyponatremia: 123 mg/dL)
Formation of FIBROUS PLAQUE
Complicated Atherosclerotic Lesion Impaired blood flow to the left ankle because of hemoconcentration or viscous flow of blood
Intracellular fluid shifts to extracellular space to compensate for EC dehydration
Progressive edema
Vomiting because of increased potassium in circulation
Intracellular dehydration
Bluish discoloration and numbness
Thirst center stimulation in the hypothalamus Increased oral fluid intake by the patient
Decreased supply of essential electrolytes to the brain Severe headache, slurred speech, weakness, Left-sided weakness, 40% sensory deficit
Tissue necrosis
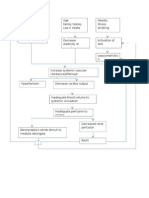
Hyperglycemia
Increased Viscosity of the Blood Increased Cardiac Output (Starling Law)
Increased resistance of the blood itself to flow Hemodynamic Dysfunction
Hypertension Arteriolar Vasoconstriction
Decreased Perihpheral Blood Flow (Hagen-Poiselles Law) Decreased Renal Blood Flow Renal Insufficiency Decreased Kidney Function
Increase Crossbridge Formation Augment Muscle Mass to bear extra Load Recruit Hormonal Mechanisms to increase contractility
Concentric Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
To Compensate For Glycosuria & Proteinuria Hematuria Regulation of Blood Volume & Pressure Excretion
Hypokalemia & Hyponatremia
Regulation of the concentration of solutes in the blood
Regulation of extracellular fluid pH. Decreased HGB Regulation of red blood cell synthesis
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Sle FinalDocument41 pagesSle FinalAsniah Hadjiadatu Abdullah100% (1)
- Patof DMDocument1 pagePatof DMxerwanePas encore d'évaluation
- Liver Cirrhosis: (Alterations in Metabolic and Endocrine Functions)Document8 pagesLiver Cirrhosis: (Alterations in Metabolic and Endocrine Functions)Jorie RocoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of DMDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of DMRgn Mckl100% (3)
- Pa Tho Physiology of Diabetes MellitusDocument3 pagesPa Tho Physiology of Diabetes MellitusPong's Teodoro SalvadorPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryJane Arian Berzabal0% (1)
- Qtsoi Concept MapDocument5 pagesQtsoi Concept MapGenella BabantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Age Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat IntakeDocument3 pagesAge Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat Intakenursing concept mapsPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 8: Parik Rabasto Patel, D Patel, J Raghuwanshi Regis Moleta Moreno NaromalDocument35 pagesGroup 8: Parik Rabasto Patel, D Patel, J Raghuwanshi Regis Moleta Moreno NaromalDominique RabastoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Rheumatoid ArthritisGerardeanne ReposarPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Nutrition 1531778509Document667 pagesHuman Nutrition 1531778509DM ProduccionesPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Lab ReportDocument5 pagesBiology Lab Reportapi-2576094460% (1)
- Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument123 pagesFluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceBrealaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology CVADocument1 pagePathophysiology CVANenette Aquino100% (2)
- Hypertension Obstruction: Chronic Renal FailureDocument3 pagesHypertension Obstruction: Chronic Renal FailureDiane-Richie PezLo100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Hyperthyroidism and Thyroid StormDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Hyperthyroidism and Thyroid StormPen MontantePas encore d'évaluation
- Hypertension PathophysiologyDocument1 pageHypertension PathophysiologyZaida Eunice EstabayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Document1 pagePathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2faula rocamora100% (3)
- Diabetes PathoDocument2 pagesDiabetes Pathodrewcel100% (1)
- Nursing Core Competency Standards 2012Document27 pagesNursing Core Competency Standards 2012JustinP.DelaCruz100% (1)
- Pathophysiology: Precipitating FactorDocument6 pagesPathophysiology: Precipitating FactorMark Anthony YabresPas encore d'évaluation
- # of Carbons Aldose Ketose: Carbons (Triose) - D. Glyceraldehyde and L. Glyceraldehyde. Notice The Positions of Both OHDocument7 pages# of Carbons Aldose Ketose: Carbons (Triose) - D. Glyceraldehyde and L. Glyceraldehyde. Notice The Positions of Both OHAngel CalambaPas encore d'évaluation
- Schematic Diag DMDocument1 pageSchematic Diag DMReynaKatPas encore d'évaluation
- TEST BANK Krause's Food & The Nutrition Care Process 13th Edition by L. Kathleen Mahan Janice L Raymond Sylvia Escott StumpDocument27 pagesTEST BANK Krause's Food & The Nutrition Care Process 13th Edition by L. Kathleen Mahan Janice L Raymond Sylvia Escott StumpKieran100% (1)
- Weaknes S/ Fatigue Polyphag IaDocument5 pagesWeaknes S/ Fatigue Polyphag IaEwert Hesketh Nillama PaquinganPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology Hemor CVADocument4 pagesPathophysiology Hemor CVAMatthew Emmanuel M. Martinez100% (2)
- Lupus Case ReportDocument1 pageLupus Case ReportMendy HararyPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetes PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesDiabetes PathophysiologyShelly_Ann_Del_9959Pas encore d'évaluation
- Path o PhysiologyDocument9 pagesPath o PhysiologyKyle Ü D. CunanersPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology HPN CvaDocument1 pagePathophysiology HPN Cvatresdos09Pas encore d'évaluation
- Schematic Diagram: Signs and Symptoms: Headache, Unconsciousness, Nausea and Vomiting, Visual DisturbancesDocument3 pagesSchematic Diagram: Signs and Symptoms: Headache, Unconsciousness, Nausea and Vomiting, Visual DisturbancesJosett RomanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pa Tho Physiology of Open FractureDocument2 pagesPa Tho Physiology of Open FracturegiffersonbPas encore d'évaluation
- PathophysiologyDocument1 pagePathophysiologynitlihpPas encore d'évaluation
- Cushing's SyndromeDocument5 pagesCushing's SyndromesummerduskPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Nephrotic SyndromeDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Nephrotic SyndromeRan MaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of StrokeACe JAyPas encore d'évaluation
- OUR LADY OF FATIMA UNIVERSITY Case Study on Post Streptococcal GlomerulonephritisDocument20 pagesOUR LADY OF FATIMA UNIVERSITY Case Study on Post Streptococcal GlomerulonephritisMikaCasimiroBalunanPas encore d'évaluation
- NSAID AND ALCOHOL INCREASE RISK OF PEPTIC ULCER BY DECREASING MUCOSAL DEFENSESDocument2 pagesNSAID AND ALCOHOL INCREASE RISK OF PEPTIC ULCER BY DECREASING MUCOSAL DEFENSESLEAH LUZADAPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of CVA D/T DMDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of CVA D/T DMDanielle Marie SamblacenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Annotated Group 2 Impetigo Concept Mapping 1Document30 pagesAnnotated Group 2 Impetigo Concept Mapping 1DHANE ANN CAMPOSANOPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Kidney DiseaseDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Kidney DiseaseSTEPHANIE JOSUE100% (1)
- NCP CvaDocument7 pagesNCP CvaEmerson SilverioPas encore d'évaluation
- Schematic Diagram Pathophysiology (Book-Based) COPD and TuberculosisDocument1 pageSchematic Diagram Pathophysiology (Book-Based) COPD and Tuberculosispragna novaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chronic Calculous CholecystitisDocument35 pagesChronic Calculous CholecystitisJoshua AgawinPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysio Chronic GlomerulonephritisDocument1 pagePathophysio Chronic GlomerulonephritisRan Ma100% (1)
- Final Case Study NCM 116Document60 pagesFinal Case Study NCM 116Marissa AsimPas encore d'évaluation
- Pa Tho Physiology Part 1Document1 pagePa Tho Physiology Part 1anonymous89ify100% (2)
- Pathophysiology-Kni Ns PLZZZDocument8 pagesPathophysiology-Kni Ns PLZZZAnna Lira Manluyang MungcalPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Acute CholecystitisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Acute CholecystitisKush KhannaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fractures, PathophysiologyDocument1 pageFractures, Pathophysiology4kscribdPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology CKDDocument2 pagesPathophysiology CKDSugar Capule - ManuelPas encore d'évaluation
- Osteoarthritis 1583-170210113823Document34 pagesOsteoarthritis 1583-170210113823Angelic khanPas encore d'évaluation
- Schematic Diagram of CKD Sec. To DM Nephropathy, DM Type 2, DM FootDocument8 pagesSchematic Diagram of CKD Sec. To DM Nephropathy, DM Type 2, DM Footbeuwolfagate50% (2)
- Non-Modifiable, Partially Modifiable, and Modifiable Risk Factors for Atherothrombotic DiseaseDocument15 pagesNon-Modifiable, Partially Modifiable, and Modifiable Risk Factors for Atherothrombotic DiseaseWiljohn de la CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Transcultural Perspective in The Nursing Care of Adults Physiologic Development During AdulthoodDocument5 pagesTranscultural Perspective in The Nursing Care of Adults Physiologic Development During AdulthoodeuLa-mayzellPas encore d'évaluation
- DB31 - Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus and HypoglycemiaDocument5 pagesDB31 - Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus and HypoglycemiaNeil Alcazaren かわいいPas encore d'évaluation
- Leptospirosis: Causes, Incidence, and Risk FactorsDocument6 pagesLeptospirosis: Causes, Incidence, and Risk FactorsJackii DoronilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Lymphocytic LeukemiaDocument12 pagesAcute Lymphocytic Leukemiajustin_sanePas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysio CRF RevisedDocument2 pagesPathophysio CRF Revisedroseanne18Pas encore d'évaluation
- Myoma PathoDocument3 pagesMyoma PathoJan Michael Artiaga100% (1)
- PPPDocument3 pagesPPPJack BangcoyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Predisposing and precipitating factors leading to ESRD, DM, atherosclerosis, and pneumoniaDocument11 pagesPredisposing and precipitating factors leading to ESRD, DM, atherosclerosis, and pneumoniaJonathan CuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Manajemen ShockDocument47 pagesManajemen ShockPutry RizqiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Shock: by Simranpreet KaurDocument10 pagesShock: by Simranpreet Kaurpreet kaurPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology Non-Modifiable Factors Modifiable FactorsDocument3 pagesPathophysiology Non-Modifiable Factors Modifiable FactorsErrol B. TiozonPas encore d'évaluation
- History of NnccsDocument3 pagesHistory of NnccsNicole Louise N. Villanueva100% (1)
- NNCCS 2012Document27 pagesNNCCS 2012Nicole Louise N. VillanuevaPas encore d'évaluation
- 671Document16 pages671ravensuichiroPas encore d'évaluation
- Base Tuttopann "F" 100: Code 02113 Name Type of ProductDocument2 pagesBase Tuttopann "F" 100: Code 02113 Name Type of ProductPedro barriaPas encore d'évaluation
- QUESTION BANK Class 9 HOME SCIENCE SUPRIYA STEWART SCHOOL 1 2Document79 pagesQUESTION BANK Class 9 HOME SCIENCE SUPRIYA STEWART SCHOOL 1 2ANANYA CHURIWALAPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochem MidtermDocument10 pagesBiochem MidtermBriones, HannahPas encore d'évaluation
- Best Berberin Suppliments 2021Document2 pagesBest Berberin Suppliments 2021fitnesstoolsPas encore d'évaluation
- AQA AS Biology 3.1.2 CarbohydratesDocument11 pagesAQA AS Biology 3.1.2 CarbohydratesChryssa EconomouPas encore d'évaluation
- Enzyme ElectrodeDocument6 pagesEnzyme Electrodevinod_kumar_mishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Biological MacromoleculesDocument18 pagesBiological MacromoleculesFarah CarbonelPas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamic Simulation of Insulin-Glucose Interaction in Type 1 Diabetes With MATLAB Simulink®Document11 pagesDynamic Simulation of Insulin-Glucose Interaction in Type 1 Diabetes With MATLAB Simulink®Jonas KristantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Hs Biology Fa Cellular Processes Book SampleDocument31 pagesHs Biology Fa Cellular Processes Book SampleKeshia DedacePas encore d'évaluation
- DR ReddyDocument159 pagesDR ReddyIssa AvenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution 1:: Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument9 pagesSolution 1:: Chemical Reactions and EquationsOjasPas encore d'évaluation
- Appendix I Estimation of Acid Phosphatase: PrincipleDocument39 pagesAppendix I Estimation of Acid Phosphatase: PrincipleSurya PrakashPas encore d'évaluation
- 1st BDS Physiology and Microbiology PDFDocument12 pages1st BDS Physiology and Microbiology PDFAshok HoneyPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification of Carbohydrates and Its StructureDocument7 pagesClassification of Carbohydrates and Its Structuresabra muneerPas encore d'évaluation
- Veterinary Basics Document ExplainedDocument119 pagesVeterinary Basics Document ExplainedSaleem Ahmed Shahwani0% (1)
- Animal Nutrition: AP BiologyDocument41 pagesAnimal Nutrition: AP BiologyJohn James AntipoloPas encore d'évaluation
- 23 Tests For CarbohydratesDocument9 pages23 Tests For CarbohydratespollyPas encore d'évaluation
- Flores Et Al 2002 L-ArgininaDocument9 pagesFlores Et Al 2002 L-ArgininaJorge ParodiPas encore d'évaluation
- PolymersDocument11 pagesPolymersdovoo lolPas encore d'évaluation
- Carbohydrates Lab SlidesDocument42 pagesCarbohydrates Lab SlidesZeian Jacob BaylaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Technician-6Document26 pagesLab Technician-6AHAMED SHIFAANPas encore d'évaluation
- Differntial Equations ProjectDocument28 pagesDifferntial Equations ProjectSai CharanPas encore d'évaluation
- Glycogen Storage Disorder PaperDocument9 pagesGlycogen Storage Disorder Paperapi-586855789Pas encore d'évaluation
- Termamyl 120LDocument8 pagesTermamyl 120Lnothing2902Pas encore d'évaluation
- 11 221 PS3Document4 pages11 221 PS3Maya Jenny0% (1)
- Icu CS CompilationDocument186 pagesIcu CS CompilationAngel YuPas encore d'évaluation